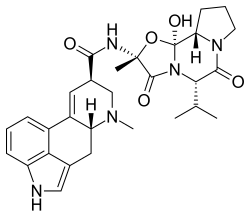
Ergovaline
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H35N5O5 |
| Molar mass | 533.629 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Ergovaline is an ergopeptine and one of the ergot alkaloids. It is usually found in endophyte-infected species of grass like Tall fescue[1] or Perennial Ryegrass.[2] It is toxic to cattle feeding on infected grass, probably because it acts as a vasoconstrictor.[1][3]
See also[]
- Neotyphodium coenophialum
References[]
- ^ a b Browning R (2003). "Tall Fescue Endophyte Toxicosis in Beef Cattle: Clinical Mode of Action and Potential Mitigation through Cattle Genetics" (PDF). Beef Improvement Federation. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - ^ Hovermale JT, Craig AM (July 2001). "Correlation of ergovaline and lolitrem B levels in endophyte-infected perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne)". Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation. 13 (4): 323–7. doi:10.1177/104063870101300407. PMID 11478604.
- ^ Schnitzius JM, Hill NS, Thompson CS, Craig AM (May 2001). "Semiquantitative determination of ergot alkaloids in seed, straw, and digesta samples using a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay". Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation. 13 (3): 230–7. doi:10.1177/104063870101300307. PMID 11482600.
External links[]
 Media related to Ergovaline at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ergovaline at Wikimedia Commons
Categories:
- Ergot alkaloids
- Oxazolopyrrolopyrazines
- Lactams
- Suspected female reproductive toxins
- Cardiovascular system drug stubs