Truman Doctrine

The Truman Doctrine was an American foreign policy with the primary goal of containing Soviet geopolitical expansion during the Cold War. It was announced to Congress by President Harry S. Truman on March 12, 1947,[1] and further developed on July 4, 1948, when he pledged to contain the communist uprisings in Greece and Turkey. Direct American military force was usually not involved, but Congress appropriated financial aid to support the economies and militaries of Greece and Turkey. More generally, the Truman Doctrine implied American support for other nations thought to be threatened by Soviet communism. The Truman Doctrine became the foundation of American foreign policy, and led, in 1949, to the formation of NATO, a military alliance that still exists. Historians often use Truman's speech to date the start of the Cold War.[2]
Truman told Congress that "it must be the policy of the United States to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures."[3] Truman contended that because totalitarian regimes coerced free peoples, they automatically represented a threat to international peace and the national security of the United States. Truman made the plea in the midst of the Greek Civil War (1946–1949). He argued that if Greece and Turkey did not receive the aid, they would inevitably fall to communism with grave consequences throughout the region. Because Turkey and Greece were historic rivals, it was considered necessary to help both equally even though the crisis in Greece was far more intense.
Critics of the policy have observed that the governments of Greece and Turkey were themselves far from democratic at this time, and neither were facing Soviet subversion in the spring of 1949. Historian Eric Foner writes that the Doctrine "set a precedent for American assistance to anticommunist regimes throughout the world, no matter how undemocratic, and for the creation of a set of global military alliances directed against the Soviet Union."[4]
For years, the United Kingdom had supported Greece, but was now near bankruptcy and was forced to radically reduce its involvement. In February 1947, Britain formally requested for the United States to take over its role in supporting the royalist Greek government.[5] The policy won the support of Congress and involved sending $400 million in American money but no military forces to the region. The effect was to end the Greek revolt, and in 1952, both Greece and Turkey joined NATO, a military alliance, to guarantee their stability.
The Truman Doctrine was informally extended to become the basis of American Cold War policy throughout Europe and around the world.[6] It shifted American foreign policy toward the Soviet Union from an anti-fascist alliance to a policy of containment of Soviet expansion as advocated by diplomat George Kennan. It was distinguished from rollback by implicitly tolerating the previous Soviet takeovers in Eastern Europe.
| ||
|---|---|---|
Senator from Missouri
33rd President of the United States
show
First term show
Second term show
Presidential and Vice presidential campaigns Post-presidency
 |
||
Turkish Straits crisis[]
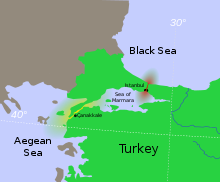
At the conclusion of World War II, Turkey was pressured by the Soviet government to allow Russian shipping to flow freely through the Turkish Straits, which connected the Black Sea to the Mediterranean. As the Turkish government would not submit to the Soviet Union's requests, tensions arose in the region, leading to a show of naval force on the side of the Straits. Since British assistance to Turkey had ended in 1947, the U.S. dispatched military aid to ensure that Turkey would retain chief control of the passage. Turkey received $100 million in economic and military aid and the U.S. Navy sent the Midway-class aircraft carrier USS Franklin D. Roosevelt. The postwar period from 1946 started with a "multi-party period" and the Democratic Party government of Adnan Menderes.[7]
Greek crisis[]

Seven weeks after the Axis powers abandoned Greece in October 1944, the British helped retake Athens from the victorious National Liberation Front (EAM), controlled effectively by the Greek Communist Party (KKE). This began with a mass killing of largely unarmed EAM supporters known as the Dekemvriana on December 3.[8] The left-wing attempted to retaliate, but were outgunned by the British-backed government and subjected to the White Terror.[9] With the full outbreak of civil war (1946–49), guerrilla forces controlled by the Greek Communist Party sustained a revolt against the internationally recognized Greek government which was formed after 1946 elections boycotted by the KKE. The British realized that the KKE were being directly funded by Josip Broz Tito in neighboring Yugoslavia. In line with the Churchill-Stalin "percentages agreement", the Greek communists received no help from the Soviet Union, and Yugoslavia provided them support and sanctuary against Stalin's wishes.[10] By late 1946, Britain informed the United States that due to its own weakening economy, it could no longer continue to provide military and economic support to royalist Greece.[11]
In 1946–47, the United States and the Soviet Union moved from being wartime allies to Cold War adversaries. The breakdown of Allied cooperation in Germany provided a backdrop of escalating tensions for the Truman Doctrine.[6] To Truman, the growing unrest in Greece began to look like a pincer movement against the oil-rich areas of the Middle East and the warm-water ports of the Mediterranean.[12]

In February 1946, Kennan, an American diplomat in Moscow, sent his famed "Long Telegram", which predicted the Soviets would only respond to force and that the best way to handle them would be through a long-term strategy of containment, that is stopping their geographical expansion. After the British warned that they could no longer help Greece, and following Prime Minister Konstantinos Tsaldaris's visit to Washington in December 1946 to ask for American assistance,[13] the U.S. State Department formulated a plan. Aid would be given to both Greece and Turkey, to help cool the long-standing rivalry between them.[citation needed]
American policy makers recognized the instability of the region, fearing that if Greece was lost to communism, Turkey would not last long. Similarly, if Turkey yielded to Soviet demands, the position of Greece would be endangered.[14] A regional domino effect threat therefore guided the American decision. Greece and Turkey were strategic allies important for geographical reasons as well, for the fall of Greece would put the Soviets on a particularly dangerous flank for the Turks, and strengthen the Soviet Union's ability to cut off allied supply lines in the event of war.[15]
Truman's address[]
To pass any legislation Truman needed the support of the Republicans, who controlled both houses of Congress. The chief Republican spokesman Senator Arthur H. Vandenberg strongly supported Truman and overcame the doubts of isolationists such as Senator Robert A. Taft.[16]: 127 Truman laid the groundwork for his request by having key congressional leaders meet with himself, Secretary of State George Marshall, and Undersecretary of State Dean Acheson. Acheson laid out the "domino theory" in the starkest terms, comparing a communist state to a rotten apple that could spread its infection to an entire barrel. Vandenberg was impressed, and advised Truman to appear before Congress and "scare the hell out of the American people."[16]: 127–8 On March 7, Acheson warned Truman that Greece could fall to the communists within weeks without outside aid.[1]: 545
When a draft for Truman's address was circulated to policymakers, Marshall, Kennan, and others criticized it for containing excess "rhetoric." Truman responded that, as Vandenberg had suggested, his request would only be approved if he played up the threat.[1]: 546
On March 12, 1947, Truman appeared before a joint session of Congress. In his eighteen-minute speech, he stated:
I believe it must be the policy of the United States to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures.
I believe that we must assist free peoples to work out their own destinies in their own way.
I believe that our help should be primarily through economic and financial aid which is essential to economic stability and orderly political processes.[1]: 547
The reaction to Truman's speech was broadly positive, though there were dissenters. Anti-communists in both parties supported both Truman's proposed aid package and the doctrine behind it, and Collier's described it as a "popularity jackpot" for the President.[1]: 548 [16]: 129 Influential columnist Walter Lippmann was more skeptical, noting the open-ended nature of Truman's pledge; he felt so strongly that he almost came to blows while arguing with Acheson over the doctrine.[1]: 549 [17]: 615 Others argued that the Greek monarchy Truman proposed to defend was itself a repressive government, rather than a democracy.[17]: 615
Despite these objections, the fear of the growing communist threat almost guaranteed the bill's passage.[17]: 616 In May 1947, two months after Truman's request, a large majority of Congress approved $400 million in military and economic aid to Greece and Turkey.[1]: 553–4 [16]: 129 Increased American aid helped defeat the KKE, after interim defeats for government forces from 1946 to 1948.[17]: 616–17 The Truman Doctrine was the first in a series of containment moves by the United States, followed by economic restoration of Western Europe through the Marshall Plan and military containment by the creation of NATO in 1949.
Long-term policy and metaphor[]
The Truman Doctrine underpinned American Cold War policy in Europe and around the world. In the words of historian James T. Patterson, "The Truman Doctrine was a highly publicized commitment of a sort the administration had not previously undertaken. Its sweeping rhetoric, promising that the United States should aid all 'free people' being subjugated, set the stage for innumerable later ventures that led to globalisation commitments. It was in these ways a major step."[16]: 129
The doctrine endured, historian Dennis Merill argues, because it addressed broader cultural insecurity regarding modern life in a globalized world. It dealt with Washington's concern over communism's domino effect, it enabled a media-sensitive presentation of the doctrine that won bipartisan support, and it mobilized American economic power to modernize and stabilize unstable regions without direct military intervention. It brought nation-building activities and modernization programs to the forefront of foreign policy.[6]
The Truman Doctrine became a metaphor for aid to keep a nation from communist influence. Truman used disease imagery not only to communicate a sense of impending disaster in the spread of communism but also to create a "rhetorical vision" of containing it by extending a protective shield around non-communist countries throughout the world. It echoed the "quarantine the aggressor" policy Truman's predecessor, Franklin D. Roosevelt, had sought to impose to contain German and Japanese expansion in 1937 ("quarantine" suggested the role of public health officials handling an infectious disease). The medical metaphor extended beyond the immediate aims of the Truman Doctrine in that the imagery combined with fire and flood imagery evocative of disaster provided the United States with an easy transition to direct military confrontation in later years with the Korean War and the Vietnam War. By framing ideological differences in life or death terms, Truman was able to garner support for this communism-containing policy.[18]
See also[]
- Liberal internationalism
- Eisenhower Doctrine
- Anti-communism
- Reverse course
- Turkey–United States relations
- Greece-United States relations
- Containment
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g McCullough, David (1992). Truman. New York: Simon & Schuster. pp. 547-549.
- ^ "The Truman Doctrine's Significance". History on the Net. November 10, 2020.
- ^ Michael Beschloss (2006). Our Documents: 100 Milestone Documents From The National Archives. Oxford University Press. pp. 194–99. ISBN 978-0-19-530959-1.
- ^ Eric Foner, Give Me Liberty! An American History (2nd ed., 2008) p. 892
- ^ Alan Bullock, Ernest Bevin: Foreign Secretary pp 368–9; Arnold Offner, Another Such Victory: President Truman and the Cold War, 1945–2002 (2002) p 197; Denise M. Bostdorff, Proclaiming the Truman Doctrine (2008) p 51
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Merrill 2006.
- ^ Barın Kayaoğlu, "Strategic imperatives, Democratic rhetoric: The United States and Turkey, 1945–52." Cold War History, Aug 2009, Vol. 9(3) pp. 321–345
- ^ Gerolymatos, André (2017-01-03). An International Civil War: Greece, 1943-1949. Yale University Press. pp. 100–111. ISBN 9780300180602.
- ^ Gerolymatos, André (2017-01-03). An International Civil War: Greece, 1943-1949. Yale University Press. pp. 194–203. ISBN 9780300180602.
- ^ Bærentzen, Lars, John O. Iatrides, and Ole Langwitz. Smith. Studies in the History of the Greek Civil War, 1945–1949. Copenhagen: Museum Tusculanum, 1987. 273-280. Google Books. Web. 28 Apr. 2010. online
- ^ Bullock, Ernest Bevin: Foreign Secretary (1983) ch 8
- ^ Painter 2012, p. 29: "Although circumstances differed greatly in Greece, Turkey, and Iran, U.S. officials interpreted events in all three places as part of a Soviet plan to dominate the eastern Mediterranean and the Middle East. Mention of oil was deliberately deleted from Truman's March 12, 1947, address before Congress pledging resistance to communist expansion anywhere in the world; but guarding access to oil was an important part of the Truman Doctrine. The Truman Doctrine was named after Harry S. Truman. This doctrine stated that that the United States would provide political, military and economic assistance to all democratic nations under threat from external or internal authoritarian forces."
One draft, for example, of Truman's speech spoke of the "great natural resources" of the Middle East at stake (Kolko & Kolko 1972, p. 341).
- ^ Freeland, Richard M. (1970). The Truman Doctrine and the Origins of McCarthyism. Alfred A. Knopf, Inc. pp. g. 90.
- ^ Spalding, Elizabeth Edwards (2006). The First Cold Warrior: Harry Truman, Containment, and the Remaking of Liberal Internationalism. The University Press of Kentucky. p. 64.
- ^ McGhee, George (1990). The US-Turkish-NATO Middle East Connection: How the Truman Doctrine Contained the Soviets in the Middle East. St. Harry’s Press. pp. g. 21.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Patterson, James T. (1996). Grand Expectations. New York: Oxford University Press.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Herring, George C. (2008). From Colony to Superpower: U.S. Foreign Relations Since 1776. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780195078220.
- ^ Ivie 1999.
Bibliography[]
- Beisner, Robert L. Dean Acheson: A Life in the Cold War (2006)
- Bostdorff, Denise M. Proclaiming the Truman Doctrine: The Cold War Call to Arms (2008) excerpt and text search
- Brands, H.W. Into the Labyrinth: The United States and the Middle East, 1945-1993 (1994) excerpt pp 12–17.
- Bullock, Alan. Ernest Bevin: Foreign Secretary, 1945–1951 (1983) on British roles
- Edwards, Lee. "Congress and the Origins of the Cold War: The Truman Doctrine," World Affairs, Vol. 151, 1989 online edition
- Frazier, Robert. "Acheson and the Formulation of the Truman Doctrine" Journal of Modern Greek Studies 1999 17(2): 229–251. ISSN 0738-1727
- Frazier, Robert. "Kennan, 'Universalism,' and the Truman Doctrine," Journal of Cold War Studies, Spring 2009, Vol. 11 Issue 2, pp 3–34
- Gaddis, John Lewis. "Reconsiderations: Was the Truman Doctrine a Real Turning Point?" Foreign Affairs 1974 52(2): 386–402. ISSN 0015-7120
- Hinds, Lynn Boyd, and Theodore Otto Windt Jr. The Cold War as Rhetoric: The Beginnings, 1945–1950 (1991) online edition
- Iatrides, John O. and Nicholas X. Rizopoulos. "The International Dimension of the Greek Civil War." World Policy Journal 2000 17(1): 87–103. ISSN 0740-2775 Fulltext: in Ebsco
- Ivie, Robert L. (1999). "Fire, Flood, and Red Fever: Motivating Metaphors of Global Emergency in the Truman Doctrine Speech". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 29 (3): 570–591. doi:10.1111/j.0268-2141.2003.00050.x.
- Jeffrey, Judith S. Ambiguous Commitments and Uncertain Policies: The Truman Doctrine in Greece, 1947–1952 (2000). 257 pp.
- Jones, Howard. "A New Kind of War": America's Global Strategy and the Truman Doctrine in Greece (1989). 327 pp
- Kayaoğlu, Barın. "Strategic imperatives, Democratic rhetoric: The United States and Turkey, 1945–52.," Cold War History, Aug 2009, Vol. 9(3). pp. 321–345
- Kolko, Joyce; Kolko, Gabriel (1972). The Limits of Power: The World and United States Foreign Policy, 1945–1954. New York, NY: Harper & Row. ISBN 978-0-06-012447-2.
- Leffler, Melvyn P. "Strategy, Diplomacy, and the Cold War: the United States, Turkey, and NATO, 1945–1952" Journal of American History 1985 71(4): 807–825. ISSN 0021-8723 in JSTOR
- Lykogiannis, Athanasios. Britain and the Greek Economic Crisis, 1944–1947: From Liberation to the Truman Doctrine. U. of Missouri Press, 2002. 287 pp. online edition
- McGhee, George. The U.S.-Turkish-NATO Middle East Connection: How the Truman Doctrine and Turkey's NATO Entry Contained the Soviets in the Middle East. (1990). 224 pp.
- Merrill, Dennis (2006). "The Truman Doctrine: Containing Communism and Modernity". Presidential Studies Quarterly. 36 (1): 27–37. doi:10.1111/j.1741-5705.2006.00284.x.
- Meiertöns, Heiko: The Doctrines of US Security Policy – An Evaluation under International Law (2010), ISBN 978-0-521-76648-7.
- Offner, Arnold A. "'Another Such Victory': President Truman, American Foreign Policy, and the Cold War." Diplomatic History 1999 23(2): 127–155.ISSN 0145-2096
- Pach Jr., Chester J. Arming the Free World: The Origins of the United States Military Assistance Program, 1945–1950, (1991) online edition
- Painter, David S. (2012). "Oil and the American Century". The Journal of American History. 99 (1): 24–39. doi:10.1093/jahist/jas073.
- Pieper, Moritz A. (2012). "Containment and the Cold War: Reexaming the Doctrine of Containment as a Grand Strategy Driving US Cold War Interventions". StudentPulse.com. Retrieved 22 August 2012.
- Spalding, Elizabeth Edwards. The First Cold Warrior: Harry Truman, Containment, And the Remaking of Liberal Internationalism (2006)
External links[]
| Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- 1947 in American politics
- Presidency of Harry S. Truman
- Foreign policy doctrines of the United States
- History of the foreign relations of the United States
- Soviet Union–United States relations
- 1947 in international relations
- Soviet Union–Turkey relations
- Turkey–United States relations
- Greece–United States relations
- March 1947 events
- 1947 introductions



