West Yorkshire
West Yorkshire | |
|---|---|
Metropolitan and Ceremonial county | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 53°45′N 1°40′W / 53.750°N 1.667°WCoordinates: 53°45′N 1°40′W / 53.750°N 1.667°W | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Constituent country | England |
| Region | Yorkshire and the Humber |
| Established | 1 April 1974 |
| Preceded by | West Riding of Yorkshire |
| Origin | Local Government Act 1972 |
| Time zone | UTC±00:00 (Greenwich Mean Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+01:00 (British Summer Time) |
| Members of Parliament | List of MPs |
| Police | West Yorkshire Police |
| Ceremonial county | |
| Lord Lieutenant | Edmund Anderson |
| High Sheriff | Jonathan Thornton[1] (2020–21) |
| Mayor | Tracy Brabin |
| Area | 2,029 km2 (783 sq mi) |
| • Ranked | 29th of 48 |
| Population (mid-2019 est.) | 2,320,214 |
| • Ranked | 4th of 48 |
| Density | 1,143/km2 (2,960/sq mi) |
| Ethnicity | 81.8% White 11.6% S. Asian 2.1% Mixed 2.1% Black 2.4% Other |
| Metropolitan county | |
| Government | • Type Combined authority • Body West Yorkshire Combined Authority • Mayor Tracy Brabin (L) |
| Admin HQ | Leeds |
| ONS code | 2F |
| GSS code | E11000006 |
| NUTS | UKE4 |
| Website | www |
| Districts | |
 Districts of West Yorkshire Metropolitan districts | |
| Districts |
|
West Yorkshire is a metropolitan and ceremonial county in England. It is an inland and, in relative terms, upland county having eastward-draining valleys while taking in the moors of the Pennines. West Yorkshire came into existence as a metropolitan county in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972[2] and has a population of 2.3 million.
West Yorkshire consists of five metropolitan boroughs (City of Bradford, Calderdale, Kirklees, City of Leeds and City of Wakefield) and is bordered by the counties of Derbyshire to the south, Greater Manchester to the south-west, Lancashire to the west and north-west, North Yorkshire to the north and east, and South Yorkshire to the south and south-east.
Remnants of strong coal, wool and iron ore industries remain in the county, having attracted people over the centuries, and this can be seen in the buildings and architecture. Major railways and two major motorways traverse the county, which also contains Leeds Bradford International Airport.
West Yorkshire includes the West Yorkshire Urban Area, which is the biggest and most built-up urban area within the historic county boundaries of Yorkshire.
Governance[]

West Yorkshire County Council was abolished in 1986, so its five districts became effectively unitary authorities. However, the metropolitan county, which covers an area of 2,029 square kilometres (783 sq mi), continues to exist in law, and as a geographic frame of reference.[3][4][5]
Since 1 April 2014, West Yorkshire has been a combined authority area, with the local authorities pooling together some functions over transport and regeneration as the West Yorkshire Combined Authority. The first Mayor of West Yorkshire, Tracy Brabin, was elected on 6 May 2021, following a devolution deal announced by the government in the March 2020 budget.[6][7]
The conurbation of Leeds, Bradford, Wakefield, Halifax, Dewsbury and Huddersfield makes up the West Yorkshire Built-up Area, which is the fourth-largest in the United Kingdom and the largest within the historic county boundaries of Yorkshire.
In Parliament, 13 out of 22 of West Yorkshire's MPs are Labour and 9 are Conservative. At local level, the councils are generally divided, apart from the Wakefield district, which has long been one of the safest Labour councils in the country.
Certain services are provided across the county by West Yorkshire Joint Services, and the West Yorkshire Police and West Yorkshire Fire and Rescue Service are also county-wide.
Geography[]

The county borders, going anticlockwise from the west: Lancashire, Greater Manchester, Derbyshire, South Yorkshire and North Yorkshire. The terrain of the county mostly consists of the Pennines and its foothills which dominate the west of the county and gradually descend into the Vale of York and Humberhead Levels in the east. Geologically, it lies almost entirely on rocks of carboniferous age which form the inner Southern Pennine fringes in the west[8] and the Yorkshire coalfield further eastwards.[9] In the extreme east of the metropolitan county there are younger deposits of Magnesian Limestone.[10] Areas in the west such as Bradford and Calderdale are dominated by the scenery of the eastern slopes of the South Pennines, dropping from upland in the west down to the east, and dissected by many steep-sided valleys while a small part of the northern Peak District extends into the south west of Kirklees. Large-scale industry, housing, public and commercial buildings of differing heights, transport routes and open countryside conjoin. The dense network of roads, canals and railways and urban development, confined by valleys creates dramatic interplay of views between settlements and the surrounding hillsides, as shaped the first urban-rural juxtapositions of David Hockney. Where most rural the land crops up in the such rhymes and folklore as On Ilkla Moor Baht 'at, date unknown, the early 19th century novels and poems of the Brontë family often in and around Haworth and long-running light comedy-drama Last of the Summer Wine in the 20th century.
The carboniferous rocks of the Yorkshire coalfield further east have produced a rolling landscape with hills, escarpments and broad valleys in the outer fringes of the Pennines. In this landscape there is widespread evidence of both current and former industrial activity. There are numerous derelict or converted mine buildings and recently landscaped former spoil heaps.[citation needed] The scenery is a mixture of built up areas, industrial land with some dereliction, and farmed open country. Ribbon developments along transport routes including canal, road and rail are prominent features of the area although some remnants of the pre industrial landscape and semi-natural vegetation still survive. However, many areas are affected by urban fringe pressures creating fragmented and downgraded landscapes and ever present are urban influences from major cities, smaller industrial towns and former mining villages.[citation needed] In the Magnesian Limestone belt to the east of the Leeds and Wakefield areas is an elevated ridge with smoothly rolling scenery, dissected by dry valleys. Here, there is a large number of country houses and estates with parkland, estate woodlands, plantations and game coverts.[citation needed]
The rivers Aire and Calder drain the area, flowing from west to east.
The table below outlines many of the county's settlements, and is formatted according to their metropolitan borough.
| Metropolitan county | Metropolitan borough | Centre of administration | Other places | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| West Yorkshire | City of Bradford | Bradford | Addingham, Baildon, Bingley, Burley in Wharfedale, Cottingley, Crossflatts, Cross Roads, Cullingworth, Denholme, East and West Morton, Eccleshill, Eldwick, Esholt, Great Horton, Gilstead, Harden, Haworth, Ilkley, Keighley, Menston, Oakworth, Oxenhope, Queensbury, Riddlesden, Saltaire, Sandy Lane, Shipley, Silsden, Stanbury, Steeton, Thornbury, Thornton, Tong, Undercliffe, Wibsey, Wilsden. | |
| Calderdale | Halifax | Bailiff Bridge, Boothtown, Brighouse, Copley, Cragg Vale, Elland, Greetland, Hebden Bridge, Heptonstall, Hipperholme, Holywell Green, Luddendenfoot, Mytholmroyd, Norwood Green, Rastrick, Ripponden, Shelf, Shibden, Sowerby Bridge, Todmorden | ||
| Kirklees | Huddersfield | Almondbury, Batley, Birkby, Birkenshaw, Birstall, Cleckheaton, Dalton, Denby Dale, Dewsbury, Emley, Golcar, Gomersal, Hartshead, Hartshead Moor, Heckmondwike, Holmfirth, Honley, Kirkburton, Kirkheaton, Linthwaite, Liversedge, Marsden, Meltham, Mirfield, New Mill, Norristhorpe, Roberttown, Scammonden, Shelley, Shepley, Skelmanthorpe, Slaithwaite, Thornhill | ||
| City of Leeds | Leeds | Allerton Bywater, Beeston, Boston Spa, Collingham, Garforth, Guiseley, Harewood, Harehills, Headingley, Holbeck, Horsforth, Hyde Park, Gipton, Kippax, Kirkstall, Ledsham, Ledston, Methley, Middleton, Morley, New Farnley, Otley, Oulton, Pool-in-Wharfedale, Pudsey, Rothwell, Rawdon, Scarcroft, Scholes, Stourton, Swillington, Walton (Leeds), Wetherby, Yeadon, Woodhouse | ||
| City of Wakefield | Wakefield | Ackworth, Alverthorpe, Castleford, Crigglestone, Crofton, Durkar, Fairburn Ings, Featherstone, Ferrybridge, Fitzwilliam, Hemsworth, Horbury, Knottingley, Newmillerdam, Normanton, Nostell, Ossett, Outwood, Pontefract, Ryhill, Sandal, Sharlston, Stanley, Walton (Wakefield), West Bretton | ||
All of these form part of the former West Riding of Yorkshire. A portion of Derbyshire borders West and South Yorkshire at Glossop and Woodhead.
A small section of West Yorkshire forms scattered settlements into Rochdale in Greater Manchester with the villages of Walsden and Rishworth in Calderdale which are only 8 and 11 miles apart from the main town centre. West Yorkshire also has close ties with Lancashire in terms of history, local identity and infrastructure including with the War of the Roses and Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway.[11][12] Up until the 19th century, the town of Todmorden was in Lancashire but was moved into Yorkshire.[13] In the 1974 boundary review. The towns of Earby and Barnoldswick were moved into the Pendle district of Lancashire.[14] The towns of Halifax, Hebden Bridge, Keighley and the city of Bradford border the boroughs of Pendle, Burnley and Rossendale. The civil parish of Saddleworth in Oldham was the only part of West Riding of Yorkshire to be moved into the county of Greater Manchester. The villages in the parish border the towns of Huddersfield and Holmfirth. There is a strong identity debate with Saddleworth residents who still maintain close connections with Yorkshire. Including the Saddleworth White Rose Society.[15]
History[]

West Yorkshire was formed as a metropolitan county in 1974, by the Local Government Act 1972, and corresponds roughly to the core of the historic West Riding of Yorkshire and the county boroughs of Bradford, Dewsbury, Halifax, Huddersfield, Leeds, and Wakefield.
West Yorkshire Metropolitan County Council inherited the use of West Riding County Hall at Wakefield, opened in 1898, from the West Riding County Council in 1974. Since 1987 it has been the headquarters of Wakefield City Council.[16]
The county initially had a two-tier structure of local government with a strategic-level county council and five districts providing most services.[17] In 1986, throughout England the metropolitan county councils were abolished. The functions of the county council were devolved to the boroughs; joint-boards covering fire, police and public transport; and to other special joint arrangements.[18] Organisations such as the West Yorkshire Police (governed by the West Yorkshire Police and Crime Commissioner) continue to operate on this basis.
Although the county council was abolished, West Yorkshire continues to form a metropolitan and ceremonial county with a Lord Lieutenant of West Yorkshire and a High Sheriff.
Wakefield's Parish Church was raised to cathedral status in 1888 and after the elevation of Wakefield to diocese, Wakefield Council immediately sought city status and this was granted in July 1888.[19] However the industrial revolution, which changed West and South Yorkshire significantly, led to the growth of Leeds and Bradford, which became the area's two largest cities (Leeds being the largest in Yorkshire). Leeds was granted city status in 1893 and Bradford in 1897. The name of Leeds Town Hall reflects the fact that at its opening in 1858 Leeds was not yet a city, while Bradford renamed its Town Hall as City Hall in 1965.[20]
| Post-1974 | Pre-1974 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metropolitan county | Metropolitan borough | County boroughs | Non-county boroughs | Urban districts | Rural districts |
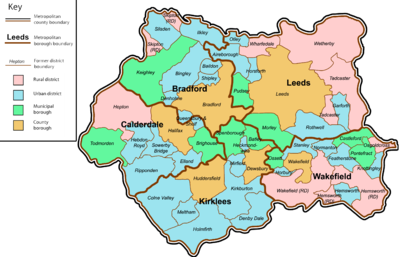 West Yorkshire is an amalgamation of 53 former local government districts, including five county boroughs and ten municipal boroughs. |
Bradford | Bradford | Keighley | Baildon • Bingley • Denholme • Ilkley • Queensbury and Shelf[21] •Silsden • Shipley | Skipton |
| Calderdale | Halifax | Brighouse • Todmorden | Elland • Hebden Royd • Queensbury and Shelf[21] • Ripponden • Sowerby Bridge | ||
| Kirklees | Huddersfield • Dewsbury | Batley • Spenborough | Colne Valley • Denby Dale • Heckmondwike • Holmfirth • Kirkburton • Meltham • Mirfield | ||
| Leeds | Leeds | Morley • Pudsey | Aireborough • Garforth • Horsforth • Otley • Rothwell | Tadcaster • Wharfedale • Wetherby | |
| Wakefield | Wakefield | Castleford • Ossett • Pontefract | Featherstone • Hemsworth • Horbury • Knottingley • Normanton • Stanley | Hemsworth • Osgoldcross • Wakefield | |
Green belt[]
West Yorkshire contains green belt interspersed throughout the county, surrounding the West Yorkshire Urban Area. It was first drawn up in the 1950s. All the county's districts contain large portions of green belt.
Climate[]
West Yorkshire has an Oceanic climate, similar to other parts of the United Kingdom. West Yorkshire tends to be cooler than counties further south, due to inland location and high elevation (especially in western areas). Snow is common, as are sub-zero temperatures. In December 2010, many rivers in West Yorkshire froze over.
Temperatures over the year usually remain between −1 °C (30 °F) and 20 °C (68 °F) with rare extremes near 30 °C (86 °F) and −16 °C (3 °F).
| hideClimate data for West Yorkshire | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 5 (41) |
5 (41) |
8 (46) |
11 (52) |
15 (59) |
18 (64) |
19 (66) |
19 (66) |
17 (63) |
13 (55) |
8 (46) |
6 (43) |
12 (54) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0 (32) |
0 (32) |
1 (34) |
3 (37) |
5 (41) |
8 (46) |
10 (50) |
10 (50) |
8 (46) |
6 (43) |
2 (36) |
1 (34) |
5 (40) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 61 (2.4) |
45 (1.8) |
52 (2.0) |
48 (1.9) |
54 (2.1) |
54 (2.1) |
51 (2.0) |
65 (2.6) |
57 (2.2) |
55 (2.2) |
57 (2.2) |
61 (2.4) |
660 (25.9) |
| Source 1: www.worldtravels.com[22] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: www.wunderground.com[23] | |||||||||||||
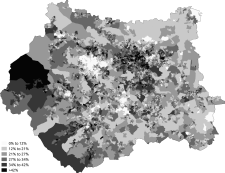
Demography[]
| District | Area km2 | Population | Population density |
|---|---|---|---|
| City of Bradford | 366.42 | 523,100 | 1,346 |
| Calderdale | 363.92 | 200,100 | 545 |
| Kirklees | 408.61 | 401,000 | 975 |
| City of Leeds | 551.72 | 761,100 | 1,360 |
| City of Wakefield | 338.61 | 321,600 | 949 |


White

White-British

White-Irish

White-Other

Asian

Asian-Indian
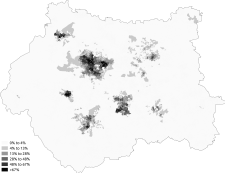
Asian-Pakistani

Asian-Bangladeshi

Asian-Chinese
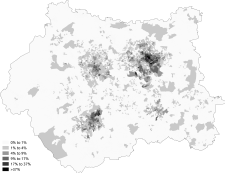
Black

Black-African
Black-Caribbean
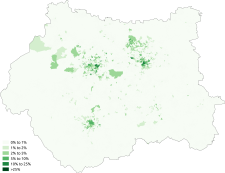
Other-Arab
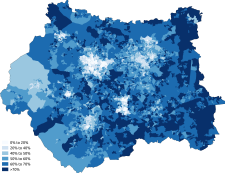
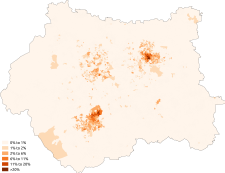
Christianity

Islam

Judaism

Hinduism

Sikhism

Buddhism

Other religion
No religion
Economy[]

This is a chart of regional gross value added for West Yorkshire at current basic prices with figures in millions of British Pounds Sterling.[24]
| Year | Regional Gross Value Added[25] | Agriculture[26] | Industry[27] | Services[28] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1995 | 21,302 | 132 | 7,740 | 13,429 |
| 2000 | 27,679 | 80 | 8,284 | 19,314 |
| 2003 | 31,995 | 91 | 8,705 | 23,199 |
Industries[]
Leeds has since attracted investment from financial institutions, to become a recognised financial centre, with many banks, building societies and insurance companies having offices in the city. Wakefield has also attracted many service-based industries, in particular call centres. Two of the big four supermarkets are from West Yorkshire. Morrisons is based in Bradford, while Asda is based in Leeds. Netto have their British headquarters in South Elmsall.
West Yorkshire grew up around several industries. Wakefield, Castleford, Pontefract and South and East Leeds were traditional coal mining areas.
- Wool
Bradford, Halifax and Huddersfield grew through the development of woollen mills. Leeds' traditional industry was the manufacturing of cloth while heavier engineering industries facilitated growth in South Leeds.
The Heavy Woollen District covered towns such as Dewsbury, Batley, Morley, Ossett, Cleckheaton and Heckmondwike. The woollen and cloth industries declined throughout the twentieth century.
- Rhubarb
The Rhubarb Triangle is wholly in West Yorkshire and still produces the vegetable in considerable quantities.[29] Twelve farmers who farm within the Rhubarb Triangle applied to have the name "Yorkshire forced rhubarb" added to the list of foods and drinks that have their names legally protected by the European Commission's Protected Food Name scheme.[30] The application was successful and the farmers in the Rhubarb Triangle were awarded Protected Designation of Origin status (PDO) in February 2010. Food protected status accesses European funding to promote the product and legal backing against other products made outside the area using the name. Other protected names include Stilton cheese, Champagne and Parma Ham.
- Coal
Many of the coal mines in West Yorkshire closed during the Robens era in the 1960s, but mining was still a significant employer in the Wakefield district at the time of the 1984–85 strike. The last pit in West Yorkshire to close was Hay Royds Colliery at Denby Dale in 2012 after a flood.[31]
Film and television productions[]
Several films and television series have been filmed in West Yorkshire's historic areas, particularly around the town of Halifax.[32][33] For example, portions of the BBC television series Happy Valley were filmed in Huddersfield; in addition to exteriors, some of the studio filming was done at North Light Film Studios at Brookes Mill, Huddersfield. As well, interiors for the BBC's Jamaica Inn, for the BBC's Remember Me and for ITV series Black Work, were also filmed at the studios.[34][35][36][37] More recently, many of the exteriors of the BBC series Jericho were filmed at the nearby Rockingstone Quarry and some interior work was done at North Light Film Studios.[38]
Tourism[]

Urban tourism varies. National interest features include sporting stadia, museums, theatre and galleries. Royal Armouries is in Leeds, as is the Leeds Playhouse (formerly the West Yorkshire Playhouse), Opera North and The Grand Theatre. The First Direct Arena in Leeds seats around 15,000 people. Sheffield Arena is also popular, as is the Bradford Alhambra, St Georges Hall and the Media and Science Museum in Bradford. Leeds is the most popular shopping destination in West Yorkshire, probably Yorkshire and rivals Manchester having claim to Briggate, the Headrow, Trinity Leeds, Victoria Gate, the Victoria and Northern Quarters, the biggest indoor market in Europe and the White Rose Centre, as well as many 'first outside of London' labels such as Harvey Nichols and Victoria's Secret. Leeds is also a popular nightlife destination domestically, which is not surprising given its accessibility and central location. All cities are well connected via rail and road, Leeds railway station is an important hub seeing 29.7 million passengers 2015–16, making it the fourth busiest station in the UK after London stations, Birmingham New Street and Glasgow Central. It is the busiest in Northern England.
Signposted walks follow rivers and the escarpment of the Pennines, which is scaled in meandering stages and tunnels by the recreational Leeds-Liverpool Canal and Rochdale Canal, navigable by barge, canoe or kayak. Other tourism features include abbeys, castles, countryside walks, landscapes, picturesque villages, architecture, stately homes, tea rooms, real ale breweries, farmer's markets, restaurants and hiking in villages including Hebden Bridge, Ilkley with its scenic riversides, cherry blossoms and suspension bridge and equally in Wharfedale, Otley.
Transport[]

West Yorkshire lies in arguably the most strategic part of Yorkshire: the M62, M1 and the A1(M) pass through the county, as well as the internal urban motorways in Leeds and Bradford. West Yorkshire has two mainline railway stations, Leeds and Wakefield Westgate. Leeds railway station is the only Network Rail principal station in Yorkshire and North East England, and one of only three in the North of England along with Manchester Piccadilly and Liverpool Lime Street. Other important railway stations in West Yorkshire include Bradford Interchange, Bradford Forster Square, Huddersfield, Halifax, Dewsbury, Keighley and Shipley. West Yorkshire also has Yorkshire's largest airport, Leeds Bradford Airport.
Unlike South Yorkshire, West Yorkshire has no light transit system; the Leeds Supertram was proposed but was later cancelled after the withdrawal of government funding. Public transport is run under the authority of West Yorkshire Metro.
Sport[]

Major football clubs in West Yorkshire include Leeds United, Huddersfield Town, and Bradford City.
Rugby league is also big in West Yorkshire. The teams who are, or have been, in the Super League are Bradford Bulls, Castleford Tigers, Halifax, Huddersfield Giants, Leeds Rhinos, and Wakefield Trinity. Other rugby league clubs in West Yorkshire include Batley Bulldogs, Dewsbury Rams, Featherstone Rovers, Hunslet Hawks and Keighley Cougars. Any combination of these teams playing against each other would be called a West Yorkshire derby even if the rivalry is not as great as other rivalries between teams in the area. The main rugby union club in the county is Yorkshire Carnegie.
Elland Road is the largest stadium in the area, hosting Leeds United. The Headingley Stadium, a stadium complex also in Leeds, consists of a cricket and a rugby ground. The cricket ground is home of the Yorkshire County Cricket Club and the rugby ground is home to both Leeds Rhinos and Yorkshire Carnegie. In Huddersfield, the John Smith's Stadium is home to Huddersfield Town and Huddersfield Giants. In Bradford, Valley Parade is the home of Bradford City, whereas the Odsal Stadium is the home of the Bradford Bulls. Other stadiums include Wheldon Road (Castleford), The Shay (Halifax), Belle Vue (Wakefield), Mount Pleasant (Batley), Crown Flatt (Dewsbury), Post Office Road (Featherstone), John Charles Centre for Sport (Hunslet) and Cougar Park (Keighley).
There are two racecourses in West Yorkshire: Pontefract and Wetherby
West Yorkshire also used to host regular speedway meetings, having the Halifax Dukes and the Bradford Dukes teams. Odsal Stadium used to host BriSCA stock cars. Leeds has a hill climb event at Harewood speed Hillclimb.
Places of interest[]
Historic environment[]
| Key | |
| Abbey/Priory/Cathedral | |
| Accessible open space | |
| Amusement/Theme Park | |
| Castle | |
| Country Park | |
| English Heritage | |
| Forestry Commission | |
| Heritage railway | |
| Historic House | |
| Mosques | |
| Museum (free/not free) | |
| National Trust | |
| Theatre | |
| Zoo | |
- Bretton Hall
- Cartwright Hall
- Cliffe Hall, also known as , Keighley
- East Riddlesden Hall


- , Esholt
- Harewood House

- Keighley & Worth Valley Railway

- Kirklees Hall/Priory

- Kirkstall Abbey

- Roman Lagentium (Castleford)
- Ledston Hall, Ledston
- , Linthwaite
- Lister Park, Bradford
- Lotherton Hall
- Middleton Railway, the world's oldest steam railway

- Nostell Priory


- Oakwell Hall
- Oulton Hall, Oulton
- Piece Hall, Halifax
- Pontefract Castle
- Pontefract Priory, Pontefract

- , Castleford
- Roundhay Park Leeds
- Saltaire, a UNESCO World Heritage Site
- Sandal Castle
- , Scarcroft
- , Shelley
- Shibden Hall
- Shipley Glen Tramway
- , Tong
- , Wetherby


Museums[]

- Abbey House Museum, Leeds
- Armley Mills Industrial Museum, Leeds
- Bagshaw Museum, Batley
- Bankfield Museum, Halifax
- Bradford Industrial Museum, Eccleshill/Fagley, Bradford
- Brontë Parsonage Museum, Haworth
- Colne Valley Museum, Golcar, Huddersfield
- Eureka, Halifax
- Leeds City Museum, Leeds
- National Coal Mining Museum for England Overton, Wakefield
- National Media Museum, Bradford
- , Ripponden, Halifax
- Pontefract Museum
- Royal Armouries Museum, Leeds
- Thackray Museum, Leeds
- The Hepworth Wakefield
- Thwaite Mills, Leeds
- Tolson Museum, Dalton, Huddersfield
- Wakefield Museum, Wakefield
- , Shibden Hall, Halifax
- Yorkshire Sculpture Park, West Bretton, Wakefield
Natural environment[]

- Emley Moor, site of the tallest self-supporting structure in the UK (a TV mast)
- Harewood Estate – Leeds Country Way public footpath runs through the estate, beautiful landscaped gardens and home to Red Kites amongst many other birds
- Ilkley Moor, part of Rombalds Moor
- New Swillington Ings Nature Reserve
- Otley Chevin – extensive wooded parkland on high ground with extensive views North over Wharfedale and South as far as the Peak District
- RSPB Fairburn Ings – wetland centre for birds
- Seckar Woods LNR, a Local Nature Reserve
- Walton Hall, West Yorkshire, home of naturalist Charles Waterton and the world's first nature reserve
Waterways[]

- Scammonden Reservoir, Deanhead Reservoir – both in the moors near Ripponden
- River Aire, River Calder, River Hebble, River Spen, River Worth
- Aire and Calder Navigation
- Calder and Hebble Navigation
- Huddersfield Broad Canal
- Huddersfield Narrow Canal, Standedge Tunnel
- Leeds and Liverpool Canal
- Rochdale Canal
See also[]
- List of Lord Lieutenants of West Yorkshire
- List of High Sheriffs of West Yorkshire
- The Kingdom of Elmet
- West Yorkshire Urban Area
- West Yorkshire Metropolitan Ambulance Service
- West Yorkshire Regiment (The Prince of Wales's Own)
- List of ceremonial counties in England by gross value added
References[]
- ^ "No. 62943". The London Gazette. 13 March 2020. p. 5161.
- ^ Arnold-Baker, C., Local Government Act 1972, (1973)
- ^ "Gazetteer of the old and new geographies of the United Kingdom" (PDF). Office for National Statistics. p. 48. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 December 2003. Retrieved 14 December 2006.
- ^ "Metropolitan Counties and Districts". Beginners' Guide to UK Geography. Office for National Statistics. 17 September 2004. Archived from the original on 6 June 2002. Retrieved 11 January 2007.
- ^ "Yorkshire and Humber Counties". The Boundary Commission for England. Archived from the original on 2 February 2007. Retrieved 14 February 2007.
- ^ "Devolution deal worth £1.8bn agreed". BBC News. 11 March 2020. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ Beecham, Richard (13 May 2020). "West Yorkshire mayor plans still on track for next May despite lockdown". Yorkshire Evening Post. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ "Yorkshire Southern Pennine Fringe". www.countryside.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 8 September 2008. Retrieved 6 October 2008.
- ^ "Nottinghamshire, Derbyshire and Yorkshire Coalfield". www.countryside.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 21 August 2008. Retrieved 6 October 2008.
- ^ "Southern Magnesian Limestone". www.countryside.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 8 September 2008. Retrieved 6 October 2008.
- ^ "Wars of the roses: How the rivalry between Yorkshire and Lancashire still exists today". The Yorkshire Post. Retrieved 9 June 2021.
- ^ Hayes, Dean (1 October 2000). "The Wars of the Roses: A History of Lancashire vs. Yorkshire Cricket Matches". Retrieved 9 June 2021 – via Amazon.
- ^ Himelfield, Dave; Macpherson, Jon (2 November 2020). "The Yorkshire town that wishes it was in Lancashire". LancsLive. Retrieved 9 June 2021.
- ^ Himelfield, Dave (30 January 2021). "More towns which aren't sure if they're in Lancashire or Yorkshire". YorkshireLive. Retrieved 9 June 2021.
- ^ Shaw, Megan (6 December 2020). "The fight to keep these historic villages in Yorkshire nearing a sad end". YorkshireLive. Retrieved 9 June 2021.
- ^ "County Hall". Wakefield City Council. 20 November 2004. Archived from the original on 11 November 2006.
- ^ Redcliffe-Maud and Wood, B., English Local Government Reformed, (1974)
- ^ Kingdom, J., Local Government and Politics in Britain, (1991)
- ^ Beckett 2005, pp. 39,40
- ^ "History of City Hall". City of Bradford Metropolitan District Council. Archived from the original on 6 October 2008. Retrieved 17 January 2009.
- ^ Jump up to: a b The urban district of Queensbury and Shelf was split between Bradford and Calderdale in 1974: Queensbury civil parish was amalgamated into Bradford; Shelf civil parish was amalgamated into Calderdale.
- ^ "Leeds average weather data". www.worldtravels.com. Archived from the original on 21 July 2015. Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- ^ "Leeds average weather data". www.wunderground.com. Archived from the original on 21 January 2016. Retrieved 21 January 2016.
- ^ "Regional Gross Value Added" (PDF). Office for National Statistics. 21 December 2005. pp. 240–253. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 July 2007. Retrieved 6 October 2008.
- ^ Components may not sum to totals due to rounding
- ^ includes hunting and forestry
- ^ includes energy and construction
- ^ includes financial intermediation services indirectly measured
- ^ Shell, Hanna Rose (2020). Shoddy: From Devil's Dust to the Renaissance of Rags. Chicago: University of Chicago. p. 159. ISBN 9780226377759.
- ^ Application to register Yorkshire Forced Rhubarb (PDF), DEFRA, archived from the original on 22 August 2013, retrieved 25 February 2010CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)
- ^ "The Drift remembers Yorkshire's industrial past". University of Bolton. Archived from the original on 29 July 2017. Retrieved 29 July 2017.
- ^ "Productions at North Light Film Studios". North Light Film Studios. North Light Film Studios. 2017. Retrieved 10 February 2017.
- ^ "Film & TV". Examiner. Huddersfield. 29 October 2016. Retrieved 10 February 2017.
- ^ Ballinger, Lauren (5 December 2014). "North Light Film Studios – Remember Me filming locations". Examiner. Huddersfield. Retrieved 10 February 2017.
- ^ Rees, Caroline (3 November 2013). "Sally Wainwright: not the same old". The Guardian. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- ^ Bremner, Jade (11 December 2013). "Last Tango in Halifax actress Sarah Lancashire begins shooting new crime drama in Yorkshire". Radio Times. Retrieved 19 January 2014.
- ^ "Creative England provides filming location and crew support to new BBC drama Happy Valley when filming in Yorkshire". Creative England. 29 April 2014. Retrieved 12 June 2014.
- ^ Gildea, Samantha (1 February 2016). "Jericho filming locations". Examiner. Huddersfield. Retrieved 10 February 2017.
Sources[]
- Beckett, J. V. (2005), City status in the British Isles,1830–2002, Ashgate Publishing, ISBN 0-7546-5067-7
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to West Yorkshire. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for West Yorkshire. |
- West Yorkshire Joint Services
- Images of West Yorkshire at the English Heritage Archive
- West Yorkshire at Curlie
- West Yorkshire
- Metropolitan counties
- Counties of England established in 1974






















