Garrapatas Fault Zone
| Garrapatas Fault | |
|---|---|
| Falla de Garrapatas | |
 | |
| Etymology | |
| Coordinates | 04°24′47″N 76°30′06″W / 4.41306°N 76.50167°WCoordinates: 04°24′47″N 76°30′06″W / 4.41306°N 76.50167°W |
| Country | |
| Region | Andean, Pacific/Chocó |
| State | Chocó, Valle del Cauca |
| Characteristics | |
| Range | & Western Ranges, Andes |
| Part of | Andean oblique faults |
| Length | 138 km (86 mi) |
| Strike | 060.8 ± 14 |
| Dip | Northwest |
| Dip angle | 50 |
| Displacement | <0.2 mm (0.0079 in)/yr |
| Tectonics | |
| Plate | North Andean |
| Status | Inactive |
| Type | Oblique thrust fault |
| Movement | Dextral reverse |
| Age | Quaternary |
| Orogeny | Andean |
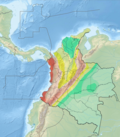
The Garrapatas Fault (Zone) (Spanish: (Zona de) Falla(s) de Garrapatas) is an inactive dextral oblique thrust fault in the departments of Chocó and Valle del Cauca in Colombia. The fault has a total length of 138 kilometres (86 mi) and is crescent-shaped, running along an average east-northeast to west-southwest strike of 060.8 ± 14 in the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes.
Etymology[]
The fault is named after the .[1]
Description[]
The Garrapatas Fault runs between the axis of the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes and the , to the west of the city of Buga. The fault displaces oceanic volcanic and sedimentary rocks and has a very well developed V-shaped valley along the upper parts of the and and probably connects with the Argelia Fault. It causes alignment of drainage and parallel streams. Dextral movement in this fault is an exception to the common sinistral (left-lateral) movement of north-south trending faults in the region.[1]
See also[]
References[]
Bibliography[]
- ; ; , and . 2000a. Map and Database of Quaternary Faults and Folds in Colombia and its Offshore Regions, 1–66. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.
Maps[]
- ; ; , and . 2000b. Map of Quaternary Faults and Folds of Colombia and Its Offshore Regions, 1. USGS. Accessed 2017-09-18.
- Seismic faults of Colombia
- Thrust faults
- Strike-slip faults
- Inactive faults
- Geography of Chocó Department
- Geography of Valle del Cauca Department