Armée secrète
show This article may be expanded with text translated from the corresponding article in French. (March 2019) Click [show] for important translation instructions. |
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2008) |
 Insignia of the Armée secrète in Haute-Savoie | |
| Formation | 11 November 1942 |
|---|---|
| Dissolved | February 1, 1944 |
| Type | Resistance network |
Region | France |
Official language | French |
Chef | Charles Delestraint |
Chef d'état-major | , later Pierre Dejussieu-Pontcarral |
Key people | Henri Frenay, Jean Moulin |
| Affiliations | Mouvements unis de la Résistance (MUR) |

The armée secrète was a French military organization active during World War II. The collective grouped the paramilitary formations of the three most important Gaullist resistance movements in the southern zone: Combat, Libération-sud and the Franc-Tireurs.
In mid-1942, in the R1 Region, these three major movements wanted to coordinate the military units at their disposal to make them more effective. Henri Frenay, leader of Combat, claimed command of the new structure, but faced opposition from Emmanuel d'Astier de La Vigerie, leader of Liberation-Sud and , head of the Franc-Tireurs. Jean Moulin insisted that the post should go to someone who with no affiliation to one of these groups, so Frenay proposed Charles Delestraint, a general recalled from his retirement during the Battle of France, who admired De Gaulle and detested Vichy. He was the only general officer who had been promoted despite that defeat; the proposal was unanimously accepted.
Jean Moulin and General Delestraint first met on August 28, 1942 in Lyon. At the end of the interview, Jean Moulin ordered the three regional chiefs of the paramilitary formations of the great movements made available to Delestraint, for him to choose the best suited to the regional direction of the Secret Army. To this position, eminently clandestine and dangerous, the general named Captain Claudius Billon. As early as September, Billon appointed each of the AS departmental heads for R1, with the exception of the AS chief for Ain, named by Delestraint himself.
In October, Delestraint was appointed (officially) by General de Gaulle. General de Lattre had also been approached for this post, but had refused. Delestraint took command on November 11, 1942. His secretary was François-Yves Guillin; the head of the 2nd AS office was . André Lassagne was the deputy of Gastaldo, before becoming Delestraint, and the information was entrusted to Albert Lacaze (4th office). Its chief of staff was , from Combat, staff in which is also integrated Raymond Aubrac.[clarification needed]
On November 27, 1942 in Collonges-au-Mont-d'Or, the constituent meeting of the Southern Zone Coordination Committee was held and the head of the Secret Army was presented by Jean Moulin. This committee intended to unite the three major resistance movements.
In December, Delestraint, inexperienced in the constraints of illegal life, crossed the demarcation line to make contact with the major movements in the northern zone: Liberation, the Civil and Military Organization (CMO) National, Libération-Nord. Then, back in the free zone, he took part in the creation of the United Movements of the Resistance (MUR) on January 26, 1943 in Miribel, in Ain.
At the beginning of February 1943, , Kommandeur of the Sipo-SD in Vichy, decapitated the Secret Army of the R1 region. On February 1 in Lyon's Place du Pont, he arrested Billon, head of the AS in R1 (eleven departments), along with his deputy Pierre Lavergne. On February 3, at 31, rue Basse-des-Rives in Saint-Étienne, during a secret meeting of the headquarters of the departmental AS, he also arrested the head of AS Loire, Lieutenant Vidiani, and his companions. On February 10, in Le Puy-en-Velay, they continued to dismantle the AS in R1 with the arrest of the chief of AS in Haute-Loire Alfred Salvatelli and his companions at his home. After the February 10 arrest, the Haute-Loire resistance joined region R6 (Auvergne). On 27 May 1943, these three arrests, orchestrated by Geissler, featured prominently at the beginning of the Ernst Kaltenbrunner's report addressed to Joachim von Ribbentrop, Minister of Foreign Affairs for the Reich.
Delestraint then fought against the advice of Frenay (who had been provisionally delegated general of the Secret Army) to put the Army under the tutelage of the MUR. Frenay, on the one hand the No. 2 of the Secret Army and on the other a member of the Coordination Committee of the same army, then wished the recall of Delestraint and his own appointment as head of the Secret Army, which were rejected by the other members of the Coordinating Committee, Moulin, d'Astier and Levy.
In London in February 1943 to meet Allied authorities, Delestraint was asked to make his troop the "nucleus of the future French army", estimated at 150,000 men. Unfortunately, Francois Morin-Forestier was arrested in March with Raymond Aubrac, and of the MUR, and only released in May, thanks to the action of his former co-detainee Raymond Aubrac. His release did not allow his return to the staff: too exposed, he was ex-filtered to London. In April, Delestraint returned to Paris, arriving April 11. By the June 4 report, Moulin deplores the risks that Delestraint was taking, working alone when he would do better if assisted.
On June 9, 1943, Delestraint, Gastaldo and their deputy Jean-Louis Théobald were arrested in Paris. On June 21, a staff meeting was held to find a successor to Delestraint in Caluire-et-Cuire. Léonard Émile Schwarzfeld, candidate to replace Delestraint, Aubrac, candidate for the leadership in the northern zone, and Lassagne for the southern zone, as well as other leaders of the Resistance such as Moulin, Henri Aubry, René Hardy, and were taken prisoner. In July 1943, Colonel Pierre Dejussieu-Pontcarral was appointed chief of staff of a Secret Army now without an official leader. The Chief of Staff of the Southern Zone was General Jouffrault, until he was also arrested in August 1943.
On February 1, 1944, the Gaullist Secret Army merged with the French Forces of the Interior (FFI), with the Army Resistance Organization (ORA) and the French Francs-tireurs et partisans (FTPF, communists, not to be confused with the Franc-Tireur movement).
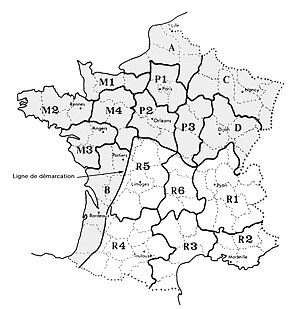
This structure was mainly found in the southern half of France: Rhône-Alpes (R1) and Auvergne (R6), but also Limousin (R5), South-East and the Southwest (R4). It corresponded to the organizational structure used by Combat.
Uniting the regions of the free zone took only a few weeks, the various chiefs being chosen from among the regional chiefs in office. In Region A, the workforce was almost entirely composed of members of the CMO.
Regions[]
| Region | Departement | Leader | Others |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | Region | General Louis-Eugène Faucher | |
| Deux-Sèvres | |||
| M | Region | General | |
| M2 | Region | General | |
| Finistère | |||
| Morbihan | Paul Chenailler |
||
| R1 - Rhône-Alpes | Region | Captain Claudius Billon Capt. |
(Maquis) André Vansteenberghe (intelligence) |
| Ain | André Bob Fornier[1] Capt. Henri Romans-Petit[2] |
Jean Perret Marcel Gagneux[3] | |
| Haute-Savoie | Cmdr. Jean Vallette d'Osia Henri Romans-Petit |
(adjoint) Tom Morel (maquis) | |
| Isère | Samuel Job [4] Cmdr. de Reyniès[5] |
Cmdr. Albert Séguin de Reyniès (genl. staff) [6] | |
| Jura | |||
| Loire | Lt. | ||
| Haute-Loire | Capt. | ||
| Saône-et-Loire | |||
| R2 - Sud-Est | Region | (volunteer corps) (volunteer corps) | |
| Bouches-du-Rhône | |||
| R3 - Sud | Region | ||
| Gard | Albert Thomas | ||
| Hérault | |||
| Pyrénées-Orientales | |||
| R4 - Sud-Ouest | Region | Delmas[7] |
|
| Ariège | |||
| Haute-Garonne | Cmdr. Rigal[8] | ||
| Tarn | |||
| R5 - Limousin | Region | ||
| Corrèze | (maquis) (civilian) | ||
| Creuse | (maquis) (maquis) | ||
| Dordogne | [7] [9] |
Maurice Loupias (Bergeret, volunteer corps)[7] | |
| Haute-Vienne | [7] | ||
| Indre | Capt. René Antoine (Carpy) |
||
| R6 - Auvergne | Region | Jean Chappat[10] |
See also[]
- Resistance during World War II
- Liberation of France
- Maquis (World War II)
- Military history of France during World War II
- Free France
- Organisation de résistance de l'armée
- zone libre
- Francs-Tireurs et Partisans
- French Forces of the Interior
References[]
- ^ "Maquis de l'Ain et du Haut-Jura" [Maquis of the Ain and Haut-Jura] (in French). Retrieved 2015-07-07.
- ^ "La Résistance armée" [Armed Resistance] (in French). Mémoire de la Déportation dans l'Ain (1939-1945). Retrieved 2014-02-22..
- ^ "Structuration de l'Armée Secrète et unification au sein des Mouvements Unis de la Résistance" [Organization of the Armée Secrète and Consolidation Within the United Resistance Movement] (PDF). Académie de Lyon (pdf) (in French). Retrieved 2011-07-01.[permanent dead link].[dead link]
- ^ Muller 2003, p. 26.
- ^ Muller 2003, p. 151.
- ^ Muller 2003, p. 152.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Boyer & Binot 2007
- ^ Maruéjol, René; Vielzeuf, Aymé (1982). Le maquis Bir-Hakeim [The Bir-Hakeim Maquis] (in French). éditions Le Camariguo..
- ^ Le Bail, Sylvain (2001). Mojzesz Goldman dit "Mireille": premier chef départemental du maquis A.S., Dordogne, 1943 [Moises "Mireille" Goldman: First Departmental Director of the Maquis] (in French). Chêne Vert..
- ^ Adler, Laure (2011-01-19). Françoise [Françoise] (in French). Grasset..
- French Resistance networks and movements
- 1942 establishments in France

