Grijalva River
| Grijalva River | |
|---|---|
 The cliffs at Sumidero Canyon overlook the Grijalva River | |
 Major rivers of Mexico, with Grijalva in the southeast of the country | |
| Native name | Río Grijalva |
| Location | |
| Country | Mexico |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | |
• location | Gulf of Mexico |
• coordinates | 18°36′10″N 92°41′33″W / 18.60278°N 92.69250°WCoordinates: 18°36′10″N 92°41′33″W / 18.60278°N 92.69250°W |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 480 km (300 mi) |
Grijalva River, formerly known as Tabasco River, (Spanish: Río Grijalva, known locally also as Río Grande de Chiapas, Río Grande and Mezcalapa River) is a 480 km (300 mi) long river in southeastern Mexico.[1] It is named after Juan de Grijalva who visited the area in 1518.[2] The river rises from Río Grande de Chiapas in southeastern Chiapas and flows from Chiapas to the state of Tabasco through the Sumidero Canyon into the Bay of Campeche. Begins as "Río Grande de Chiapas" or "Río Mezcalapa", later, Río Grande is stopped at the Angostura Dam (Mexico), one of the largest reservoirs in Mexico, and then its course is now named "Grijalva River". The river's drainage basin is 134,400 km2 (51,900 sq mi) in size.[3] Because of the close connection to the Usumacinta River (the two combine, flowing into the Gulf of Mexico in a single delta), they are often regarded as a single river basin, the Grijalva-Usumacinta River.[4] Río Grande de Chiapas rises into Sierra de los Cuchumatanes, Guatemala;[5] in Guatemala receives the name "Selegua River" and also is a large river.
After flowing from , an artificial lake created by the hydroelectric Malpaso Dam, Grijalva River turns northward and eastward, roughly paralleling the Chiapas-Tabasco state border. It flows through Villahermosa (where, in 2001, a new cable-stayed bridge was constructed to cross the river) and empties into the Gulf of Mexico, approximately 10 km (6.2 mi) northwest of Frontera. The river is navigable by shallow-draft boats for approximately 100 mi (160 km) upstream.
Gallery[]

Juan de Grijalva, expedition in 1518. Discovery by the Europeans of the Grijalva River.
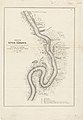
Sketch of the River Tabasco, 1847-48


Grijalva River flowing through Villahermosa.

See also[]
- Chiapas bridge
- List of longest rivers of Mexico
References[]
- ^ "Grijalva." Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary, 3rd ed. 2001. (ISBN 0-87779-546-0) Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., p. 450.
- ^ Diaz del Castillo, Bernal. The Discovery and Conquest of Mexico. Da Capo Press, 1996. p. 21
- ^ World Delta Database
- ^ Contreras-MacBeath, T.; M.B. Rodríguez; V. Sorani; C. Goldspink; G.M. Reid (2014). "Richness and endemism of the freshwater fishes of Mexico". Journal of Threatened Taxa. 6 (2): 5421–5433. doi:10.11609/JoTT.o3633.5421-33.
- ^ SECTUR D.F. "JARDÍN GRIJALVA" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Grijalva River. |
- Rivers of Chiapas
- Rivers of Tabasco
- Mexico river stubs








