Wurtsmith Air Force Base
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2017) |
Wurtsmith Air Force Base | |
|---|---|
| Part of Air/Aersopace Defense Command (ADC) and Strategic Air Command (SAC) | |
| Oscoda Township, Iosco County, Michigan | |
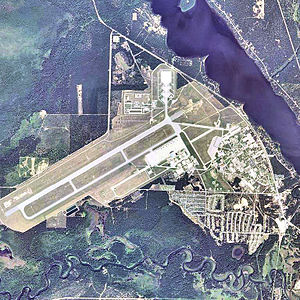 2006 USGS Airphoto. Note the christmas tree alert staging area at top center. | |
 Wurtsmith Air Force Base Location of Wurtsmith Air Force Base | |
| Coordinates | 44°27′09″N 083°22′49″W / 44.45250°N 83.38028°W |
| Type | Air Force Base |
| Site information | |
| Controlled by | United States Air Force |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1923 |
| In use | 1923–1993 |
| Garrison information | |
| Garrison | 379th Bombardment Wing |

Wurtsmith Air Force Base is a decommissioned United States Air Force base in Iosco County, Michigan. It operated from 1923 until decommissioned in 1993.
During the Cold War, it was one of three Strategic Air Command (SAC) bases in Michigan with the B-52 bomber, the others (Kincheloe, Sawyer) were in the Upper Peninsula. The base was named in honor of Major General Paul Wurtsmith, commander of SAC's Eighth Air Force, who was killed when his North American B-25 Mitchell bomber crashed on Cold Mountain near Asheville, North Carolina, on September 13, 1946.[1][2]
Previous names[]
- Camp Skeel, November 1931
- Oscoda Army Air Field, August 1942
- Oscoda Air Force Base, 24 June 1948
- Wurtsmith Air Force Base, 15 February 1953 – 30 June 1993
Major commands to which assigned[]
- General Headquarters Air Force, 26 June 1936
- Third Air Force, 2 September 1942
- Air Service Command, 12 December 1942
- Third Air Force, 5 March 1943
- First Air Force, 14 August 1943
- Continental Air Forces, 16 April 1945
- Re-designated Strategic Air Command, 21 March 1946
- Continental Air Command,1 January 1949
- Air Defense Command, 1 January 1951
- Strategic Air Command, 1 April 1960
- Air Combat Command, 1 June 1992 – 30 June 1993
Major units assigned[]
- First Pursuit Group, 15 October 1927
- 100th Base HQ and Air Base Squadron, 31 October 1942
- 524th Base HQ and Air Base Squadron, 21 June 1943
- 134th AAF Base Unit, 14 April 1944 – 12 April 1945
- 4301st Base Services Squadron, 1 August 1948
- Re-designated 2476th Base Service Squadron, 1 January 1949
- Re-designated 4655th Base Service Squadron, 1 December 1950
- 332d Fighter Group, 2 April 1943 – 9 July 1943
- 100th Fighter Squadron, 29 October 1943 – 8 November 1943
- 301st Fighter Squadron, 21 May 1943 – 10 July 1943
- 302d Fighter Squadron, 19 November 1943 – December 1943
- 403d Fighter Squadron, May 1943 – 15 December 1943
- 754th Aircraft Control and Warning Squadron, 27 November 1950 – 20 July 1951
- 63d Fighter-Interceptor Squadron, 5 January 1951 – 17 August 1955
- 527th Air Service Group
- Re-designated 527th Air Defense Group, 16 February 1953 – 15 October 1955
- 75th Fighter-Interceptor Squadron, 1 October 1968 - 30 November 1969
- 445th Fighter-Interceptor Squadron, 15 August 1955 – 30 September 1968
- 31st Fighter-Interceptor Squadron, 8 June 1956 – 20 August 1957
- 18th Fighter-Interceptor Squadron, 20 August 1957 – 27 April 1960
- 4026th Strategic Wing, 1 August 1958 – 9 January 1961
- 40th Air Division, 1 July 1959 – 8 June 1988
- 920th Air Refueling Squadron, 15 July 1960 – 15 June 1993
- 379th Bombardment Wing, 9 January 1961 – 30 June 1993
- 94th Fighter-Interceptor Squadron, 1 December 1969 - 30 June 1971
PFAS Contamination[]
The Michigan Department of Environment, Great Lakes, and Energy (EGLE) became aware of PFAS concentrations in groundwater in March 2010 when EGLE staff performed sampling at a former fire training area on the base. Air Force has completed the PFAS Preliminary Assessment, Site Inspection, and is currently planning the Remedial Investigation under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act. Air Force has performed three removal actions and is currently planning two interim remedial actions to address PFAS.[3]
See also[]
- Michigan World War II Army Airfields
- Central Air Defense Force (Air Defense Command)
References[]
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency website http://www.afhra.af.mil/.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency website http://www.afhra.af.mil/.
- ^ "Dedication Program of Wurtsmith Air Force Base, July 4th, 1953". wafb.net.
- ^ "Major General Paul B. Wurtsmith 1906 - 1946". wafb.net.
- ^ "PFAS Response - Former Wurtsmith Air Force Base, Iosco County". www.michigan.gov.
- Maurer, Maurer. Air Force Combat Units of World War II. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office 1961 (republished 1983, Office of Air Force History, ISBN 0-912799-02-1).
- Ravenstein, Charles A. Air Force Combat Wings Lineage and Honors Histories 1947–1977. Maxwell Air Force Base, Alabama: Office of Air Force History 1984. ISBN 0-912799-12-9.
- Mueller, Robert (1989). Volume 1: Active Air Force Bases Within the United States of America on 17 September 1982. USAF Reference Series, Office of Air Force History, United States Air Force, Washington, D.C. ISBN 0-912799-53-6, ISBN 0-16-002261-4
- USAF Aerospace Defense Command publication, The Interceptor, January 1979 (Volume 21, Number 1).
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Wurtsmith Air Force Base. |
- Air Force BRAC Recommendations
- Oscoda-Wurtsmith Airport
- Renaissance Zones
- Oscoda-Wurtsmith Airport airport information
- Wurtsmith Air Museum
Coordinates: 44°27′09″N 83°22′49″W / 44.4525°N 83.380278°W
- Installations of the United States Air Force in Michigan
- 1923 establishments in Michigan
- Buildings and structures in Iosco County, Michigan
- Military installations closed in 1993
- Strategic Air Command military installations
- Military Superfund sites
- Superfund sites in Michigan
- 1993 disestablishments in Michigan




