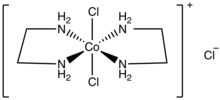
trans-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(OC-6-12′)-Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine-κ2N,N′)cobalt(1+) chloride(1−)
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H16Cl3CoN4 | |
| Molar mass | 285.48 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | green solid |
| Melting point | decomposes |
| good | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
Signal word
|
Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P305+P351+P338 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
trans-Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is a salt with the formula [CoCl2(en)2]Cl (en = ethylenediamine). It is a green diamagnetic solid that is soluble in water. It is the monochloride salt of the cationic coordination complex [CoCl2(en)2]+. One chloride ion in this salt readily undergoes ion exchange but the two other chlorides are less reactive, being bound to the metal center. The more stable trans-dichlorobis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride is also known.
Synthesis[]
The compound is synthesized by the reaction of cobalt(II) chloride and ethylenediamine in hydrochloric acid in the presence of oxygen:
- 4 CoCl2 + 8 en + 4 HCl + O2 → 4 trans-[CoCl2(en)2]Cl + 2 H2O
The initial product contains HCl, which is removed by heating. Alternatively, (carbonato)bis(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride reacts with hydrochloric acid at 10 °C to give the same species.[1]
- [Co(CO3)(en)2]Cl + 2 HCl → trans-[CoCl2(en)2]Cl + CO2 + H2O
Comparison of cis and trans isomers[]
This salt is more soluble than the cis isomer. This pair of isomers was significant in the development of the area of coordination chemistry.[2]
The trans isomer cation has idealized D2h point group symmetry, whereas the cis isomer cation has C2 symmetry.
References[]
- ^ Springbørg, J.; Schaffer, C. E. (1973). "Dianionobis(Ethylenediamine)Cobalt(III) Complexes". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. 14. p. 63-77. doi:10.1002/9780470132456.ch14. ISBN 9780470132456.
- ^ Jörgensen, S.M. "Ueber Metalldiaminverbindungen" Journal für praktische Chemie (in German), 1889, volume 39, page 8. doi:10.1002/prac.18890390101
- Chlorides
- Chloro complexes
- Cobalt complexes
- Cobalt(III) compounds
- Ethylenediamine complexes
- Metal halides