Virginia House of Delegates
Coordinates: 37°32′19″N 77°26′00″W / 37.53865°N 77.43331°W
Virginia House of Delegates | |
|---|---|
| Virginia General Assembly | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | Lower House of the Virginia General Assembly |
Term limits | None |
| History | |
| Established | 1776 |
| Preceded by | House of Burgesses |
New session started | January 8, 2020 |
| Leadership | |
Speaker | |
Majority Leader | Charniele Herring (D) since January 8, 2020 |
Minority Leader | |
Clerk | Suzette Denslow since January 8, 2020 |
| Structure | |
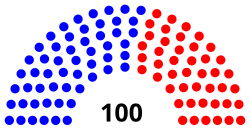
| Seats | 100 |
 | |
Political groups | Majority
Minority
|
Length of term | 2 years |
| Authority | Article IV, Virginia Constitution |
| Salary | $17,640/year + per diem |
| Elections | |
Last election | November 5, 2019 |
Next election | November 2, 2021 |
| Redistricting | By 16-member bipartisan commission, approved by General Assembly |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| House of Delegates Chamber Virginia State Capitol Richmond, Virginia | |
| Website | |
| Virginia General Assembly | |
The Virginia House of Delegates is one of the two parts of the Virginia General Assembly, the other being the Senate of Virginia. It has 100 members elected for terms of two years; unlike most states, these elections take place during odd-numbered years. The House is presided over by the Speaker of the House, who is elected from among the House membership by the Delegates. The Speaker is usually a member of the majority party and, as Speaker, becomes the most powerful member of the House. The House shares legislative power with the Senate of Virginia, the upper house of the Virginia General Assembly. The House of Delegates is the modern-day successor to the Virginia House of Burgesses, which first met at Jamestown in 1619. The House is divided into Democratic and Republican caucuses. In addition to the Speaker, there is a majority leader, majority whip, majority caucus chair, minority leader, minority whip, minority caucus chair, and the chairs of the several committees of the House.
Only Maryland, Virginia and West Virginia refer to their lower house as the House of Delegates.
History and location[]
The House of Burgesses was the first elected legislative body in the New World.[1] Originally having 22 members, the House of Burgesses met from 1619 through 1632 in the choir of the church at Jamestown.[2] From 1632 to 1699 the legislative body met at four different state houses in Jamestown. The first state house convened at the home of Colonial Governor Sir John Harvey from 1632 to 1656. The burgesses convened at the second state house from 1656 until it was destroyed in 1660. Historians have yet to precisely identify its location.[3]
The House of Burgesses had its final meeting in May 1776, and the House of Delegates took its place in October of that year.
The House has met in Virginia's Capitol Building, designed by Thomas Jefferson, since 1788. The legislative body met from 1788 to 1904 in what is known as today the Old Hall of the House of Delegates or commonly referred to as the Old House Chamber. The Old House Chamber is part of the original Capitol building structure. It measures 76 feet in width and is filled today with furnishings that resemble what the room would have looked like during its time of use. There are many bronze and marble busts of historic Virginians on display in the Old House Chamber, including: George Mason, George Wythe, Patrick Henry, Richard Henry Lee, and Meriwether Lewis. From 1904 to 1906, University of Virginia graduate and architect John K. Peeples designed and built compatible classical wings to the west and east side of the Capitol building. The new wings added to provide more space and serve as the legislative chambers in the Virginia General Assembly, the Senate of Virginia resides in the west chamber and the House of Delegates resides in the east chamber. The General Assembly members and staff operate from offices in the General Assembly Building, located in Capitol Square. Prior to 1788 the House of Delegates met in the Colonial Capital of Williamsburg.
In 1999, Republicans took control of the House of Delegates for the first time since Reconstruction (with the exception of a brief 2-year period in which the Readjuster Party was in the majority in the 1880s). The Republican Party held the majority until 2019, when the Democratic Party won a majority of the seats, thus regaining control of the House of Delegates. The majority was sworn in on January 8, 2020, after which Eileen Filler-Corn (D-Fairfax) was elected as the first female and Jewish Speaker of the Virginia House of Delegates.[4]
On November 4, 2020, Virginia voters approved a constitutional amendment that removed the authority to redistrict congressional and state legislative districts from the General Assembly, and gave that power to a newly-established 16-member composed of eight lawmakers and eight non-lawmaker citizens. The maps created by this commission are subject to the approval of the General Assembly, but lawmakers cannot change the commission's lines.[5]
Salary and qualifications[]
The annual salary for delegates is $17,640 per year.[6] Each delegate represents roughly 84,702 people.[6] Candidates for office must be at least 21 years of age at the time of the election, residents of the districts they seek to represent, and qualified to vote for General Assembly legislators.[7][8] The regular session of the General Assembly is 60 days long during even numbered years and 30 days long during odd numbered years, unless extended by a two-thirds vote of both houses.[7][9]
Composition[]
Article IV, Section 3 of the Constitution of Virginia stipulates that the House of Delegates shall consist of between 90 and 100 members. It does not put any condition on the number of districts and only speaks of "several house districts". While there used to be multi-member districts, since 1982, there have been 100 districts electing one member each.
Current political composition[]
| 55 | 45 | |
| Democratic | Republican | |
| Affiliation | Party (Shading indicates majority caucus)
|
Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Democratic | Vacant | ||
| Previous legislature (2016–2018) | 66 | 34 | 100 | 0 |
| Previous legislature (2018-2020) | 51 | 49 | 100 | 0 |
| Begin 2020 | 45 | 55 | 100 | 0 |
| June 28, 2020 | 44 | 55 | 99 | 1[10] |
| November 15, 2020 | 44 | 54 | 98 | 2[11] |
| November 19, 2020 | 45 | 54 | 99 | 1[12] |
| December 12, 2020 | 45 | 53 | 98 | 2[13] |
| January 11, 2021 | 45 | 55 | 100 | 0[14] |
| Latest voting share | 45% | 55% | ||
Historical party control[]
(The party control table shows the balance of power after each recent general election. The preceding Makeup table includes results of special elections since the last general election.)
| Years | Democrats | Republicans | Independents |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1900–1904 | 93 | 7 | 0 |
| 1904–1912 | 86 | 14 | 0 |
| 1912–1914 | 90 | 10 | 0 |
| 1914–1916 | 92 | 8 | 0 |
| 1916–1922 | 88 | 12 | 0 |
| 1922–1924 | 95 | 5 | 0 |
| 1924–1926 | 97 | 3 | 0 |
| 1926–1928 | 95 | 5 | 0 |
| 1928–1930 | 93 | 7 | 0 |
| 1930–1934 | 95 | 5 | 0 |
| 1934–1940 | 93 | 7 | 0 |
| 1940–1944 | 97 | 3 | 0 |
| 1944–1946 | 94 | 6 | 0 |
| 1946–1950 | 93 | 7 | 0 |
| 1950–1960 | 94 | 6 | 0 |
| 1960–1962 | 96 | 4 | 0 |
| 1962–1964 | 94 | 5 | 1 |
| 1964–1966 | 89 | 11 | 0 |
| 1966–1968 | 87 | 12 | 1 |
| 1968–1970 | 86 | 14 | 0 |
| 1970–1972 | 75 | 24 | 1 |
| 1972–1974 | 73 | 24 | 3 |
| 1974–1976 | 65 | 20 | 15 |
| 1976–1978 | 78 | 17 | 5 |
| 1978–1980 | 76 | 21 | 3 |
| 1980–1982 | 74 | 25 | 1 |
| 1982–1984 | 66 | 32 | 2 |
| 1984–1986 | 65 | 34 | 1 |
| 1986–1988 | 65 | 33 | 2 |
| 1988–1990 | 64 | 35 | 1 |
| 1990–1992 | 59 | 40 | 1 |
| 1992–1994 | 58 | 41 | 1 |
| 1994–1996 | 52 | 47 | 1 |
| 1996–1998 | 52 | 47 | 1 |
| 1998–2000 | 50[15] | 49 | 1 |
| 2000–2002 | 47 | 52 | 1 |
| 2002–2004 | 34 | 64 | 2 |
| 2004–2006 | 37 | 61 | 2 |
| 2006–2008 | 40 | 57 | 3 |
| 2008–2010 | 44 | 54 | 2 |
| 2010–2012 | 39 | 59 | 2 |
| 2012–2014 | 32 | 66 | 2 |
| 2014–2016 | 32 | 67 | 1 |
| 2016–2018 | 34 | 66 | 0 |
| 2018–2020 | 49 | 51 | 0 |
| 2020–2022 | 55 | 45 | 0 |
House leadership[]
| Speaker | Eileen Filler-Corn |
| Majority Leader | Charniele Herring |
| Minority Leader | Todd Gilbert |
| Caucus Chair | Kathy Byron |
Committee chairs and ranking members[]
The House has 14 standing committees.[16]
| Committee | Chair | Senior Minority Member |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture, Chesapeake and Natural Resources | Kenneth R. Plum | R. Lee Ware |
| Appropriations | Luke Torian | M. Kirkland Cox |
| Communications, Technology and Innovation | Cliff Hayes Jr. | Kathy Byron |
| Counties Cities and Towns | Kaye Kory | Charles Poindexter |
| Courts of Justice | Charniele Herring | Terry Kilgore |
| Education | Roslyn Tyler | Mark L. Cole |
| Finance | Vivian E. Watts | Robert D. Orrock, Sr. |
| General Laws | David Bulova | Thomas C. Wright, Jr. |
| Health, Welfare and Institutions | Mark D. Sickles | Robert D. Orrock, Sr. |
| Labor and Commerce | Jeion Ward | Terry Kilgore |
| Privileges and Elections | Marcus Simon | Robert D. Orrock, Sr. |
| Public Safety | Patrick Hope | Thomas C. Wright, Jr. |
| Rules | Eileen Filler-Corn | M. Kirkland Cox |
| Transportation | Delores McQuinn | Robert B. Bell |
Members[]
The Virginia House of Delegates is reelected every two years, with intervening vacancies filled by special election. The list below contains the House delegates that are currently serving in the 161st Virginia General Assembly, which convened in January 2020.
| District | Name | Party | Areas Represented | First Election | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Counties | Cities | ||||
| 1 | Terry Kilgore | Rep | Lee, Scott, Wise (part) | Norton | 1993 |
| 2 | Candi King | Dem | Prince William (part), Stafford (part) | 2021 | |
| 3 | Will Morefield | Rep | Bland, Buchanan, Russell (part), Tazewell | 2009 | |
| 4 | Will Wampler | Rep | Dickenson, Russell (part), Washington (part), Wise (part) | 2019 | |
| 5 | Israel O'Quinn | Rep | Grayson, Smyth (part), Washington (part) | Bristol, Galax | 2011 |
| 6 | Jeff Campbell | Rep | Carroll, Smyth (part), Wythe | 2013 | |
| 7 | Nick Rush | Rep | Floyd, Montgomery (part), Pulaski (part) | 2011 | |
| 8 | Joseph McNamara | Rep | Craig, Montgomery (part), Roanoke (part) | Salem | 2018 |
| 9 | Charles Poindexter | Rep | Franklin (part), Henry (part), Patrick | 2007 | |
| 10 | Wendy Gooditis | Dem | Clarke (part), Frederick (part), Loudoun (part) | 2017 | |
| 11 | Sam Rasoul | Dem | Roanoke (part) | 2013 | |
| 12 | Chris Hurst | Dem | Giles, Montgomery (part), Pulaski (part) | Radford | 2017 |
| 13 | Danica Roem | Dem | Prince William (part) | Manassas Park | 2017 |
| 14 | Danny Marshall | Rep | Henry (part), Pittsylvania (part) | Danville | 2001 |
| 15 | Todd Gilbert | Rep | Page, Rockingham (part), Shenandoah, Warren (part) | 2005 | |
| 16 | Les Adams | Rep | Henry (part), Pittsylvania (part) | Martinsville | 2013 |
| 17 | Chris Head | Rep | Botetourt (part), Roanoke (part) | Roanoke (part) | 2011 |
| 18 | Michael Webert | Rep | Culpeper (part), Fauquier (part), Rappahannock, Warren (part) | 2011 | |
| 19 | Terry Austin | Rep | Alleghany, Bedford (part), Botetourt (part) | Covington | 2013 |
| 20 | John Avoli | Rep | Augusta (part), Highland, Nelson(part) | Staunton, Waynesboro | 2019 |
| 21 | Kelly Fowler | Dem | Virginia Beach (part) Chesapeake (part) | 2017 | |
| 22 | Kathy Byron | Rep | Bedford (part), Campbell (part), Franklin (part) | Lynchburg (part) | 1997 |
| 23 | Wendell Walker | Rep | Amherst (part), Bedford (part) | 2019 | |
| 24 | Ronnie R. Campbell | Rep | Amherst (part), Augusta (part), Bath, Rockbridge | Buena Vista, Lexington | 2018 |
| 25 | Chris Runion | Rep | Albemarle (part), Augusta (part), Rockingham (part) | 2019 | |
| 26 | Tony Wilt | Rep | Rockingham (part) | Harrisonburg | 2010 |
| 27 | Roxann Robinson | Rep | Chesterfield (part) | 2010 | |
| 28 | Joshua G. Cole | Dem | Stafford (part) | Fredericksburg (part) | 2019 |
| 29 | Bill Wiley | Rep | Frederick (part), Warren (part) | Winchester | 2020 |
| 30 | Nick Freitas | Rep | Culpeper (part), Madison, Orange | 2015 | |
| 31 | Elizabeth Guzmán | Dem | Fauquier (part), Prince William (part) | 2017 | |
| 32 | David A. Reid | Dem | Loudoun (part) | 2017 | |
| 33 | Dave LaRock | Rep | Clarke (part), Frederick (part), Loudoun (part) | 2013 | |
| 34 | Kathleen Murphy | Dem | Fairfax (part), Loudoun (part) | 2015 | |
| 35 | Mark Keam | Dem | Fairfax (part) | 2009 | |
| 36 | Kenneth R. Plum | Dem | 1981 | ||
| 37 | David Bulova | Dem | Fairfax | 2005 | |
| 38 | Kaye Kory | Dem | 2009 | ||
| 39 | Vivian Watts | Dem | 1995 | ||
| 40 | Dan Helmer | Dem | Fairfax (part), Prince William (part) | 2019 | |
| 41 | Eileen Filler-Corn | Dem | Fairfax (part) | 2010 | |
| 42 | Kathy Tran | Dem | 2017 | ||
| 43 | Mark Sickles | Dem | 2003 | ||
| 44 | Paul Krizek | Dem | 2015 | ||
| 45 | Mark Levine | Dem | Arlington (part), Fairfax (part) | Alexandria (part) | 2015 |
| 46 | Charniele Herring | Dem | 2009 | ||
| 47 | Patrick Hope | Dem | Arlington (part) | 2009 | |
| 48 | Rip Sullivan | Dem | Arlington (part), Fairfax (part) | 2014 | |
| 49 | Alfonso H. Lopez | Dem | 2011 | ||
| 50 | Lee J. Carter | Dem | Prince William (part) | Manassas | 2017 |
| 51 | Hala Ayala | Dem | 2017 | ||
| 52 | Luke Torian | Dem | 2009 | ||
| 53 | Marcus Simon | Dem | Fairfax (part) | Falls Church | 2013 |
| 54 | Bobby Orrock | Rep | Caroline (part), Spotsylvania (part) | 1989 | |
| 55 | Buddy Fowler | Rep | Caroline (part), Hanover (part), Spotsylvania (part) | 2009 | |
| 56 | John McGuire | Rep | Goochland (part), Henrico (part), Louisa, Spotsylvania (part) | 2017 | |
| 57 | Sally L. Hudson | Dem | Albemarle (part) | Charlottesville | 2019 |
| 58 | Rob Bell | Rep | Albemarle (part), Fluvanna (part), Greene, Rockingham (part) | 2001 | |
| 59 | Matt Fariss | Rep | Albemarle (part), Appomattox, Buckingham, Campbell (part), Nelson (part) | 2011 | |
| 60 | James E. Edmunds | Rep | Campbell (part), Charlotte, Halifax, Prince Edward | 2009 | |
| 61 | Thomas C. Wright | Rep | Amelia, Cumberland, Lunenburg (part), Mecklenburg, Nottoway | 2000 | |
| 62 | Carrie Coyner | Rep | Chesterfield (part), Henrico (part), Prince George (part) | Hopewell (part) | 2019 |
| 63 | Lashrecse Aird | Dem | Chesterfield (part), Dinwiddie (part), Prince George (part) | Hopewell (part), Petersburg | 2015 |
| 64 | Emily Brewer | Rep | Isle of Wight (part), Prince George (part), Southampton (part), Surry (part), Sussex (part) | Franklin (part), Suffolk (part) | 2017 |
| 65 | Lee Ware | Rep | Chesterfield (part), Fluvanna (part), Goochland (part), Powhatan | 1998 | |
| 66 | Kirk Cox | Rep | Chesterfield (part) | Colonial Heights | 1989 |
| 67 | Karrie Delaney | Dem | Fairfax (part), Loudoun (part) | 2017 | |
| 68 | Dawn Adams | Dem | Chesterfield (part), Henrico (part) | Richmond (part) | 2017 |
| 69 | Betsy B. Carr | Dem | Chesterfield (part) | 2009 | |
| 70 | Delores McQuinn | Dem | Chesterfield (part), Henrico (part) | 2009 | |
| 71 | Jeff Bourne | Dem | Henrico (part) | 2017 | |
| 72 | Schuyler VanValkenburg | Dem | 2017 | ||
| 73 | Rodney Willett | Dem | Richmond (part) | 2019 | |
| 74 | Lamont Bagby | Dem | Charles City, Henrico (part) | 2015 | |
| 75 | Roslyn Tyler | Dem | Brunswick, Dinwiddie (part) Greensville, Isle of Wight (part), Lunenburg (part), Southampton (part), Surry (part), Sussex (part) | Emporia, Franklin (part) | 2005 |
| 76 | Clinton Jenkins | Dem | Chesapeake (part), Suffolk (part) | 2019 | |
| 77 | Cliff Hayes Jr. | Dem | 2016 | ||
| 78 | Jay Leftwich | Rep | Chesapeake (part) | 2013 | |
| 79 | Steve Heretick | Dem | Norfolk (part), Portsmouth (part) | 2015 | |
| 80 | Don Scott | Dem | Chesapeake (part), Norfolk (part), Portsmouth (part), Suffolk (part) | 2019 | |
| 81 | Barry Knight | Rep | Chesapeake (part), Virginia Beach (part) | 2009 | |
| 82 | Jason Miyares | Rep | Virginia Beach (part) | 2015 | |
| 83 | Nancy Guy | Dem | Norfolk (part), Virginia Beach (part) | 2019 | |
| 84 | Glenn Davis | Rep | Virginia Beach (part) | 2013 | |
| 85 | Alex Askew | Dem | 2019 | ||
| 86 | Ibraheem Samirah | Dem | Fairfax (part), Loudoun (part) | 2019 | |
| 87 | Suhas Subramanyam | Dem | Loudoun (part), Prince William (part) | 2019 | |
| 88 | Mark Cole | Rep | Fauquier (part), Spotsylvania (part), Stafford (part) | Fredericksburg (part) | 2001 |
| 89 | Jay Jones | Dem | Norfolk (part) | 2017 | |
| 90 | Angelia Williams Graves | Dem | Norfolk (part), Virginia Beach (part) | 2021 | |
| 91 | Martha Mugler | Dem | York (part) | Hampton (part), Poquoson | 2019 |
| 92 | Jeion Ward | Dem | Hampton (part) | 2003 | |
| 93 | Michael P. Mullin | Dem | James City (part), York (part) | Newport News (part), Williamsburg | 2016 |
| 94 | Shelly Simonds | Dem | Newport News (part) | 2019 | |
| 95 | Marcia Price | Dem | Hampton (part), Newport News (part) | 2015 | |
| 96 | Amanda Batten | Rep | James City (part), York (part) | 2019 | |
| 97 | Scott Wyatt | Rep | Hanover (part), King William (part), New Kent | 2019 | |
| 98 | Keith Hodges | Rep | Essex, Gloucester, King and Queen, King William (part), Mathews, Middlesex | 2011 | |
| 99 | Margaret Ransone | Rep | Caroline (part), King George, Lancaster, Northumberland, Richmond, Westmoreland | 2011 | |
| 100 | Robert Bloxom, Jr. | Rep | Accomack, Northampton | Norfolk (part), Virginia Beach (part) | 2014 |
Database of Members past and present[]
Marking the 400th anniversary of the House of Burgesses, the House Clerk's Office announced a new Database of House Members called "DOME" that chronicles the "9,700-plus men and women who served as burgesses or delegates in the Virginia General Assembly over the past four centuries."[17][18][19]
See also[]
- List of Virginia state legislatures
- Mace of the Virginia House of Delegates
- Political party strength in Virginia
- Redistricting in Virginia
- Virginia House of Delegates elections, 2017
- Category:Members of the Virginia House of Delegates
Notes[]
- ^ "This Day in History". Retrieved March 23, 2016.
- ^ Commonwealth of Virginia. "Capitol Square Timeline". Retrieved April 26, 2011.
- ^ Commonwealth of Virginia. "Timeline".
- ^ "Newly-Empowered Virginia Democrats Promise Action". Voice of America. Associated Press. January 8, 2020. Retrieved September 6, 2020.
- ^ "Proposed Amendments for 2020 - Virginia Department of Elections". www.elections.virginia.gov. Retrieved February 23, 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Virginia House of Delegates". DailyPress.com. Retrieved September 11, 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Virginia State Legislature" (PDF). VAKids.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 17, 2008. Retrieved September 11, 2008.
- ^ "Constitution of Virginia, Article IV, Section 4. Qualifications of senators and delegates". Commonwealth of Virginia. Retrieved November 7, 2017.
- ^ "Constitution of Virginia, Article IV, Section 6. Legislative sessions". Virginia General Assembly. Archived from the original on December 18, 2008. Retrieved October 22, 2008.
- ^ Chris Collins resigned in order to accept a state judgeship, leaving his seat vacant. [1]
- ^ Joseph C. Lindsey resigned in order to accept a judgeship, leaving his seat vacant. [2]
- ^ Bill Wiley takes office after winning special election to replace Delegate Chris Collins.
- ^ Jennifer Carroll Foy resigns to focus on her campaign for Governor.
- ^ Candi King and Angelia Williams Graves win special elections.
- ^ The 1997 general election yielded a 51-48-1 Democratic majority. David Brickley resigned his seat right afterward, however, and a special election for District 51 was called. His seat flipped to the Republicans, and with Independent Lacey Putney siding with the Republicans, the chamber was tied. Democrats retained the Speakership through a power-sharing agreement. [3] [4]
- ^ "Virginia House of Delegates Committees List". virginiageneralassembly.gov. Retrieved February 2, 2018.
- ^ "Virginia House unveils new searchable website of its members". Village News. January 8, 2019. Retrieved January 25, 2019.
- ^ "Virginia House of Delegates unveils searchable website". Henrico Citizen. Retrieved January 25, 2019.
- ^ Hankerson, Mechelle (January 3, 2019). "New database holds 400 years worth of information on members of Virginia's legislature". Virginia MErcury. Retrieved January 25, 2019.
External links[]
- Virginia General Assembly
- State lower houses in the United States
