Conwy
This article needs additional citations for verification. (February 2016) |
| Conwy | |
|---|---|
 Conwy Castle and the bridges | |
 Conwy Location within Conwy | |
| Population | 14,723 (2011) |
| OS grid reference | SH775775 |
| Community |
|
| Principal area | |
| Ceremonial county | |
| Country | Wales |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | CONWY |
| Postcode district | LL31, LL32 |
| Dialling code | 01492 |
| Police | North Wales |
| Fire | North Wales |
| Ambulance | Welsh |
| UK Parliament | |
| Senedd Cymru – Welsh Parliament |
|
Conwy (/ˈkɒnwi/, Welsh: [ˈkɔnʊɨ] (![]() listen)), previously known in English as Conway, is a walled market town and community in Conwy County Borough on the north coast of Wales. The town, which faces Deganwy across the River Conwy, formerly lay in Gwynedd and prior to that in Caernarfonshire. The community, which includes Deganwy and Llandudno Junction, had a population of 14,753 at the 2011 census.[1] and is a popular tourist destination. The size of the resident population in Conwy County Borough on 30 June 2015 was estimated to be 116,200 people.[2]
The town itself has a population of 4,065.[3]
listen)), previously known in English as Conway, is a walled market town and community in Conwy County Borough on the north coast of Wales. The town, which faces Deganwy across the River Conwy, formerly lay in Gwynedd and prior to that in Caernarfonshire. The community, which includes Deganwy and Llandudno Junction, had a population of 14,753 at the 2011 census.[1] and is a popular tourist destination. The size of the resident population in Conwy County Borough on 30 June 2015 was estimated to be 116,200 people.[2]
The town itself has a population of 4,065.[3]
The name 'Conwy' derives from the old Welsh words cyn (chief) and gwy (water), the river being originally called the 'Cynwy'.[4][5][6][7]
History[]

Castle and town walls[]

Conwy Castle and the town walls were built, on the instructions of Edward I of England, between 1283 and 1289, as part of his conquest of the principality of Wales.[8] The church standing in Conwy has been marked as the oldest building in Conwy and has stood in the walls of Conwy since the 14th century. However, the oldest structure is part of the town walls, at the southern end of the east side. Here one wall and the tower of a llys (palace/court house) belonging to Llywelyn the Great and his grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffydd have been incorporated into the wall. Built on a rocky outcrop, with an apsidal tower, it is a classic, native, Welsh build and stands out from the rest of the town walls, due to the presence of four window openings. It dates from the early 13th century and is the most complete remnant of any of his llysoedd.
The walls are part of a World Heritage Site, Castles and Town Walls of King Edward in Gwynedd.
People born within the town walls of Conwy are nicknamed "Jackdaws", after the jackdaws which live on the walls there. A Jackdaw Society existed until 2011.[9][10]
The population of the town in 1841 was 1,358.[11]
Abbey[]
Conwy was the original site of Aberconwy Abbey, founded by Llywelyn the Great. Edward and his troops took over the abbey site and moved the monks up the Conwy valley to a new site at Maenan, establishing Maenan Abbey.[12] The parish church still retains some parts of the original abbey church in the east and west walls. English settlers were given incentives to move to the walled garrison town, which the Welsh were forbidden from entering for decades.
Suspension bridge[]
Conwy has other tourist attractions. Conwy Suspension Bridge, designed by Thomas Telford to replace the ferry, was completed in 1826 and spans the River Conwy next to the castle.[13] Telford designed the bridge's supporting towers to match the castle's turrets. The bridge is now open to pedestrians only and, together with the toll-keeper's house, is in the care of the National Trust.
Railway bridge[]
The Conwy Railway Bridge, a tubular bridge, was built for the Chester and Holyhead Railway by Robert Stephenson. The first tube was completed in 1848, the second in 1849.[14] The bridge is still in use on the North Wales Coast Line, along with the station, which is located within the town walls. In addition to a modern bridge serving the town, the A55 road passes under the river in a tunnel, Britain's first immersed tube tunnel, which was built between 1986 and 1991.[15] The old mountain road to Dwygyfylchi and Penmaenmawr runs through the Sychnant Pass, at the foot of Conwy Mountain.
Aberconwy House[]
The National Trust owns Aberconwy House, which is Conwy's only surviving 14th-century merchant's house, one of the first buildings built inside the walls of Conwy.[16]
Plas Mawr[]
Plas Mawr is an Elizabethan house built in 1576 by the Wynn family, which has been extensively refurbished to its 16th-century appearance and is now in the care of Cadw and open to the public.[17]

Smallest house in Great Britain[]

The house named in the Guinness Book of Records as the Smallest House in Great Britain, with dimensions of 3.05 × 1.8 metres, can be found on the quay. It was in continuous occupation from the 16th century (and was even inhabited by a family at one point) until 1900 when the owner (a 6-foot (1.8 m) fisherman – Robert Jones) was forced to move out on the grounds of hygiene. The rooms were too small for him to stand up in fully. The house is still owned by his descendants today, and visitors can look around it for a small charge.
Vardre Hall[]
Vardre Hall is a 19th century Grade II listed building directly opposite to Conwy Castle. It was erected by Conservative Buckinghamshire MP William Edward FitzMaurice in the mid 1850s. In 1869 the building was sold to solicitor William Jones. The building was used as a solicitor's office until 1972, when it was bought out and became The Towers Restaurant.[18] The Towers Coffee House remains next door. After lying empty for a number of years Vardre Hall changed hands again, and in 1999 was refurbished as a shop.[19]
Medieval watchtower[]
Across the estuary is Bodysgallen Hall, which incorporates a medieval tower that was possibly built as a watch tower for Conwy Castle.[20]
Notable locations[]
Conwy Morfa, a marshy spit of land on the west side of the estuary, was probably the location where golf was first played on Welsh soil.[21] It was also the place where Hugh Iorys Hughes developed, and later built, the floating Mulberry Harbour, used in Operation Overlord in World War II.[22]
Conwy Hospital closed in 2003 and has since been demolished.[23]
Conwy railway station bus stop has services to Llandudno, a four-hourly service to Holyhead, and a hop-on, hop-off tour bus, The Llandudno and Conwy Tour.
Lifeboat[]
A lifeboat station was established by the RNLI in 1966 and currently operates the D-class inshore lifeboat The May Bob.[24]
Governance[]
A Conwy electoral ward exists for elections to Conwy County Borough Council. The ward extends west of the River Conwy only with a total population of 4,065.[25] The other county wards within the Conwy community are Deganwy, Marl and Pensarn.
Conwy also has a town council, comprising 17 town councillors elected from the five community wards of Aberconwy, Castle, Deganwy, Marl and Pensarn.[26]
References[]
- ^ "Town population 2011". Retrieved 21 May 2015.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 4 November 2016. Retrieved 3 November 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Ward population 2011". Retrieved 21 May 2015.
- ^ Llandudno: its history and natural history, 1861, Richard Parry
- ^ A guide through North Wales, 1860, William Cathrall & Andrew Crombie Ramsay
- ^ Transactions, 1822, Cymmrodorion society
- ^ The pedestrian's guide through North Wales, 1838, George John Bennett
- ^ "Conwy Castle Facts and Information". History for Kids.
- ^ "Joining the Jackdaws". BBC Northwest Wales. September 2009. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ^ Evans, Kath (11 March 2011). "Jackdaw Society for those Born within Conwy Walls Folds". BBC Northwest Wales. Retrieved 4 April 2012.
- ^ The National Cyclopaedia of Useful Knowledge, Vol.III, (1847) London, Charles Knight, p.1,018
- ^ "Aberconwy Abbey". Ein Treftadaeth (Our Heritage). Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ^ "Conwy Suspension Bridge". Engineering Timelines. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ^ "Conwy Tubular Bridge". Engineering Timelines. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ^ "Conwy Immersed Tube Tunnel". Engineering Timelines. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ^ "Aberconwy House". National Trust Collections. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ^ "Plas Mawr - Elizabethan Mansion House Conwy". www.conwy.com.
- ^ "History Points – Footnotes Vardre Hall, Conwy". historypoints.org. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ^ "About Us – The Knight Shop | The Knight Shop". www.theknightshop.com. Retrieved 1 October 2018.
- ^ "History". Bodysgallen Hall & Spa. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ^ "History". Conwy Golf Club. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ^ "Engineer Biography: Hugh Iorys Hughes". Engineering Timelines. Retrieved 28 January 2017.
- ^ "Conwy Hospital Collection". Archives Hub. Retrieved 26 February 2019.
- ^ "RNLI: Conwy". Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- ^ "Ward population 2011". Retrieved 21 May 2015.
- ^ "About Cyngor Tref Conwy Town Council". Cyngor Tref Conwy Town Council. Retrieved 17 March 2018.
Gallery[]
Images showing changes over time

Conwy castle before the bridge was built, 1795
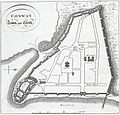
Conway Town and Castle, 1800

'Conway Castle: from the wood opposite', 1823

Conwy Castle, 1838

Conway Bridge and Castle ca 1840

The river bank at Conwy with the castle and bridge in the background ca 1850

Conway c.1850

'Conway Bridge & Castle' ca 1850
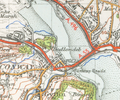
Map of Conwy from 1947

Conwy Castle - bridge view 2007

Conwy bridges in 2012
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Conwy (town). |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Conwy. |
- Conwy
- Fortified settlements
- Towns in Conwy County Borough












