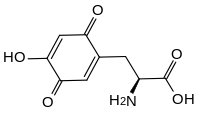
Topaquinone
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S)-2-Amino-3-(4-hydroxy-3,6-dioxocyclohexa-1,4-dien-1-yl)propanoic acid
| |
| Other names
6-Hydroxydopaquinone
| |
| Identifiers | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C9H9NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 211.173 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Topaquinone (TPQ) is a redox cofactor derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Its name derives from 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenylalanine-quinone. Its structure was first identified in 1990.[1] It is used by copper amine oxidases which contain a tyrosine residue near the active site. This residue catalyses its own transition, first to dopaquinone and then to topaquinone, in a Cu2+ dependent manner.[1]
References[]
Categories:
- Cofactors
- Amino acid derivatives
- 1,4-Benzoquinones
- Hydroxybenzoquinones
- Propionic acids