Cork City Council
Cork City Council Comhairle Cathrach Chorcaí | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
Colm Kelleher, FF | |
| Structure | |
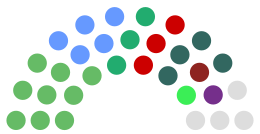
| Seats | 31 |
 | |
Political groups |
|
| Elections | |
Last election | 24 May 2019 |
| Motto | |
| Statio Bene Fida Carinis (Latin) "A safe harbour for ships"[1][2] | |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| City Hall, Cork | |
| Website | |
| corkcity | |
Cork City Council (Irish: Comhairle Cathrach Chorcaí) is the authority responsible for local government in the city of Cork in Ireland. As a city council, it is governed by the Local Government Act 2001. Prior to the enactment of the 2001 Act, the council was known as Cork Corporation. The council is responsible for housing and community, roads and transportation, urban planning and development, amenity and culture, environment and the management of some emergency services (including Cork City Fire Brigade).[3] The council has 31 elected members. Elections are held every five years and are by single transferable vote. The head of the council has the honorific title of Lord Mayor of Cork. The city administration is headed by a Chief Executive, Ann Doherty. The council meets at City Hall, Cork.
2019 boundary change[]
The boundary of Cork City Council was extended from 31 May 2019, taking in territory formerly part of Cork County Council.[4] This implemented changes under the Local Government Act 2019.[5]
The 2015 Cork Local Government Review recommended merging Cork City Council and Cork County Council into a single "super council", within which a metropolitan district council will govern the Metropolitan Cork area; however, a minority report opposed the merger.[6][7] This was subsequently followed in 2017 by a report published by an expert advisory group recommending a city boundary extension.[8] The city boundary was to be extended to include Little Island, Cork Airport, Ballincollig, Blarney, and Carrigtwohill, adding a population of over 100,000, however the final extension will not include either Little Island or Carrigtwohill.[9] Places farther out will remain part of the county, including Cobh, Carrigaline, and Midleton, as well as Ringaskiddy, the centre of the Port of Cork.[9] The report gives parameters for compensation to be paid by the city to the county for the consequent reduction in its revenue.[10][11] The revised proposal was welcomed by Micheál Martin but criticised by some county councillors.[9] The city council voted unanimously to accept it.[12] Barry Roche of The Irish Times wrote that the Mackinnon Report "has proven almost as divisive as its predecessor", except with the city and county councils' positions reversed.[13] On 6 June 2018 Cabinet approval was given for the boundary extension, to include the surrounding areas of Cork Airport, Douglas and others.[14][15]
Local Electoral Areas[]
Cork City Council has 31 seats, which for the 2019 local elections was divided into the following five local electoral areas, defined by electoral divisions and wards.[16]
| LEA | Definition | Seats |
|---|---|---|
| Cork City North-East | The electoral divisions of Blackpool A, Blackpool B, Mayfield, Montenotte A, Montenotte B, St. Patrick's A, St. Patrick's B, St. Patrick's C, The Glen A, The Glen B, Tivoli A and Tivoli B as described in the County Borough of Cork (Wards) Regulations 1970 (S.I. No. 246 of 1970)[17] and therein referred to as a ward;
in the electoral division of St. Mary's (part); the townlands of Ballincolly, Ballincrokig and Kilbarry; and that part of the townland of Ballyvolane that is contained within the electoral division of St. Mary's (part); and those parts of the electoral divisions of Caherlag, Rathcooney (Part) and Riverstown that are contained within the City of Cork. |
6 |
| Cork City North-West |
The electoral divisions of Churchfield, Commons, Fair Hill A, Fair Hill B, Fair Hill C, Farranferris A, Farranferris B, Farranferris C, Gurranebraher A, Gurranebraher B, Gurranebraher C, Gurranebraher D, Gurranebraher E, Knocknaheeny, Shanakiel, Shandon A, Shandon B, Sundays Well A and Sundays Well B as described in the County Borough of Cork (Wards) Regulations 1970 (S.I. No. 246 of 1970) and therein referred to as a ward; in the electoral division of St. Mary's (part); the townlands of Ballycannon, Ballygrohan, Ballysheedy, Clogheen, Coolymurraghue, Killard, Killeens, Knocknacullen East, Knocknagorty, Mount Desert; and those parts of the townlands of Commons, Garranabraher and Knocknacullen West that are contained within the electoral division of St. Mary's (part); and those parts of the electoral divisions of Blarney, Carrigrohanebeg, Matehy and Whitechurch that are contained within the City of Cork. |
6 |
| Cork City South-Central |
The electoral divisions of Ballyphehane A, Ballyphehane B, Centre A, Centre B, City Hall A, Evergreen, Gillabbey A, Gillabbey B, Gillabbey C, Greenmount, Mardyke, Pouladuff A, Pouladuff B, South Gate A, South Gate B, The Lough, Togher B, Tramore A, Tramore B, Tramore C, Turners Cross A, Turners Cross B, Turners Cross C and Turners Cross D as described in the County Borough of Cork (Wards) Regulations 1970 (S.I. No. 246 of 1970) and therein referred to as a ward; in the electoral division of Lehenagh; the townlands of Ballycurreen, Curraghconway, Grange and Inchisarsfield; and in the electoral division of Douglas; the townlands of Ballinvuskig, Rathmacullig East and Rathmacullig West. |
6 |
| Cork City South-East |
The electoral divisions of Ballinlough A, Ballinlough B, Ballinlough C, Browningstown, City Hall B, Knockrea A, Knockrea B, Mahon A, Mahon B, and Mahon C as set out in the County Borough of Cork (Wards) Regulations 1970 (S.I. No. 246 of 1970) and therein referred to as a ward; in the electoral division of Douglas; the townlands of Ardarrig, Ballinimlagh Ballybrack, Castletreasure, Douglas, Grange, Hop Island, Knocknamullagh, Maryborough, Moneygurney, Monfieldstown, Mounthovel, Oldcourt, Rochestown; and that part of the townland of Ballyorban that is contained within the City of Cork; and those parts of the electoral divisions of Carrigaline (in the former rural district of Cork) and Monkstown Rural that are contained within the City of Cork. |
6 |
| Cork City South-West |
The electoral divisions of Bishopstown A, Bishopstown B, Bishopstown C, Bishopstown D, Bishopstown E, Glasheen A, Glasheen B, Glasheen C and Togher A as described in the County Borough of Cork (Wards) Regulations 1970 (S.I. No. 246 of 1970) and therein referred to as a ward; those parts of the townlands of Ballinaspig More and Inchigaggin that are contained within the electoral division of Bishopstown (part); in the electoral division of Lehenagh; the townlands of Ballyduhig North, Gortagoulane, Lehenagh Beg and Lehenagh More; and those parts of the electoral divisions of Ballincollig, Ballygarvan, Inishkenny and Ovens that are contained within the City of Cork. |
7 |
Councillors[]
The following were elected at the 2019 Cork City Council election, following the 2019 boundary extension.[18]
| Area | Seats |
|---|---|
| Cork City North East | 6 |
| Cork City North West | 6 |
| Cork City South Central | 6 |
| Cork City South East | 6 |
| Cork City South West | 7 |
2019 seats summary[]
| Party | Seats | |
|---|---|---|
| Fianna Fáil | 8 | |
| Fine Gael | 7 | |
| Green | 4 | |
| Sinn Féin | 4 | |
| Labour | 1 | |
| PBP/Solidarity | 1 | |
| Workers' Party | 1 | |
| Independent | 5 | |
Councillors by electoral area[]
This list reflects the order in which councillors were elected on 24 May 2019.[19]
| Council members from 2019 election | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Local electoral area | Name | Party | |
| Cork City North East | Kenneth Noel O'Flynn | Fianna Fáil | |
| John Daniel Maher | Labour | ||
| Ger Keohane | Independent | ||
| Joe Kavanagh | Fine Gael | ||
| Oliver Moran | Green | ||
| Ted Tynan | Workers' Party | ||
| Cork City North West | Tony Fitzgerald | Fianna Fáil | |
| Thomas Gould[b] | Sinn Féin | ||
| Kenneth Collins | Sinn Féin | ||
| Damian Boylan | Fine Gael | ||
| John Sheehan | Fianna Fáil | ||
| Fiona Ryan[c] | Solidarity–PBP | ||
| Cork South Central | Mick Finn | Independent | |
| Dan Boyle | Green | ||
| Seán Martin | Fianna Fáil | ||
| Shane O'Callaghan | Fine Gael | ||
| Fiona Kerins | Sinn Féin | ||
| Paudie Dineen | Independent | ||
| Cork South East | Des Cahill | Fine Gael | |
| Lorna Bogue[d][a] | Green | ||
| Mary Rose Desmond | Fianna Fáil | ||
| Terry Shannon | Fianna Fáil | ||
| Kieran McCarthy | Independent | ||
| Deirdre Ford | Fine Gael | ||
| Cork South West | Derry Canty | Fine Gael | |
| Fergal Dennehy | Fianna Fáil | ||
| Colette Finn | Green | ||
| Colm Kelleher | Fianna Fáil | ||
| Garret Kelleher | Fine Gael | ||
| Thomas Moloney | Independent | ||
| Henry Cremin | Sinn Féin | ||
- Notes
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lorna Bogue is a member of the unregistered An Rabharta Glas party and therefore sits as an independent on the council.
- ^ Replaced during term, see table below for details.
- ^ Solidarity–People Before Profit was renamed as People Before Profit/Solidarity in June 2021.
- ^ Changed party, see table below for details.
Co-options[]
| Party | Outgoing | Electoral area | Reason | Date | Co-optee | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sinn Féin | Thomas Gould | Cork City North West | Elected to Dáil Éireann at the 2020 general election | February 2020 | Mick Nugent | |
Changes in affiliation[]
| Name | Electoral area | Elected as | New affiliation | Date | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lorna Bogue | Cork South East | Green | Independent | October 2020 | ||
| Lorna Bogue | Cork South East | Independent | An Rabharta Glas | June 2021 | ||
References[]
- ^ statiō bene fīdā carīnīs: literally "a good trust-station for keels", adapted by inversion from Virgil's Aeneid (II, 23: statio male fida carinis, "an unsafe harbour"). Sometimes corrupted to "fide".
- ^ "Cork City Coat of Arms". Cork City Council. Archived from the original on 15 September 2015. Retrieved 21 February 2016.
- ^ "Council Services". corkcity.ie. Cork City Council. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- ^ "Local Government Act 2019 (Transfer Day) Order 2019". Irish Statute Book. 30 January 2019. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- ^ "Local Government Act 2019". Irish Statute Book. 25 January 2019. Retrieved 17 March 2019.
- ^ Cork Local Government Committee (September 2015). "Local Government Arrangements in Cork" (PDF). Department of the Environment, Community and Local Government. Retrieved 8 September 2015.
- ^ "Merger of Cork councils to be in place for 2019 elections". Evening Echo. 7 September 2015. Archived from the original on 10 October 2015. Retrieved 8 September 2015.
- ^ "Cork city to double in size taking in Ballincollig, Blarney and Carrigtwohill". 9 June 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Riegel, Ralph (9 June 2017). "How Cork's 'super council' has been dismissed - and the city is getting a border extension". Irish Independent. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ English, Eoin (9 June 2017). "Cork council merger plans to be axed but extension of city boundary recommended". Irish Examiner. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ Expert Advisory Group on Local Government Arrangements in Cork 2017, §§9.11,13.2
- ^ English, Eoin (13 June 2017). "Cork City councillors accept boundary extension findings". Irish Examiner. Retrieved 13 June 2017.
- ^ Roche, Barry (15 July 2017). "Cork City Council needs 'extended boundary' to tackle housing crisis". The Irish Times. Retrieved 16 July 2017.
- ^ "County Hall spends more than €30,000 on legal advice on boundary changes". Evening Echo. 6 June 2018.
- ^ "Boundary increase for Cork City Council approved by Cabinet". The Irish Times. 6 June 2018.
- ^ "City Of Cork Local Electoral Areas Order 2019". 31 January 2019. Retrieved 19 March 2019.
- ^ "County Borough of Cork (Wards) Regulations 1970". 22 October 1970. Retrieved 19 March 2019.
- ^ "Local Elections 2019: Results, Transfer of Votes and Statistics" (PDF). Department of Housing, Planning and Local Government. pp. 14–23. Retrieved 10 June 2020.
- ^ "2019 Local elections: Cork City Council". Local Government. Retrieved 27 May 2019.
External links[]
- City councils in the Republic of Ireland
- Politics of Cork (city)