Zonitoides nitidus
| Zonitoides nitidus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Two shells of Zonitoides nitidus | |
NE[1]
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Gastropoda |
| Order: | Stylommatophora |
| Family: | Gastrodontidae |
| Genus: | Zonitoides |
| Species: | Z. nitidus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Zonitoides nitidus | |
Zonitoides nitidus (sometimes Zonitoides nitida)[3] is a species of small, air-breathing land snail, a terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusk in the family Gastrodontidae.
Zonitoides nitidus is the type species of the genus Zonitoides.
Distribution[]
The distribution of Zonitoides nitidus includes the Holarctic zone. It is found almost all over Europe except the southernmost regions:[4]
- Czech Republic - least concern (LC)[5]
- Netherlands[6]
- Russia - Sverdlovsk oblast[7]
- Ukraine[8]
- Slovakia
- Great Britain - north British highland zones and not in north Scotland.[4] In some regions in Britain the species has declined due to drainage.[4]
- Ireland
- Hebrides[4]
- Orkney[4]
- Shetland[4]
- rare in northern Greece[4]
- Canada
The non-indigenous distribution of this species includes:
Description[]
The shell is reddish brown.[4] The umbilicus is large (almost 25% of shell diameter).[4] The shell is with radial growth lines.[4] The width of the shell is 6–7 mm.[4] The height of the shell is 3.5-4.0 mm.[4]
The animal is black with a characteristic orange dash: the (mantle gland is visible under the shell's aperture).[4]
Juveniles are whitish grey with light brown translucent shells.[4]
 Photo of the shell. |
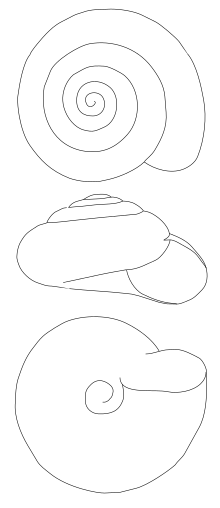 Drawing of the shell. |
Ecology[]
Zonitoides nitidus occurs in wet meadows and river woods, usually near water bodies, swamps and swampy forests, in the zone of emergent vegetation.[4] Man-made habitats such as pools in old quarries are sometimes colonized after a few years.[4] In Switzerland it is found up to 2100m of altitude.[4]
Zonitoides nitidus is herbivorous.[4] These snails feed on disintegrating leaves, mushrooms, roots and fruit.[4] They do not eat dry leaves.[4] Humid leaves are preferred.[4] When consuming soft food such as mushrooms or soft fruits, Zonitoides nitidus penetrates perpendicularly inside, producing characteristic holes; the entire animal including its shell can penetrate inside the fruit.[4]
In Germany up to three clutches of 2-9 eggs per individual are laid in all seasons, with some days or weeks spacing between egg-laying.[4] Egg diameter is 1.0-1.6 mm.[4] Eggs are laid loose into the soil.[4] Juveniles have 1.5 whorls (diameter 1-1.2 mm) after hatching.[4] They start feeding on disintegrating plant remains in the soil.[4] After 3 months the shell diameter reaches up to 3 mm under favourable conditions, after 10 months 6 mm, and full size after slightly more than one year.[4] Maximum age is 18 months under laboratory conditions.[4]
Parasites of Zonitoides nitidus include:
- Elaphostrongylus spp.[9]
- Parelaphostrongylus tenuis[10]
References[]
This article incorporates public domain text from the reference.[4]
- ^ 2006 IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. <www.iucnredlist.org>. Cited 4 March 2007.
- ^ Müller O. F. 1774. Vermivm terrestrium et fluviatilium, seu animalium infusoriorum, helminthicorum, et testaceorum, non marinorum, succincta historia. Volumen alterum. pp. I-XXVI [= 1-36], 1-214, [1-10]. Havniæ & Lipsiæ. (Heineck & Faber).
- ^ "Zonitoides nitida". Utah Division of Wildlife Resources. Archived from the original on 2017-05-19. Retrieved May 18, 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae "Species summary for Zonitoides nitidus". AnimalBase, last modified 29 August 2010, accessed 3 September 2010.
- ^ Juřičková L., Horsák M. & Beran L. (2001). "Check-list of the molluscs (Mollusca) of the Czech Republic". Acta Soc. Zool. Bohem. 65: 25-40.
- ^ "Anemoon > Flora en Fauna > Soorteninformatie". www.anemoon.org.
- ^ [1][permanent dead link]
- ^ Balashov I. & Gural-Sverlova N. 2012. An annotated checklist of the terrestrial molluscs of Ukraine. Journal of Conchology. 41 (1): 91-109.
- ^ Olsson I.-M., Stéen M. & Mann H. (1993). "Gastropod hosts of Elaphostrongylus spp. (Protostrongylidae, Nematoda)". Rangifer 13(1): 53-55. PDF.
- ^ Michigan Department of Natural Resources and Environment. "Brainworm". accessed 14 December 2010.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Zonitoides nitidus. |
- Gastrodontidae
- Gastropods described in 1774
- Taxa named by Otto Friedrich Müller