Fan-tailed cuckoo
| Fan-tailed cuckoo | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Cuculiformes |
| Family: | Cuculidae |
| Genus: | Cacomantis |
| Species: | C. flabelliformis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cacomantis flabelliformis Latham, 1801
| |
| |
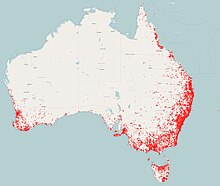
| Australian Distribution of the fan-tailed cuckoo Data from The Atlas Of Living Australia | |
The fan-tailed cuckoo (Cacomantis flabelliformis) is a species of cuckoo in the family Cuculidae. It is found in Australia, Fiji, New Caledonia, New Zealand, New Guinea, Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu.
Taxonomy[]
Six subspecies have been recognised:[2][3]
- Cacomantis flabelliformis excitus (Rothschild & Hartert, 1907)[4] – Mountains of New Guinea.
- Cacomantis flabelliformis flabelliformis (Latham, 1802)[5] – Eastern Australia from Cape York through to southern South Australia; south-western Western Australia.
- Cacomantis flabelliformis meeki (Rothschild & Hartert, 1902)[6] – Solomon Islands including Santa Isabel, Kolombangara, Guadalcanal and Bellona. Originally designated Cacomantis meeki.
- Cacomantis flabelliformis pyrrhophanus (Vieillot, 1817) – New Caledonia including the Loyalty Islands.
- Cacomantis flabelliformis schistaceigularis (Sharpe, 1900) – Vanuatu.
- Cacomantis flabelliformis simus (Peale, 1848) – Fiji.
Description[]
The fan-tailed cuckoo is about 25–27 cm (9.8–10.6 in) long. The fan-tailed cuckoo has a slate-grey head, back and wings, rufous underparts and barred black and white tail. Its eye is surrounded by a yellow orbital eye ring which helps to distinguish it from the smaller and paler brush cuckoo (C. variolosus) and the also smaller chestnut-breasted cuckoo (C. castaneiventris).[7]
Habitat[]
Its natural habitats are temperate forests, subtropical or tropical mangrove forests, subtropical or tropical moist montane forests, paddocks, orchards and gardens. The Australian range is from Cape York in Queensland following the coast south to Shark Bay in Western Australia. Along the west coast, its range extends no more than 1000 km inland. In South Australia the range is along the coast except in the south-east corner around Mount Gambier and the Eyre Peninsula. It also inhabits Tasmania.
Breeding and social habits[]
In Australia the species breeds from July to January. They only lay one mauve white with red and/or brown spotted egg in the nest of other birds (see brood parasitism) like fairywrens or thornbills. The nest preferred is usually domed in shape. Its voice is similar to descending trill with a grasshopper-like chirrip.
Diet[]
The species in Australia eats a variety of insect and their larvae, fruits and vegetables, small reptiles, mammals and birds, especially bird chicks. It perches in an exposed position to locate its prey and then pounces, catching it in the air or on the ground.[7]
Status[]
The fan-tailed cuckoo is listed by the IUCN as being of "Least Concern". No particular threats have been identified and the bird has a wide range and presumed large population and is common in much of its range. Even if the population trend is downward, this is not at such a rate as to justify putting the bird in a more threatened category.[8]
References[]
- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Cacomantis flabelliformis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22683941A93008713. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22683941A93008713.en. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- ^ "Cacomantis flabelliformis". Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Retrieved 20 September 2019.
- ^ "Fan-tailed Cuckoo (Cacomantis flabelliformis)". Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Retrieved 20 September 2019.
- ^ Rothschild, Walter; Hartert, Ernst (1907). "Notes on Papuan birds". Novitates Zoologicae. 14 (2): 433–446. doi:10.5962/bhl.part.25382.
- ^ Latham, John (1801). Index Ornithologicus (in Latin). London: Leigh & Sotheby. OCLC 643866396.
- ^ Rothschild, Walter; Hartert, Ernst (1907). "List of a collection of birds made on Ysabel Island in the Solomon group by Mr. A. S. Meek". Novitates Zoologicae. 9 (2): 581–594.
- ^ a b "Fan-tailed Cuckoo". Birds in backyards. Retrieved 2013-12-18.
- ^ "Species factsheet: Cacomantis flabelliformis". BirdLife International. Retrieved 2013-12-18.
- Field guide to the birds of Australia Graham Pizzey and Frank Knight, Angus & Robertson 1997, 3rd edition 2000. ISBN 0-207-19714-8
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Cacomantis flabelliformis. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Cacomantis flabelliformis. |
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Cacomantis
- Birds of Australia
- Birds of Melanesia
- Birds described in 1801

