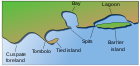
Gulf

A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline.[1] Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden.[2]
See also[]
- List of gulfs – Wikipedia list article
References[]
- ^ Gregory, George (1816). A Dictionary of Arts and Sciences. Vol. Volume 2 (First American ed.). Philadelphia: Isaac Peirce. p. 269. Retrieved 25 June 2020.
A sea is a smaller collection of waters; as the Black Sea. A gulf is a part of the sea which is nearly surrounded with land; as the gulf of Venice. A bay has a wider entrance than a gulf; as the Bay of Biscay. A strait is a narrow passage that joins.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help) - ^ Duggal, Gita. Chowdhury, Baruna Ray (ed.). Madhubun ICSE Geography 6. New Delhi: Vikas Publishing House. p. 32. ISBN 9789325994645. Retrieved 25 June 2020.
A gulf is an inlet of an ocean or a sea deep into the land with a narrow mouth. It is more highly indented, more enclosed by the coast and larger than a bay. Some examples of gulfs are Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico, Gulf of Eden and Gulf of...
External links[]
 Media related to Gulfs at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Gulfs at Wikimedia Commons
Categories:
- Gulfs
- Bodies of water
- Coastal and oceanic landforms
- Coastal geography
- Oceanographical terminology