Geminiraptor
| Geminiraptor Temporal range: Early Cretaceous,
| |
|---|---|
| |
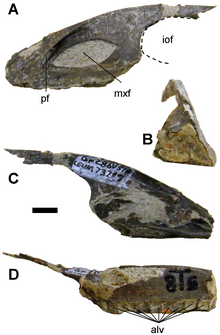
| The holotype maxilla in multiple views | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Troodontidae |
| Genus: | †Geminiraptor et al., 2010 |
| Species: | †G. suarezarum
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Geminiraptor suarezarum Senter et al., 2010
| |
Geminiraptor (meaning "twin seizer") is a genus of troodontid theropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Early Cretaceous period. Geminiraptor was a small, ground-dwelling bipedal carnivorous paravian. The type species of Geminiraptor is G. suarezarum.[1]
Disovery and naming[]
The holotype and only known specimen of Geminiraptor is CEUM 7319, a maxilla recovered from the Lower Yellow Cat Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation, in Utah, dating from the early to late Valanginian stage (about 139 to 134 million years ago). Geminiraptor was named by Phil Senter, James I. Kirkland, John Bird and Jeff A. Bartlett in 2010. The generic name is from the Latin geminae (“twins,” in honor of the Suarez sisters) and raptor ("seizer"). The specific name refers to Drs. Celina and , the twin geologists who discovered the Suarez site.[1]
Description[]


The maxilla is long and low, with the process above the antorbital fenestra being horizontal, similar to other advanced troodontids. However, some features of the maxilla are more similar to the condition in basal troodontids such as Sinovenator. These include the presence of a promaxillary fenestra which is visible in lateral view, a narrow promaxillary strut (the bar of bone between the maxillary and promaxillary fenestrae), and a narrow interfenestral strut (the bar of bone between the maxillary and antorbital fenestrae).[1]
Geminiraptor is uniquely characterized by the presence of a large pneumatic chamber which expands the maxilla into a triangular shape in cross section, with the base formed by a bony shelf lingual to the teeth. Nine alveoli are preserved, although since both the anterior and caudal tips of the maxilla are missing, certainly more were present. By comparing Geminiraptor's maxilla to that of other troodontids, it was inferred that at least three more teeth were present in the missing anterior part of the maxilla and at least seven in the missing caudal area, for a total of at least nineteen teeth in the maxilla. The alveoli are characteristically square-shaped and separated by small walls of bone, a feature only known in Sinovenator among other troodontids.[1]
The paleontologist Thomas R. Holtz Jr. has estimated its weight around 2.27–9.1 kg (5.0–20.1 lb) and a possible length of 1.5 m (4.9 ft).[2] Although still a rather small dinosaur, Geminiraptor is larger than most other Early Cretaceous troodontids, with its maxillary proportions more similar to those of Late Cretaceous genera.[1]
Classification[]

Geminiraptor is considered a troodontid, a classification supported due to its large number of small teeth. The phylogenetic analysis conducted by its describers placed it in a clade with derived troodontids due to the oblong shape of its maxillary fenestra. Due to the large amount of missing data for the genus, its position within the family is not completely certain, and Geminiraptor may instead be a close relative of Sinovenator due to each of them having interdental bone walls, unlike all other known troodontids.[1]
Below is the proposed placement for Geminiraptor conducted by Senter et al. 2010:[1]
| Deinonychosauria |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Paleoecology[]

Geminiraptor was the first report of a troodontid in the Early Cretaceous of North America, proving their existence. It lived in the Lower Yellow Cat Member of the Cedar Mountain Formation[1] about 139-134 million years ago.[2] The environments were semiarid areas with floodplain prairies, riverine forests, and open woodlands.[3] It has been also interpreted that there was a waterlogged bog-like environment.[4]
Paleofauna that lived alongside Geminiraptor in the lower bed, included other Theropods: Falcarius and Yurgovuchia. The sauropod Mierasaurus, the large iguanodontian Iguanacolossus and the turtle Naomichelys.[5][6][3] There are also indeterminate Goniopholidids crocodiles and an unnamed velociraptorine known from the Lower Yellow Cat.[6][7]
See also[]
- Timeline of troodontid research
- Cedar Mountain Formation
- 2010 in paleontology
References[]
- ^ a b c d e f g h Senter, P.; Kirkland, J. I.; Bird, J.; Bartlett, J. A. (2010). "A New Troodontid Theropod Dinosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of Utah". PLOS ONE. 5 (12): e14329. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014329. PMC 3002269. PMID 21179513.
- ^ a b Holtz, T. R.; Rey, L. V. (2007). Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages. Random House. Supplementary Information 2012 Weight Information
- ^ a b Paul, Gregory S. (2016). The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs (2nd ed.). Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. pp. 151, 163, 229, 252, 314, 319, 326, 327. ISBN 9780691167664.
- ^ Royo-Torres, R.; Upchurch, P.; Kirkland, J.I.; DeBlieux, D.D.; Foster, J.R.; Cobos, A.; Alcalá, L. (2017). "Descendants of the Jurassic turiasaurs from Iberia found refuge in the Early Cretaceous of western USA". Scientific Reports. 7 (1): 14311. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-14677-2. PMC 5662694. PMID 29085006.
- ^ McDonald, A. T.; Kirkland, J. I.; DeBlieux, D. D.; Madsen, S. K.; Cavin, J.; Milner, A. R. C.; Panzarin, L. (2010). "New Basal Iguanodonts from the Cedar Mountain Formation of Utah and the Evolution of Thumb-Spiked Dinosaurs". PLOS ONE. 5 (11): e14075. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014075. PMC 2989904. PMID 21124919.
- ^ a b Kirkland, J.I. (December 1, 2016). "The Lower Cretaceous in East-Central Utah—The Cedar Mountain Formation and its Bounding Strata". Geology of the Intermoutain West. 3: 1–130.
- ^ Senter, P.; Kirkland, J. I.; Deblieux, D. D.; Madsen, S.; Toth, N. (2012). Dodson, Peter (ed.). "New Dromaeosaurids (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the Lower Cretaceous of Utah, and the Evolution of the Dromaeosaurid Tail". PLOS ONE. 7 (5): e36790. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0036790. PMC 3352940. PMID 22615813.
- Early Cretaceous dinosaurs of North America
- Troodontids
- Fossil taxa described in 2010
- Taxa named by James I. Kirkland
- Paleontology in Utah