HandyLinux
 | |
 HandyLinux Desktop | |
| Developer | thuban, Starsheep, arpinux and users community. |
|---|---|
| OS family | Linux |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model | Open source |
| Initial release | September 2013 |
| Latest release | HandyLinux 2.5 / 11 June 2016 |
| Available in | Multilingual[1] |
| Update method | APT |
| Package manager | dpkg (Synaptic) |
| Platforms | I586, I686 et amd64 |
| Kernel type | Monolithic Linux kernel |
| Userland | GNU |
| Default user interface | Xfce/Compiz |
| License | Free software licenses (mainly GPL) |
| Official website | handylinux |
HandyLinux is a Linux distribution originating in France and derived from the Debian stable branch.[2] It is designed especially with inexperienced computer users in mind.[3] The distribution has low system requirements, allowing it to be used on a range of older hardware that is no longer supported by the latest versions of proprietary operating systems. It is aimed particularly at older people with dated hardware who do not need or possess the skill to use many features afforded by state-of-the-art operating systems. It may also be useful for computer users with disabilities, such as visual impairment.[citation needed]
Goals[]
The goal of the HandyLinux project is to provide a "stable" Debian-based OS for the elderly, novices and people seeking freedom and full functionality on a user-friendly desktop. HandyLinux is an official Debian derivative with a simple and clear graphical user interface called the HandyMenu.[4]
It features built-in tools that facilitate the handling of home computing.[5]
Documentation teaches users desktop navigation and helps them to learn the HandyLinux distribution.[6][7] Prospective users are encouraged to browse the HandyLinux online forum[8] and ask questions about the operating system.
Features[]
HandyLinux can be installed on any modern computer, with a processor Pentium 4 or higher and 512 MB[9] of RAM, and the system requires 3.7 GB of available hard drive storage.[10]
The distribution can be run as either of two "live" versions, live CD (handylinuxlight) or live USB, to sample the prepackaged software and test its compatibility with the installed hardware.[11] Alternatively it can be installed on a netbook equipped with at least 4 GB memory[12] on computers built before 2005 (handylinux i486 non pae)[13] and on computers built from 2005 onward (handylinux I686-PAE).
If they choose, users can "remove castors", i.e., remove the default HandyMenu and substitute the classical menu of the Xfce desktop environment,[14] add software packages, and customize the look and feel of the distribution after becoming more experienced with the OS by reading the documentation.[15]
All the software needed for a functional desktop is included in the disk image, and an Internet connection is not necessary[16] to install the program bundle prepackaged for the HandyLinux operating system.[citation needed]
Applications[]
- File manager: Thunar
- Internet: Firefox, Icedove, Transmission
- Multimedia: Clementine, VLC media player
- Office: LibreOffice
- Remote Assistance: TeamViewer (optional with graphic installer)
- Printer installation by: CUPS
Tools have been integrated for improving accessibility: an inverter color, a filter screen, direct access to documentation, a screen magnifier, copy and paste button, a virtual keyboard and voice synthesis integrated into the browser.
Small practical programs are also included: screenshot, calendar, file search, automatic sorting download folder, Bleachbit for cleaning, archive manager "Archive Manager", Disk Utility for formatting, Hardinfo for system information, Xl-wallpaper wallpaper changer.
Desktop environment[]
HandyLinux's native desktop environment is based on Xfce, and the Compiz compositing window manager is optional.[17] Users may switch to the more traditional Xfce menu if they prefer it to the HandyMenu.[18]
A seven-tab menu with a large computer icon enables users to graphically launch applications,[19] and only a single click is necessary to open files and folders or run a program.

latest

internet
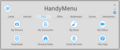
files

office
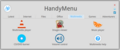
multimedia

games

adventurers
Releases[]
HandyLinux updates generally follow updates of the Debian stable branch.[20]
| Name | Release date | Megabytes | Base | 32 bits | Supported platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| handylinux-2.5-i386[21] | 2016-06-11 | 1344 | Debian based 8.5 | 32bits | I586 & I686-pae |
| handylinux-2.5-amd64 | 2016-06-11 | 1212 | Debian based 8.5 | 64bits | amd64 |
| handylinux-2.4-i386 | 2016-04-10 | 1367 | Debian based 8.4 | 32bits | I586 & I686-pae |
| handylinux-2.4-amd64 | 2016-04-10 | 1240 | Debian based 8.4 | 64bits | amd64 |
| handylinux-2.3-i386 | 2016-01-24 | 1378 | Debian based 8.3 | 32bits | I586 & I686-pae |
| handylinux-2.3-amd64 | 2016-01-24 | 1244 | Debian based 8.3 | 64bits | amd64 |
| handylinux-2.2 | 2015-09-06 | 1359 | Debian based 8.2 | 32bits | I586 & I686-pae |
| handylinux-2.2-amd64 | 2015-09-06 | 1182 | Debian based 8.2 | 64bits | amd64 |
| handylinux-2.1 | 2015-06-09 | 1335 | Debian based 8.1 | 32bits | I586 & I686-pae |
| handylinux-2.0[22] | 2015-05-16 | 1325 | Debian based 8.0 | 32bits | I586 & I686-pae |
| handylinuxlight-2.0[23] | 2015-05-23 | 697 | Debian based 8.0 | 32bits | I586 & I686-pae |
| handylinux-1.9 wheezy[24] | 2015-04-11 | 1250 | Debian based 7.8 | 32bits | I486 & I686-pae |
| handylinuxlight-1.8[25] | 2015-01-17 | 656 | Debian based 7.8 | 32bits | I486 & I686-pae |
| handylinux-compiz 1.6.1[26] | 2014-08-16 | 1160 | Debian based 7.6 | 32bits | I486 & I686-pae |
A development fork of HandyLinux in the Finnish language was published May 29, 2014.[27]
See also[]
References[]
- ^ Debian derivatives HandyLinux available in French and English
- ^ Wiki Debian HandyLinux Debian Derivatives Census
- ^ dokuwiki HandyLinux Getting started with HandyLinux Archived 2015-05-18 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ HandyMenu documentation
- ^ (in French)Techandtux Handylinux la dérivée de Debian à portée de main (fr) 2014-01-10
- ^ Handylinux light documentation
- ^ HandyLinux Documentation
- ^ HandyLinux Forum
- ^ Debian configuration minimum
- ^ (in French) Frédéric Bezies Test de Handylinux 1.0 2013-10-02
- ^ (in French) documentation handylinux the material tested and certified for HandyLinux Retrieved 2014-03-25
- ^ (in French) Cyrille Borne Handylinux pour eeepc Archived 2014-03-11 at archive.today Retrieved 11 March 2014
- ^ (in French) @bc l'actualité installation sur un pc de 2002 avec le CD handylinuxlight Retrieved 2014-02-21
- ^ (in French) La Fabrique du Web HandyLinux : Debian sans se prendre la tête Archived 2014-04-21 at the Wayback Machine 2014-04-20
- ^ Documentation HandyLinux Archived 2015-04-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ (in French) Alain Bach Installer handylinux Archived 2014-04-22 at the Wayback Machine 2014-01-31
- ^ softpedia HandyLinux Compiz
- ^ menu in the Raiders section
- ^ (in French) Solidrnet.fr HandyLinux, Linux sans se prendre la tête Archived 2014-02-21 at the Wayback Machine 2013-12-23
- ^ Softpedia Handylinux Changelog
- ^ HandyLinux Is a Great Toolbox for Linux Newbies
- ^ Softpedia HandyLinux 2.0 Officially Released, Based on Debian 8 Jessie
- ^ wiki handylinux handylinuxlight 2.0 Archived 2015-04-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Softpedia HandyLinux 1.9 Out Now, the Last Release Based on Debian 7 Wheezy
- ^ HandyLinuxLight on Softpedia
- ^ Softpedia HandyLinux Compiz
- ^ HandyLinux Puolanka Edition
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to HandyLinux. |
- Debian
- Debian-based distributions
- Operating system distributions bootable from read-only media
- Linux distributions







