Trigonal trapezohedral honeycomb
| Trigonal trapezohedral honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| (No image) | |
| Type | Dual uniform honeycomb |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | |
| Cell |  Trigonal trapezohedron (1/4 of rhombic dodecahedron) |
| Faces | Rhombus |
| Space group | Fd3m (227) |
| Coxeter group | ×2, [[3[4]]] (double) |
| vertex figures | |
| Dual | Quarter cubic honeycomb |
| Properties | Cell-transitive, Face-transitive |
The trigonal trapezohedral honeycomb is a uniform space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. Cells are identical trigonal trapezohedron or rhombohedra. Conway, Burgiel, and Goodman-Strauss call it an oblate cubille.[1]
Related honeycombs and tilings[]
This honeycomb can be seen as a rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb, with the rhombic dodecahedra dissected with its center into 4 trigonal trapezohedra or rhombohedra.
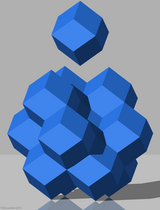 rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb |
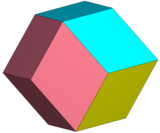 Rhombic dodecahedra dissection |
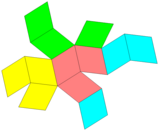 Rhombic net |
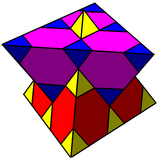
It is analogous to the regular hexagonal being dissectable into 3 rhombi and tiling the plane as a rhombille. The rhombille tiling is actually an orthogonal projection of the trigonal trapezohedral honeycomb. A different orthogonal projection produces the quadrille where the rhombi are distorted into squares.

|
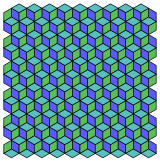
|
Dual tiling[]
It is dual to the quarter cubic honeycomb with tetrahedral and truncated tetrahedral cells:
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Conway, John H.; Burgiel, Heidi; Goodman-Strauss, Chaim (2008), The Symmetries of Things, Wellesley, Massachusetts: A K Peters, p. 294, ISBN 978-1-56881-220-5, MR 2410150
- 4-polytopes stubs
- Honeycombs (geometry)