Western Australia
Western Australia | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
State | |||||||||||||||||||
 Flag  Coat of arms | |||||||||||||||||||
| Nickname(s): The Wildflower State; The Golden State | |||||||||||||||||||
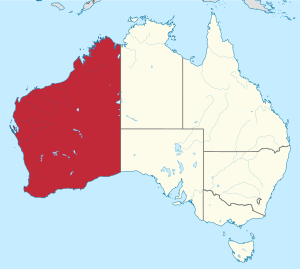 Location of Western Australia in Australia | |||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates: 26°S 121°E / 26°S 121°ECoordinates: 26°S 121°E / 26°S 121°E | |||||||||||||||||||
| Country | |||||||||||||||||||
| Established (as the Swan River Colony) | 2 May 1829 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Responsible govt. as Colony of Western Australia | 21 October 1890 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Federation | 1 January 1901 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Australia Act | 3 March 1986 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Capital | Perth | ||||||||||||||||||
| Largest city | Perth | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||||||||||
| • Type | Parliamentary constitutional monarchy | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Body | Government of Western Australia | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Governor | Kim Beazley | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Premier | Mark McGowan (ALP) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Legislature | Parliament of Western Australia
Legislative Council (36 seats) Legislative Assembly (59 seats) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Judiciary |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Federal representation | Parliament of Australia
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||||||||
| • Total | 2,642,753 km2 (1,020,373 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Land | 2,527,013 km2 (975,685 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Water | 115,740 km2 (44,690 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Area rank | 1st | ||||||||||||||||||
| Highest elevation | 1,249 m (4,098 ft) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Population (September 2020)[1] | |||||||||||||||||||
| • Total | 2,667,130 | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Rank | 4th | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Density | 1.0/km2 (2.6/sq mi) | ||||||||||||||||||
| • Density rank | 7th | ||||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Western Australian, Sandgroper (colloquial) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Time zones | UTC+08:00 (AWST) | ||||||||||||||||||
| UTC+08:45 (ACWST) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Postal code | WA | ||||||||||||||||||
| ISO 3166 code | AU-WA | ||||||||||||||||||
| GSP year | 2019–20[2] | ||||||||||||||||||
| GSP ($A million) | $292,284 (4th) | ||||||||||||||||||
| GSP per capita | $110,752 (1st) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Website | www | ||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Western Australia (abbreviated as WA) is a state occupying the western 32.9 percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories.[3] It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, and the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australia's largest state, with a total land area of 2,527,013 square kilometres (975,685 sq mi),[3] and the second-largest country subdivision in the world, surpassed only by Russia's Sakha Republic. As of 2017, the state has about 2.6 million inhabitants – around 11 percent of the national total – of whom the vast majority (92 percent) live in the south-west corner; 79 percent of the population lives in the Perth area,[4] leaving the remainder of the state sparsely populated.
The first Europeans to visit Western Australia belonged to the Dutch Dirk Hartog expedition, who visited the Western Australian coast in 1616. The first permanent European settlement of Western Australia occurred following the landing by Major Edmund Lockyer on 26 December 1826 of an expedition on behalf of the New South Wales colonial government,[5] although Wiebbe Hayes Stone Fort—the oldest surviving European building in Australia—was built 197 years prior in 1629 on West Wallabi Island in Western Australia by survivors of the Batavia shipwreck and massacre. Lockyer established a convict-supported military garrison at King George III Sound, at present-day Albany, and on 21 January 1827[5] formally took possession for the British Crown of the western part of the continent that was not already claimed by the British Crown.[6]:5 This was followed by the establishment of the Swan River Colony in 1829, including the site of the present-day capital, Perth.
York was the first inland settlement in Western Australia. Situated 97 kilometres (60 miles) east of Perth, it was settled on 16 September 1831.[7] Western Australia achieved responsible government in 1890 and federated with the other British colonies in Australia in 1901. Today, its economy mainly relies on mining, oil and gas, services and construction. The state produces 46 per cent of Australia's exports.[8] Western Australia is the largest iron ore producer in the world.[9] Its motto is "Cygnis Insignis" ("Bearing the Sign of the Swan"). Its nickname is "The Wildflower State".[10]
History[]
The first modern human inhabitants of Australia arrived from the north about 40,000 to 60,000 years ago. Over thousands of years they eventually spread across the whole landmass. These Indigenous Australians were long established throughout Western Australia by the time European explorers began to arrive in the early 17th century.
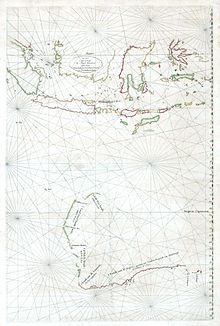
The first Europeans to visit Western Australia were those of the Dutch Dirk Hartog expedition, who on 25 October 1616 landed at what is now known as Cape Inscription, Dirk Hartog Island. For the rest of the 17th century, other Dutch and British navigators encountered the coast of what Abel Tasman named New Holland in 1644, usually unintentionally as demonstrated by the many shipwrecks along the coast of ships that deviated from the Brouwer Route (because of poor navigation and storms).[12] By the late 18th century, British and French sailors had begun to explore the Western Australian coast. The Baudin expedition of 1800–03 included the coast of Western Australia, and resulted in the Freycinet Map of 1811, the first published map featuring the full outline of Australia. The name New Holland remained in popular and semi-official use until at least the mid-1850s; that is, it was in use for about 206 years in comparison to the name Australia which to date has been in use for about 192 years.[13]:11
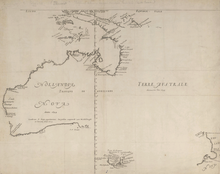
The origins of the present state began with the establishment by Lockyer[5] of a convict-supported settlement from New South Wales at King George III Sound. The settlement was formally annexed on 21 January 1827 by Lockyer when he commanded the Union Jack be raised and a feu de joie fired by the troops. The settlement was founded in response to British concerns about the possibility of a French colony being established on the coast of Western Australia.[5] On 7 March 1831 it was transferred to the control of the Swan River Colony,[7] and named Albany in 1832.
In 1829 the Swan River Colony was established on the Swan River by Captain James Stirling. By 1832, the British settler population of the colony had reached around 1,500, and the official name of the colony was changed to Western Australia on 6 February that year.[16][17] The two separate townsites of the colony developed slowly into the port city of Fremantle and the state's capital, Perth. York was the first inland settlement in Western Australia, situated 97 kilometres (60 mi) east of Perth and settled on 16 September 1831. York was the staging point for early explorers who discovered the rich gold reserves of Kalgoorlie.
Population growth was very slow until significant discoveries of gold were made in the 1890s around Kalgoorlie.

In 1887, a new constitution was drafted, providing for the right of self-governance of European Australians and in 1890, the act granting self-government to the colony was passed by the British Parliament. John Forrest became the first Premier of Western Australia.
In 1896, the Western Australian Parliament authorised the raising of a loan to construct a pipeline to transport 23 megalitres (5 million imperial gallons) of water per day to the Goldfields of Western Australia. The pipeline, known as the Goldfields Water Supply Scheme, was completed in 1903. C. Y. O'Connor, Western Australia's first engineer-in-chief, designed and oversaw the construction of the pipeline. It carries water 530 km (330 mi) from Perth to Kalgoorlie, and is attributed by historians as an important factor driving the state's population and economic growth.[18]
Following a campaign led by Forrest, residents of the colony of Western Australia (still informally called the Swan River Colony) voted in favour of federation, resulting in Western Australia officially becoming a state on 1 January 1901.
Geography[]
Western Australia is bounded to the east by longitude 129°E, the meridian 129 degrees east of Greenwich, which defines the border with South Australia and the Northern Territory, and bounded by the Indian Ocean to the west and north. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) designates the body of water south of the continent as part of the Indian Ocean; in Australia it is officially gazetted as the Southern Ocean.[b][19][20]
The total length of the state's eastern border is 1,862 km (1,157 mi).[21] There are 20,781 km (12,913 mi) of coastline, including 7,892 km (4,904 mi) of island coastline.[22] The total land area occupied by the state is 2.5 million km2 (970 thousand sq mi).[23]
Geology[]
The bulk of Western Australia consists of the extremely old Yilgarn craton and Pilbara craton which merged with the Deccan Plateau of India, Madagascar and the Kaapvaal and Zimbabwe cratons of Southern Africa, in the Archean Eon to form Ur, one of the oldest supercontinents on Earth (3 – 3.2 billion years ago). In May 2017, evidence of the earliest known life on land may have been found in 3.48-billion-year-old geyserite and other related mineral deposits (often found around hot springs and geysers) uncovered in the Pilbara craton.[24][25]
Because the only mountain-building since then has been of the Stirling Range with the rifting from Antarctica, the land is extremely eroded and ancient, with no part of the state above 1,245 metres (4,085 ft) AHD (at Mount Meharry in the Hamersley Range of the Pilbara region). Most of the state is a low plateau with an average elevation of about 400 metres (1,200 ft), very low relief, and no surface runoff. This descends relatively sharply to the coastal plains, in some cases forming a sharp escarpment (as with the Darling Range/Darling Scarp near Perth).
The extreme age of the landscape has meant that the soils are remarkably infertile and frequently laterised. Even soils derived from granitic bedrock contain an order of magnitude less available phosphorus and only half as much nitrogen as soils in comparable climates in other continents. Soils derived from extensive sandplains or ironstone are even less fertile, nearly devoid of soluble phosphate and deficient in zinc, copper, molybdenum and sometimes potassium and calcium.
The infertility of most of the soils has required heavy application by farmers of fertilisers. These have resulted in damage to invertebrate and bacterial populations.[citation needed] The grazing and use of hoofed mammals and, later, heavy machinery through the years have resulted in compaction of soils and great damage to the fragile soils.
Large-scale land clearing for agriculture has damaged habitats for native flora and fauna. As a result, the South West region of the state has a higher concentration of rare, threatened or endangered flora and fauna than many areas of Australia, making it one of the world's biodiversity "hot spots". Large areas of the state's wheatbelt region have problems with dryland salinity and the loss of fresh water.
Climate[]

The southwest coastal area has a Mediterranean climate. It was originally heavily forested, including large stands of karri, one of the tallest trees in the world.[26] This agricultural region is one of the nine most bio-diverse terrestrial habitats, with a higher proportion of endemic species than most other equivalent regions. Thanks to the offshore Leeuwin Current, the area is one of the top six regions for marine biodiversity and contains the most southerly coral reefs in the world.
Average annual rainfall varies from 300 millimetres (12 in) at the edge of the Wheatbelt region to 1,400 millimetres (55 in) in the wettest areas near Northcliffe, but from November to March, evaporation exceeds rainfall, and it is generally very dry. Plants are adapted to this as well as the extreme poverty of all soils.
The central two-thirds of the state is arid and sparsely inhabited. The only significant economic activity is mining. Annual rainfall averages less than 300 millimetres (8–10 in), most of which occurs in sporadic torrential falls related to cyclone events in summer.[27]
An exception to this is the northern tropical regions. The Kimberley has an extremely hot monsoonal climate with average annual rainfall ranging from 500 to 1,500 millimetres (20–60 in), but there is a very long almost rainless season from April to November. Eighty-five percent of the state's runoff occurs in the Kimberley, but because it occurs in violent floods and because of the insurmountable poverty of the generally shallow soils, the only development has taken place along the Ord River.
Snow is rare in the state and typically occurs only in the Stirling Range near Albany, as it is the only mountain range far enough south and sufficiently elevated. More rarely, snow can fall on the nearby Porongurup Range. Snow outside these areas is a major event; it usually occurs in hilly areas of southwestern Australia. The most widespread low-level snow occurred on 26 June 1956 when snow was reported in the Perth Hills, as far north as Wongan Hills and as far east as Salmon Gums. However, even in the Stirling Range, snowfalls rarely exceed 5 cm (2 in) and rarely settle for more than one day.[28]
The highest observed maximum temperature of 50.5 °C (122.9 °F) was recorded at Mardie Station on 19 February 1998. The lowest minimum temperature recorded was −7.2 °C (19.0 °F) at Eyre Bird Observatory on 17 August 2008.[29]
| hideClimate data for Western Australia | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 49.8 (121.6) |
50.5 (122.9) |
48.1 (118.6) |
45.0 (113.0) |
40.6 (105.1) |
37.8 (100.0) |
38.3 (100.9) |
41.2 (106.2) |
43.1 (109.6) |
46.9 (116.4) |
48.0 (118.4) |
49.8 (121.6) |
50.5 (122.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 0.9 (33.6) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−6.7 (19.9) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−5.1 (22.8) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
| Source: Bureau of Meteorology[30] | |||||||||||||
Flora and fauna[]


Western Australia is home to around 540 species of birds (depending on the taxonomy used). Of these around 15 are endemic to the state. The best areas for birds are the southwestern corner of the state and the area around Broome and the Kimberley.
The Flora of Western Australia comprises 10,162 published native vascular plant species, along with a further 1,196 species currently recognised but unpublished. They occur within 1,543 genera from 211 families; there are also 1,276 naturalised alien or invasive plant species, more commonly known as weeds.[31][32] In the southwest region are some of the largest numbers of plant species for its area in the world. Western Australia's ecoregions include the sandstone gorges of The Kimberley on the northern coast, and below that the drier Victoria Plains tropical savanna inland, and the semi-desert Pilbara shrublands, Carnarvon xeric shrublands, and Western Australian mulga shrublands to the southwest. Southwards along the coast are the Southwest Australia savanna and the Swan Coastal Plain around Perth, with the Jarrah-Karri forest and shrublands on the southwest corner of the coast around the Margaret River wine-growing area. Going east along the Southern Ocean coast is the Goldfields-Esperance region, including the Esperance mallee and the Coolgardie woodlands inland around town of Coolgardie. Deserts occupy the interior, including the Great Sandy-Tanami desert, Gibson Desert, Great Victoria Desert, and Nullarbor Plain.
In 1831 Scottish botanist Robert Brown produced a scientific paper, General view of the botany of the vicinity of Swan River. It discusses the vegetation of the Swan River Colony.[33]
Demographics[]


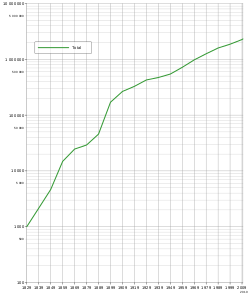

Europeans began to settle permanently in 1826 when Albany was claimed by Britain to forestall French claims to the western third of the continent. Perth was founded as the Swan River Colony in 1829 by British and Irish settlers, though the outpost languished. Its officials eventually requested convict labour to augment its population. In the 1890s, interstate immigration, resulting from a mining boom in the Goldfields region, resulted in a sharp population increase.
Western Australia did not receive significant flows of immigrants from Britain, Ireland or elsewhere in the British Empire until the early 20th century. At that time, its local projects—such as the Group Settlement Scheme of the 1920s, which encouraged farmers to settle the southwest—increased awareness of Australia's western third as a destination for colonists.
Led by immigrants from the British Isles, Western Australia's population developed at a faster rate during the twentieth century than it had previously. After World War II, both the eastern states and Western Australia received large numbers of Italians, Croatians and Macedonians. Despite this, Britain has contributed the greatest number of immigrants to this day. Western Australia—particularly Perth—has the highest proportion of British-born of any state: 10.3% in 2011, compared to a national average of 5.1%. This group is heavily concentrated in certain parts, where they account for a quarter of the population.[34]
Perth's metropolitan area (including Mandurah) had an estimated population of 2,043,138[4] in June 2017 (79% of the state). Other significant population centres include Bunbury (73,989),[35] Geraldton (37,961),[35] Kalgoorlie-Boulder (30,420),[35] Albany (33,998),[35] Karratha (16,446),[35] Broome (14,501)[35] and Port Hedland (14,285).[35]
Ancestry and immigration[]
| Birthplace[N 1] | Population |
|---|---|
| Australia | 1,492,842 |
| England | 194,163 |
| New Zealand | 79,221 |
| India | 49,385 |
| South Africa | 41,008 |
| Philippines | 30,835 |
| Malaysia | 29,126 |
| Mainland China | 27,126 |
| Scotland | 26,063 |
| Italy | 19,210 |
At the 2016 census, the most commonly nominated ancestries were:[N 2][36][37]
- English (40.7%)
- Australian (33.2%)[N 3]
- Irish (9.8%)
- Scottish (9.4%)
- Italian (5.4%)
- Chinese (4.5%)
- German (3.2%)
- Indigenous (3.1%)[N 4]
- Indian (3%)
- Dutch (2.1%)
- Filipino (1.6%)
- New Zealander (1.4%)
- South African (1.3%)
- Maori (1.2%)
3.1% of the population, or 75,978 people, identified as Indigenous Australians (Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islanders) in 2016.[N 5][36][37]
Language[]
At the 2016 census, 75.2% of inhabitants spoke only English at home, with the next most common languages being Mandarin (1.9%), Italian (1.2%), Vietnamese (0.8%), Cantonese (0.8%) and Tagalog (0.6%).[36][37]
Religion[]
At the 2016 census, 55.5% of respondents identified as Christian and 32.5% as having no religion. 10.3% chose not to state a religion. The most commonly nominated responses were Catholicism (21.4%) and Anglicanism (14.3%).[39][37]
Economy[]

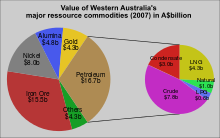
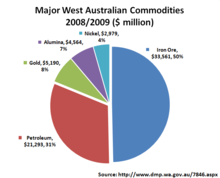
Western Australia's economy is largely driven by extraction and processing of a diverse range of mineral and petroleum commodities. The structure of the economy is closely linked to these natural resources, providing a comparative advantage in resource extraction and processing. As a consequence:
- Western Australia contributes an estimated 58% of Australia's Mineral and Energy Exports,[40] potentially earning up to 4.64% of Australia's total GDP.[41]
- Gross state product per person ($97,940 in 2017–18) is higher than any other state and well above the national average ($73,267).[42]
- Diversification (i.e. a greater range of commodities) over the past 15 years has provided a more balanced production base and less reliance on just a few major export markets, insulating the economy from fluctuations in world prices to some extent.[citation needed]
- Finance, insurance and property services and construction have grown steadily and have increased their share of economic output.[43]
- Recent growth in global demand for minerals and petroleum, especially in China (iron-ore) and Japan (for LNG), has ensured economic growth above the national average.
In 2019 Western Australia's overseas exports accounted for 46% of the nation's total.[8][44] The state's major export commodities included iron-ore, petroleum, gold, alumina, nickel, wheat, copper, lithium, chemicals and mineral sands.[45]
Western Australia is the world's largest iron-ore producer (32% of the world's total), and extracts 67% (6% of world production) of Australia's 324 tonnes of gold. It is a major world producer of bauxite, which is processed into alumina at four refineries providing 11% of total world production. Diamonds are extracted at the world's largest diamond mine in the far north Kimberley region. Coal mined at Collie is the main fuel for baseload electricity generation in the state's south-west.[45][46]
Agricultural production in WA is a major contributor to the state and national economy. Although tending to be highly seasonal, in the period 2010–2019 wheat production in WA has averaged nearly 10 million tonnes ($2.816 billion in 2019), accounting for half the nation's total and providing $2–3 billion in export income.[47][48]
Other significant farm output includes wool, beef, lamb, barley, canola, lupins, oats and pulses.[47] There is a high level of overseas demand for live animals from WA, driven mainly by southeast Asia's feedlots and Middle Eastern countries, where Islamic dietary laws and a lack of storage and refrigeration facilities favour live animals over imports of processed meat. About half of Australia's live cattle exports come from Western Australia.[49]
Resource sector growth in recent years has resulted in significant labour and skills shortages, leading to recent efforts by the state government to encourage interstate and overseas immigration.[50] According to the 2006 census,[51] the median individual income was A$500 per week in Western Australia (compared to A$466 in Australia as a whole). The median family income was A$1246 per week (compared to A$1171 for Australia). Recent growth has also contributed to significant rises in average property values in 2006, although values plateaued in 2007. Perth property prices are still the second highest in Australia behind Sydney, and high rental prices continue to be a problem.
Located south of Perth, the heavy industrial area of Kwinana has the nation's largest oil refinery with a capacity of 146,000 barrels of oil per day, producing most of the state's petrol and diesel.[52][53][54] Kwinana also hosts alumina and nickel processing plants, port facilities for grain and other bulk exports, and support industries for mining and petroleum such as heavy and light engineering, and metal fabrication. Shipbuilding (e.g. Austal Ships) and associated support industries are found at nearby Henderson, just north of Kwinana. Significant secondary industries include cement and building product manufacturing, flour milling, food processing, animal feed production, automotive body building and printing.
Western Australia has a significant fishing industry. Products for local consumption and export include western rock lobsters, prawns, crabs, shark and tuna, as well as pearl fishing in the Kimberley region of the state. Processing is conducted along the west coast. Whaling was a key marine industry but ceased at Albany in 1978.
Western Australia has the world's biggest plantations of both Indian sandalwood (northern WA)[55] and Australian sandalwood (semi-arid regions), which are used to produce sandalwood oil and incense.[56] The WA sandalwood industry provides about 40 per cent of the international sandalwood oil market.[57]
Tourism[]
In recent years, tourism has grown in importance, with significant numbers of visitors to the state coming from the UK and Ireland (28%), other European countries (14%) Singapore (16%), Japan (10%) and Malaysia (8%).[48] Revenue from tourism is a strong economic driver in many of the smaller population centres outside of Perth, especially in coastal locations.
Tourism forms a major part of the Western Australian economy with 833,100 international visitors making up 12.8% of the total international tourism to Australia in the year ending March 2015. The top three source markets include the United Kingdom (17%), Singapore (10%) and New Zealand (10%) with the majority of purpose for visitation being holiday/vacation reasons.[58] The tourism industry contributes $9.3 billion to the Western Australian economy and supports 94,000 jobs within the state. Both directly and indirectly, the industry makes up 3.2% of the state's economy whilst comparatively, WA's largest revenue source, the mining sector, brings in 31%.[59]
Tourism WA is the government agency responsible for promoting Western Australia as a holiday destination.[60]
Government[]
Western Australia was granted self-government in 1890[61] with a bicameral Parliament located in Perth, consisting of the Legislative Assembly (or lower house), which has 59 members; and the Legislative Council (or upper house), which has 36 members. Suffrage is universal and compulsory for citizens over 18 years of age.
With the federation of the Australian colonies in 1901, Western Australia became a state within Australia's federal structure; this involved ceding certain powers to the Commonwealth (or Federal) government in accordance with the Constitution; all powers not specifically granted to the Commonwealth remained solely with the State. However over time the Commonwealth has effectively expanded its powers through broad interpretation of its enumerated powers and increasing control of taxation and financial distribution (see Federalism in Australia).
Whilst the sovereign of Western Australia is the Queen of Australia (Elizabeth II) and executive power is nominally vested in her state representative, the Governor (currently Kim Beazley), executive power rests with the premier and ministers drawn from the party or coalition of parties holding a majority of seats in the Legislative Assembly. Mark McGowan is the premier, having defeated Colin Barnett at the state election on 11 March 2017 and retained power at the 2021 election.
Secession[]

Secessionism has been a recurring feature of Western Australia's political landscape since shortly after European settlement in 1826. Western Australia was the most reluctant participant in the Commonwealth of Australia.[62] Western Australia did not participate in the earliest federation conference. Longer-term residents of Western Australia were generally opposed to federation; however, the discovery of gold brought many immigrants from other parts of Australia. It was these residents, primarily in Kalgoorlie but also in Albany who voted to join the Commonwealth, and the proposal of these areas being admitted separately under the name Auralia was considered.[citation needed]
In a referendum in April 1933, 68% of voters voted for the state to leave the Commonwealth of Australia with the aim of returning to the British Empire as an autonomous territory. The State Government sent a delegation to Westminster, but the British Government ruled the referendum invalid and therefore no action was taken.[63]
Local government[]
Western Australia is divided into 139 Local Government Areas, including Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands. Their mandate and operations are governed by the Local Government Act 1995.[64]
Education[]
Education in Western Australia consists of one year of pre-school at age 4 or 5, followed by six years of primary education for all students as of 2015.[65] At age 12 or 13, students begin six years of secondary education. Students are required to attend school up until they are 16 years old. Sixteen and 17 year olds are required to be enrolled in school or a training organisation, be employed or be in a combination of school/training/employment.[66] Students have the option to study at a TAFE college after Year 10,[67] or continue through to Year 12 with vocational courses or a university entrance courses.[68]
There are five universities in Western Australia. They consist of four Perth-based public universities; the University of Western Australia, Curtin University, Edith Cowan University and Murdoch University; and one Fremantle-based private Roman Catholic university, the University of Notre Dame Australia. The University of Notre Dame is also one of only two private universities in Australia, along with Bond University, a not-for-profit private education provider based in Gold Coast, Queensland.
Media[]
Print[]
Western Australia has two daily newspapers: the Seven West Media-owned tabloid The West Australian and The Kalgoorlie Miner. Also published is one weekend paper, The Weekend West, and one Sunday tabloid newspaper, which is also owned by Seven West Media after purchase from News Corporation's The Sunday Times. There are also 17 weekly Community Newspapers with distribution from Yanchep in the north to Mandurah in the south. There are two major weekly rural papers in the state, Countryman and the Rural Press-owned Farm Weekly. The interstate broadsheet publication The Australian is also available, although with sales per capita lagging far behind those in other states.
Television[]

Metropolitan Perth has six broadcast television stations;
- ABC TV WA. (Callsign: ABW – Channel 12 Digital)
- SBS WA (Callsign: SBS – Channel 29 Digital)
- Seven Network Perth. (Callsign: TVW – Channel 6 Digital)
- Nine Network Perth. (Callsign: STW – Channel 8 Digital)
- Network Ten Perth. (Callsign: NEW – Channel 11 Digital)
- West TV. A free-to-air community television channel that began broadcasting in April 2010. It replaced Access 31, which ceased broadcasting in August 2008.
Regional WA has a similar availability of stations, with the exception of West TV. Geographically, it is one of the largest television markets in the world, including almost one-third of the continent.
- Golden West Network (GWN7). Affiliated with Seven. (Callsigns: SSW South West, VEW Goldfields/Esperance, GTW Central West, WAW remote areas)
- WIN Television WA. Affiliated with Ten (Callsign: WOW)
- West Digital Television. Affiliated with Nine. (Callsigns: SDW South West, VDW Goldfields/Esperance, GDW Central West, WDW remote areas)
- Westlink. An open-narrowcast community-based television channel. (Satellite only)
In addition, broadcasters operate digital multichannels:
- ABC HD (Carried by ABW)
- ABC2 (Carried by ABW)
- ABC Me (Carried by ABW)
- ABC News (Carried by ABW)
- SBS HD (Carried by SBS)
- SBS Viceland (Carried by SBS)
- Food Network (Carried by SBS)
- NITV (Carried by SBS)
- 7HD (Carried by TVW)
- 7TWO (Carried by TVW and affiliates)
- 7mate (Carried by TVW and affiliates)
- 7flix (Carried by TVW)
- Racing.com (Carried by TVW and affiliates)
- 9HD (Carried by STW)
- 9Gem (Carried by STW and affiliates)
- 9Go! (Carried by STW and affiliates)
- 9Life (Carried by STW)
- Extra (Australian TV channel) (Carried by STW)
- One (Carried by NEW and affiliate)
- 10 Peach (Carried by NEW and affiliate)
- Ten HD (Carried by NEW and affiliate)
- TVSN (Carried by NEW and affiliate)
- Spree TV (Carried by NEW)
Pay TV services are provided by Foxtel, which acquired many of the assets and all the remaining subscribers of the insolvent Galaxy Television satellite service in 1998. Some metropolitan suburbs are serviced by Pay TV via cable; however, most of the metropolitan and rural areas can only access Pay TV via satellite.
Radio[]
Perth has many radio stations on both AM and FM frequencies. ABC stations include ABC NewsRadio (6PB 585 am), 720 ABC Perth (6WF 720 am), ABC Radio National (6RN 810 am), ABC Classic FM (6ABC 97.7FM) and Triple J (6JJJ 99.3FM). The six commercial stations are: FM 92.9 (6PPM), Nova 93.7 (6PER), Mix 94.5 (6MIX), 96fm (6NOW), and AM 882 (6PR), AM 1080 (6IX) and AM 1116 ()
The leading community radio stations are Curtin FM 100.1, 6RTR FM 92.1, Sonshine FM 98.5 (6SON) and 91.3 SportFM (6WSM).
Culture[]
Arts and entertainment[]
Western Australia is home to one of the country's leading performance training institutions, the acclaimed Western Australian Academy of Performing Arts (WAAPA), as well as a burgeoning theatrical and musical scene. Notable musicians and bands to have been born in or lived in Western Australia include Adam Brand, Ammonia, Karnivool, Birds of Tokyo, Bon Scott, Eskimo Joe, Johnny Young, Gyroscope, the John Butler Trio, Tame Impala, Kevin Mitchell, Tim Minchin, Troye Sivan, The Kill Devil Hills, Pendulum, The Pigram Brothers, Rolf Harris, Stella Donnelly and The Triffids. The West Australian Music Industry Awards (WAMis) have been awarded every year to the leading musicians and performers in WA since 2001.
Notable actors and television personalities from Western Australia include Heath Ledger, Sam Worthington, Ernie Dingo, Jessica Marais, Megan Gale, Rove McManus, Isla Fisher, and Melissa George. Films and television series filmed or partly filmed in Western Australia include Rabbit-Proof Fence, The Heights, Mystery Road, These Final Hours, Cloudstreet, Jasper Jones, Australia, Bran Nu Dae, Red Dog, ABBA: the Movie and Last Train to Freo.
Noted Western Australian Indigenous painters and artisans include Jack Dale Mengenen, Paddy Bedford, Queenie McKenzie, and siblings Nyuju Stumpy Brown and Rover Thomas.[69]
The West Australian Symphony Orchestra (WASO) is based at the Perth Concert Hall. Other concert, performance and indoor sporting venues in Western Australia include His Majesty's Theatre, the State Theatre Centre of Western Australia, the Crown Theatre and Perth Arena, which opened in 2012.
Western Australia has served as the setting for a number of works of Australian literature. Prominent authors include Katharine Susannah Prichard, Randolph Stow, Tim Winton, Kim Scott, Sally Morgan, Joan London, Mary Durack and Craig Silvey.
Sport[]

A number of national or international sporting teams and events are based in the state, including:
- Australian rules football: The West Coast Eagles and the Fremantle Dockers compete in the Australian Football League (AFL). The Fremantle Dockers also have a women's team of the same name playing in the AFL Women's league, founded in September 2016. The West Coast Eagles also received an AFLW team in 2020. The West Australian Football League (WAFL) is the main local football competition, but other local and amateur football leagues exist across the state.
- Baseball: The Perth Heat compete in the Australian Baseball League.
- Basketball: The Perth Wildcats (men) and Perth Lynx (women) compete in the National Basketball League and Women's National Basketball League, respectively.
- Cricket: Western Australia represent the state in first-class and List A domestic cricket, with the Perth Scorchers competing in the Twenty20 Big Bash League.
- Field hockey: The Thundersticks (men) and Diamonds (women) compete in the Australian Hockey League.
- Netball: The West Coast Fever compete in the ANZ Championship.
- Rugby league: The West Coast Pirates compete in the S. G. Ball Cup.
- Rugby union: The Western Force competes in the National Rugby Championship.
- Soccer: Perth Glory field men's and women's teams in the A-League and W-League, respectively.
- Tennis: The ITF Hopman Cup, an annual international team indoor hardcourt tennis tournament.
- Water Polo: The UWA Torpedoes water polo club competes in the National Water Polo League (NWPL).
International sporting events hosted in the past in Western Australia include the Tom Hoad Cup (water polo), the Perth International (golf), the 2006 Gravity Games (extreme sports), the 2002 Women's Hockey World Cup, the 1991 FINA World Aquatics Championships, the World Rally Championships and the 1962 British Empire and Commonwealth Games.
Wine[]
Winemaking regions are concentrated in the cooler climate of the south-western portion of the state. Western Australia produces less than 5% of the country's wine output, but in quality terms is considered to be very much near the top.[70][71][72][73] Major wine producing regions include: Margaret River, The Great Southern, Swan Valley as well as smaller districts including Blackwood Valley, Manjimup, Pemberton, Peel, Chittering Valley, Perth Hills, and Geographe.[74]
Sister states[]
Western Australia has four sister states:[75]
- East Java, Indonesia
- Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan
- Tuscany Region, Italy
- Zhejiang Province, China
In 1981, a sister state agreement was drawn up between Western Australia and Hyōgo Prefecture in Japan that was aimed at improving cultural ties between the two states.[76][77] To commemorate the 10th anniversary of this agreement, the Hyōgo Prefectural Government Cultural Centre was established in Perth in 1992.[78] Prior to that, the Western Australian government opened an office in Kobe, the largest city in Hyōgo, to facilitate maintenance of the relationship in 1989.[77][79]
Following the Great Hanshin earthquake that devastated southern Hyōgo in January 1995, Western Australian groups and businesses raised funds and provided materials, whilst individuals travelled to Hyōgo to help with emergency relief and the subsequent reconstruction process.[80][81][82] The two governments signed a memorandum of understanding on the 20th anniversary in 2001 that aimed to improve the economic relationship between the two states.[77]
Further to the sister state relationship, the City of Rockingham in Western Australia and the City of Akō in Hyōgo signed a sister city agreement in 1997. It is one of nine sister city relationships between Western Australian and Japanese cities.[83]
See also[]
- Outline of Australia
- Index of Australia-related articles
- Government of Western Australia
- Mining in Western Australia
- Petroleum in Western Australia
- Western Australian shark cull
Lists[]
- List of Western Australian towns
- List of statues in Western Australia
- Local Government Areas of Western Australia
Notes[]
- ^ In accordance with the Australian Bureau of Statistics source, England, Scotland, Mainland China and the Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and Macau are listed separately
- ^ As a percentage of 2,286,107 persons who nominated their ancestry at the 2016 census.
- ^ The Australian Bureau of Statistics has stated that most who nominate "Australian" as their ancestry are part of the Anglo-Celtic group.[38]
- ^ Of any ancestry. Includes those identifying as Aboriginal Australians or Torres Strait Islanders. Indigenous identification is separate to the ancestry question on the Australian Census and persons identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander may identify any ancestry.
- ^ Of any ancestry. Includes those identifying as Aboriginal Australians or Torres Strait Islanders. Indigenous identification is separate to the ancestry question on the Australian Census and persons identifying as Aboriginal or Torres Strait Islander may identify any ancestry.

a "West Australia" and its related demonym "West Australian" are occasionally used, including in the names of the main daily newspaper, The West Australian, and the state-based West Australian Football League, but are rarely used in an official sense. The terms "Westralia" and "Westralian" were regularly used in the 19th and 20th century.[84][85] The terms are still found in the names of certain companies and buildings, e.g. Westralia House in Perth and Westralia Airports Corporation, which operates Perth Airport, as well as in the names of several ships.[86][87]
b In Australia, the body of water south of the continent is officially gazetted as the Southern Ocean, whereas the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) designates it as part of the Indian Ocean.[88][89]
References[]
- ^ "National, state and territory population – September 2020". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 18 March 2021. Retrieved 18 March 2021.
- ^ "Western Australian Economic Notes - Gross State Product - 2019-20" (PDF). Retrieved 19 January 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Area of Australia - States and Territories". Geoscience Australia. Geoscience Australia, Commonwealth of Australia. 15 May 2014. Archived from the original on 26 July 2020. Retrieved 2 August 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "3218.0 – Regional Population Growth, Australia, 2016–17: Main Features". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 24 April 2018. Retrieved 13 October 2018. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "King George's Sound Settlement". State Records Authority of New South Wales. Retrieved 30 August 2016.
- ^ Reid, Dorothy V. (August 2008). French Exploration and Intentions with Regard to the West Coast of Australia 1772–1829 (PDF) (MSSc thesis). Bentley, Western Australia: Department of Social Sciences, Curtin University of Technology. Retrieved 28 April 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Knibbs, G.H. (1911). "The Creation of the Several Colonies". Official Year Book of the Commonwealth of Australia. 4. Melbourne: Commonwealth Bureau of Census and Statistics. p. 16.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Curran, Enda (21 February 2012). "Western Australia Plans Sovereign Wealth Fund". The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 15 March 2012.
- ^ "US Geological Survey" (PDF). Minerals.usgs.gov. 2014. Retrieved 11 June 2016.
- ^ Thomas, Abbie (2 August 2002). "Western Australian wildflowers bloom". www.abc.net.au. Retrieved 3 November 2020.
- ^ Gerritsz, Hessel (1618–1638). "Chart of the Malay Archipelago and the Dutch discoveries in Australia". Octroy Vande H.M. Heeren de Staten Generael der Vereenichde Neerlanden. The discoveries after 1618 were added to the engraved plate between 1628 and 1632. Amsterdam: Hessel Gerritsz. Retrieved 3 August 2020 – via Trove.
- ^ Green, J.N. (1977). "Australia's oldest wreck: The Loss of the Trial, 1622" (PDF). British Archaeological Reports, Supplementary Series. Oxford. 27.
- ^ W. M. Bartlett (1979). Western Australian Year Book (PDF). Western Australian Office: Australian Bureau of Statistics. ISSN 0083-8772. OCLC 223554105. Retrieved 13 September 2020.
- ^ Thévenot, Melchisédech (1664). Relations de divers voyages curieux (in French). Paris: Iacques Langlois. OCLC 1052538974. Retrieved 6 August 2020.
- ^ Blaeu, Johannes Willemszoon (1659). "Archipelagus Orientalis sive Asiaticus (Karte 27)" [Archipelago Eastern or Asiatic (Map 27)]. Atlas des Großen Kurfürsten [Atlas of the Great Elector]. Amsterdam. Archived from the original on 4 August 2020. Retrieved 5 August 2020 – via Berlin State Library (German: Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin).
- ^ "Swan River Colony Proclaimed". POI Australia. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ "On this day, 6th February 1832". State Library of New South Wales. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ^ Tauman, Merab Harris (1988). O'Connor, Charles Yelverton (1843–1902). MUP. pp. 51–54. Retrieved 12 July 2008.
- ^ "Limits of Oceans and Seas (Special Publication No 23)" (PDF). International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 October 2009. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ "Canberra all at sea over position of Southern Ocean". The Age. 22 December 2003. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ "State And Territory Borders". Geoscience Australia. 11 September 2007. Archived from the original on 28 November 2007. Retrieved 25 September 2008.
- ^ "Coastline Lengths". Geoscience Australia. 18 November 2010. Archived from the original on 22 January 2011. Retrieved 21 January 2011.
- ^ "Area of States and Territories". Geoscience Australia. 31 August 2005. Archived from the original on 30 July 2008. Retrieved 25 September 2008.
- ^ "Oldest evidence of life on land found in 3.48-billion-year-old Australian rocks". Phys.org. 9 May 2017. Retrieved 13 May 2017.
- ^ Djokic, Tara; Van Kranendonk, Martin J.; Campbell, Kathleen A.; Walter, Malcolm R.; Ward, Colin R. (9 May 2017). "Earliest signs of life on land preserved in ca. 3.5 Ga hot spring deposits". Nature Communications. 8: 15263. Bibcode:2017NatCo...815263D. doi:10.1038/ncomms15263. PMC 5436104. PMID 28486437.
- ^ "Climate of Western Australia". Bureau of Meteorology. Archived from the original on 17 March 2009. Retrieved 6 December 2009.[dead link]
- ^ "Average annual, seasonal and monthly rainfall". Commonwealth of Australia, Bureau of Meteorology. 26 October 2011. Retrieved 1 June 2014.
- ^ Snow in Western Australia: About Snow in WA Archived 11 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 4 February 2007.
- ^ "Rainfall and Temperature Records: National" (PDF). Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 14 November 2009.
- ^ "Australian Daily Extremes Table". Bureau of Meteorology. Retrieved 25 November 2020.
- ^ "2016 Vascular Flora Statistics". Flora Base. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- ^ "New linear systematic sequence for vascular plants". Flora Base. Archived from the original on 15 February 2017. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- ^ Diels, Ludwig; Carr, D. J. (translator) (1981). "Extra-tropical Western Australia". In Carr, D. J.; Carr, S. G. M. (ed.). People and plants in Australia. Academic Press Australia. pp. 47–78. ISBN 978-0-12-160720-3.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ "Country of Birth" (xls). Australian Bureau of Statistics. 1 October 2014. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g "3218.0 – Regional Population Growth, Australia, 2016–17: Population Estimates by Significant Urban Area, 2007 to 2017". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 24 April 2018. Retrieved 12 October 2018. Estimated resident population, 30 June 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "2016 Census Community Profiles: Western Australia". quickstats.censusdata.abs.gov.au.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "2016 - Census Output". www.censusdata.abs.gov.au/.
- ^ Statistics, c=AU; o=Commonwealth of Australia; ou=Australian Bureau of (January 1995). "Feature Article - Ethnic and Cultural Diversity in Australia (Feature Article)". www.abs.gov.au.
- ^ Australian Bureau of Statistics (27 June 2017). "Western Australia". 2016 Census QuickStats. Retrieved 26 June 2019.

- ^ "Department of Mines and Petroleum". WA Department of Mines and Petroleum. 9 November 2011. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- ^ "Australian Bureau of Statistics". WA Australian Bureau of Statistics. 9 November 2011. Retrieved 9 November 2011.
- ^ "Australian National Accounts: State Accounts, 2017–18". Australian Bureau of Statistics. 16 November 2018. Retrieved 19 April 2019.
- ^ "Structure of the WA Economy" (PDF). WA Department of Treasury and Finance. 24 January 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 October 2008. Retrieved 10 September 2008.[full citation needed][dead link]
- ^ "Australian Economic Indicators" (PDF). Australian Bureau of Statistics. 2008. Retrieved 11 September 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Western Australia Economic Profile" (PDF). Perth, WA: Government of Western Australia, Department of Jobs, Tourism, Science and Innovation. March 2020. p. 8. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ Tuck, Christopher A. (20 January 2020). "Iron ore" (PDF). Mineral commodity summaries 2020. Reston, Virginia: U.S. Geological Survey. pp. 88–89. ISBN 978-1-4113-4362-7. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Wilkinson, Ian (9 April 2019). "Western Australian wheat industry". South Perth, WA: Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development, Agriculture and Food division. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "WA at a Glance 2008" (PDF). Australian Bureau of Statistics. 2 April 2008. Retrieved 10 September 2008.
- ^ "2008 Live Exports" (PDF). ABARE. 31 March 2008. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2008. Retrieved 15 September 2008.
- ^ "Go West Now". Government of Western Australia. 2008. Archived from the original on 21 November 2011. Retrieved 16 September 2008.
- ^ "2006 Census QuickStats: Western Australia, October 2007". Censusdata.abs.gov.au. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ "Refining". Bp.com. Retrieved 30 August 2016.
- ^ McKinnon, Stuart (3 April 2014). "BP sticks by Kwinana despite Qld closure". The West Australian. Retrieved 27 October 2014.
- ^ "Downstream_Petroleum 2007 Report" (PDF). Australian Institute of Petroleum. 15 July 2008. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 October 2008. Retrieved 12 September 2008.
- ^ Jasper, Clint (21 March 2017). "Tropical Forestry Services becomes Quintis as the company shifts focus". ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation). Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions". WA Sandalwood Plantations. Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ Stevens, Rhiannon; Moussalli, Isabel (5 September 2020). "From the Gibson Desert to New York, these sandalwood harvesters are winning over the perfume market". ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation). Retrieved 19 September 2020.
- ^ "Tourism Western Australia : Fast Facts Year Ending March 2015" (PDF). Tourism.wa.gov.au. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ "Tourism Satellite Account : Western Australia 2013 – 2014 : Fact Sheet" (PDF). Tourism.wa.gov.au. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ "Tourism Western Australia". Tourism.wa.gov.au. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Proclamation Day". Government of Western Australia. 11 June 2015. Archived from the original on 29 October 2017. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- ^ Review Essay, New Federation History, Melbourne University Law Review www.austlii.edu.au
- ^ "25 May 1935 – W. A. Secession Petition Disallowed Committee's ..." Nla.gov.au. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "Local Government Act 1995". Austlii.edu.au. Retrieved 26 July 2011.
- ^ "Year 7 students move to secondary school – School education – The Department of Education". 17 July 2014. Archived from the original on 17 July 2014. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ "Enrolling in school – The Department of Education". Education.wa.edu.au. Retrieved 31 May 2018.
- ^ "TAFE Admissions guide for entry to full time courses" (PDF). Northmetrotafe.wa.edu.au. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 May 2018. Retrieved 31 May 2018.
- ^ "Western Australian Certificate of Education: WACE Manual: General information for senior secondary schooling 2018" (PDF). School Curriculum and Standards Authority. 31 May 2018.
- ^ Lee, Tim (12 February 2013). "'Grand old man of the Kimberley' dies". ABC News (Australia). Retrieved 2 March 2013.
- ^ Hugh Johnson & Jancis Robinson (2007). The World Atlas of Wine; 6th Revised edition. Mitchell Beazley. ISBN 978-1-84533-414-7.
- ^ T. Stevenson "The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia" pg 589 Dorling Kindersley 2005 ISBN 0-7566-1324-8
- ^ "Wine Australia". Wineaustralia.com. Archived from the original on 22 July 2008. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ winepros.com.au, The Oxford Companion to Wine pg 765 Western Australia
- ^ "Australian Wine and Brandy Corporation – Western Australian Wine". Wineaustralia.com. Archived from the original on 22 July 2008. Retrieved 14 June 2010.
- ^ Arts, Department of Culture and. "Sister State Relationships ~ DCA". Dca.wa.gov.au. Archived from the original on 18 February 2019. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ "Hyogo-WA Sister State Relationship". Hyogo Prefectural Government Cultural Centre. 10 April 2015. Archived from the original on 23 April 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "WA-Hyogo Sister State". Government of Western Australia. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ "About the centre". Hyogo Prefectural Government Cultural Centre. 27 March 2015. Archived from the original on 23 April 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ "Japanese garden a tribute to Sister State relationship with Hyogo prefecture". Government of Western Australia. 1 June 2013. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ "About Us". Australia Japan Society of WA. Archived from the original on 9 April 2013. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ "Memorial service pays tribute to Japanese earthquake victims". City of Perth. January 2016. Archived from the original on 8 May 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ "Hansard, Western Australian Legislative Assembly". Parliament of Western Australia. 21 October 1997. Archived from the original on 22 April 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ "WA-Japan Sister City Relationships". Government of Western Australia. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ "SLWA Online Catalogue /Entire Sta". Henrietta.liswa.wa.gov.au. Archived from the original on 9 November 2011. Retrieved 2 November 2012.
- ^ "Search results for 'westralia' – Trove". Trove.nla.gov.au. Retrieved 16 September 2015.
- ^ "SLWA Online Catalogue /Entire Sta". Henrietta.liswa.wa.gov.au. Archived from the original on 9 November 2011. Retrieved 2 November 2012.
- ^ "SLWA Online Catalogue /Entire Sta". Henrietta.liswa.wa.gov.au. Archived from the original on 9 November 2011. Retrieved 2 November 2012.
- ^ [1] Archived 2 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Canberra all at sea over position of Southern Ocean". Theage.com.au. 22 December 2003. Retrieved 2 November 2012.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Western Australia. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Western Australia. |
 Geographic data related to Western Australia at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Western Australia at OpenStreetMap- Welcome to Western Australia, a tourist website run by Tourism Western Australia, the statutory authority responsible for promoting Western Australia as a tourist destination
- Western Australia government's website
- Watch historical footage of Western Australia from the National Film and Sound Archive of Australia's collection.
- Watch audiovisual material relating to Western Australia on the National Film and Sound Archive's australianscreen online.
- Western Australia
- Former British colonies and protectorates in Oceania
- States and territories established in 1829
- 1829 establishments in Australia



