Tekezé River
 | |
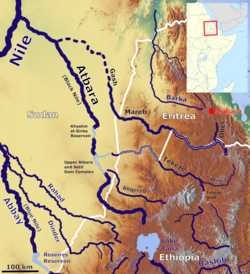 The Tekezé River in the Atbara basin | |
 Location of mouth in Ethiopia | |
| Location | |
|---|---|
| Countries |
|
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | |
• coordinates | 14°15′27″N 36°33′37″E / 14.25750°N 36.56028°ECoordinates: 14°15′27″N 36°33′37″E / 14.25750°N 36.56028°E |
The Tekezé or Täkkäze River (Amharic: ተከዜ, Tigrinya: ተከዘ; originally meaning "river" in Ge’ez),[1] also spelled Takkaze,[2] is a major river of Ethiopia. For part of its course it forms a section of the westernmost border of Ethiopia and Eritrea. The river is also known as the Setit in Eritrea, western Ethiopia, and eastern Sudan. According to materials published by the Ethiopian Central Statistical Agency, the Tekezé River is 608 kilometers (378 mi) long.[3] The canyon which it has created is the deepest in Africa and one of the deepest in the world, at some points having a depth of over 2000 meters (6,562 feet).[4]
Course[]


The Tekezé River rises in the central Ethiopian Highlands near within Lasta, from where it flows west, north, then west again, forming the westernmost border of Ethiopia and Eritrea from the confluence of the Tomsa with the Tekezé at 14°11′N 37°31.7′E / 14.183°N 37.5283°E to the tripoint between the two countries and Sudan at 14°15′27″N 36°33′37″E / 14.25750°N 36.56028°E.[5] After entering northeastern Sudan at the tripoint it joins the Atbarah River, which is a tributary of the Nile. The Tekezé is perhaps the true upper course of the Atbarah, as the former follows the longer course prior to the confluence of the two rivers.
The names of its main tributaries in Ethiopia from its source are: on the right bank Tahali, Meri, , Sullo, Arekwa, Gheoa, Wari, Firafira, Tocoro, and Gumalo Rivers; on the left bank , Balagas, Saha, Bembea, Ataba, Zarima, and Kwalema Rivers.
History[]

The earliest known mention of the Tekezé is in an inscription from Aksum of king Ezana of Axum, where he boasts of a victory in a battle on its lower banks, near "the ford of Kemalke".[6] The Tekezé served as an early link between Ethiopia and Egypt; for example, the Kebra Nagast, which received its current form in the 13th century, states that king Menelik I returned to Ethiopia by following this river from Egypt (ch. 53). records a related tradition that near the source of the Tekezé, at the location of Eyela Kudus Michael church, is the true resting-place of the Ark of the Covenant.[7]
In February and March 1936, during the Second Italo-Abyssinian War, thousands of Ethiopian troops were killed when the Italian Royal Air Force (Regia Aeronautica) attacked them with bombs and mustard gas as they retreated across the Tekezé.[8]
On 1 July 2021, the bridge crossing the Tekezé river was destroyed by an unknown force during Tigray War. The International Rescue Committee was concerned that the war region would "even more severely hampered than before".[9]
Tekezé Dam[]
The Ethiopian government announced in July 2002 that they had formed a partnership with the to construct a hydroelectric dam on the Tekezé, which would generate 300 megawatts of electricity. The project would cost US$224 million and take five years to complete.[10] Oweys Ibrahim, the project coordinator, announced on 12 December 2007 that construction was 82% complete, and included a 105-kilometer power line to Mekele.[11]
The Tekeze Hydro Electric project constructed the highest double curve arch dam in Africa, topping the previous highest, in Lesotho. The contractors behind the project were CWGS and it was completed in 2009. The resulting reservoir is 105 km² large and it has a capacity of 9.3 billion m³ of water.[12]
See also[]
Notes[]
- ^ Ritler, Alfons. 2010. "Täkkäze." In Encyclopaedia Aethiopica: O-X: Vol. 4, edited by Siegbert Uhlig, 823-825. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz.
- ^ Webster's New Geographical Dictionary, Springfield, Massachusetts: Merriam-Webster Inc., 1988, ISBN 0-87779-446-4, p. 1,194.
- ^ "Climate, 2012 National Statistics (Abstract)"[permanent dead link], Table A.2. Central Statistical Agency website (accessed 25 October 2015)
- ^ "Ethiopia's Water Dilemma" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-02-08.
- ^ Eritrea - Ethiopia Boundary Commission Decision Regarding Delimitation of the Border..., pp. 97, 101
- ^ Translated with commentary in G.W.B. Huntingford, The Historical Geography of Ethiopia (London: British Academy, 1989), pp. 56-59.
- ^ Augustus B. Wylde, Modern Abyssinia (London: Methuen, 1901), p. 352
- ^ Barker, A. J., The Rape of Ethiopia 1936, New York: Ballantine Books Inc., 1971, pp. 84, 91.
- ^ "Bridge on Tekeze River in Ethiopia's Tigray destroyed - aid group". Reuters. 2021-07-01. Retrieved 2021-07-14.
- ^ China People's Daily Online. Accessed 20 April 2006.
- ^ "Construction of Tekeze Hydro Electric Power Project nearing completion" Archived 2007-12-05 at the Wayback Machine (Walta Information Center), accessed 2 December 2007.
- ^ ANNYS, Sofie; GHEBREYOHANNES, Tesfaalem; NYSSEN, Jan. Impact of hydropower dam operation and management on downstream hydrogeomorphology in semi-arid environments (Tekeze, Northern Ethiopia). Water, 2020, 12.8: 2237.
External links[]
- Maps of Ethiopia - Perry–Castañeda Library Map Collection, University of Texas at Austin
- Rivers of Eritrea
- Rivers of Ethiopia
- International rivers of Africa
- Atbarah River
- Rivers of Sudan
- Ethiopian Highlands
- Eritrea–Ethiopia border
- Border rivers
