Bernardo de Gálvez
The Most Excellent Field Marshal The Viscount of Galveston | |
|---|---|
 Portrait of Gálvez, c. 1785 | |
| 49th Viceroy of New Spain | |
| In office 18 June 1785 – 30 November 1786 | |
| Monarch | Charles III |
| Preceded by | Matías de Gálvez y Gallardo |
| Succeeded by | Alonso Núñez de Haro y Peralta |
| 5th Spanish Governor of Louisiana | |
| In office 1777–1783 | |
| Monarch | Charles III |
| Preceded by | Luis de Unzaga |
| Succeeded by | Esteban Rodríguez Miró |
| Personal details | |
| Born | Bernardo de Gálvez y Madrid 23 July 1746 Macharaviaya, Málaga, Crown of Castile, Spain |
| Died | 30 November 1786 (aged 40) Tacubaya District, Mexico City, New Spain |
| Nationality | Spanish |
| Awards | Order of Charles III |
| Signature | 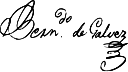 |
| Military service | |
| Allegiance | |
| Branch/service | Spanish Army |
| Years of service | 1762–1786 |
| Rank | Captain General Marshal |
| Battles/wars |
American Revolutionary War |
Bernardo Vicente de Gálvez y Madrid, 1st Viscount of Galveston, 1st Count of Gálvez (23 July 1746 – 30 November 1786) was a Spanish military leader and colonial administrator who served as colonial governor of Spanish Louisiana and Cuba, and later as Viceroy of New Spain.
Gálvez aided France and the newly formed nation the United States of America in the international war against Britain, defeating the British at the siege of Pensacola (1781) and conquering West Florida. Following Gálvez's successful campaign the whole of Florida was returned to Spain in the Treaty of Paris. He spent the last two years of his life as Viceroy of New Spain, succeeding his father Matías de Gálvez y Gallardo. The city of Galveston, Texas, was named after him.
Gálvez is one of only eight people to have been awarded honorary United States citizenship.[1]
Origins and military career[]
Bernardo de Gálvez was born in Macharaviaya, a mountain village in the province of Málaga, Spain, on 23 July 1746.[2][3][4][5] He studied military sciences at the Academia de Ávila and at the age of 16 participated in the Spanish invasion of Portugal, which stalled after the Spanish had captured Almeida. Following the conflict he was promoted to infantry lieutenant.[6] He arrived in Mexico, which was then part of New Spain, in 1769.[7][8] As a captain, he fought the Apaches, with his Opata Indian allies.[9][10] He received many wounds, several of them serious.[11] In 1770, he was promoted to commandant of arms of Nueva Vizcaya and Sonora, northern provinces of New Spain.[12]

In 1772, Gálvez returned to Spain in the company of his uncle, José de Gálvez. Later, he was sent to Pau, France, where he served with the Royal Cantabria regiment,[13] an elite Franco-Spanish unit, for three years. There, he learned to speak French, which served him well when he became governor of Louisiana. He was transferred to Seville in 1775, and then he participated in Alejandro O'Reilly's disastrous expedition to Algiers. Gálvez himself was seriously wounded in the line of duty when Spanish forces assaulted the fortress that guarded the city;[14][15] he was later appointed a professor at the military academy of Ávila and promoted to lieutenant colonel. He was made colonel in 1776.[11]
Spanish governor of Louisiana[]
On 1 January 1777, Bernardo de Gálvez became the new governor of the formerly French province of Louisiana,[11][16] the vast territory that later became the object of the Louisiana Purchase. It had been ceded by France to Spain in 1762, ostensibly as compensation for the loss of Florida to Britain, when Spain was urged late in the Seven Years' War to enter into battle on the French side. In 1779, he was promoted to brigadier.[17]
In November 1777, Gálvez married Marie Félicité de Saint-Maxent d'Estrehan, the Creole daughter of Gilbert Antoine de Saint-Maxent and young widow of Jean-Baptiste d'Estrehan's son. This marriage to the daughter of a Frenchman and the Creole Elizabeth La Roche[18][19] won Gálvez the favor of the local Creole population.[20][21] They had three children, Miguel, Matilde, and Guadalupe.[22]
Gálvez practiced an anti-British policy as governor, taking measures against British smuggling and promoting trade with France.[23][24] He damaged British interests in the region and kept it open for supplies to reach George Washington's Army.[25][26][27] He founded Galvez Town in 1779,[26] promoted the colonization of Nueva Iberia, and established free trade with Cuba and Yucatán.[28] Galvez Street in New Orleans is named for him.
American Revolutionary War[]

In December 1776, King Charles III of Spain decided that covert assistance to the United States would be strategically useful, but Spain did not enter into a formal alliance with the U.S.[29] In 1777, José de Gálvez, newly appointed as minister of the Council of the Indies, sent his nephew, Bernardo de Gálvez, to New Orleans as governor of Luisiana with instructions to secure the friendship of the United States.[30] On 20 February 1777, the Spanish king's ministers in Madrid secretly instructed Gálvez to sell the Americans desperately needed supplies.[24] The British had blockaded the colonial ports of the Thirteen Colonies, and consequently the route from New Orleans up the Mississippi River was an effective alternative. Gálvez worked with Oliver Pollock, an American patriot, to ship gunpowder, muskets, uniforms, medicine, and other supplies to the American colonial rebels.[31]
Although Spain had not yet joined the American cause, when an American raiding expedition led by James Willing showed up in New Orleans with booty and several captured British ships taken as prizes, Gálvez refused to turn the Americans over to the British.[31][32][33] In 1779, Spanish forces commanded by Gálvez seized the province of West Florida, later known as the Florida Parishes, from the British.[34] Spain's motive was the chance both to recover territories lost to the British, particularly Florida, and to remove the ongoing British threat.[35][36][37]
On 21 June 1779, Spain formally declared war on Great Britain.[38][39][40] On 25 June, a letter from London, marked secret and confidential, went to General John Campbell at Pensacola from King George III and Lord George Germain.[41] Campbell was instructed that it was the object of greatest importance to organize an attack upon New Orleans.[42] If Campbell thought it was possible to reduce the Spanish fort at New Orleans, he was ordered to make preparations immediately. These included securing from Vice-Admiral Sir Peter Parker as many fighting ships as the fleet at Jamaica could spare,[43] gathering all forces in the province that could be assembled, recruiting as many loyal Indians as the Superintendent could provide,[44] and drawing on His Majesty's Treasury through the Lords Commissioners to pay expenses.[45] As an unfortunate twist of fate for Campbell, upon which his whole career was decided, the secret communication fell into the hands of Gálvez. After reading the communication from King George III and Germain, Gálvez, Governor of Louisiana, swiftly and secretly organized Louisiana and New Orleans for war.[46]
Gálvez carried out a masterful military campaign and defeated the British colonial forces at Fort Bute, Baton Rouge, and Natchez in 1779.[47][48] The Battle of Baton Rouge, on 21 September 1779, freed the lower Mississippi Valley of British forces and relieved the threat to the capital of Louisiana, New Orleans. In March, 1780, he recaptured Mobile from the British at the Battle of Fort Charlotte.[49][50]
Gálvez's most important military victory over the British forces occurred 8 May 1781, when he attacked and took by land and by sea Pensacola, the British (and formerly, Spanish) capital of West Florida from General John Campbell of Strachur.[51][52] The loss of Mobile and Pensacola left the British with no bases along the Gulf coast.[53] In 1782, forces under Gálvez's overall command captured the British naval base at Nassau on New Providence Island in the Bahamas. He was angry that the operation had proceeded against his orders to cancel, and ordered the arrest and imprisonment of Francisco de Miranda, aide-de-camp of Juan Manuel Cajigal, the commander of the expedition. Miranda later ascribed this action on the part of Gálvez to jealousy of Cajigal's success.[54][55]
Gálvez received many honors from Spain for his military victories against the British, including promotion to lieutenant general and field marshal,[56] governor and captain general of Louisiana and Florida (now separated from Cuba), the command of the Spanish expeditionary army in America, and the titles of viscount of Gálveztown and count of Gálvez.[57]
The American Revolutionary War ended while Gálvez was preparing a new campaign to take Jamaica. The importance of Gálvez's campaign from the American perspective was that he denied the British the opportunity of encircling the American rebels from the south, and kept open a vital conduit for supplies. Gálvez also assisted the American revolutionaries with supplies and soldiers, much of it through Oliver Pollock,[58] from whom he received military intelligence concerning the British in West Florida.[59][60] Gálvez found it convenient for France and Spain to advance the cause of the American revolutionaries; his military success led to the inclusion of provisions in the Peace of Paris (1783) that officially returned Florida, now divided into two provinces, East and West Florida, to Spain. The treaty recognized the political independence of the former British colonies to the north, and its signing ended their war with the British.[61][62]
Viceroy of New Spain[]

In 1783, Bernardo de Gálvez was ennobled to the rank of count, promoted to lieutenant-general of the army, and appointed governor and captain-general of Cuba.[63] He returned to the Indies in October of the following year to assume his new office. Shortly after he arrived in Havana, his father, Matías de Gálvez y Gallardo (then the viceroy of New Spain), died in November, and Bernardo de Gálvez was appointed to fill the position.[64] He arrived in Vera Cruz, on 21 May 1785,[65] and made his formal entry into Mexico City in June.
During his administration two great calamities occurred: the freeze of September 1785, which led to famine in 1786,[66] and a typhus epidemic that killed 300,000 people the same year.[67] During the famine, Gálvez donated 12,000 pesos of his inheritance and 100,000 pesos he raised from other sources to buy maize and beans for the populace.[68] He also implemented policies to increase future agricultural production.
In 1785, Gálvez initiated construction of Chapultepec Castle.[69][70][71] He also ordered the construction of the towers of the cathedral and paving of the streets, as well as the installation of street lights in Mexico City.[72] He continued work on the highway to Acapulco,[68][73][74] and took measures to reduce the abuse of Indian labor on the project. He dedicated 16% of the income from the lottery and other games of chance to charity.
Gálvez helped advance science in the colony by sponsoring the Royal Botanical Expedition to New Spain, led by Martín Sessé y Lacasta. This expedition of botanists and naturalists resulted in a comprehensive catalog, a collaborative work published in Spain as the Flora Mexicana, which catalogued the diverse species of plants, birds, and fish found in New Spain.[75]
On one occasion, when the viceroy was riding on horseback to meet with the Audiencia (according to his own report), he encountered a party of soldiers escorting three criminals to the gallows. He suspended the hanging, and later had the criminals freed.[73][7][76]
After the typhus epidemic of 1786 had abated in early autumn, Bernardo de Gálvez apparently became one of its last victims,[77] and was confined to his bed. On 8 November 1786, he turned over all his governmental duties except the captain generalship to the Audiencia.[78] On 30 November 1786, Galvez died at the age of 40 in Tacubaya (now part of Mexico City). Gálvez was buried next to his father at San Fernando Church in Mexico City.[79][80]
Bernardo de Gálvez left some writings, including Ordenanzas para el Teatro de Comedias de México[81] and Instrución para el Buen Gobierno de las Provincias Internas de la Nueva España (Instructions for Governing the Interior Provinces of New Spain, 1786),[82] the latter of which remained in effect until the colonial period ended.[83] In his "Instructions", Gálvez advocated a policy of selling the Indians rifles and trade goods to make them dependent on the Spanish government,[84] and sanctioned war against the Apache if these inducements failed to pacify them.[85][86]
Legacy[]

Galveston, Texas, Galveston Bay, Galveston County, Galvez, Louisiana, and St. Bernard Parish, Louisiana were, among other places, named after him. The Louisiana parishes of East Feliciana and West Feliciana (originally a single parish) were said to have been named for his wife Marie Felicite de Saint-Maxent d'Estrehan.[87]
The Cabildo, a branch of the Louisiana State Museum located on Jackson Square in New Orleans, has a portrait of General Gálvez accompanied by a display of biographical information. Spanish Plaza, in the Central Business District of the city, has an equestrian statue of Gálvez adjacent to the New Orleans World Trade Center.[88] There is also a Galvez Street in New Orleans.[89] Mobile, Alabama, also has a Spanish Plaza with a statue of Gálvez.[90]
In Baton Rouge, Louisiana (present-day state capital), Galvez Plaza is laid out next to City Hall and used frequently as a site for municipal events.[91] Also, the 13-story Galvez Building is part of the state government's administrative office-building complex in the Capitol Park section of downtown Baton Rouge.
In 1911 in Galveston, the Hotel Galvez was built and named after him; Avenue P, where the hotel is located, is known as Bernardo de Galvez Avenue. The hotel was added to the National Register of Historic Places on 4 April 1979.
On December 16, 2014, the United States Congress conferred honorary citizenship on Gálvez, citing him as a "hero of the Revolutionary War who risked his life for the freedom of the United States people and provided supplies, intelligence, and strong military support to the war effort."[92] In 2019, the Spanish Government placed a 32-inch-tall (80 cm) statue of Galvez in front of the Spanish Embassy in Washington, D.C.[93]
See also[]
- Bernardo de Gálvez, the 1976 equestrian statue in Washington, D.C.
- Gálveztown (brig sloop) – captured British ship renamed and participated in the capture of Mobile (1780); replica built in Spain more than 200 years later.
- Spain and the American Revolutionary War
- Matías de Gálvez y Gallardo, Bernardo's father
- José de Gálvez, Bernardo's uncle
Notes[]
- ^ Bridget Bowman (29 December 2014). "Bernardo de Gálvez y Madrid's Very Good Year". Roll Call. The Economist Group. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ José Antonio Calderón Quijano (1968). Los Virreyes de nueva España en el reinado de Carlos III.: Martín de Mayorga (1779-1783), por J. J. Real Díaz y A. M. Heredia Herrera. Matías de Gálvez (1783-1784), por M. Rodríguez del Valle y A. Conejo Díez de la Cortina. Bernardo de Gálvez (1785-1786), por Ma. del Carmen Galbis Díez. Alonso Núnez de Haro, 1787, por A. Rubio Gil. Escuela Gráfica Salesiana. p. 327.
- ^ David J. Weber (1992). The Spanish Frontier in North America. Yale University Press. p. 443. ISBN 978-0-300-05917-5.
- ^ Luis Navarro García (1964). Don José de Gálvez y la Comandancia General de las Provincias Internas del norte de Nueva España. Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas. p. 143.
- ^ José Miguel Morales Folguera (1985). "I. Antecedentes, causas y modalidades de la nueva expansión colonial española hacia norteamérica en el siglo xviii". Urbanismo hispanoamericano en el sudeste de los EE.UU. (Luisiana y Florida). La obra del malagueño Bernardo de Gálvez y Gallardo (1746-1789). Andalucia y America en el siglo XVIII: actas de las IV Jornadas de Andalucia y America (Universidad de Santa María de la Rábida, marzo, 1984) (in Spanish). Seville: Editorial CSIC - CSIC Press. p. 122. ISBN 84-00-06091-1.
- ^ José Rodulfo Boeta (1977). Bernardo de Gálvez. Publicaciones Españolas. p. 42.
- ^ Jump up to: a b John Walton Caughey (1934). Bernardo de Gálvez in Louisiana, 1776-1783. University of California Press. p. 62.
- ^ René Chartrand (20 March 2013). American War of Independence Commanders. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 53. ISBN 978-1-4728-0300-9.
- ^ Kieran McCarty (1994). "Bernardo de Galvez on the Apache Frontier: The Education of a Future Viceroy". Journal of the Southwest. 36 (2): 127. JSTOR 40169957.
- ^ Pekka Hämäläinen (2008). The Comanche Empire. Yale University Press. p. 124. ISBN 978-0-300-15117-6.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Light Townsend Cummins (2006). "The Gálvez Family and Spanish Participation In the Independence of the United States of America" (pdf). Revista Complutense de Historia de América. Facultad de Geografía e Historia, Universidad Complutense de Madrid. 32: 187. ISSN 1132-8312. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ Max L. Moorhead (1991). The Presidio: Bastion of the Spanish Borderlands. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 99. ISBN 978-0-8061-2317-2.
- ^ Eduardo Garrigues (9 February 2016). El que tenga valor que me siga: En vida de Bernardo de Gálvez (in Spanish). La Esfera de los Libros. p. 301. ISBN 978-84-9060-614-8.
- ^ José Rodulfo Boeta (1977). Bernardo de Gálvez. Publicaciones Españolas. p. 46.
- ^ José Montero de Pedro (2000). The Spanish in New Orleans and Louisiana. Pelican Publishing. p. 48. ISBN 978-1-4556-1227-7.
- ^ Michael Klein. "Louisiana: European Explorations and the Louisiana Purchase – Louisiana under Spanish Rule" (PDF). loc.gov/collections. United States Library of Congress. p. 40. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ Thomas E. Chávez (11 April 2002). Spain and the Independence of the United States: An Intrinsic Gift. UNM Press. p. 153. ISBN 978-0-8263-2795-6.
- ^ Madame Calderón de la Barca (Frances Erskine Inglis) (1959). La vida en Mexico durante una residencia de dos afios en ese pais. Porrúa. p. 44.
- ^ Sanders, Mary Elizabeth (2002). "II". St. Mary Parish, Louisiana, Heirship Series Vol. II: Selected Annotated Abstracts of Marriage Book 1, 1811-1829. Pelican Publishing. p. 122. ISBN 978-1-4556-1234-5.
- ^ Virginia Parks; Pensacola Historical Society (1 April 1981). Siege! Spain and Britain: Battle of Pensacola, March 9-May 8, 1781. Pensacola Historical Society. p. 24.
- ^ Larrie D. Ferreiro (2016). Brothers at Arms: American Independence and the Men of France and Spain Who Saved It. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. p. 133. ISBN 978-1-101-87524-7.
- ^ Dictionary of Louisiana Biography (2008). "ST. MAXENT, Marie Félicité (Felicítas)". www.lahistory.org. Louisiana Historical Association. Archived from the original on July 16, 2016. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ Paul E. Hoffman (1 January 2004). The Louisiana Purchase and Its Peoples: Perspectives from the New Orleans Conference. Louisiana Historical Association and Center for Louisiana Studies, University of Louisiana at Lafayette. p. 119. ISBN 978-1-887366-51-9.
- ^ Jump up to: a b William R. Nester (2004). The Frontier War for American Independence. Stackpole Books. p. 182. ISBN 978-0-8117-0077-1.
- ^ "Caughey 1934, p. 250"
- ^ Jump up to: a b Louisiana Review. Conseil pour le développement du français en Louisiane. 1975. p. 68.
- ^ David Narrett (5 March 2015). Adventurism and Empire: The Struggle for Mastery in the Louisiana-Florida Borderlands, 1762-1803. UNC Press Books. pp. 78–82, 101. ISBN 978-1-4696-1834-0.
- ^ Fernando Benítez (7 October 2014). De la Conquista a la Independencia (in Spanish). Ediciones Era. p. 566. ISBN 978-607-445-280-8.
Estableció el libre tráfico de Nueva Orleáns con Cuba y Yucatán y fomentó la colonización de Nueva Iberia." (English): "He established New Orleans' free trade with Cuba and Yucatán and promoted the colonization of New Iberia.
- ^ Paul W. Mapp (2015). "The Revolutionary War and Europe's Great Powers". In Edward G. Gray; Jane Kamensky (eds.). The Oxford Handbook of the American Revolution. Oxford University Press. p. 318. ISBN 978-0-19-025776-7.
- ^ Library of Congress (2002). The Impact of the American Revolution Abroad. The Minerva Group, Inc. p. 167. ISBN 978-0-89875-978-5.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Larrie D. Ferreiro (15 November 2016). Brothers at Arms: American Independence and the Men of France and Spain Who Saved It. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group. p. 134. ISBN 978-1-101-87525-4.
- ^ Sam Willis (15 February 2016). The Struggle for Sea Power: A Naval History of the American Revolution. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 172. ISBN 978-0-393-24883-8.
- ^ Naval History & Heritage Command (U.S.) (14 July 2014). Naval Documents of the American Revolution Volume 12, American Theater, April 1, 1778-May 31, 1778; European Theater, April 1, 1778- May 31, 1778. Government Printing Office. p. 252. ISBN 978-0-945274-72-8.
- ^ Samuel C. Hyde, Jr. (1 February 1998). Pistols and Politics: The Dilemma of Democracy in Louisiana's Florida Parishes, 1810--1899. LSU Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-0-8071-2270-9.
- ^ Helen Hornbeck Tanner (1963). Zéspedes in East Florida, 1784-1790. University of Miami Press. p. 11.
- ^ Wilbert H. Timmons (1990). El Paso: A Borderlands History. University of Texas at El Paso. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-87404-207-8.
- ^ Desmond Gregory (1990). Minorca, the Illusory Prize: A History of the British Occupations of Minorca Between 1708 and 1802. Associated University Presses. p. 208. ISBN 978-0-8386-3389-2.
- ^ David Marley (1998). Wars of the Americas: A Chronology of Armed Conflict in the New World, 1492 to the Present. ABC-CLIO. p. 321. ISBN 978-0-87436-837-6.
- ^ "Chávez 2002" p. 135
- ^ Terry M. Mays (18 November 2009). Historical Dictionary of the American Revolution. Scarecrow Press. p. 79. ISBN 978-0-8108-7503-6.
- ^ Piers Mackesy (1964). The War for America: 1775-1783. U of Nebraska Press. p. 266. ISBN 0-8032-8192-7.
- ^ George C. Osborn (April 1949). "Major-General John Campbell in British West Florida". Florida Historical Quarterly. XXVII (4): 335. Retrieved 11 June 2017.
Again, in November 1780, Germain informed Campbell that it was "the King’s Wish" that Governor Dalling, Vice-Admiral Parker and he collaborate in an attack on New Orleans. General Campbell was to do all in his power to render the attack successful.
- ^ Virginia Parks (1 April 1981). Siege! Spain and Britain: Battle of Pensacola, March 9-May 8, 1781. Pensacola Historical Society. p. 34.
- ^ Robert Marshall Utley; Wilcomb E. Washburn (1985). Indian Wars. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. pp. 109–. ISBN 0-618-15464-7.
- ^ Great Britain. Royal Commission on Historical Manuscripts (1906). Report on American Manuscripts in the Royal Institution of Great Britain ... H. M. Stationery Office. p. 162.
- ^ "Osborn1949" p. 326
- ^ Henry Putney Beers (1 March 2002). French and Spanish Records of Louisiana: A Bibliographical Guide to Archive and Manuscript Sources. LSU Press. p. 90. ISBN 978-0-8071-2793-3.
- ^ James W. Raab (5 November 2007). Spain, Britain and the American Revolution in Florida, 1763-1783. McFarland. p. 135. ISBN 978-0-7864-3213-4.
- ^ Robert D. Bush (15 October 2013). The Louisiana Purchase: A Global Context. Routledge. p. 19. ISBN 978-1-135-07772-3.
- ^ Joseph G. Dawson III (1 February 1990). The Louisiana Governors: From Iberville to Edwards. LSU Press. p. 57. ISBN 978-0-8071-1527-5.
- ^ N. Orwin Rush (1966). Spain's Final Triumph Over Great Britain in the Gulf of Mexico: The Battle of Pensacola March 9 to May 8, 1781. Florida State University. pp. 82–83.
- ^ "Ferreiro 2016", p.253–254
- ^ Greg O'Brien (20 May 2015). Pre-removal Choctaw History: Exploring New Paths. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 124. ISBN 978-0-8061-4988-2.
- ^ William Spence Robertson (1909). Francisco de Miranda and the Revolutionizing of Spanish America. U.S. Government Printing Office. pp. 240–242.
- ^ "Chávez 2002" pp. 208–209
- ^ Paul K. Davis (2003). Besieged: 100 Great Sieges from Jericho to Sarajevo. Oxford University Press. p. 188. ISBN 978-0-19-521930-2.
- ^ Lawrence N. Powell (13 April 2012). The Accidental City. Harvard University Press. pp. 185–186. ISBN 978-0-674-06544-4.
- ^ "Chávez 2002" p. 108
- ^ F. Todd Smith (17 November 2014). Louisiana and the Gulf South Frontier, 1500-1821. LSU Press. p. 160. ISBN 978-0-8071-5711-4.
- ^ Alan Taylor (6 September 2016). American Revolutions: A Continental History, 1750-1804. W. W. Norton. p. 148. ISBN 978-0-393-25387-0.
- ^ Department of Defense (August 1997). "American Revolution (1775–1783)". Hispanics in America's Defense. Diane Publishing Company. pp. 5–6. ISBN 978-0-7881-4722-7.
- ^ Kathleen DuVal (April 2016). Independence Lost: Lives on the Edge of the American Revolution. Random House Publishing Group. pp. 229–230. ISBN 978-0-8129-8120-9.
- ^ J. Chu (14 April 2012). Stumbling Towards the Constitution: The Economic Consequences of Freedom in the Atlantic World. Springer. p. 10. ISBN 978-1-137-01080-3.
- ^ David J. Weber (14 May 2014). Spanish Frontier in North America. Yale University Press. p. 169. ISBN 978-0-300-15621-8.
- ^ James Madison (1962). The Papers of James Madison. University of Chicago Press. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-226-36300-4.
- ^ Carol Helstosky (3 October 2014). The Routledge History of Food. Routledge. p. 81. ISBN 978-1-317-62113-3.
- ^ David W. Stahle; Edward R. Cook; Dorian J. Burnette; Jose Villanueva; Julian Cerano; Jordan N. Burns; Daniel Griffin; Benjamin I. Cook; Rodolfo Acuna; Max C.A. Torbenson; Paul Sjezner; Ian M. Howard (1 October 2016). "The Mexican Drought Atlas: Tree-ring reconstructions of the soil moisture balance during the late pre-Hispanic, colonial, and modern eras". Quaternary Science Reviews. 149: 43. Bibcode:2016QSRv..149...34S. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.06.018.
The worst famine of the colonial era in Mexico occurred in 1786, and is referred to as El Ano de Hambre the year of hunger (Florescano and Swan, 1995; Therrell, 2005). Two to three years of drought and an early fall frost in 1785 again appear to have led to crop failure and famine in 1786 (Therrell, 2005; Therrell et al., 2006). An estimated 300,000 people died during El Ano de Hambre due to both famine and an outbreak of epidemic typhus in 1785–1787 (Cooper, 1965; Burns et al., 2014). The MXDA indicates that drought conditions were most serious during the two-year period from 1785 to 1786 when drought extended over most of Mexico, most severely over central and northeastern Mexico
- ^ Jump up to: a b Steven Otfinoski (September 2008). The New Republic. Marshall Cavendish. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-7614-2938-8.
- ^ Juan Pedro Viqueira Albán (1999). Propriety and Permissiveness in Bourbon Mexico. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-8420-2467-9.
- ^ "Chávez 2002", p. 12
- ^ Eduardo Philibert Mendoza (15 April 2011). Personajes Notables de la Historia de México 2. Panorama Editorial. p. 66. ISBN 978-607-452-266-2.
- ^ Juana Vázquez Gómez (1997). Dictionary of Mexican Rulers, 1325-1997. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 45. ISBN 978-0-313-30049-3.
- ^ Jump up to: a b The Historical Magazine, and Notes and Queries Concerning the Antiquities, History, and Biography of America. VIII. C. Benjamin Richardson. 1864. p. 141.
- ^ Elías Trabulse (January 1994). Ciencia y tecnología en el Nuevo Mundo. El Colegio de México. p. 145. ISBN 978-968-16-4390-4.
- ^ Shelley E. Garrigan (2012). Collecting Mexico: Museums, Monuments, and the Creation of National Identity. U of Minnesota Press. pp. 71–72. ISBN 978-0-8166-7092-5.
- ^ José Rodulfo Boeta (1977). Bernardo de Gálvez. Publicaciones Españolas. p. 130.
- ^ Publications of the University of California at Los Angeles in Social Sciences. University of California Press. 1934. p. 256.
- ^ Artes de México. Frente Nacional de Artes Plásticas. 1960. p. 90.
- ^ "Chávez 2002", p. 219
- ^ Revista complutense de historia de América. Facultad de Geografía e Historia, Universidad Complutense de Madrid. 2006. p. 192.
- ^ Francisco Pimentel (1904). Obras completas. IV. Tipografía económica. p. 351.
- ^ New Spain; Bernardo de Gálvez (1951). Instructions for Governing the Interior Provinces of New Spain, 1786. Quivira Society.
- ^ David J. Weber (2005). Bárbaros: Spaniards and Their Savages in the Age of Enlightenment. Yale University Press. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-300-10501-8.
- ^ Raphael Brewster Folsom (2014). The Yaquis and the Empire: Violence, Spanish Imperial Power, and Native Resilience in Colonial Mexico. Yale University Press. p. 251. ISBN 978-0-300-19689-4.
- ^ William B. Griffen (1 September 1998). Apaches at War and Peace: The Janos Presidio, 1750-1858. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 53. ISBN 978-0-8061-3084-2.
- ^ Roberto Mario Salmón (1991). Indian Revolts in Northern New Spain: A Synthesis of Resistance, 1680-1786. University Press of America. p. 117. ISBN 978-0-8191-7983-8.
- ^ Lawrence N. Powell (13 April 2012). The Accidental City. Harvard University Press. p. 180. ISBN 978-0-674-06544-4.
- ^ Robert Jeanfreau (14 March 2012). The Story Behind the Stone. Pelican Publishing Company, Inc. p. 23. ISBN 978-1-4556-1519-3.
- ^ Sally Asher (18 March 2014). Hope & New Orleans: A History of Crescent City Street Names. Arcadia Publishing. p. 31. ISBN 978-1-62584-509-2.
- ^ Robert B. Kane (August 2, 2016). "Bernardo de Gálvez". Encyclopedia of Alabama. Auburn University. Archived from the original on June 25, 2017. Retrieved 25 June 2017.
- ^ David K. Gleason (1991). Baton Rouge: Photographs and Text. Louisiana State University Press. p. 35. ISBN 978-0-8071-1715-6.
- ^ "H.J.Res.105 - Conferring honorary citizenship of the United States on Bernardo de Gálvez y Madrid, Viscount of Galveston and Count of Gálvez". Congress.gov. 2014-12-16. Retrieved 20 December 2014.
- ^ John Kelly (July 17, 2019), “The Spaniard Who Helped Win the Revolutionary War Has a New Statue in D.C.,” The Washington Post.
Further reading[]
- Caughey, John Walton (1998). Bernardo de Gálvez in Louisiana 1776-1783, Gretna: Pelican Publishing Company.
- Chávez, Thomas E. (2002). Spain and the Independence of the United States: An Intrinsic Gift, Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press.
- Gálvez, Bernardo de (1967) [1786]. Instructions for Governing the Interior Provinces of New Spain, 1786. New York: Arno Press.
- Mitchell, Barbara (Autumn 2010). "America's Spanish Savior: Bernardo de Gálvez marches to rescue the colonies". MHQ: The Quarterly Journal of Military History: 98–104.
- Quintero Saravia, Gonzalo M. Bernardo de Gálvez: Spanish Hero of the American Revolution (2018). 616 pp Scholarly biography; online review
- Ritter, Luke. "The American Revolution on the Periphery of Empires: Don Bernardo de Gálvez & the Spanish-American Alliance, 1763–1783." Journal of Early American History (2017) 7#2:177-201.
- Thonhoff, Robert H. (2000). The Texas Connection With The American Revolution. Austin, TX: Eakin Press. ISBN 1-57168-418-2.
- Woodward, Ralph Lee Jr. Tribute to Don Bernardo de Gálvez. Baton Rouge : Historic New Orleans Collection, 1979.
- (in Spanish) "Gálvez, Bernardo de," Enciclopedia de México, v. 6. Mexico City: 1987.
- (in Spanish) García Puron, Manuel (1984). México y sus gobernantes, v. 1. Mexico City: Joaquín Porrua.
- (in Spanish) Orozco L., Fernando (1988). Fechas Históricas de México. Mexico City: Panorama Editorial, ISBN 968-38-0046-7.
- (in Spanish) Orozco Linares, Fernando (1985). Gobernantes de México. Mexico City: Panorama Editorial, ISBN 968-38-0260-5.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bernardo de Gálvez. |
| Wikisource has the text of an 1879 American Cyclopædia article about Bernardo de Gálvez. |
- De Gálvez entry at United States National Park Service
- Bernardo de Gálvez at Texas A & M University
- Spain's Role in the American Revolution at AmericanRevolution.org
- 1746 births
- 1786 deaths
- Colonial United States (Spanish)
- Counts of Spain
- Governors of Spanish Louisiana
- Governors of the Bahamas
- People from the Province of Málaga
- People of New Spain
- Spanish colonial governors and administrators
- Spanish colonial period of Cuba
- Spanish generals
- Spanish military personnel of the American Revolutionary War
- Spanish West Indies
- Viceroys of New Spain
- Viscounts of Spain
- Deaths from typhus
- Infectious disease deaths in Mexico




