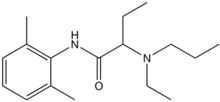
Etidocaine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Duranest |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a603026 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Parenteral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | n/a |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 2.5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.296 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H28N2O |
| Molar mass | 276.424 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Etidocaine, marketed under the trade name Duranest, is an amide-type local anesthetic given by injection during surgical procedures and labor and delivery. Etidocaine has a long duration of activity, and the main disadvantage of using during dentistry is increased bleeding during surgery.[1]
References[]
- ^ Sisk AL (1992). "Long-acting local anesthetics in dentistry". Anesthesia Progress. 39 (3): 53–60. PMC 2148750. PMID 1308373.
External links[]
- Duranest (RxList)
Categories:
- Local anesthetics
- Anilides
- Nervous system drug stubs