Unicast
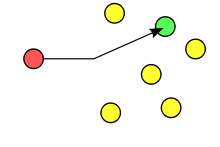
Unicast is data transmission from a single sender (red) to a single receiver (green). Other devices on the network (yellow) do not participate in the communication.
| Routing schemes |
|---|
| Unicast |
| Broadcast |
| Multicast |
| Anycast |
In computer networking, unicast is a one-to-one transmission from one point in the network to another point; that is, one sender and one receiver, each identified by a network address.[1]
Unicast is in contrast to multicast and broadcast which are one-to-many transmissions.
Internet Protocol unicast delivery methods such as Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) are typically used.
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Godred Fairhurst. "Unicast, Broadcast, and Multicast".[dead link][self-published source?]
External links[]
- "Differences Between Multicast and Unicast". Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2008-02-03. Retrieved 2008-02-04.
- "What Is Unicast IPv4 Routing?". Microsoft. Retrieved 2010-09-30.
Categories:
- Internet architecture
- Computer network stubs