Interventricular septum
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2015) |
| Interventricular septum | |
|---|---|
 Section of the heart showing the ventricular septum. | |
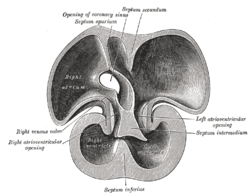 Interior dorsal half of heart of nearly 5 weeks old human embryo. (Labeled as 'septum inferius') | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Heart |
| Artery | anterior interventricular branch of left coronary artery and Posterior interventricular artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | septum interventriculare cordis |
| MeSH | D054088 |
| TA98 | A12.1.00.013 |
| TA2 | 3970 |
| FMA | 7133 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The interventricular septum (IVS, or ventricular septum, or during development septum inferius) is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior and posterior interventricular sulci. The lower part of the septum, which is the major part, is thick and muscular, and its much smaller upper part is thin and membraneous.[1]
During each cardiac cycle the interventricular septum contracts by shortening longitudinally and becoming thicker.
Structure[]

The interventricular septum is the stout wall separating the ventricles, the lower chambers of the heart, from one another.
The ventricular septum is directed obliquely backward to the right, and curved with the convexity toward the right ventricle; its margins correspond with the anterior and posterior longitudinal sulci. The greater portion of it is thick and muscular and constitutes the muscular interventricular septum. Its upper and posterior part, which separates the aortic vestibule from the lower part of the right atrium and upper part of the right ventricle, is thin and fibrous, and is termed the membranous ventricular septum.
Blood supply[]
The posterior interventricular artery, a branch of right coronary artery, supplies the posterior 1/3 of the interventricular septum. The remaining anterior 2/3 is supplied by the anterior interventricular artery which is a septal branch of the left anterior descending artery, which is a branch of left coronary artery.
Development[]
The muscular part of the interventricular septum derives from the bulboventricular flange which is developed due to differential growth of primitive ventricle and bulbous cordis. Membranous part has a neural crest origin which connects the upper free margin of the bulboventricular flange and anterior and posterior endocardial cushions of atrio ventricular canal. It also gets attached to lower border of spiral septum or the aortico pulmonary septum.
Clinical significance[]
A ventricular septal defect (VSD), a hole in the interventricular septum is one of the four congenital defects of the condition of tetralogy of Fallot. A VSD can cause a left-to-right shunt of blood flow in the heart, and is one of the most common of the congenital heart defects. This type of shunt is an acyanotic disorder that can result in ventricular hypertrophy.[2]
Additional images[]
Heart normal short axis echo
References[]
- ^ "Interventricular septum".
- ^ Pillitteri, Adele (2010). Maternal & Child Health Nursing: Care of the Childbearing & Childrearing Family. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9781582559995.
External links[]
| Look up interventricular septum in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to ECHOpedia case 'Ventricular septum defect with right to left shunt'. |
- Histology image: 128_06 at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center - "Heart and semilunar valve"
- Cardiac anatomy
