Uggleviken
| Uggleviken | |
|---|---|
 Uggleviken, November 2007 | |
 Uggleviken | |
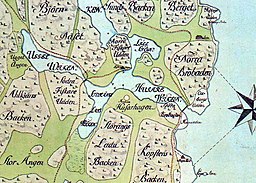 Historical map showing the area in the 17th century. The lake is labeled Uggel-wiken on the left. | |
| Coordinates | 59°21′17″N 18°4′30″E / 59.35472°N 18.07500°ECoordinates: 59°21′17″N 18°4′30″E / 59.35472°N 18.07500°E |
| Primary inflows | Subsoil water, stormwater |
| Primary outflows | , Lilla Värtan |
| Catchment area | 114 ha (280 acres) |
| Basin countries | Sweden |
| Surface area | 12.4 ha (31 acres) |
| Settlements | Norra Djurgården |
| References | [1] |
Uggleviken (Swedish: (the) Owl Bay) is a former bay and lake in Norra Djurgården, a semi-rural area in north-eastern central Stockholm, Sweden, forming part of the Royal National City Park.
Together with Lillsjön, Laduviken and , Uggleviken used to be part of a bay forking across Norra Djurgården. Today it is reduced to a marsh or a wet alder forest with patches of reeds in its centre. It is regarded as of great natural value and have been mentioned as one of the most interesting botanical and ornithological areas in Stockholm.[2]
History[]
The spring of the lake first appears in historical records in the end of the 18th century and during the 19th century and early 20th century it became a popular Trinity spring to which Stockholmers in huge numbers would go on Trinity Sunday to drink at a ceremony. A pavilion constructed in 1902 is still reminding of the era.[3]
Catchment area[]
The marsh's catchment area, considered as one of the most important wetlands in Stockholm and an important biotope for many species, is relatively untouched by humans and mostly contains forest and open terrain. Björnnäsvägen, a densely trafficked road stretching along the northern side of Uggleviken, reduces accessibility to the wetland, as do the suburban railway Roslagsbanan and an industrial railway south of it. The Royal Institute of Technology occupies approximately 20 per cent of the catchment area and on the west side are a number of allotment-gardens.[4]
Environmental influences[]
The major inflow comes from stormwater and surface runoff. Pipes from settled areas opening out on the southern side are believed to be the major environmental burden, together with run-off water from the road north of the wetland. High levels of phosphorus have been recorded in the outflow.[4]
Flora and fauna[]
Botanically, many rare species such as water sedge, lesser tussock-sedge, alternate-leaved golden-saxifrage, small water-pepper, marsh stitchwort, and marsh fern are present. Specimens in isolated ponds in the area contain species of Oligochaeta, and Gastropoda, such as Valvata cristata and Anisus leucostoma. Many species of birds are found in the marsh, including thrush nightingale, redwing, dunnock, and Eurasian wren. Smooth newt and common toad were both reported in 1996.[4]
Visiting[]
Both the wetland and the surrounding national park are easily accessible. The nearest metro station is Tekniska högskolan.
See also[]
- Geography of Stockholm
- Lakes of Sweden
- Uggleviksreservoaren
- Lill-Janskogen
Notes[]
References[]
- "Vattenprogram för Stockholm 2000 - Uggleviken" (PDF) (in Swedish). Stockholm Vatten. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2007-05-27.
- "Uggleviken" (in Swedish). Stockholm vatten. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2007-05-27.
- "Ugglevikskällan" (in Swedish). Stockholm City Museum. Retrieved 2007-05-27.
- Geography of Stockholm
- Lakes of Stockholm County
- Lakes in Djurgården
