W85
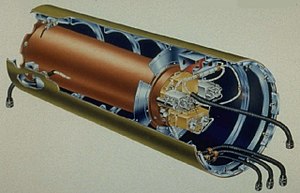 A DOE drawing of the W85 warhead. | |
| Type | Nuclear weapon |
| Place of origin | United States |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Los Alamos National Laboratory |
| No. built | 215 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | Less than 591 pounds (268 kg)[1] |
| Blast yield | 0.3, 5, 10 or 80 kt. |


The W85 was a thermonuclear warhead developed by the United States of America to arm the Pershing II missile. It was a variable yield device with a selectable yield of 0.3, 5, 10 or 80 kt.[2][3]
Overview[]
The Pershing Ia missile was armed with a 400 kiloton W50 warhead. By the early 1970s it was clear that this was far too large to allow the missile to be used as a tactical nuclear weapon — by this time 400 kt was larger than many strategic warheads. The Pershing II had a high accuracy maneuverable reentry vehicle (MARV) equipped with a radar terminal guidance system which allowed it use the lower yield W85 warhead. The warhead was derived from the B61 Mod 3 and utilized the same pit in the primary stage of the warhead,[4] but has also been described as having a nuclear design similar to that of the B61-4.[5] The total weight of the Pershing II warhead section was 591 pounds (268 kg) which included the reentry vehicle.[6]
After the Pershing missiles were scrapped, all of the W85 warheads produced were modified into B61 Mod 10 bombs[7][8] 215 W85 warheads were manufactured.[9]
References[]
- ^ Pershing II Weapon System TM 9-1425-386-10-1 (PDF). United States Army. June 1986. p. 5-1. Archived from the original on 6 August 2020.
- ^ "The B61 Bomb". www.nuclearweaponarchive.org. Retrieved 2018-10-16.
- ^ "List of All U.S. Nuclear Weapons". www.nuclearweaponarchive.org. Retrieved 2018-10-16.
- ^ Jill C Fahrenholtz (September 1997). Development of an Automated Pit Packaging System for Pantex (PDF) (Report). Sandia National Labs. p. 15. doi:10.2172/534478. S2CID 107183716. SAND 97-2163. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-02-15. Retrieved 2021-02-09.
- ^ Sandia Weapon Review: Nuclear Weapon Characteristics Handbook (PDF) (Report). Sandia National Labs. September 1990. p. 79. SAND90-1238.
- ^ Pershing II Weapon System, p. 5-1.
- ^ "The B61 Bomb". www.nuclearweaponarchive.org. Retrieved 2018-10-16.
- ^ Pike, John. "B61". www.globalsecurity.org. Archived from the original on 2010-04-17. Retrieved 2018-10-16.
- ^ Kristensen, Hans; Norris, Robert (27 November 2015). "The B61 family of nuclear bombs". Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists. 70 (3): 79–84. doi:10.1177/0096340214531546. S2CID 146744069.
- Nuclear warheads of the United States
- Military equipment introduced in the 1980s