Huanglong Scenic and Historic Interest Area
| UNESCO World Heritage Site | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Location | Songpan County, Sichuan, People's Republic of China |
| Criteria | Natural: (vii) |
| Reference | 638 |
| Inscription | 1992 (16th Session) |
| Area | 60,000 ha (230 sq mi) |
| Coordinates | 32°44′36″N 103°49′59″E / 32.7432°N 103.8330°ECoordinates: 32°44′36″N 103°49′59″E / 32.7432°N 103.8330°E |
 Location of Huanglong Scenic and Historic Interest Area in Sichuan | |
Huanglong (simplified Chinese: 黄龙; traditional Chinese: 黃龍; pinyin: Huánglóng; lit. 'yellow dragon') is a scenic and historic interest area in the northwest part of Sichuan, China. It is located in the southern part of the Minshan mountain range, 370 kilometres (230 mi) north-northwest of the capital Chengdu.[1] This area is known for its colorful travertine pools formed by calcite deposits, especially in Huanglonggou (Yellow Dragon Gully), as well as diverse forest ecosystems, snow-capped peaks, waterfalls and hot springs. Huanglong is also home to many endangered species including the giant panda and the Sichuan golden snub-nosed monkey.[1] In addition, a large population of the endemic orchid species 'Cypripedium plectrochilum' was discovered at the site [2] Huanglong was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1992 because of its outstanding travertine formations, waterfalls and limestone formations as well as its travertine terraces and lakes rating among the three most outstanding examples in the world. [1][3]

Description[]
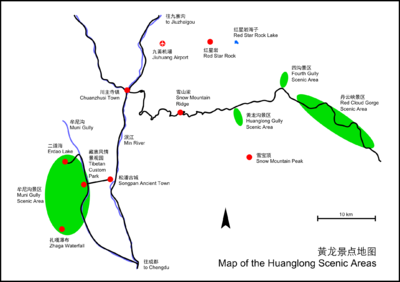
Repeated glaciation events, the unique terrane structure, the formation of tufa, the stratum of carbonic acid rock, and climatic conditions such as Arctic-alpine sunlight have created this world-famous travertine landscape. Huanglong covers an area of 700 km2 at an altitude between 1700m and 5588m. Major scenic areas include:
- Huanglong Valley (黄龙沟)
- Danyun Gorge (Chinese: 丹云峽; lit. 'red cloud gorge'): A canyon more than 1,000 meters in depth. The snow melt from the nearby Mount Xuebaoding travels through this canyon, providing much of the water for the region.[4]
- Muni Valley (牟尼沟)
- Xuebaoding (雪宝顶; 'snow treasure peak') – 5,588 m (18,333 ft). The highest peak in the Min Mountains
- Xueshan Ridge (雪山梁; 'snow mountain ridge') – 4,007 m (13,146 ft), the highest point on the road from Jiuhuang Airport to Huanglong Valley.
- Red Star Rock (红星岩)
- Sigou (四沟; 'fourth gully')
Huanglong Valley[]
The total length of the travertine in Huanglong Valley is 3.6 km and it is thought to look like a huge golden dragon wheeling through the snow-capped mountains of the valley. The main landscapes are travertine banks, colorful ponds and travertine waterfalls and caves. The main body of water starts from the ancient Buddhist/ temple at the top of the valley and ends at the Guests Welcome Pond in the north with a length of 2.5 km and a width of 30–170m. The colours of Huanglong's waters consist of yellows, greens, blues and browns.

| Scenic spots in Huanglong Valley | Sea level | Remarks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Guests Welcome Pond 迎宾池 | 3230m | 350 pools | 
|
| 2 | Marvelous Flying Waterfall 飛瀑流輝 | 3245m | 14m tall 68m wide | 
|
| 3 | Lianyan Pond 瀲灩湖 | 3251m | 2000sq.m | 
|
| 4 | Flying Waterfall on Lotus Platform 蓮台飛瀑 | 3260m | 45m tall 19m wide | 
|
| 5 | Washing Cave 洗身洞 | 3280m | 10m tall 40m wide | 
|
| 6 | Golden Sand Pavement 金沙鋪地 | 3305m | 1300m long | 
|
| 7 | Seven Mile Golden Sand 七里金沙 | 3400m | 
| |
| 8 | Bonsai Pond 盆景池 | 3320m | 330 pools | 
|
| 9 | Mirror Pond 明鏡倒映池 | 3400m | 180 pools | 
|
| 10 | Azalea Pond 娑蘿映彩池 | 3415m | 400 pools | 
|
| 11 | Flamboyant Pond 爭豔池 | 3414m | 658 pools | 
|
| 12 | Huanglong Middle Temple 黃龍中寺 | 3470m | 
| |
| 13 | Huanglong Ancient Temple 黃龍古寺 | 3568m | 
| |
| 14 | Multi-Colored Pond 五彩池 | 3576m | 693 pools | 
|
Gallery[]
See also[]
- Baishuitai, Yunnan, China
- Badab-e Surt in Iran
- Mammoth Hot Springs in Yellowstone Park, United States
- Band-e Amir in Afghanistan
- Semuc Champey in Guatemala
- Plitvice Lakes in Croatia
- Pamukkale in Turkey
- Travertine
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Huanglong Scenic and Historic Interest Area".
- ^ Li, P.; Luo, Y.; Bernhardt, P.; Kou, Y.; Perner, H. (27 February 2008). "Pollination of Cypripedium plectrochilum (Orchidaceae) by Lasioglossum spp. (Halictidae): the roles of generalist attractants versus restrictive floral architecture". Plant Biology. 10 (2): 220–230. doi:10.1111/j.1438-8677.2007.00020.x. PMID 18304196.
- ^ Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "Huanglong Scenic and Historic Interest Area". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved 2021-04-22.
- ^ Huadong, Guo (2013). Atlas of Remote Sensing for World Heritage: China. Springer. p. 282-287. ISBN 978-3-642-32823-7.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Huanglong. |
- World Heritage Sites in China
- Biosphere reserves of China
- National parks of China
- Geography of Sichuan
- Tourist attractions in Sichuan
- Sichuan geography stubs






