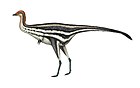
Microvenator
| Microvenator Temporal range: Early Cretaceous,
| |
|---|---|
| |
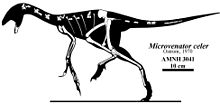
| Skeletal restoration | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Clade: | Saurischia |
| Clade: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Caenagnathidae |
| Genus: | †Microvenator Ostrom, 1970 |
| Species: | †M. celer
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Microvenator celer Ostrom, 1970
| |
Microvenator (meaning "small hunter") is a genus of dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous Cloverly Formation in what is now south central Montana. Microvenator was an oviraptorosaurian theropod. The holotype fossil is an incomplete skeleton, most likely a juvenile, with a living length of about 1.2 m. The adult size of Microvenator is estimated to be closer to 3 m long. Microvenator celer is primitive and may be the "sister taxon to all other oviraptorosaurs."[1][2]
Discovery[]

Barnum Brown collected the type specimen (AMNH 3041) in 1933 by a field party working for the American Museum of Natural History and he erroneously included Deinonychus teeth with the specimen. Because of this, Brown informally dubbed it "Megadontosaurus" ("big-toothed lizard"), Brown made illustrations of it, but never published the name, a fate shared with several other Cloverly Formation dinosaurs (Deinonychus, Sauropelta and Tenontosaurus). AMNH 3041 consists of a partial posterior skull, right dentary, 23 vertebrae, four ribs, the left coracoid, a partial left forelimb, a partial pelvis, and partial hindlimbs.[3] It was not until 1970 that John Ostrom described the type specimen as part of his work on the Cloverly Formation, naming it Microvenator celer meaning "swift small hunter" due to its long legs.[2] Ostrom originally theorized it was part of Othniel Marsh's Coeluridae due to features in the cervical vertebrae.[2] Ostrom also referred a single tooth from the Yale Peabody Museum collection, YPM 5366, to this new species that likely belongs to Deinonychus.[2] The illustrations that Brown had prepared were finally published in a detailed and exhaustive monograph by Mackovicky and Sues in 1998. They confirmed that Microvenator is an oviraptorosaurian, and that it is the earliest known member of this group from North America.[3]
Paleoenvironment[]
Microvenator fossils are extremely rare, with only the type specimen described, likely due to lack of teeth and frail bones.[4] Microvenator coexisted with notable dinosaurs like Deinonychus, Sauropelta, and Acrocanthosaurus in the Himes Member of the Cloverly Formation.
See also[]
- Clovery Formation
- Timeline of oviraptorosaur research
References[]
- ^ Varricchio, D. J. 2001. Late Cretaceous oviraptorosaur (Theropoda) dinosaurs from Montana. pp. 42–57 in D. H. Tanke and K. Carpenter (eds.), Mesozoic Vertebrate Life. Indiana University Press, Indianapolis, Indiana.
- ^ a b c d OSTROM, JOHN H. Stratigraphy and Paleontology of the Cloverly Formation (Lower Cretaceous) of the Bighorn Basin Area, Wyoming and Montana. Yale University Press, 2020, https://doi.org/10.2307/j.ctvxkn7tk.
- ^ a b Makovicky, Peter J.; Sues, Hans-Dieter (1998). "Anatomy and phylogenetic relationships of the theropod dinosaur Microvenator celer from the Lower Cretaceous of Montana. American Museum novitates ; no. 3240".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Carrano, Matthew T.; Oreska, Matthew P. J.; Lockwood, Rowan (2016-03-03). "Vertebrate paleontology of the Cloverly Formation (Lower Cretaceous), II: Paleoecology". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 36 (2): e1071265. doi:10.1080/02724634.2015.1071265. ISSN 0272-4634.
- Caenagnathids
- Early Cretaceous dinosaurs of North America
- Taxa named by John Ostrom
- Fossil taxa described in 1970
- Cloverly fauna
- Paleontology in Montana
- Theropod stubs