1810s
This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2010) |

| Millennium: | 2nd millennium |
| Centuries: |
|
| Decades: | |
| Years: |
|
| Categories: |
|
The 1810s (pronounced "eighteen-tens") was a decade of the Gregorian calendar that began on January 1, 1810, and ended on December 31, 1819.
The decade was opened with a very hostile political climate around the world. Napoleon was invading France's neighbours in efforts to build a French Empire, causing a chain of global-scaled conflicts known as the Napoleonic Wars. Here, France's Napoleonic empire saw its rise and fall through events such as Napoleon's attempts to conquer Russia, the War of 1812 (spillover to America), and the Battle of Waterloo (Napoleon's ultimate defeat). Imperialism began to encroach towards African and Asian territories through trade, as the United States saw mass-scaled migration that headed westward towards the American frontier (mostly through the opening of the Oregon Trail.)
Politics and wars[]
Napoleonic Wars[]

In 1810, the French Empire reached its greatest extent. On the continent, the British and Portuguese remained restricted to the area around Lisbon and to besieged Cadiz. Napoleon married Marie-Louise, an Austrian Archduchess, with the aim of ensuring a more stable alliance with Austria and of providing the Emperor with an heir. As well as the French Empire, Napoleon controlled the Swiss Confederation, the Confederation of the Rhine, the Duchy of Warsaw and the Kingdom of Italy. Territories allied with the French included: the Kingdom of Spain, the Kingdom of Westphalia, the Kingdom of Naples, the Principality of Lucca and Piombino, and Napoleon's former enemies, Prussia and Austria. Denmark–Norway also allied with France in opposition to Great Britain and Sweden in the Gunboat War.
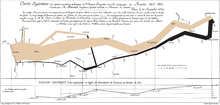
The French invasion of Russia of 1812 was a turning point, which reduced the French and allied invasion forces (the Grande Armée) to a tiny fraction of their initial strength and triggered a major shift in European politics, as it dramatically weakened the previously dominant French position on the continent. After the disastrous invasion of Russia, a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Sweden, the United Kingdom, and a number of German States, and the rebels in Spain and Portugal united to battle France in the War of the Sixth Coalition. Two-and-a-half million troops fought in the conflict and the total dead amounted to as many as two million. This era included the battles of Smolensk, Borodino, Lützen, Bautzen, and the Dresden. It also included the epic Battle of Leipzig in October, 1813 (also known as the Battle of Nations), which was the largest battle of the Napoleonic wars, which drove Napoleon out of Germany.
The final stage of the War of the Sixth Coalition, the defense of France in 1814, saw the French Emperor temporarily repulse the vastly superior armies in the Six Days Campaign. Ultimately, the Allies occupied Paris, forcing Napoleon to abdicate and restoring the Bourbons. Napoleon was exiled to Elba. Also in 1814, Denmark–Norway was defeated by Great Britain and Sweden and had to cede the territory of mainland Norway to the King of Sweden at the Treaty of Kiel.
Napoleon shortly returned from exile, landing in France on March 1, 1815, marking the War of the Seventh Coalition, heading toward Paris while the Congress of Vienna was sitting. On March 13, seven days before Napoleon reached Paris, the powers at the Congress of Vienna declared him an outlaw; four days later the United Kingdom, Russia, Austria and Prussia, members of the Seventh Coalition, bound themselves to put 150,000 men each into the field to end his rule.[1] This set the stage for the last conflict in the Napoleonic Wars, the defeat of Napoleon at the Battle of Waterloo, the restoration of the French monarchy for the second time and the permanent exile of Napoleon to the distant island of Saint Helena, where he died in May 1821.
Spanish American wars of independence[]
Spain in the 1810s was a country in turmoil. Occupied by Napoleon from 1808 to 1814, a massively destructive "war of independence" ensued, driven by an emergent Spanish nationalism. Already in 1810, the Caracas and Buenos Aires juntas declared their independence from the Bonapartist government in Spain and sent ambassadors to the United Kingdom. The British blockade against Spain had also moved most of the Latin American colonies out of the Spanish economic sphere and into the British sphere, with whom extensive trade relations were developed. The remaining Spanish colonies had operated with virtual independence from Madrid after their pronouncement against Joseph Bonaparte.
The Spanish government in exile (Cortes of Cádiz) created the first modern Spanish constitution. Even so, agreements made at the Congress of Vienna (where Spain was represented by Pedro Gómez Labrador, Marquis of Labrador) would cement international support for the old, absolutist regime in Spain.
King Ferdinand VII, who assumed the throne after Napoleon was driven out of Spain, refused to agree to the liberal Spanish Constitution of 1812 on his accession to the throne in 1814. The Spanish Empire in the New World had largely supported the cause of Ferdinand VII over the Bonapartist pretender to the throne in the midst of the Napoleonic Wars. When Ferdinand's rule was restored, these juntas were cautious of abandoning their autonomy, and an alliance between local elites, merchant interests, nationalists, and liberals opposed to the abrogation of the Constitution of 1812 rose up against the Spanish in the New World.

The arrival of Spanish forces in the American colonies began in 1814, and was briefly successful in restoring central control over large parts of the Empire. Simón Bolívar, the leader of revolutionary forces in New Granada, was briefly forced into exile in British-controlled Jamaica, and independent Haiti. In 1816, however, Bolivar found enough popular support that he was able to return to South America, and in a daring march from Venezuela to New Granada (Colombia), he defeated Spanish forces at the Battle of Boyacá in 1819, ending Spanish rule in Colombia. Venezuela was liberated June 24, 1821, when Bolivar destroyed the Spanish army on the fields of Carabobo on the Battle of Carabobo. Argentina declared its independence in 1816 (though it had been operating with virtual independence as a British client since 1807 after successfully resisting a British invasion). Chile was retaken by Spain in 1814, but lost permanently in 1817 when an army under José de San Martín, for the first time in history, crossed the Andes Mountains from Argentina to Chile, and went on to defeat Spanish royalist forces at the Battle of Chacabuco in 1817.
Spain would also lose Florida to the United States during this decade. First, in 1810, the Republic of West Florida declared its independence from Spain, and was quickly annexed by the United States. Later, in 1818, the United States invaded Florida, resulting in the Adams-Onís Treaty, wherein Spain ceded the rest of Florida to the United States.
In 1820, Mexico, Peru, Ecuador, and Central America still remained under Spanish control. Although Mexico had been in revolt in 1811 under Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla, resistance to Spanish rule had largely been confined to small guerrilla bands in the countryside. King Ferdinand was still dissatisfied with the loss of so much of the Empire and resolved to retake it. A large expedition was assembled in Cadiz with the aim of reconquest. However, Ferdinand's plans would be disrupted by Liberal Revolution, and Ferdinand was eventually forced to give up all of the New World colonies, except for Cuba and Puerto Rico.
War of 1812[]
In 1812, the United States declared war on Britain in the War of 1812. The U.S. reasons for war included the humiliation in the "Chesapeake incident" of 1807, continued British impressment of American sailors into the Royal Navy, restrictions on trade with France, and arming hostile American Indians in Ohio and the western territories.[2] United States President James Madison signed a declaration of war on June 18, 1812.
The United States conducted two failed invasion attempts in 1812, first by General William Hull across the Detroit River into what is now Windsor, Ontario, and a second offensive at the Niagara peninsula. A major American success came in 1813, when the American Navy destroyed the British fleet on Lake Erie, and forced the British and their American Indian allies to retreat back toward Niagara.[3] They were intercepted and destroyed by General William Henry Harrison at the Battle of the Thames in October 1813. Tecumseh, the leader of the tribal confederation, was killed, and his Indian coalition disintegrated.[4]
At sea, the powerful Royal Navy blockaded much of the coastline, conducting frequent raids. The most famous episode was a series of British raids on the shores of Chesapeake Bay, including an attack on Washington that resulted in the British burning of the White House, the Capitol, the Navy Yard, and other public buildings, in the "Burning of Washington" in 1814.
Once Napoleon was defeated in 1814, France and Britain became allies and Britain ended the trade restrictions and the impressment of American sailors. Running out of reasons for war and stuck in a military stalemate, the two countries signed the Treaty of Ghent on December 24, 1814. News of the peace treaty took two months to reach the U.S., during which fighting continued. In this interim, the British made one last major invasion, attempting to capture New Orleans, but were decisively defeated with very heavy losses by General Andrew Jackson at the Battle of New Orleans in January 1815. The ending of the war opened a long era of peaceful relations between the United States and the British Empire.
1804–1813 Russo-Persian War[]
The 1804–1813 Russo-Persian War was one of the many wars between the Persian Empire and Imperial Russia, and was well underway at the beginning of the decade. In 1810, the Persians scaled up their efforts late in the war, declaring a holy war on Imperial Russia. However, Russia's superior technology and tactics ensured a series of strategic victories. Even when the French were in occupation of the Russian capital Moscow, Russian forces in the south were not recalled but continued their offensive against Persia, culminating in Pyotr Kotlyarevsky's victories at Aslanduz and Lenkoran, in 1812 and 1813 respectively. Upon the Persian surrender, the terms of the Treaty of Gulistan ceded the vast majority of the previously disputed territories to Imperial Russia. This led to the region's once-powerful khans being decimated and forced to pay homage to Russia.
Concert of Europe[]
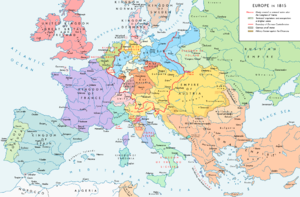
By 1815, Europe had been almost constantly at war. During this time, the military conquests of France had resulted in the spread of liberalism throughout much of the continent, resulting in many states adopting the Napoleonic code. Largely as a reaction to the radicalism of the French Revolution,[5] the victorious powers of the Napoleonic Wars resolved to suppress liberalism and nationalism, and revert largely to the status quo of Europe prior to 1789.[6]
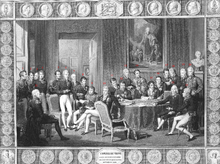
The result was the Concert of Europe, also known as the "Congress System". It was the balance of power that existed in Europe from 1815 until the early 20th century. Its founding members were the United Kingdom, Austrian Empire, Russian Empire and Kingdom of Prussia, the members of the Quadruple Alliance responsible for the downfall of the First French Empire; in time France became established as a fifth member of the concert. At first, the leading personalities of the system were British foreign secretary Lord Castlereagh, Austrian chancellor Klemens Wenzel, Prince von Metternich and Tsar Alexander I of Russia.
The Kingdom of Prussia, Austrian Empire and Russian Empire formed the Holy Alliance with the expressed intent of preserving Christian social values and traditional monarchism.[7] Every member of the coalition promptly joined the Alliance, save for the United Kingdom.
Among the meetings of the Powers in the latter part of the 1810s were the Congresses of Vienna (1814–1815), Aix-la-Chappelle (1818), and Carlsbad (1819).
Other political events[]
Australia[]
- Black War (1804–1835)
- Hawkesbury and Nepean Wars (1795-1816)
Asia[]
- 1810: Ching Shih and Chang Pao surrender their pirate fleet to the Chinese government.
- 1810: Russia acquires Sukhumi through a treaty with the Abkhazian dukes, and declares a protectorate over the whole of Abkhazia.
- Russo-Turkish War (1806–1812)
- May 28, 1812 – Russian Field Marshal Mikhail Kutuzov signs the Treaty of Bucharest, ending the Russo-Turkish War, 1806–1812 and making Bessarabia a part of Imperial Russia.
- October 31, 1817 – Emperor Ninkō accedes to the throne of Japan.
- 1818: The Third Anglo-Maratha War is fought between the Marathas and the British East India Company troops resulting in the defeat of the Peshwa, the breakup of the Maratha Empire, and the loss of Maratha independence to the British as they annexed Central India. The last Peshwa is exiled to Bithur near Kanpur. His adopted son and heir Nana Saheb was one of the principal revolutionary commanders in the Indian Mutiny.
Europe[]
- August 21, 1810 – Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte, Marshal of France, is elected Crown Prince of Sweden by the Swedish Riksdag of the Estates.
- September 26, 1810 – A new Act of Succession is adopted by the Riksdag of the Estates and Jean Baptiste Bernadotte becomes heir to the Swedish throne.
- October 12, 1810 – First Oktoberfest: The Bavarian royalty invites the citizens of Munich to join the celebration of the marriage of Crown Prince Ludwig of Bavaria to Princess Therese of Saxe-Hildburghausen.
- February 5, 1811 – British Regency: George, Prince of Wales becomes Prince Regent because of the perceived insanity of his father, King George III of the United Kingdom.
- September, 1811 – Nathan of Breslov leads the first annual Rosh Hashana kibbutz (pilgrimage) of Breslov Hasidim to the grave of Rabbi Nachman of Breslov in Uman, Ukraine.
- January 1, 1812 – The Allgemeines bürgerliches Gesetzbuch (the Austrian civil code) enters into force in the Austrian Empire.
- May 11, 1812 – John Bellingham assassinates British Prime Minister Spencer Perceval in the lobby of the British House of Commons.
- July 18, 1812 – Russia's Patriotic War, 1812 – Battle of Klyastitsy: Kulnev defeats Oudinot but sustains a mortal wound.
- October 18–October 20, 1812 – Second Battle of Polotsk – Russia
- December 30, 1812 – Convention of Tauroggen was signed.
- 1812 – The capital of Finland is moved from Turku to Helsinki.
- November 10, 1813 – A general election in the United Kingdom sees victory for the Tory Party under Robert Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool.
- 1813 – George Hamilton-Gordon serves as ambassador extraordinaire in Vienna.
- Norway in 1814
- January 14, 1814 – Denmark cedes Norway to Sweden in exchange for west Pomerania, as part of the Treaty of Kiel.
- February 11, 1814 – Norway's independence is proclaimed, marking the ultimate end of the Kalmar Union.
- April 12, 1814 – The Royal Norwegian Navy is re-established.
- May 17, 1814 – The Constitution of Norway is signed and the Danish Crown Prince Christian Frederik is elected King of Norway by the Norwegian Constituent Assembly.
- May 3, 1814 – The Duke of Provence, the future Louis XVIII of France, returns to Paris.
- May 17, 1814 – The occupation of Monaco changes from French to Austrian hands.
- May 30, 1814 – The First Treaty of Paris is signed returning France's borders to their 1792 extent. Napoleon I of France is exiled to Elba on the same day.
- August 12, 1814 – In England, the last hanging under the Black Act is carried out, of William Potter for cutting down an orchard (even the judge petitioned for reprieve).
- August 13, 1814 – The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814 is signed.
- January 3, 1815 – Austria, Britain, and Bourbon-restored France form a secret defensive alliance treaty against Prussia and Russia.
- March 15, 1815 – Joachim Murat, King of Naples declares war on Austria in an attempt to save his throne, starting the Neapolitan War.
- March 16, 1815 – William I becomes King of the Netherlands.
- April 23, 1815 – The Second Serbian Uprising against Ottoman rule takes place in Takovo, Serbia. By the end of the year Serbia is acknowledged as a semi-independent state; the ideals of the First Serbian Uprising have thus been temporarily achieved.
- May 3, 1815 – Battle of Tolentino: Austria defeats the Kingdom of Naples, which quickly ends the Neapolitan War. Joachim Murat, the defeated King of Naples, is forced to flee to Corsica and is later executed.
- 1815: In Britain, use of the pillory is limited to punishment for perjury.
- January 1, 1816 – Tsar Alexander I of Russia signs an order for the expulsion of the Jesuits from the Russian Empire.
- March 25, 1816 – Friedrich Karl Ludwig, Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Beck dies and is succeeded by the later Friedrich Wilhelm, Duke of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg, his son and founder of the Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Glücksburg.
- 1816: The Senate of Finland is established.
- 1816: The Ottomans grant Serbia local autonomy.
- April 3, 1817 – Princess Caraboo appears in Almondsbury in Gloucestershire, England.
- May 11, 1818 – Charles XIV of Sweden-Norway is crowned king of Sweden.
- September 7, 1818 – Carl III of Sweden-Norway is crowned king of Norway, in Trondheim.
- September 23, 1818 – Border markers are formally installed for the European territory of Moresnet.
- September 20, 1819 – The Carlsbad Decree is issued throughout the German Confederation.
Africa[]
- 1810: Amadou Lobbo initiates his jihad in present-day Mali.
- 1810: The Battle of Vieux Grand Port (Great Old Port) in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the Island of Mauritius, was the only naval victory won by Napoleon. This battle has very often been ignored by scholars, but was of great importance for the control of the Indian Ocean as a trade route between Europe and the East.
- March 1, 1811 – Citadel Massacre: Egyptian ruler Mohammed Ali kills the last Mamluk leaders.
- 1813: Following the death of his father Wossen Seged, Sahle Selassie arrives at the capital Qundi before his other brothers, and is made Méridazmach of Shewa.
- 1816: Banjul, capital of the Gambia, is founded as a trading post, and named Bathurst.
- August 27, 1816 – Bombardment of Algiers: Various European Allie ships force the Dey of Algiers to free Christian slaves.
- 1818: Shaka starts to rule.
- Mtetwa Empire Expansion
North America[]
- May 1, 1810 – Macon's Bill Number 2 becomes law.
- June 4, 1810 – The Society in Dedham for Apprehending Horse Thieves is founded in Dedham, Massachusetts.
- 1811: The Red River Colony is founded in Manitoba, Canada.
- March 22, 1811 – The Commissioners' Plan of 1811 for Manhattan is presented.
- November 6, 1811 – Battle of Tippecanoe: American troops led by William Henry Harrison defeat the Native American chief Tecumseh.
- February 11, 1812 – Massachusetts governor Elbridge Gerry invents gerrymandering.
- April 4, 1812 – U.S. President James Madison enacts a 90-day embargo on trade with the United Kingdom.
- April 30, 1812 – Louisiana is admitted as the 18th U.S. state.
- June 4, 1812 – Following Louisiana's admittance as a U.S. state, the territory by that name is renamed the Missouri Territory.
- October 1812 – The capital of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States is permanently moved from Lancaster to Harrisburg.
- November 5, 1812 – James Madison defeats DeWitt Clinton in the U.S. presidential election.
- March 27, 1814 – Creek War – Battle of Horseshoe Bend: In northern Alabama, United States forces under General Andrew Jackson defeat the Creek Indians.
- December 15, 1814 – The Hartford Convention is convened by members of the American Federalist Party.
- February – The Hartford Convention arrives in Washington, D.C..
- August 24, 1816 – The Treaty of St. Louis is signed in St. Louis, Missouri.
- November 6, 1816 – James Monroe defeats Rufus King in the U.S. presidential election.
- December 11, 1816 – Indiana is admitted as the 19th U.S. state.
- 1816: The Second Bank of the United States obtains its charter.
- The Era of Good Feelings (1816–1823/1824) in the U.S.
- March 3
- President James Madison vetoes John C. Calhoun's Bonus Bill.
- U.S. Congress passes law to split the Mississippi Territory, after Mississippi drafts a constitution, creating the Alabama Territory effective in August.[8]
- March 4, 1817 – James Monroe succeeds James Madison as President of the United States of America.
- April 29, 1817 – The Rush–Bagot Treaty is signed.
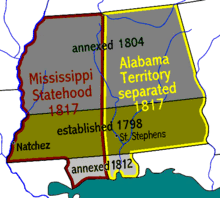
- August 15, 1817 – By act of the U.S. Congress (March 3), the Alabama Territory is created by splitting the Mississippi Territory in half, on the day the Mississippi constitution is drafted, 4 months before Mississippi becomes a U.S. state.[8]
- November 20, 1817 – The First Seminole War begins in Florida.
- December 10, 1817 – Mississippi is admitted as the 20th U.S. state, formerly the Mississippi Territory.[8]
- April 4, 1818 – The U.S. Congress adopts the flag of the United States as having 13 red and white stripes and one star for each state (20 stars) with additional stars to be added whenever a new state is added to the Union.
- August 1, 1818 – Separate Topographical Bureau of the War Department.
- October 20, 1818 – The Treaty of 1818 between the United States and the United Kingdom establishes the northern boundary as the 49th parallel from the Lake of the Woods to the Rocky Mountains, also creating the Northwest Angle.
- December 3, 1818 – Illinois is admitted as the 21st U.S. state.
- February 2, 1819 – The Supreme Court under John Marshall rules in favor of Dartmouth College in the famous Dartmouth College v. Woodward case, allowing Dartmouth to keep its charter and remain a private institution.
- March 6, 1819 – McCulloch v. Maryland: The U.S. Supreme Court rules that the Bank of the United States is constitutional.
- 1819: The ʻAi Noa movement takes power in Hawaii.
- The city of Fernandina of Jagua (later Cienfuegos City) is founded in Cuba.
- December 14, 1819 – Alabama is admitted as the 22nd U.S. state.
South America[]
- 1814: Guyana is transferred from the Netherlands to Britain; it is renamed British Guiana.
- August 22, 1817 – The city of Araraquara, Brazil is founded.
- The Spanish colony of New Granada declares independence as the Republic of Gran Colombia under President Simón Bolívar (1800–1900)* Stars the period of Latin American revolutions. Several states declare their independence from Spain.
- 1817: The Pernambucan Revolt breaks out in Brazil.
Commerce[]
Trading companies[]
- June 23, 1810 – John Jacob Astor forms the Pacific Fur Company.
- September 8, 1810 – The Tonquin sets sail from New York Harbor with 33 employees of John Jacob Astor's newly created Pacific Fur Company on board. After a 6-month journey around the tip of South America, the ship arrives at the mouth of the Columbia River and Astor's men establish the fur-trading town of Astoria.
- 1810: Palm oil sales from West Africa to Britain reach 1,000 tons.
- February 2, 1812 – Russia establishes a fur trading colony at Fort Ross, California.
- June 19, 1816 – Battle of Seven Oaks: The Hudson's Bay Company is defeated by the , near Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada.
- 1818: Lord Hastings, governor-general of India, gives approval to Sir Stamford Raffles to establish trading station at the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula (modern-day Singapore).
- 1818: The British East India Company controls territory occupied by 180 million Indians.
- January 29, 1819 – Sir Stamford Raffles lands on the island of Singapore.
- February 6, 1819 – A formal treaty between Hussein Shah of Johor and the British Sir Thomas Stamford Raffles establishes a trading settlement in Singapore.
Establishments[]
- 1812: The Old Oscar Pepper Distillery (now the Woodford Reserve Distillery), the oldest Kentucky Bourbon distillery, is established along in Woodford County, Kentucky.
- February 3, 1815 – The first commercial cheese factory is founded in Switzerland.
- 1816: E. Remington and Sons (the famous firearm and later typewriter manufacturing company) is founded.
- April 7, 1818 – Brooks Brothers, the oldest men's clothier in the United States, opens its first store on the northeast corner of Catherine and Cherry Streets in New York City, where the South Street Seaport now stands.
- March 20, 1819 – Burlington Arcade opens in London.
Slavery, Serfdom and Labor[]
- 1810: Adult cotton spinners stage a general strike in Manchester.
- 1810: 18,000 Angolans are sold at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
- January 8, 1811 – An unsuccessful slave revolt is led by Charles Deslandes in St. Charles and St. James Parishes, Louisiana.
- March 23, 1816 – Estonia emancipates its peasants from serfdom.
- February 15, 1819 – The United States House of Representatives agrees to the Tallmadge Amendment barring slaves from the new state of Missouri (the opening vote in a controversy that leads to the Missouri Compromise).
- August 16, 1819 – Peterloo Massacre: The cavalry charges into a crowd of protesters in Manchester, UK, resulting in 11 deaths and over 400 injuries.
- 1819: Serfdom is abolished in Livonia.
Luddites[]
- The Luddites (1811–1816) in Britain were machine-wreckers, protesting against machines perceived as taking their jobs.
- November, 1811 – Luddite uprisings begin in northern England and the Midlands.
- February 27, 1812 – Poet Lord Byron gives his first address as a member of the House of Lords, in defense of Luddite violence against Industrialism in his home county of Nottinghamshire.
- March 15, 1812 – Luddites attack the wool processing factory of Frank Vickerman in West Yorkshire.
Economics[]
- February 21, 1814 – Great Stock Exchange Fraud of 1814.
- January 2, 1819 – The Panic of 1819 (the first major financial crisis in the United States) begins.
Science and technology[]
- Gas lighting becomes a practical technology and is implemented in cities in Europe and the United States.
- June – Nicolas Appert publishes L'art de conserver pendant plusieurs années toutes les substances animales ou végétales, the first description of modern food preservation using airtight containers
- 1810: Johann Wolfgang von Goethe publishes his Theory of Colours.
- July 11, 1811 – Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro publishes his memoire about the molecular content of gases.
- February 12, 1812 – Napoleon authorizes the usage of "Mesures usuelles", a system of measurement introduced as compromise between the metric system and traditional French measurements. The system was restricted to use in the retail industry and continued in use until 1840, when the laws of measurement from the 1795 and 1799 were reinstituted. (see also: Units of measurement in France)
- 1813: Mathieu Orfila publishes his groundbreaking Traité des poisons, formalizing the field of toxicology.
- October 21, 1815 – Humphry Davy patents the miner's safety lamp for use in coal mining.
- January 9, 1816 – Sir Humphry Davy tests the Davy lamp for Miners at Hebburn Colliery.
- 1816 – René Laennec invents the stethoscope.
- 1816 – Robert Stirling patents his Stirling engine, then known as Stirling's air engine.
- John Kidd extracts naphthalene from coal tar.
Astronomy[]
- March 25, 1811 – The Great Comet of 1811 is discovered by Honoré Flaugergues.
- July 1, 1819 – Johann Georg Tralles discovers the Great Comet of 1819, (C/1819 N1). It was the first comet analyzed using polarimetry, by François Arago.
Steamboats[]

The 1810s continued a trend of increasing commercial viability of steamboats in North America, following the early success of Robert Fulton and others in the preceding years. In 1811 the first in a continuously operating line of river steamboats left the dock at Pittsburgh to steam down the Ohio River to the Mississippi and on to New Orleans.[9] Inventor John Stevens' boat, the Juliana, began operation as the first steam-powered ferry October 11, 1811, with service between New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey. John Molson's PS Accommodation was the first steamboat on the St. Lawrence and in Canada.[10] Unlike Fulton, Molson did not show a profit. Molson had also two paddle steamboats "Swiftsure" of 1811 and "Malsham" of 1813 with engines by B&W.[11] The experience of these vessels, especially that they could now offer a regular service, being independent of wind and weather, helped make the new system of propulsion commercially viable, and as a result its application to the more open waters of the Great Lakes was next considered. That idea went on hiatus due to the War of 1812.
In a 25-day trip in 1815, the Enterprise further demonstrated the commercial potential of the steamboat with a 2,200-mile voyage from New Orleans to Pittsburgh.[12][13] In 1817, a consortium in Sackets Harbor, New York, funded the construction of the first US steamboat, Ontario, to run on Lake Ontario and the Great Lakes, beginning the growth of lake commercial and passenger traffic.[14]
The first commercially successful steamboat in Europe, Henry Bell's Comet of 1812, started a rapid expansion of steam services on the Firth of Clyde, and within four years a steamer service was in operation on the inland Loch Lomond, a forerunner of the lake steamers still gracing Swiss lakes. On the Clyde itself, within ten years of Comet's start in 1812 there were nearly fifty steamers, and services had started across the Irish Sea to Belfast and on many British estuaries. P.S."Thames", ex "Argyle" was the first seagoing steamer in Europe, having steamed from Glasgow to London in May 1815.[15] P.S."Tug", the first tugboat, was launched by the Woods Brothers, Port Glasgow, on November 5, 1817; in the summer of 1817 she was the first steamboat to travel round the North of Scotland to the East Coast.[16]
The first steamship credited with crossing the Atlantic Ocean between North America and Europe was the American ship SS Savannah, though she was actually a hybrid between a steamship and a sailing ship. The SS Savannah left the port of Savannah, Georgia, on May 22, 1819, arriving in Liverpool, England, on June 20, 1819; her steam engine having been in use for part of the time on 18 days (estimates vary from 8 to 80 hours).
Locomotives[]
- July 25, 1814 –George Stephenson tests his locomotive Blucher successfully.
- February 6, 1815 – New Jersey grants the first American railroad charter to a John Stevens.
- 1816: A rail capable of supporting a heavy locomotive is developed.
Other transportation[]
- July 4, 1817 – At Rome, New York, construction on the Erie Canal begins.
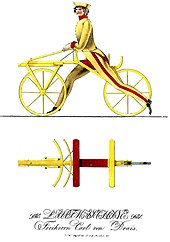
- 1818 - Baron Karl Drais patents the laufmaschine, a forerunner to the bicycle
Natural events[]
- December 16, 1811 – The New Madrid earthquake in Mississippi Valley near New Madrid reverses the course of the river for a while. Other earthquakes along the fault occur on January 23, 1812, and February 7, 1812.
- February 7, 1812 – The last New Madrid earthquake strikes New Madrid, Missouri, with an estimated moment magnitude of over 8;
- March 26, 1812 – An earthquake destroys Caracas, Venezuela.
- April, 1817 – An earthquake strikes Palermo, Italy.
- August 23, 1817 – An earthquake near the site of the ancient Greek city of Helike results in 65 deaths.
Year Without a Summer[]

- April 5–April 12, 1815 – Mount Tambora in the Dutch East Indies blows its top explosively during an eruption, killing upwards of 92,000 and propelling thousands of tons of aerosols (Sulfide gas compounds) into the upper atmosphere (stratosphere). The following year (1816) becomes known as "Year Without a Summer", as the high level gases reflect sunlight and cause the widespread cooling (known as a volcanic winter) and heavy rains, snows in June and July in the northern hemisphere, and widespread crop failures.
Culture[]
Literature[]
Lord Byron, regarded as one of the greatest British poets and remains widely read and influential, wrote his most well-known work during this decade. Amongst Byron's works are the brief poems She Walks in Beauty, When We Two Parted, and So, we'll go no more a roving, in addition to the narrative poems Childe Harold's Pilgrimage and Don Juan.
Other events in literature:
- December 20, 1812 - The first volume of Grimm's Fairy Tales is published.
- January 28, 1813 – Jane Austen's Pride and Prejudice is published.
- September, 1813 – Robert Southey becomes Poet Laureate of Britain.
- 1813: The Philomathean Society of the University of Pennsylvania is founded (the oldest continuously existing literary society in the United States).
- 1814: Missionaries attempt to write down the Māori language.
- 1814: Sir Walter Scott writes Waverley.
- 1816: Jane Austen's Emma is published.
- 1817: Samuel Taylor Coleridge publishes Biographia Literaria.
- January 1, 1818 – Mary Shelley's Frankenstein is published.
Fashion[]
Theatre[]
- 1818: Old Vic founded (as Royal Coburg Hall).
Music[]
- April 27, 1810 – Beethoven composes his famous piano piece, Für Elise.
- January 24, 1813 – The Philharmonic Society founded in London (later the Royal Philharmonic Society).
- December 8, 1813 – Beethoven's seventh symphony is performed for the first time in Vienna.
- February 27, 1814 – Beethoven's eighth symphony is performed for the first time in Vienna, less than three months after his seventh symphony was first performed. Beethoven reportedly told one of his pupils that he seventh symphony was more popular because his eighth symphony was better.[17] It would be over ten years before the first performance of his next symphony in Vienna.
- February 20, 1816 – Gioachino Rossini's The Barber of Seville debuts at Teatro Argentina, with a fiasco.
- December 24, 1818 – Silent Night composed by Franz Xaver Gruber and Josef Mohr.
Other[]

- 1815: First-class cricket begins.
- 1817: Elgin Marbles are displayed in the British Museum.
- 1818: The first edition of the Farmer's Almanac is published.
People[]
Authors[]
- Mary Shelley (Frankenstein)
Disasters[]
- June 9, 1811 – The Great fire of the Podil breaks out in Kiev, Ukraine.
- May 25, 1812 – Felling mine disaster: A mine explosion at the Felling colliery near Jarrow, England leaves 96 dead.
- February 12, 1814 – A fire destroys the Custom House in London.
- October – A large vat full of porter (beer) owned by Meux's Brewery of London bursts, demolishing houses and killing 9 people. See London Beer Flood.
- May 30, 1815 – The Arniston, an East Indiaman repatriating wounded troops to England from Ceylon, is wrecked near Waenhuiskrans, South Africa with the loss of 372 of the 378 people on board.
- September 23, 1815 – The Great September Gale of 1815 is the first hurricane to strike New England in 180 years.
- October 3, 1815 – The Chassigny Mars meteorite falls in Chassigny, Haute-Marne, France.
- February 12, 1816 – Fire nearly destroys the city of St. John's, Newfoundland.
- July 17, 1816 – The French passenger ship Medusa runs aground off the coast of Senegal, with 140 lives lost in the botched rescue that takes weeks, leading to a scandal in the French government.
- June 25, 1817 – A large riot breaks out in Copenhagen Prison; the army is sent to quell it.
- 1817 – A typhus epidemic occurs in Edinburgh and Glasgow.
Establishments[]
- 1812 – The Bishop James Madison Society is founded at the College of William & Mary, Williamsburg, Virginia.
- August 7, 1814 – Pope Pius VII decrees the bull Sollicitudo omnium ecclesiarum reestablishing the Society of Jesus (Jesuits) all over the world, after having approved their survival and existence in Russia.
- February 4, 1815 – The first Dutch student association, the Groninger Studenten Corps, Vindicat atque Polit is founded in the Netherlands. The first rector of the senate was B.J. Winter.
- April 11, 1816 – In Philadelphia, the African Methodist Episcopal Church is established by Richard Allen and other African-American Methodists, the first such denomination completely independent of White churches.
- 1816 – Rammohun Roy founds Hindu College in Calcutta, offering instructions in Western languages and subjects.
- April 15, 1817 – The first American school for the deaf opens in Hartford, Connecticut.
- May, 1817 – The General Convention of the Episcopal Church founds the General Theological Seminary while meeting in New York City.
- November 11, 1818 – Anglo-Chinese College is founded by Robert Morrison in Malacca (later renamed Ying Wa College).
- January 25, 1819 – Thomas Jefferson founds the University of Virginia.
- August 6, 1819 – Norwich University is founded by Captain Alden Partridge in Vermont as the first private military school in the United States.
Other events[]
- August 3, 1811 – First ascent of Jungfrau, third highest summit in the Bernese Alps,
- July 13, 1813 – Missionaries Adoniram Judson and his wife Ann Hasseltine Judson arrive in Burma.
- 1815 – British missionaries arrive in New Zealand.
- 1815 – The second wave of Amish immigration to North America begins.
- 1816 – Tsultrim Gyatso becomes the 10th Dalai Lama.
- November 22, 1817 – Frédéric Cailliaud discovers the old Roman emerald mines at , Egypt.
References[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1810s. |
- ^ Hamilton-Williams, David p. 59
- ^ Wood, Empire of Liberty (2009) ch 18
- ^ Heidler and Heidler, Encyclopedia of the War of 1812, pp 290-93
- ^ Hickey, War of 1812 p. 183
- ^ Wood, Empire of Liberty (2009), pg. 329.
- ^ Wood, Empire of Liberty (2009), pg 330.
- ^ Spahn, M. (1910). Holy Alliance. In The Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Retrieved May 15, 2010, from New Advent.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "An 1820 Claim to Congress: Alabama Territory : 1817", The Intruders, TNGenNet Inc., 2001, quick webpage: TN-537[permanent dead link].
- ^ [1] Archived September 27, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Canadian Encyclopedia", 2010.
- ^ Boulton & Watt Engine Order Book, Birmingham Public Library, England.
- ^ Western Courier [Louisville, Ky.], 1 June 1815: "Arrived in this port, in 25 days from New-Orléans, the Steam-Boat Enterprize, capt. SHRIEVE. The celerity and safety with which this boat descends and ascends the currents of these mighty waters, the improvement of the navigation of which is so advantageous to the western world, must be equally interesting to the farmer and the merchant. The facility and convenience of the passage, in ascending the rivers, are such as to give a decided preference to this mode of navigation, while the size and construction of the boat entitles it to all the advantages which the Ætna and Vesuvius have in vain attempted to monopolize over the free waters of our common country."
- ^ American Telegraph [Brownsville, Pa.], 5 July 1815: "Arrived at this port on Monday last, the Steam Boat Enterprize, Shreve, of Bridgeport, from New Orleans, in ballast, having discharged her cargo at Pittsburgh. She is the first steam boat that ever made the voyage to the Mouth of the Mississippi and back. She made the voyage from New Orleans to this port, in fifty four days, twenty days on which were employed in loading and unloading freight at different towns on the Mississippi and Ohio, so that she was only thirty four days in active service, in making her voyage, which our readers will remember must be performed against powerful currents, and is upwards of two thousand two hundred miles in length."
- ^ Barlow Cumberland Archived 2005-02-06 at the Wayback Machine, A Century of Sail and Steam on the Niagara River, 1911, accessed 20 August 2010
- ^ John Kennedy,"The History of Steam Navigation" Liverpool,1903.
- ^ A.I.Bowman, "Swifts & Queens", Strathkelvin, 1983.
- ^ Steinberg, Michael. "The Symphony: a listeners guide". pp. 44–47. Oxford University Press, 1995.
- 1810s
