Ennatosaurus
| Ennatosaurus Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | †Caseasauria |
| Family: | †Caseidae |
| Genus: | †Ennatosaurus Efremov, 1956 |
| Type species | |
| Ennatosaurus tecton Efremov, 1956
| |
Ennatosaurus (meaning "the 9th reptile") was a synapsid that lived in European Russia during the Wordian stage of the Permian period. It is included in the synapsid clade Caseidae in the order Pelycosauria.[1]
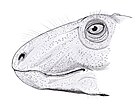
Ennatosaurus was a herbivore, and may have potentially been aquatic,[2] using its broad forefeet for paddling. Like all caseids, Ennatosaurus had a small head compared to its wide, lizard-like body. Its mouth was lined with blunt, peg-like teeth. It lived alongside other Permian creatures, such as the herbivorous Nyctiphruretus and the carnivorous Biarmosuchus.
The adult size for Ennatosaurus is unknown. Fossil remains show an animal about the size of a cat, but these are likely juvenile specimens, the adults growing to sizes that may have rivaled those of 20-foot (6.1 m)-long cousin, Cotylorhynchus.[1] Ennatosaurus is known from only one fossil site, where several juveniles were buried simultaneously in sand. One adult skull was found among the juvenile skeletons.
See also[]
References[]
- ^ "Ennatosaurus". Fossilworks.
- ^ Lambertz, M.; Shelton, C.D.; Spindler, F.; Perry, S.F. (2016). "A caseian point for the evolution of a diaphragm homologue among the earliest synapsids". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1385 (1): 3–20. doi:10.1111/nyas.13264. PMID 27859325.
https://web.archive.org/web/20080224042643/http://www.palaeos.com/Paleozoic/Permian/Wordian.htm
Lucas, Spencer G. (1998) Permian Tetrapod Biochronology, Permophiles: Newsletter of the Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy 32: 17–33
- Caseasaurs
- Prehistoric synapsid genera
- Guadalupian synapsids
- Extinct animals of Russia
- Taxa named by Ivan Yefremov
- Fossil taxa described in 1956
- Wordian genus first appearances
- Wordian genus extinctions
- Prehistoric synapsid stubs