Base Presidente Eduardo Frei Montalva
Teniente Rodolfo Marsh Martin Aerodrome | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | airstrip | ||||||||||
| Serves | Base Presidente Eduardo Frei Montalva | ||||||||||
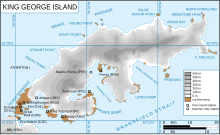
| Location | King George Island South Shetland Islands Antarctica | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Base Presidente Eduardo Frei Montalva is the most important Antarctic base of Chile. It is located at Fildes Peninsula, an ice-free area, in front of Fildes Bay (Maxwell Bay), west of King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Situated alongside the Escudero Station and only 200 metres from the Russian Bellingshausen Station, its geographic coordinates are 62°12′0″S 58°57′51″W / 62.20000°S 58.96417°W, at an altitude of 10 metres above sea-level. The base is located in the Chilean commune of Antártica, which is the Antarctic territory claimed by Chile[1] (Antártica Chilena Province, Magallanes y la Antártica Chilena Region).
Also nearby are the bases of Great Wall (China), General Artigas Station (Uruguay), King Sejong Station (Republic of Korea), Carlini Base (Argentina), Commandante Ferraz (Brazil), Henryk Arctowski (Poland) and Machu Picchu Base (Peru). Further away is Captain Arturo Prat Base, also Chilean, 50 km to the west.
Description[]
It has a 1300 metres long airstrip (Teniente Rodolfo Marsh Martin Aerodrome, ICAO Code SCRM),[2] with 50 intercontinental and 150 intracontinental flights each season, serving as a means of transport to many nearby bases. It also includes the Villa Las Estrellas residential area that has a hospital, a school, a bank, a small supermarket, etc. The maximum population during summer is of 150 people, and the average during winter is of about 80 people.[3]
It began to operate in 1969 as Centro Meteorológico Eduardo Frei. When the installations were expanded, it was renamed as Base Teniente Rodolfo Marsh, with the meteorology center keeping its original name. During the 1990 decade, all of the installations came to be named Base Presidente Eduardo Frei Montalva, with the airstrip retaining the name Teniente Rodolfo Marsh.[4]
Climate[]
Like the coastal areas of Antarctic Peninsula and the subantarctic islands south of the 60º parallel, the area has a tundra climate, that could be considerably borderline "maritime-influenced polar climate", thanks to temperatures that rarely drop below −15 °C (5 °F) in winter (which is commonplace in most of Antarctica), and temperatures that could soar a few digits above freezing for most parts of the year. The base's area and its vicinity (the entire island, actually) experiences a rather heavy precipitation, with an average precipitation rate of 405 millimetres (15.9 in) yearly,[5] which makes it unusual on the Antarctic continent, as the continent is significantly drier than the islands are to the north.[6]
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °C (°F) | 13.0 (55.4) |
9.2 (48.6) |
8.3 (46.9) |
5.9 (42.6) |
4.6 (40.3) |
4.2 (39.6) |
5.0 (41.0) |
3.8 (38.8) |
4.4 (39.9) |
4.4 (39.9) |
6.0 (42.8) |
8.2 (46.8) |
13.0 (55.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.7 (36.9) |
2.9 (37.2) |
2.2 (36.0) |
0.6 (33.1) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
0.0 (32.0) |
2.1 (35.8) |
0.3 (32.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) |
1.6 (34.9) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
−1.0 (30.2) |
0.6 (33.1) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.3 (32.5) |
0.6 (33.1) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−8.2 (17.2) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−13.2 (8.2) |
−11.3 (11.7) |
−8.0 (17.6) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −5.1 (22.8) |
−5.8 (21.6) |
−9.9 (14.2) |
−16.8 (1.8) |
−23.6 (−10.5) |
−24.2 (−11.6) |
−28.5 (−19.3) |
−28.7 (−19.7) |
−23.0 (−9.4) |
−17.0 (1.4) |
−10.7 (12.7) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−28.7 (−19.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 53.8 (2.12) |
52.3 (2.06) |
52.5 (2.07) |
46.6 (1.83) |
31.0 (1.22) |
29.2 (1.15) |
32.2 (1.27) |
34.5 (1.36) |
42.0 (1.65) |
47.7 (1.88) |
41.0 (1.61) |
30.1 (1.19) |
492.9 (19.41) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 91 | 89 | 89 | 89 | 88 | 90 | 89 | 88 | 89 | 90 | 89 | 81 | 89 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 83.8 | 71.2 | 57.3 | 23.6 | 8.3 | 1.2 | 3.9 | 15.8 | 44.2 | 93.2 | 104.5 | 98.1 | 605.1 |
| Source: Dirección Meteorológica de Chile (temperature data:1970-2004, all other 1990-2000) [7] | |||||||||||||
See also[]
 | |
| Location | Ardley Island, King George Island, Chile |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 62°12′03″S 58°57′37″W / 62.200778°S 58.960167°W |
| Foundation | concrete base |
| Construction | fiberglass tower |
| Tower height | 3 metres (9.8 ft)[8] |
| Tower shape | cylindrical tower with side panels[9] |
| Markings | white tower and panels with red horizontal band |
| Power source | solar power |
| Focal height | 5 metres (16 ft)[8] |
| Range | 6 nautical miles (11 km; 6.9 mi)[8] |
| Characteristic | Fl W 5s.[8] |
| NGA no. | 2721[8] |
| Admiralty no. | G1387.9 |
- List of lighthouses in Antarctica
- List of Antarctic research stations
- List of Antarctic field camps
References[]
- ^ Antarctica
- ^ Great Circle Mapper. "SCRM - Airport". Gc.kls2.com. Retrieved 27 February 2012.
- ^ (in Spanish) Expedicion Antartica Archived September 30, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Chilean "EDUARDO FREI" Antarctic Base
- ^ Presidente Eduardo Frei Montalva - permanent station of Chile, Antarctica - Sunrise, sunset, dawn and dusk times for the whole year - Gaisma
- ^ Presidente Eduardo Frei Montalva - permanent station of Chile, Antarctica - Sunrise, sunset, dawn and dusk times for the whole year - Gaisma
- ^ Cerda, Jorge; Zamora, Monica (2007). "CLIMATOLOGÍA DE LA PENINSULA ANTARTICA Y DE LA BASE PRESIDENTE EDUARDO FREI MONTALVA" (PDF). Climatologica Antartica (in Spanish). Dirección Meteorológica de Chile. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 17, 2012. Retrieved May 10, 2013.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e List of Lights, Pub. 111: The West Coasts of North and South America (Excluding Continental U.S.A. and Hawaii), Australia, Tasmania, New Zealand, and the Islands of the North and South Pacific Oceans (PDF). List of Lights. United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. 2017.
- ^ Rowlett, Russ. "Lighthouses of Antarctica". The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved 15 May 2017.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eduardo Frei Montalva Station. |
62°11′35″S 58°58′55″W / 62.193126°S 58.981986°WCoordinates: 62°11′35″S 58°58′55″W / 62.193126°S 58.981986°W
- Outposts of Antarctica
- Outposts of the South Shetland Islands
- Argentine Antarctica
- British Antarctic Territory
- Chilean Antarctic Territory
- Lighthouses in Antarctica
- 1969 establishments in Antarctica
 WikiMiniAtlas
WikiMiniAtlas