List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
hideThis article has multiple issues. Please help or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian.
A number of cities in Dacia and Thrace were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian Astibo and Latin Astibus. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.[1] The only known attempt to build a polis by the Thracians was Seuthopolis.,[2][3] although Strabo considered the Thracian cities with "bria" ending polises. Some of the Dacian settlements and fortresses employed the traditional Murus Dacicus construction technique.
Note: Throughout these lists, an asterisk [*] indicates that the toponym is reconstructed.
Daco-Thracian[]
This section contains information of unclear or questionable importance or relevance to the article's subject matter. (September 2009) |


Many city names were composed of an initial lexical element affixed to -dava, -daua, -deva, -deba, -daba, or -dova, which meant "city" or "town" Endings on more southern regions are exclusively -bria ("town, city"), -disza, -diza, -dizos ("fortress, walled settlement"), -para, -paron, -pera, -phara ("town, village"). Strabo translated -bria as polis, but that may not be accurate.[4] Thracian -disza, -diza, and -dizos are derived from Proto-Indo-European *dheigh-, "to knead clay", hence to "make bricks", "build walls", "wall", "walls", and so on. These Thracian lexical items show a satemization of PIE *gh-. Cognates include Ancient Greek teichos ("wall, fort, fortified town", as in the town of Didymoteicho) and Avestan da?za ("wall").
It is suggested that the "dava" endings are from the Dacian language, while the rest from the Thracian language. However "dava" towns can be found as south as Sandanski and Plovdiv. Some "dava" toponyms contain the same linguistic features as "diza" toponyms, e.g. and . The first written mention of the name "Dacians" is in Roman sources. Strabo specified that the Daci are the Getae, identified as a Thracian tribe. The Dacians, Getae and their kings were always considered as Thracians by the ancients (Dio Cassius, Trogus Pompeius, Appian, Strabo, Herodotus and Pliny the Elder) and were said to speak the same language. The Dacian language is considered a variety of the Thracian language.[5] Such lexical differentiation -dava vs. para, would be hardly enough evidence to separate Dacian from Thracian, thus they are classified as dialects.[6] It is also possible that '-dava' and '-bria' mean two different things in the same language, rather than meaning the same thing in two different languages. Thus bria could have been used for urbanized settlements, similar in scale and design to those of the "civilised" peoples like Greeks and Romans, whereas '-dava' could mean a settlement which is rural, being situated in the steppe-like part of the Thracian lands.
- Abydos
- Acidava[7] (Acidaua), a fortress town close to the Danube, located in today's Piatra-Olt, Olt County, Romania
- Acmonia
- Abdera
- Aedava[8] (Aedeva, Aedabe, Aedeba or Aedadeba), placed by Procopius on the between and ,[9] in Moesia (the present Northern Bulgaria)
- Aedeva, modern Pernik
- Aiadava[9] (Aiadaba or Aeadaba, Greek: Αἰάδαβα[10]), a locality in the Remesiana region in present-day Bela Palanka, Serbia[11]
- Aizis
- (Aixis, Aixim, Airzis, Azizis, Azisis, Aizisis, Alzisis, Aigis, Aigizidava*, Zizis), mentioned by Emperor Trajan in Dacica
- Amutria (Amutrion, Amutrium, Ancient Greek: Ἀμο��τριον), a Dacian town close to the Danube, possibly today's Motru, Gorj County, Romania [12]
- Apulon (Apoulon, Apula), a fortress city close to modern Alba-Iulia, Romania from which the Latin name of Apulum is derived
- [7] (), a fortress town in Wallachia
- Arcobadara [13]
- Argedava[14] (Argedauon, Sargedava, Sargedauon, Zargedava, Zargedauon, Ancient Greek: Αργεδαυον, Σαργεδαυον), mentioned in the Decree of Dionysopolis, potentially the dava discovered at Popeşti, a district in the town of Mihăileşti, Giurgiu County, Romania and maybe Burebista's court or capital
- Argidava (Argidaua, Arcidava, Arcidaua, Argedava, Argedauon, Sargedava, Sargedauon, Zargedava, Zargedauon, Ancient Greek: Ἀργίδαυα, Αργεδαυον, Σαργεδαυον), potentially Burebista's court or capital, located in today's Vărădia, Caraş-Severin County, Romania
- Artanes, modern Lom
- Arutela
- Apulon
- Atipara
- Bergula
- Berzobis,[7] ancient Bârzava, Romania
- Bergula, modern (Luleburgaz)
- Beroea,[15] modern Stara Zagora
- of the Bessi tribe, today Sinitovo
- Bizye, capital of the Odrysae
- Bregedava
- , near modern Komotini
- Buricodava[7]
- Buridava [13] (Burridava), today's Ocnele Mari, Romania
- Buteridava [7]
- Cabassus[16]
- Capidava[7] (Kapidaua), a fortress town on the southern side of the lower Danube
- Caria, modern Shabla
- Carsidava or
- Cedonia, near Sibiu
- Crenides
- Cumidava [7] (Comidava, ), ancient Râşnov, Romania
- Cypasis
- Danedebai, [17]
- Dausdava (, [7]), "The shrine of wolves", a fortress town close to the Danube
- Debelt
- Dentheletica, capital of the Dentheletae tribe, modern Kyustendil
- Desudaba or of the Maedi tribe, modern Sandanski
- [7]
- Dierna
- Dinogetia, [7] located above the Danube delta
- Docidava or
- Drabeskos[18]
- Drobeta, [7] located on the left bank of the Danube at Turnu Severin
- Drusipara
- [17]
- , later Pulpudeva translating Philippopolis, the name resulted in modern Plovdiv, prehistoric settlement
- Gatae
- Gazoros
- Genucla, [17] settlement located south of the Danube
- Germania, "hot water", modern Sapareva Banya, site of the Dentheletae tribe
- Germisara "hot water"
- Gildova[17] (Gildoba), located along the Vistula river
- Giridava[17]
- Iamphorynna, capital of the Maedi tribe[19]
- Itadeba[17] (Itadava)
- Ismara
- Istria (Olbia)
- Jidava,[7] near Câmpulung Muscel, Romania
- [7]
- Kabyle of the tribe, capital of the Odrysae[20]
- , modern Ipsala
- Lygos, modern Istanbul
- , a Dacian settlement where Roman Romula was built[citation needed]
- Marcodava (Dacia) ()
- , modern Nessebar
- , modern Lovech
- Murideba
- * Napoca, ancient Cluj-Napoca, Romania
- , modern Obzor
- [13] (Netindaua), ancient Slobozia, Romania
- ,[7] ancient Olteniţa, Romania
- Netindava
- near Panisus
- Oescus of the Triballi tribe
- or Uscudama, modern Edirne, capital of the Odrysae or Bessi tribe[21]
- , capital residence of the Odrysae, possibly modern Starosel
- ()
- Patruissa
- Pelendava[7] (), ancient Craiova, Romania
- Perburidava
- Perperikon
- Piroboridava
- Petra, fort of Maedi[22]
- [13] (), located in Piatra Neamţ
- Piroboridava (Piroboridaua)
- Polondava
- Potaissa (Patavissa), ancient Turda, Romania
- Quemedava, mentioned by Procopius in Dardania[23]
- Ramidava (Rhamidaua)
- Ratiaria
- Recidava
- Remesiana
- Rusidava[7] (Rusidava)
- Sacidava ()
- Sagadava
- Salmydessos, modern Kıyıköy, residence of the Odrysae
- Sarmizegetusa[17] (Sarmisegetuza), Decebalus's capital and holy place
- Scaidava ()
- Scaptopara, of the Dentheletae tribe, modern Blagoevgrad[24]
- Selymbria, modern Silivri in European Turkey[25]
- Serdica of the Serdi tribe, modern Sofia
- Setidava[7] (), mentioned by Ptolemy as a thriving settlement
- Seuthopolis[3]
- Singidava ()
- Sintica of the Sintoi tribe
- [26]
- Sucidava[7] (, ), located in Corabia, Olt County, Romania
- ,[7] mentioned by Ptolemy as a thriving settlement
- Tamasidava ()
- Tapae, a Dacian outpost guarding Sarmisegetuza and the site of two major battles between Dacians and Romans
- Teichos, residence of the
- Therma of the Mygdones tribe, modern Thessaloniki[27][28][29]
- Thermidava, placed by Ptolemy on the Lissus-Naissus route. The toponym is most probably a misreading of a settlement which most scholars in contemporary research locate near present-day Banat, Serbia.[30]
- Thynia, town of the Thyni
- Tibiscum
- Tirista ([7])
- [31]
- (Dierna[7])
- Tyrida
- Tyrodiza
- , modern Kiten
- ()
- Zaldapa[17]
- Zargidava ()
- Zeugma
- Zidava
- Zikideva
- Zimnicea,[7] site where Alexander the Great fought the Dacians
- Ziridava (Ziridaua), identified archaeologically with Pecica, Arad, Romania [32]
- [7] (, ), located in Dacian Moesia
- Zurobara
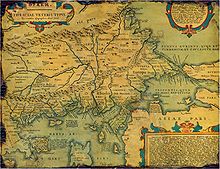
Unknown names[]
- Aghireșu
- Ardan
- Ardeu
- Arpașu de Sus
- Augustin
- Băile Tușnad
- Băleni-Români
- Bănița
- Bâzdâna
- Beidaud
- Bocșa
- Boroșneu Mic
- Boșorod
- Botfei
- Breaza
- Bretea Mureșană
- Bucium
- Căpâlna
- Cernat
- Cetățeni
- Cioclovina
- Clopotiva
- "Costești-Blidaru"
- "Costești-Cetățuie"
- Cotnari
- Coțofenii din Dos
- Covasna
- Cozia
- Crăsanii de Jos
- Crivești
- Crizbav
- Cuciulata
- "Cucuiș - Dealul Golu"
- "Cucuiș - Vârful Berianului"
- Cugir
- Cârlomănești
- Dalboșeț
- Densuș
- Divici
- Drajna de Sus
- Dumitrița
- Eliseni
- Feldioara
- "Fețele Albe"
- Grădiștea de Munte
- Iedera de Jos
- Feleac
- Jigodin
- Liubcova
- Mala Kopania
- Marca
- Mataraua
- Merești
- Moinești
- Monariu
- Monor
- Moșna
- Ocolișu Mic
- Odorheiu Secuiesc
- Olteni
- Orăștie Mountains
- Petrila
- Petroșani
- "Piatra Roșie"
- Pietroasa Mică
- Pinticu
- Pisculești
- Poiana cu Cetate
- Polovragi
- Ponor
- Popești (Călărași)
- Porumbenii Mari
- Praid
- Racoș
- Racu
- Radovanu - Gorgana I
- Radovanu - Jidovescu
- Roadeș
- Rovinari
- Rușor
- Sacalasău
- Satu Mare (Harghita)
- Satu Nou
- Sânzieni
- Seimeni
- Socol
- Sprâncenata
- Stâncești
- Stoina
- Șeica Mică
- Tășad
- Telița
- Teliu
- Tilișca
- Timișu de Jos
- Turia
- Unip
- Uroi
- Valea Seacă
- Viișoara Moșneni
- Zemplín
- Zetea
Thraco-Illyrian[]
- Scupi of the Dardani tribe
- Sirmium
Greek[]
Thrace, from Strymon to Nestos[]
- Amphipolis, founded by colonists from Athens
- Akontisma[33]
- [33]
- , modern Kilkis
- Datos, founded by colonists from Thasos[34]
- Drabeskos[33]
- Eion, founded by colonists from Athens
- [33]
- , founded by colonists from Thasos[35]
- [33]
- Krenides, founded by colonists from Thasos[34]
- Mastira, mentioned by Demosthenes (341 BCE) in his "The Oration on the State of the Chersonesus". This town was unknown to the scholar Harpocration (100-200 CE), who suggests that instead of "Mastira" we should read "", a known Thracian town of that name.
- Myrkinos, founded by colonists from Miletus[36] in 497 BC
- Neapolis, founded by colonists from Thasos,[37] modern Kavala
- Oesyme, founded by colonists from Thasos[36]
- [38]
- [38]
- Phagres, founded by colonists from Thasos[37]
- Philippi, founded by Philip II of Macedon,[37] rebuilt Crenides
- Pistyros, founded by colonists from Thasos[39]
- Sirra, founded by Philip II of Macedon,[37] rebuilt town of the , modern Serres
- [38]
- [38]
- [38]
Thrace, from Nestos to Hebros[]
- Abdera, founded by colonists from Klazomenai[40]
- Ainos (Poltymbria) founded by colonists from , Mytilene, and Kyme[41]
- Bergepolis,[37] founded by colonists from Abdera
- Doriskos[37]
- Drys, founded by colonists from Samothrace
- Dikaia, founded by colonists from Samos[42]
- Kypsela[37]
- Larissa[43]
- Maroneia, founded by colonists from Chios[42]
- Menebria, founded by colonists from Samothrace[44] on a town named Melsambria, modern Nessebar
- Orthagoria[37]
- Sale, founded by colonists from Samothrace[37]
- Stryme, founded from colonists from Thasos[45]
- Zone, founded by colonists from Samothrace[37]
Inland Thrace[]
- Alexandropolis Maedica[46]
- Beroea, founded by Phillip II of Macedon[47][48][49][50] in 342 BC
- Philippopolis| Pulpudeva (Philippopolis), today's city of Plovdiv in Bulgaria, founded by Philip II of Macedon in a town formerly called Eumolpias.[51]
- , founded by colonists from Istiaia, modern Asenovgrad
- Pistiros,[52] founded by Pistyrians from the coast
Thracian Chersonesos[]
- Aegospotami (Aegospotamos)[53]
- Alokopennesos, founded by colonists from Aeolis[37]
- Araplos[37]
- Callipolis
- Chersonesos (Agora), founded by colonists from Athens[37]
- Derris[37]
- Elaious, founded by colonists from Athens[54]
- Ide[37]
- Kardia, founded by colonists from Athens[54]
- Kressa[37]
- Krithotai, founded by colonists from Athens
- Limnae, founded by colonists from Miletus[55][56]
- Madytos, founded by colonists from Lesbos[37]
- Pactya, founded by colonists from Athens[37]
- Paion[37]
- Sestos, founded by colonists from Lesbos[57]
Propontic Thrace[]
- Athyra[58][59]
- Byzantion, founded by colonists from Megara on a town called Lygos, modern Istanbul
- Bisanthe, founded by colonists from Samos[60]
- Daminon Teichos[61]
- Ergiske[62]
- Heraclea (Perinthus)[citation needed]
- Heraion, founded by colonists from Samos[63]
- Lysimachia[citation needed]
- Neapolis (Thracian Chersonese), founded by colonists from Athens
- Orestias, rebuilt
- Perinthus, founded by colonists from Samos[37]
- Rhaedestus[citation needed], founded by colonists from Samos
- Serrion Teichos[37]
- Selymbria, modern Silivri in European Turkey,[25] of Thracian etymology
- Tyrodiza,[64][65] of Thracian etymology
West Pontic coast[]
- Aegyssos, modern Tulcea[66]
- Aquae Calidae
- Ahtopol, founded by colonists from Athens
- Anchialos, modern Pomorie, founded by colonists from Appolonia
- Apollonia, modern Sozopol, founded by Ionians[37]
- Berga, founded by colonists from Thasos[37]
- Bizone, founded by colonists from Miletus,[37] modern Kavarna
- Krutoi, modern Balchik founded by Miletian colonists
- Dionysopolis, modern Balchik, founded by colonists from Miletus[37]
- Heliopolis, modern Obzor
- Histria, founded by colonists from Miletus[37]
- Kallatis (Callatis), founded from colonists from Herakleia Pontike,[67] modern-day Mangalia, Romania
- Mesembria, modern Nesebar, settled during the 6th century BC by Dorians from Megara
- Odessos, modern Varna, founded by colonists from Miletus[68]
- Nikonion, founded by colonists from Istros[37]
- Salmydessos (from IE *salm-udes, "salty water"; cf. Greek álmē, "sea water, brine"; ýdos, "water")[69]
- Tomis, modern Constanta, rebuilt Scythian town
Other[]
- [citation needed]
- , founded by colonists from Athens,[37]
- Gazoros
- Heraclea Sintica[70] on a tribe of the Sintoi tribe
- [citation needed]
Persian[]
- Boryza (city)[71][72]
- Doriscus
Roman[]
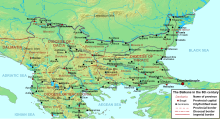
- Abritus
- Acumincum
- ()
- Appiaria
- Apros
- Augusta Traiana (formerly Beroe, later Stara Zagora)
- Burgenae
- Caenophrurium
- Deultum, rebuilt Debelt
- Doracium
- , modern Silistra
- Drobeta
- Gensis
- Hadrianople, rebuild Uscudama
- Justiniana Prima
- Margus
- Marcianopolis, modern Devnya
- Maximianopolis
- Morisena
- Montana
- Nicopolis ad Istrum
- Nicopolis ad Nestum, rebuilt Alexandrupolis
- Novae
- Oescus
- Pautalia, modern Kyustendil
- Pescium, modern Peć
- Plotinopolis, modern ,
- Porolissum
- , modern Ruse
- Sirmium
- Theranda
- Traianopolis
- Transmarisca, modern Tutrakan
- Tropaeum Traiani
- Turres, modern Pirot
- Ulmetum
- Ulpiana
- Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa
- Valve, modern Vratsa
- Vicianum, modern Vučitrn
- Viminacium
- Zaldapa
- Zikideva
- the rest after conquest
Celtic[]
- Dunonia, modern Vidin
- Malata
- Naissus, modern Niš
- Noviodunum
- Serdica, modern Sofia
- Singidunum, modern Belgrade
- Taurunum
- Tylis
See also[]
- List of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia
- List of rulers of Thrace and Dacia
- List of ancient cities in Illyria
- List of rulers of Illyria
- Dacian Dava
- Dacian Fortresses of the Orăştie Mountains
- Tabula Peutingeriana
- Notitia Dignitatum
Notes[]
- ^ The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,ISBN 0-521-22717-8, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in villages and hamlets..."
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 888, "It was meant to be a polis but this was no reason to think that it was anything other than a native settlement."
- ^ Jump up to: a b The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 by Christopher Webber, ISBN 1-84176-329-2, 2001, page 1, "...the city of Seuthopolis seems to be the only significant town in Thrace not built by Greeks..."
- ^ The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond, ISBN 0-521-22717-8, 1992, page 612: "According to Strabo (vii.6.1cf.st.Byz.446.15) the Thracian -bria word meant polis but it is an inaccurate translation."
- ^ Peregrine, Peter N.; Ember, Melvin (2001). Encyclopedia of Prehistory. 4 : Europe. Springer. ISBN 978-0-306-46258-0.
- ^ Polomé, Edgar Charles (1982). "20e". In Boardman, John. Balkan Languages (Illyrian, Thracian and Daco-Moesian). The Cambridge Ancient History. Vol. 3, Part 1: The Prehistory of the Balkans; and the Middle East and the Aegean world, tenth to eighth centuries B.C. (2nd ed.). London: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-22496-3.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w Grumeza 2009, p. 13.
- ^ Velkov 1977, p. 92.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Olteanu.
- ^ *Procopii Caesariensis opera omnia. Edited by J. Haury; revised by G. Wirth. 3 vols. Leipzig: Teubner, 1976-64. Greek text.
- ^ TSR9, Proc. 123. 26
- ^ Schütte 1917, p. 96.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Grumeza 2009, p. 12.
- ^ Grumeza 2009, p. 88.
- ^ A History of the Byzantine State and Society by Warren Treadgold, 1997, page 419: "...Internal Reforms, 780-842 419 army, refounding Thracian Beroea under the name of Irenopolis, and reaching Philippopolis..."
- ^ "The Cambridge Ancient History 1992, page 612"
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h Grumeza 2009, p. 14.
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 856, "A thracian settlement"
- ^ History of Rome, VII, Books 26-27 (Loeb Classical Library No. 367) by Livy and Frank Gardner Moore, 1943, page 96: "... waste the country and to besiege the city of Iamphorynna, the capital and citadel of Maedica..."
- ^ http://www.novinite.com/articles/168495/Kabile%3A+When+One+Is+Curious, kabileti tribe
- ^ The History of Rome, Volume 4 by Theodor Mommsen, 2009, page 53: "... defeated the Bessi in their mountains, took their capital Uscudama (Adrianople), and compelled them to submit to the Roman supremacy."
- ^ Valeva, Julia; Nankov, Emil; Graninger, Denver (15 June 2015). A Companion to Ancient Thrace. ISBN 9781444351040.
- ^ Ethnic continuity in the Carpatho-Danubian area by Elemér Illyés, 1988, ISBN 0-88033-146-1, page 223
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 8 August 2016. Retrieved 31 May 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 465: "Megara was principal or sole founder of...Kalchedo...Selymbria...Byzantion...Astakos...Herakleia pontike and possible Olbia..."
- ^ A New Classical Dictionary of Greek And Roman Biography, Mythology And Geography V2, 2006, ISBN 1-4286-4561-6, page 196, "Subzupara (now in Zarvi), a town in Thrace on the road from Phillipopolis to Hadrianopolis..."
- ^ [1]
- ^ "МИГДОНИЯ - В. Д. Гладкий. Древний мир. Энциклопедический словарь в 2-х томах - История".
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 18 June 2015. Retrieved 31 May 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ Lepper, F. A. (1988). Trajan's Column: A New Edition of the Cichorius Plates. Alan Sutton. p. 138. ISBN 9780862994679.
Stuart Jones noted the Dacian - sounding place - name ' Thermidava ' on the Lissus Naissus road : but see Miller col . 557, for the evidence on this. The place was most probably called ' Theranda ' and there is no evidence for any settlement there of pro-Roman Dacians now, nor is it very likely. (..) Most scholars, however, have supposed, as did Cichorius, that we are now north of the Danube, somewhere in the Banat area where the local inhabitants are frightened that they may lose their recently acquired 'liberty'.
- ^ The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 1: The Prehistory of the Balkans, the Middle East and the Aegean World, Tenth to Eighth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, N. G. L. Hammond, and E. Sollberger,1982, page 876: "... proper and the southern Danube borderland, e.g. in Bessapara, Keipenapa, Tranupara; of -dita 'fortified town', found only in Thracia proper; ..."
- ^ Taylor & 2001 214.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 856
- ^ Jump up to: a b An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 855: "The Thasians... they founded Krenides and Daton"
- ^ Hatzfeld, Jean. History of Ancient Greece (trans. by Andre Aymard, 1968, W.W. Norton & Co., New York), pp. 34–35.
- ^ Jump up to: a b An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 782, "The Thasians are said to have colonised the Hedonian city of Myrkinos, Galepsos and Oisyme..."
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, Index
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 857
- ^ Readings in Greek History: Sources and Interpretations by D. Brendan Nagle and Stanley M. Burstein, 2006, page 232: A GREEK TRADING POST IN THRACE"... Maronea, Apollonia, and Thasos living in the trading post of Pistiros."
- ^ The Histories, by Herodotus, Carolyn Dewald, and Robin Waterfield, 2008, page 442: "... bed of the Lisus, Xerxes passed the Greek towns of Maronea, Dicaea, and Abdera. His route also took him past a..."
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 870: "Colonists from Mytilene and Kyme founded Ainos"
- ^ Jump up to: a b The Histories by Herodotus, Carolyn Dewald, and Robin Waterfield, 2008, page 442: "... bed of the Lisus, Xerxes passed the Greek towns of Maronea, Dicaea, and Abdera. His route also took him past a ..."
- ^ Back Matter: "... sites identified solely by coins' location site Thessaly, Atrax, Kieron, Larissa, Thrace, Ainos, Bizye, Byzantium, Deultum, Maroneia, Mesembra, Pantalia..."
- ^ Hammond Concise Atlas of World History by Geoffrey Barraclough, 2001, Index, "Mesembria/Greek Colony"
- ^ The Histories, by Herodotus, John M. Marincola, and Aubery de Selincourt, 2003, page 451: "... most westerly of which is Mesembria; the next place is Stryme, a town belonging to the Thasians. ..."
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 892
- ^ Women and slaves in Greco-Roman culture: differential equations, by Sandra Rae Joshel, Sheila Murnaghan, 1998, page 214: "Philip II founded cities at Beroe, Kabyle, and Philippopolis in 342/1, and Aegean-style urban life began to penetrate Thrace."
- ^ Late Roman villas in the Danube-Balkan region, by Lynda Mulvin, 2002, page 19: "Other roads went through Beroe (founded by Philip II of Macedon)"
- ^ Philip of Macedon, by Louïza D. Loukopoulou, 1980, page 98: "Upriver in the valley between the Rhodope and Haimos Philip founded Beroe (Stara Zagora) and Philippolis (Plovdiv)."
- ^ Velkov 1977, p. 128.
- ^ From Mycenae to Constantinople: Major Cities of the Greek and Roman World, by Richa Tomlinson, 1992, page 8: "...this means, a Macedonian city established in a non-Macedonian area (Philippopolis in Thrace, for example) becomes a means of establishing a..."
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 895: "The emporion of Pistiros was an inland trading station originally founded by merchants coming from the polis of Pistiros a dependency of Thasos situated piston the Thracian coast"
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 903: "Aigos potamoi is called a deserted polichne by Strabo and a polis by Steph.Byz."
- ^ Jump up to: a b An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 636: "In the archaic period Athens colonised Sigeion, Elaious, Chersonesus, Paktye, Sestus, Kardia..."
- ^ The Penguin Historical atlas of Ancient Greece by Robert Morkot, page 48
- ^ "Texas edu Colonies and Metropoleis". Archived from the original on 25 January 2012. Retrieved 27 August 2009.
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 910: "Sestos was colonised by Lesbians"
- ^ Ancient Greek Colonies in the Black Sea 2, Dēmētrios V. Grammenos, ISBN 1-4073-0110-1, 2007, page 1182
- ^ Velkov 1977, p. 124.
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 914: "Bisanthe was a colony founded by the Samians"
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 918
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 913
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 919: "Heraion Teichos was a colony of Samos"
- ^ a town near Perinthus, Xerxes' commissariat there: Hdt. 7.25
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 912: "The European coast of Propontis was settled by Megarians and Samians.By 480 four colonies are recorded; viz from the east to the west, Megarian Byzantion and Selymbria and Samian Perinthos and Bisanthe along with two smaller and presumably dependant settlements, Tyrodiza and Heraion."
- ^ Grumeza 2009, p. 132.
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 934: "Kallatis was colonized by Herakleia"
- ^ A Companion to Archaic Greece, by Kurt A. Raaflaub and Hans van Wees, 2009, page 337: "... On the western shore, Odessos was founded by the Milesians, and the expansion of existing Greek cities in the western ..."
- ^ Katičic', Radoslav. Ancient Languages of the Balkans, Part One. Paris: Mouton, 1976: 147
- ^ The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 6: The Fourth Century BC, by D. M. Lewis, page 469: "Philip's new foundation at Heracle Sintica"
- ^ The Greek Wars: The Failure of Persia, by George Cawkwell, 2006, page 58: "... 'The lands beyond the sea' Persian city, Boryza' on the Black Sea coast (FGH t Fí66) but that ..."
- ^ An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 891, "Note that the only one which is explicitly called a polis by Hekataios is Boryza (fr.166) and here we learn that it is a polis inhabited by Persians i.e not by Greeks or Thracians."
References[]
- (2009). Dacia: Land of Transylvania, Cornerstone of Ancient Eastern Europe. Hamilton Books. ISBN 978-0-7618-4465-5.
The shores of the Danube were well monitored from the Dacian fortresses Acidava, Buricodava, Dausadava (the shrine of the wolves), Diacum, Drobeta (Turnu Severin), Nentivava (Oltenia), Suvidava (Corabia), Tsirista, Tierna/Dierna (Orsova) and what is today Zimnicea. Downstream were also other fortresses: Axiopolis (Cernadova), Barbosi, Buteridava, Capidava(Topalu), Carsium(Harsova), Durostorum(Silistra), Sacidava/Sagadava (Dunareni) along with still others...
[better source needed] - Olteanu, Sorin. "Linguae Thraco-Daco-Moesorum - Toponyms Section". Linguae Thraco-Daco-Moesorum (in Romanian and English). Archived from the original on 16 July 2011. Retrieved 8 December 2010.[self-published source?]
- Schütte, Gudmund (1917). Ptolemy's maps of northern Europe: a reconstruction of the prototypes. Copenhagen: .
- Taylor, Timothy (2001). Northeastern European Iron Age. Springer Published in conjunction with the Human Relations Area Files. ISBN 978-0-306-46258-0.
- (1977). The cities in Thrace and Dacia in late antiquity: (studies and materials). . ISBN 90-256-0723-3.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ancient Thrace and Ancient Thracians. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dacia and Dacians. |
- Durdinov, Ivan. "The Language of the Thracians".
- Sorin Olteanu's Project: Linguae Thraco-Daco-Moesorum - Toponyms Section
- Duridanov's paper on Thracian toponyms
- Placenames in the Compilation 'notitia dignitatum' (Cnd)
- Lists of Dacian fortresses, towns and citadels
- Dacia
- Dacian Map[permanent dead link]
- Thracians and Dacians
- Thracians 700-46 BC
- Geography of ancient Thrace
- Dacian towns
- Ancient Thrace
- Celtic towns
- Thracian towns
- Greek colonies in Thrace
- Greek colonization
- Former populated places in the Balkans
- Archaeological sites in Romania
- Balkans-related lists
