List of mammals of China

This is a list of the mammal species recorded in China. There are 495 mammal species in China, of which thirteen are critically endangered, twenty-four are endangered, forty-seven are vulnerable, and seven are near threatened. One of the species listed for China can no longer be found in the wild.[1]
The following tags are used to highlight each species' conservation status as assessed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature:
| EX | Extinct | No reasonable doubt that the last individual has died. |
| EW | Extinct in the wild | Known only to survive in captivity or as a naturalized populations well outside its previous range. |
| CR | Critically endangered | The species is in imminent risk of extinction in the wild. |
| EN | Endangered | The species is facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. |
| VU | Vulnerable | The species is facing a high risk of extinction in the wild. |
| NT | Near threatened | The species does not meet any of the criteria that would categorise it as risking extinction but it is likely to do so in the future. |
| LC | Least concern | There are no current identifiable risks to the species. |
| DD | Data deficient | There is inadequate information to make an assessment of the risks to this species. |
Some species were assessed using an earlier set of criteria. Species assessed using this system have the following instead of near threatened and least concern categories:
| LR/cd | Lower risk/conservation dependent | Species which were the focus of conservation programmes and may have moved into a higher risk category if that programme was discontinued. |
| LR/nt | Lower risk/near threatened | Species which are close to being classified as vulnerable but are not the subject of conservation programmes. |
| LR/lc | Lower risk/least concern | Species for which there are no identifiable risks. |
Order: Sirenia (manatees and dugongs)[]

Sirenia is an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit rivers, estuaries, coastal marine waters, swamps, and marine wetlands. All four species are endangered.
- Family: Dugongidae
- Genus: Dugong
- Dugong, D. dugon VU[2]
- Genus: Dugong
Order: Proboscidea (elephants)[]

The elephants comprise three living species and are the largest living land animals.
- Family: Elephantidae (elephants)
- Genus: Elephas
- Asian elephant, E. maximus EN[3]
- Indian elephant, E. m. indicus
- Asian elephant, E. maximus EN[3]
- Genus: Elephas
Order: Scandentia (treeshrews)[]
The treeshrews are small mammals native to the tropical forests of Southeast Asia. Although called treeshrews, they are not true shrews and are not all arboreal.
- Family: Tupaiidae (tree shrews)
- Genus: Tupaia
- Northern treeshrew, T. belangeri LC[4]
- Genus: Tupaia
Order: Primates[]

The order Primates contains humans and their closest relatives: lemurs, lorisoids, monkeys, and apes.
- Suborder: Strepsirrhini
- Infraorder: Lemuriformes
- Superfamily: Lorisoidea
- Infraorder: Lemuriformes
- Suborder: Haplorhini
- Infraorder: Simiiformes
- Parvorder: Catarrhini
- Superfamily: Cercopithecoidea
- Family: Cercopithecidae (Old World monkeys)
- Genus: Macaca
- Subfamily: Colobinae
- Genus: Semnopithecus
- Nepal gray langur, S. schistaceus LC[10]
- Genus: Trachypithecus
- Indochinese grey langur, T. crepusculus EN
- Francois' langur, T. francoisi EN
- Shan State langur, T. melamera EN
- Bonneted langur, T. pileatus VU
- White-headed langur, T. leucocephalus CR
- Genus: Rhinopithecus
- Black snub-nosed monkey, R. bieti EN
- Gray snub-nosed monkey, R. brelichi EN
- Golden snub-nosed monkey, R. roxellana EN
- Genus: Semnopithecus
- Family: Cercopithecidae (Old World monkeys)
- Superfamily: Hominoidea
- Family: Hylobatidae (gibbons)
- Genus: Hoolock
- Genus: Hylobates
- Lar gibbon, H. lar EN[14]
- Genus: Nomascus
- Black crested gibbon, N. concolor CR
- Hainan black crested gibbon, N. hainanus CR[15]
- White-cheeked crested gibbon, N. leucogenys CR
- Eastern black crested gibbon, N. nasutus CR
- Family: Hylobatidae (gibbons)
- Superfamily: Cercopithecoidea
- Parvorder: Catarrhini
- Infraorder: Simiiformes
Order: Rodentia (rodents)[]






Rodents make up the largest order of mammals, with over 40% of mammalian species. They have two incisors in the upper and lower jaw which grow continually and must be kept short by gnawing. Most rodents are small though the capybara can weigh up to 45 kg (99 lb).
- Suborder: Hystricognathi
- Suborder: Sciurognathi
- Family: Castoridae (beavers)
- Genus: Castor
- Eurasian beaver, C. fiber LC[18]
- Genus: Castor
- Family: Sciuridae (squirrels)
- Subfamily: Ratufinae
- Genus: Ratufa
- Black giant squirrel, Ratufa bicolor
- Genus: Ratufa
- Subfamily: Sciurinae
- Tribe: Sciurini
- Genus: Sciurus
- Red squirrel, S. vulgaris LC[19]
- Genus: Sciurus
- Tribe: Pteromyini
- Genus: Aeretes
- Groove-toothed flying squirrel, Aeretes melanopterus
- Genus: Belomys
- Hairy-footed flying squirrel, Belomys pearsonii
- Genus: Hylopetes
- Particolored flying squirrel, Hylopetes alboniger EN
- Indochinese flying squirrel, Hylopetes phayrei
- Genus: Petaurista
- Red and white giant flying squirrel, Petaurista alborufus
- Spotted giant flying squirrel, Petaurista elegans
- Japanese giant flying squirrel, Petaurista leucogenys
- Bhutan giant flying squirrel, Petaurista nobilis
- Red giant flying squirrel, Petaurista petaurista
- Indian giant flying squirrel, Petaurista philippensis
- Chinese giant flying squirrel, Petaurista xanthotis
- Genus: Pteromys
- Siberian flying squirrel, Pteromys volans
- Genus: Trogopterus
- Complex-toothed flying squirrel, Trogopterus xanthipes EN
- Genus: Aeretes
- Tribe: Sciurini
- Subfamily: Callosciurinae
- Genus: Callosciurus
- Pallas's squirrel, Callosciurus erythraeus
- Inornate squirrel, Callosciurus inornatus
- Phayre's squirrel, Callosciurus phayrei
- Irrawaddy squirrel, Callosciurus pygerythrus VU
- Anderson's squirrel, Callosciurus quinquestriatus VU
- Genus: Dremomys
- Orange-bellied Himalayan squirrel, Dremomys lokriah
- Perny's long-nosed squirrel, Dremomys pernyi
- Red-hipped squirrel, Dremomys pyrrhomerus
- Asian red-cheeked squirrel, Dremomys rufigenis
- Genus: Tamiops
- Himalayan striped squirrel, Tamiops macclellandi
- Maritime striped squirrel, Tamiops maritimus
- Swinhoe's striped squirrel, Tamiops swinhoei
- Genus: Callosciurus
- Subfamily: Xerinae
- Tribe: Marmotini
- Genus: Marmota
- Gray marmot, Marmota baibacina
- Long-tailed marmot, Marmota caudata
- Himalayan marmot, Marmota himalayana
- Tarbagan marmot, Marmota sibirica
- Genus: Sciurotamias
- Père David's rock squirrel, Sciurotamias davidianus
- Forrest's rock squirrel, Sciurotamias forresti VU
- Genus: Spermophilus
- Alashan ground squirrel, Spermophilus alashanicus
- Daurian ground squirrel, Spermophilus dauricus
- Red-cheeked ground squirrel, Spermophilus erythrogenys
- Yellow ground squirrel, Spermophilus fulvus
- Long-tailed ground squirrel, Spermophilus undulatus
- Genus: Tamias
- Siberian chipmunk, Tamias sibiricus
- Genus: Marmota
- Tribe: Marmotini
- Subfamily: Ratufinae
- Family: Gliridae (dormice)
- Subfamily: Leithiinae
- Genus: Dryomys
- Forest dormouse, Dryomys nitedula
- Genus: Chaetocauda
- Chinese dormouse, Chaetocauda sichuanensis EN
- Genus: Dryomys
- Subfamily: Leithiinae
- Family: Dipodidae (jerboas)
- Subfamily: Allactaginae
- Genus: Allactaga
- Balikun jerboa, Allactaga balikunica
- Gobi jerboa, Allactaga bullata
- Small five-toed jerboa, Allactaga elater
- Mongolian five-toed jerboa, Allactaga sibirica
- Genus: Pygeretmus
- Dwarf fat-tailed jerboa, Pygeretmus pumilio
- Genus: Allactaga
- Subfamily: Cardiocraniinae
- Genus: Cardiocranius
- Five-toed pygmy jerboa, Cardiocranius paradoxus VU
- Genus: Salpingotus
- Thick-tailed pygmy jerboa, Salpingotus crassicauda VU
- Kozlov's pygmy jerboa, Salpingotus kozlovi
- Genus: Cardiocranius
- Subfamily: Dipodinae
- Genus: Dipus
- Northern three-toed jerboa, Dipus sagitta
- Genus: Stylodipus
- Andrews's three-toed jerboa, Stylodipus andrewsi
- Mongolian three-toed jerboa, Stylodipus sungorus
- Thick-tailed three-toed jerboa, Stylodipus telum
- Genus: Dipus
- Subfamily: Euchoreutinae
- Genus: Euchoreutes
- Long-eared jerboa, Euchoreutes naso EN
- Genus: Euchoreutes
- Subfamily: Sicistinae
- Genus: Sicista
- Long-tailed birch mouse, Sicista caudata EN
- Chinese birch mouse, Sicista concolor
- Southern birch mouse, Sicista subtilis
- Tien Shan birch mouse, Sicista tianshanica
- Genus: Sicista
- Subfamily: Zapodinae
- Genus: Eozapus
- Chinese jumping mouse, Eozapus setchuanus VU
- Genus: Eozapus
- Subfamily: Allactaginae
- Family: Platacanthomyidae
- Genus: Typhlomys
- Chinese pygmy dormouse, Typhlomys cinereus
- Genus: Typhlomys
- Family: Spalacidae
- Subfamily: Myospalacinae
- Genus: Eospalax
- Chinese zokor, Eospalax fontanierii VU
- Rothschild's zokor, Eospalax rothschildi
- Smith's zokor, Eospalax smithii
- Genus: Myospalax
- False zokor, Myospalax aspalax
- Transbaikal zokor, Myospalax psilurus
- Genus: Eospalax
- Subfamily: Rhizomyinae
- Genus: Cannomys
- Lesser bamboo rat, Cannomys badius
- Genus: Rhizomys
- Hoary bamboo rat, Rhizomys pruinosus
- Chinese bamboo rat, Rhizomys sinensis
- Large bamboo rat, Rhizomys sumatrensis
- Genus: Cannomys
- Subfamily: Myospalacinae
- Family: Cricetidae
- Subfamily: Cricetinae
- Genus: Allocricetulus
- Mongolian hamster, Allocricetulus curtatus
- Genus: Cansumys
- Gansu hamster, Cansumys canus
- Genus: Cricetulus
- Tibetan dwarf hamster, Cricetulus alticola
- Chinese striped hamster, Cricetulus barabensis
- Kam dwarf hamster, Cricetulus kamensis
- Long-tailed dwarf hamster, Cricetulus longicaudatus
- Grey dwarf hamster, Cricetulus migratorius
- Sokolov's dwarf hamster, Cricetulus sokolovi
- Genus: Cricetus
- European hamster, C. cricetus CR presence uncertain
- Genus: Phodopus
- Campbell's dwarf hamster, Phodopus campbelli
- Djungarian hamster, Phodopus sungorus
- Roborovski hamster, Phodopus roborovskii
- Genus: Tscherskia
- Greater long-tailed hamster, Tscherskia triton
- Genus: Allocricetulus
- Subfamily: Arvicolinae
- Genus: Alticola
- Silver mountain vole, Alticola argentatus
- Gobi Altai mountain vole, Alticola barakshin
- Royle's mountain vole, Alticola roylei
- Stolička's mountain vole, Alticola stoliczkanus
- Strachey's mountain vole, Alticola stracheyi
- Flat-headed vole, Alticola strelzowi
- Genus: Arvicola
- Water vole, Arvicola terrestris
- Genus: Clethrionomys
- Tien Shan red-backed vole, Clethrionomys centralis
- Bank vole, Clethrionomys glareolus
- Grey red-backed vole, Clethrionomys rufocanus
- Northern red-backed vole, Clethrionomys rutilus
- Genus: Ellobius
- Zaisan mole vole, Ellobius tancrei
- Genus: Eolagurus
- Yellow steppe lemming, Eolagurus luteus
- Przewalski's steppe lemming, Eolagurus przewalskii
- Genus: Eothenomys
- Pratt's vole, Eothenomys chinensis
- Southwest China vole, Eothenomys custos
- Ganzu vole, Eothenomys eva
- Kolan vole, Eothenomys inez
- Père David's vole, Eothenomys melanogaster
- Chaotung vole, Eothenomys olitor
- Yulungshan vole, Eothenomys proditor
- Shansei vole, Eothenomys shanseius
- Genus:
- Steppe lemming, Lagurus lagurus
- Genus: Lasiopodomys
- Brandt's vole, Lasiopodomys brandtii
- Plateau vole, Lasiopodomys fuscus
- Mandarin vole, Lasiopodomys mandarinus
- Genus: Microtus
- Field vole, Microtus agrestis
- Reed vole, Microtus fortis
- Narrow-headed vole, Microtus gregalis
- Chinese scrub vole, Microtus irene
- Juniper vole, Microtus juldaschi
- Blyth's vole, Microtus leucurus
- Lacustrine vole, Microtus limnophilus
- Maximowicz's vole, Microtus maximowiczii
- Mongolian vole, Microtus mongolicus
- Common vole, Microtus arvalis
- Sikkim vole, Microtus sikimensis
- Social vole, Microtus socialis
- Genus: Myopus
- Wood lemming, Myopus schisticolor
- Genus: Proedromys
- Duke of Bedford's vole, Proedromys bedfordi
- Genus: Volemys
- Clarke's vole, Volemys clarkei
- Szechuan vole, Volemys millicens
- Marie's vole, Volemys musseri
- Genus: Alticola
- Subfamily: Cricetinae
- Family: Muridae (mice, rats, voles, gerbils, hamsters)
- Subfamily: Gerbillinae
- Genus: Brachiones
- Przewalski's gerbil, Brachiones przewalskii
- Genus: Meriones
- Cheng's jird, Meriones chengi CR
- Libyan jird, Meriones libycus LC
- Midday jird, Meriones meridianus
- Tamarisk jird, Meriones tamariscinus
- Mongolian gerbil, Meriones unguiculatus
- Genus: Rhombomys
- Great gerbil, Rhombomys opimus
- Genus: Brachiones
- Subfamily: Murinae
- Genus: Apodemus
- Striped field mouse, Apodemus agrarius
- Chevrier's field mouse, Apodemus chevrieri
- South China field mouse, Apodemus draco
- Sichuan field mouse, Apodemus latronum
- Korean field mouse, Apodemus peninsulae
- Ural field mouse, Apodemus uralensis
- Genus: Bandicota
- Greater bandicoot rat, Bandicota indica
- Genus: Berylmys
- Bower's white-toothed rat, Berylmys bowersi
- Kenneth's white-toothed rat, Berylmys mackenziei
- Genus: Chiropodomys
- Pencil-tailed tree mouse, Chiropodomys gliroides
- Genus: Dacnomys
- Millard's rat, Dacnomys millardi
- Genus: Hadromys
- Manipur bush rat, Hadromys humei
- Genus: Hapalomys
- Delacour's marmoset rat, Hapalomys delacouri
- Genus: Leopoldamys
- Edwards's long-tailed giant rat, Leopoldamys edwardsi
- Genus: Micromys
- Harvest mouse, Micromys minutus
- Genus: Mus
- Ryukyu mouse, Mus caroli
- Cook's mouse, Mus cookii
- Gairdner's shrewmouse, Mus pahari
- Genus: Nesokia
- Short-tailed bandicoot rat, Nesokia indica LC
- Genus: Niviventer
- Anderson's white-bellied rat, Niviventer andersoni
- Chinese white-bellied rat, Niviventer confucianus
- Smoke-bellied rat, Niviventer eha
- Large white-bellied rat, Niviventer excelsior
- Chestnut white-bellied rat, Niviventer fulvescens
- Genus: Rattus
- Lesser ricefield rat, Rattus losea
- Himalayan field rat, Rattus nitidus
- Brown rat, Rattus norvegicus
- Sikkim rat, Rattus sikkimensis VU
- Tanezumi rat, Rattus tanezumi
- Turkestan rat, Rattus turkestanicus
- Genus: Vandeleuria
- Asiatic long-tailed climbing mouse, Vandeleuria oleracea
- Genus: Vernaya
- Red climbing mouse, Vernaya fulva VU
- Genus: Apodemus
- Subfamily: Gerbillinae
- Family: Castoridae (beavers)
Order: Lagomorpha (lagomorphs)[]


The lagomorphs comprise two families, Leporidae (hares and rabbits), and Ochotonidae (pikas). Though they can resemble rodents, and were classified as a superfamily in that order until the early 20th century, they have since been considered a separate order. They differ from rodents in a number of physical characteristics, such as having four incisors in the upper jaw rather than two.
- Family: Ochotonidae (pikas)
- Genus: Ochotona
- Alpine pika, Ochotona alpina
- Helan Shan pika, Ochotona argentata CR
- Gansu pika, Ochotona cansus
- Black-lipped pika, Ochotona curzoniae
- Daurian pika, Ochotona dauurica
- Chinese red pika, Ochotona erythrotis
- Forrest's pika, Ochotona forresti
- Gaoligong pika, Ochotona gaoligongensis DD
- Glover's pika, Ochotona gloveri
- Himalayan pika, Ochotona himalayana
- Northern pika, Ochotona hyperborea
- Ili pika, Ochotona iliensis VU
- Koslov's pika, Ochotona koslowi EN
- Ladak pika, Ochotona ladacensis
- Large-eared pika, Ochotona macrotis
- Muli pika, Ochotona muliensis DD
- Nubra pika, Ochotona nubrica
- Pallas's pika, Ochotona pallasi
- Royle's pika, Ochotona roylei
- Turkestan red pika, Ochotona rutila
- Moupin pika, Ochotona thibetana
- Thomas's pika, Ochotona thomasi
- Genus: Ochotona
- Family: Leporidae (rabbits, hares)
- Genus: Lepus
Order: Erinaceomorpha (hedgehogs and gymnures)[]

The order Erinaceomorpha contains a single family, Erinaceidae, which comprise the hedgehogs and gymnures. The hedgehogs are easily recognised by their spines while gymnures look more like large rats.
- Family: Erinaceidae (hedgehogs)
- Subfamily: Erinaceinae
- Genus: Erinaceus
- Amur hedgehog, Erinaceus amurensis LR/lc
- Genus: Hemiechinus
- Long-eared hedgehog, Hemiechinus auritus LR/lc
- Genus: Mesechinus
- Daurian hedgehog, Mesechinus dauuricus LR/lc
- Hugh's hedgehog, Mesechinus hughi VU
- Genus: Erinaceus
- Subfamily: Galericinae
- Genus: Hylomys
- Hainan gymnure, Hylomys hainanensis EN
- Shrew gymnure, Hylomys sinensis LR/nt
- Short-tailed gymnure, Hylomys suillus LR/lc
- Genus: Hylomys
- Subfamily: Erinaceinae
Order: Soricomorpha (shrews, moles, and solenodons)[]



The "shrew-forms" are insectivorous mammals. Shrews and solenodons closely resemble mice, while moles are stout-bodied burrowers.
- Family: Soricidae (shrews)
- Subfamily: Crocidurinae
- Genus: Crocidura
- Asian gray shrew, Crocidura attenuata
- Southeast Asian shrew, Crocidura fuliginosa
- Gmelin's white-toothed shrew, Crocidura gmelini
- Gueldenstaedt's shrew, Crocidura gueldenstaedtii
- Horsfield's shrew, Crocidura horsfieldii
- Ussuri white-toothed shrew, Crocidura lasiura
- Taiga shrew, Crocidura pullata
- Asian lesser white-toothed shrew, Crocidura shantungensis DD
- Siberian shrew, Crocidura sibirica
- Lesser white-toothed shrew, Crocidura suaveolens
- Genus: Suncus
- Etruscan shrew, Suncus etruscus LC
- Asian house shrew, S. murinus LC[24]
- Genus: Crocidura
- Subfamily: Soricinae
- Tribe: Anourosoricini
- Genus: Anourosorex
- Chinese mole shrew, Anourosorex squamipes LR/lc
- Genus: Anourosorex
- Tribe: Blarinellini
- Genus: Blarinella
- Northern short-tailed shrew, Blarinella quadraticauda LR/lc
- Southern short-tailed shrew, Blarinella wardi LR/nt
- Genus: Blarinella
- Tribe: Nectogalini
- Genus: Chimarrogale
- Himalayan water shrew, Chimarrogale himalayica LR/lc
- Chinese water shrew, Chimarrogale styani LR/lc
- Genus: Nectogale
- Elegant water shrew, Nectogale elegans LR/lc
- Genus: Neomys
- Eurasian water shrew, Neomys fodiens LR/lc
- Genus: Episoriculus
- Hodgsons's brown-toothed shrew, Episoriculus caudatus LR/lc
- Long-tailed brown-toothed shrew, Episoriculus leucops LR/lc
- Long-tailed mountain shrew, Episoriculus macrurus LR/lc
- Genus: Chodsigoa
- De Winton's shrew, Chodsigoa hypsibius LR/lc
- Lamulate shrew, Chodsigoa lamula LR/lc
- Lowe's shrew, Chodsigoa parca LR/lc
- Salenski's shrew, Chodsigoa salenskii CR
- Smith's shrew, Chodsigoa smithii LR/lc
- Genus: Soriculus
- Himalayan shrew, Soriculus nigrescens LR/lc
- Genus: Chimarrogale
- Tribe: Soricini
- Genus: Sorex
- Tien Shan shrew, Sorex asper LR/lc
- Lesser striped shrew, Sorex bedfordiae LR/lc
- Laxmann's shrew, Sorex caecutiens LR/lc
- Gansu shrew, Sorex cansulus CR
- Greater stripe-backed shrew, Sorex cylindricauda EN
- Siberian large-toothed shrew, Sorex daphaenodon LR/lc
- Chinese highland shrew, Sorex excelsus DD
- Slender shrew, Sorex gracillimus LR/lc
- Taiga shrew, Sorex isodon LR/lc
- Kozlov's shrew, Sorex kozlovi CR
- Eurasian least shrew, Sorex minutissimus LR/lc
- Eurasian pygmy shrew, Sorex minutus LR/lc
- Ussuri shrew, Sorex mirabilis LR/lc
- Chinese shrew, Sorex sinalis VU
- Tibetan shrew, Sorex thibetanus LR/lc
- Tundra shrew, Sorex tundrensis LR/lc
- Genus: Sorex
- Tribe: Anourosoricini
- Subfamily: Crocidurinae
- Family: Talpidae (moles)
- Subfamily: Scalopinae
- Tribe: Scalopini
- Genus: Scapanulus
- Gansu mole, Scapanulus oweni LR/lc
- Genus: Scapanulus
- Tribe: Scalopini
- Subfamily: Talpinae
- Tribe: Scaptonychini
- Genus: Scaptonyx
- Long-tailed mole, Scaptonyx fusicaudus LR/lc
- Genus: Scaptonyx
- Tribe: Talpini
- Genus: Euroscaptor
- Greater Chinese mole, Euroscaptor grandis LR/lc
- Long-nosed mole, Euroscaptor longirostris LR/lc
- Himalayan mole, Euroscaptor micrura LR/lc
- Genus: Mogera
- Insular mole, Mogera insularis LR/lc
- Large mole, Mogera robusta LR/lc
- Genus: Parascaptor
- White-tailed mole, Parascaptor leucura LR/lc
- Genus: Scaptochirus
- Short-faced mole, Scaptochirus moschatus LR/lc
- Genus: Euroscaptor
- Tribe: Scaptonychini
- Subfamily: Uropsilinae
- Genus: Uropsilus
- Anderson's shrew mole, Uropsilus andersoni LR/lc
- Gracile shrew mole, Uropsilus gracilis LR/lc
- Inquisitive shrew mole, Uropsilus investigator EN
- Chinese shrew mole, Uropsilus soricipes EN
- Genus: Uropsilus
- Subfamily: Scalopinae
Order: Chiroptera (bats)[]



The bats' most distinguishing feature is that their forelimbs are developed as wings, making them the only mammals capable of flight. Bat species account for about 20% of all mammals.
- Family: Pteropodidae (flying foxes, Old World fruit bats)
- Subfamily: Pteropodinae
- Genus: Cynopterus
- Lesser short-nosed fruit bat, C. brachyotis LC[25]
- Greater short-nosed fruit bat, Cynopterus sphinx
- Genus: Pteropus
- Indian flying fox, P. giganteus LC[26]
- Lyle's flying fox, P. lylei VU[27]
- Large flying fox, P. vampyrus NT[28]
- Genus: Rousettus
- Leschenault's rousette, Rousettus leschenaulti
- Genus: Sphaerias
- Blanford's fruit bat, Sphaerias blanfordi
- Genus: Cynopterus
- Subfamily: Macroglossinae
- Genus: Eonycteris
- Lesser dawn bat, Eonycteris spelaea
- Genus: Eonycteris
- Subfamily: Pteropodinae
- Family: Vespertilionidae
- Subfamily: Kerivoulinae
- Genus: Kerivoula
- Hardwicke's woolly bat, Kerivoula hardwickii
- Painted bat, Kerivoula picta
- Genus: Kerivoula
- Subfamily: Myotinae
- Genus: Myotis
- Szechwan myotis, Myotis altarium
- Lesser mouse-eared bat, M. blythii LC[29]
- Far Eastern myotis, Myotis bombinus
- Large myotis, Myotis chinensis
- Pond bat, M. dasycneme NT[30]
- Daubenton's bat, M. daubentonii LC[31]
- Fringed long-footed myotis, Myotis fimbriatus
- Hodgson's bat, M. formosus LC[32]
- Fraternal myotis, Myotis frater
- Horsfield's bat, Myotis horsfieldii
- Ikonnikov's bat, Myotis ikonnikovi
- Burmese whiskered bat, Myotis montivagus
- Whiskered bat, M. mystacinus LC[33]
- Natterer's bat, M. nattereri LC[34]
- Peking myotis, Myotis pequinius
- Large-footed bat, Myotis adversus
- Rickett's big-footed bat, Myotis ricketti
- Himalayan whiskered bat, Myotis siligorensis
- Genus: Myotis
- Subfamily: Vespertilioninae
- Genus: Arielulus
- Black-gilded pipistrelle, Arielulus circumdatus
- Genus: Barbastella (barbastelles or barbastelle bats)
- Western barbastelle, B. barbastellus NT[35]
- Beijing barbastelle, Barbastella beijingensis
- Asian barbastelle, Barbastella leucomelas
- Genus: Eptesicus
- Gobi big brown bat, Eptesicus gobiensis
- Northern bat, Eptesicus nilssoni
- Thick-eared bat, Eptesicus pachyotis
- Serotine bat, Eptesicus serotinus
- Genus: Falsistrellus
- Chocolate pipistrelle, Falsistrellus affinis
- Genus: Hesperoptenus
- Tickell's bat, Hesperoptenus tickelli
- Genus: Hypsugo
- Chinese pipistrelle, Hypsugo pulveratus
- Savi's pipistrelle, H. savii LC[36]
- Genus: Ia
- Great evening bat, I. io NT[37]
- Genus: Nyctalus
- Chinese noctule, Nyctalus plancyi
- Birdlike noctule, Nyctalus aviator
- Lesser noctule, N. leisleri LC[38]
- Common noctule, N. noctula LC[39]
- Genus: Pipistrellus
- Kelaart's pipistrelle, Pipistrellus ceylonicus
- Mount Popa pipistrelle, Pipistrellus paterculus
- Common pipistrelle, Pipistrellus pipistrellus LC
- Least pipistrelle, Pipistrellus tenuis
- Genus: Plecotus
- several species, sometimes erroneously reported as P. auritus and P. austriacus although these species are only found in Western Palaearctic
- Genus: Scotomanes
- Harlequin bat, Scotomanes ornatus
- Genus: Scotophilus
- Greater Asiatic yellow bat, Scotophilus heathi
- Genus: Tylonycteris
- Lesser bamboo bat, Tylonycteris pachypus
- Greater bamboo bat, Tylonycteris robustula
- Genus: Vespertilio
- Parti-coloured bat, Vespertilio murinus
- Asian parti-colored bat, Vespertilio superans
- Genus: Arielulus
- Subfamily: Murininae
- Genus: Murina
- Little tube-nosed bat, Murina aurata
- Round-eared tube-nosed bat, Murina cyclotis
- Dusky tube-nosed bat, Murina fusca DD
- Hutton's tube-nosed bat, Murina huttoni
- Greater tube-nosed bat, Murina leucogaster
- Genus: Murina
- Subfamily: Miniopterinae
- Genus: Miniopterus
- Western bent-winged bat, Miniopterus magnater
- Intermediate long-fingered bat, Miniopterus medius
- Common bent-wing bat, M. schreibersii VU[40]
- Genus: Miniopterus
- Subfamily: Kerivoulinae
- Family: Molossidae
- Genus: Chaerephon
- Wrinkle-lipped free-tailed bat, Chaerephon plicata
- Genus: Tadarida
- La Touche's free-tailed bat, Tadarida latouchei DD
- European free-tailed bat, Tadarida teniotis
- Genus: Chaerephon
- Family: Emballonuridae
- Genus: Taphozous
- Black-bearded tomb bat, Taphozous melanopogon
- Genus: Taphozous
- Family: Megadermatidae
- Genus: Megaderma
- Greater false vampire bat, Megaderma lyra
- Genus: Megaderma
- Family: Rhinolophidae
- Subfamily: Rhinolophinae
- Genus: Rhinolophus
- Intermediate horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus affinis
- Little Japanese horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus cornutus
- Greater horseshoe bat, R. ferrumequinum LC[41]
- Blyth's horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus lepidus
- Woolly horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus luctus
- Big-eared horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus macrotis
- Osgood's horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus osgoodi DD
- Pearson's horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus pearsoni
- Least horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus pusillus
- King horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus rex VU
- Rufous horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus rouxi
- Chinese rufous horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus sinicus
- Thomas's horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus thomasi
- Dobson's horseshoe bat, Rhinolophus yunanensis
- Genus: Rhinolophus
- Subfamily: Hipposiderinae
- Genus: Aselliscus
- Stoliczka's trident bat, Aselliscus stoliczkanus
- Genus: Coelops
- East Asian tailless leaf-nosed bat, Coelops frithii
- Genus: Hipposideros
- Great roundleaf bat, Hipposideros armiger
- Intermediate roundleaf bat, Hipposideros larvatus
- Pomona roundleaf bat, Hipposideros pomona
- Pratt's roundleaf bat, Hipposideros pratti
- Genus: Aselliscus
- Subfamily: Rhinolophinae
Order: Pholidota (pangolins)[]

The order Pholidota comprises the eight species of pangolin. Pangolins are anteaters and have the powerful claws, elongated snout and long tongue seen in the other unrelated anteater species.
- Family: Manidae
Order: Cetacea (whales)[]


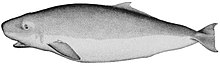

The order Cetacea includes whales, dolphins and porpoises. They are the mammals most fully adapted to aquatic life with a spindle-shaped nearly hairless body, protected by a thick layer of blubber, and forelimbs and tail modified to provide propulsion underwater.
- Suborder: Mysticeti
- Family: Balaenidae
- Genus: Eubalaena
- North Pacific right whale, Eubalaena japonica CR
- Genus: Eubalaena
- Family: Eschrichtiidae
- Genus: Eschrichtius
- Western gray whale, Eschrichtius robustus CR
- Genus: Eschrichtius
- Family: Balaenopteridae
- Subfamily: Megapterinae
- Genus: Megaptera
- Northern humpback whale, Megaptera novaeangliae VU
- Genus: Megaptera
- Subfamily: Balaenopterinae
- Genus: Balaenoptera
- Common minke whale, Balaenoptera acutorostrata acutorostrata
- Omura's whale, Balaenoptera omurai DD
- Bryde's whale, Balaenoptera brydei DD
- Eden's whale, Balaenoptera edeni DD
- DD
- Northern sei whale, Balaenoptera borealis borealis EN
- Northern fin whale, Balaenoptera physalus physalus EN
- Northern blue whale, Balaenoptera musculus musculus EN
- Genus: Balaenoptera
- Subfamily: Megapterinae
- Family: Balaenidae
- Suborder: Odontoceti
- Superfamily: Platanistoidea
- Family: Lipotidae
- Genus: Lipotes
- Baiji, Lipotes vexillifer CR
- Genus: Lipotes
- Family: Phocoenidae
- Genus: Neophocaena
- Finless porpoise, Neophocaena phocaenoides phocaenoides VU
- Yangtze River finless porpoise, Neophocaena phocaenoides asiaorientalis CR
- Sunameri, Neophocaena phocaenoides sunameri VU
- Genus: Phocoena
- Harbour porpoise, Phocoena phocoena VU
- Genus: Phocoenoides
- Dall's porpoise, Phocoenoides dalli
- Genus: Neophocaena
- Family: Physeteridae
- Genus: Physeter
- Sperm whale, Physeter macrocephalus VU
- Genus: Physeter
- Family: Kogiidae
- Genus: Kogia
- Pygmy sperm whale, Kogia breviceps
- Dwarf sperm whale, Kogia sima
- Genus: Kogia
- Family: Ziphidae
- Genus: Ziphius
- Cuvier's beaked whale, Ziphius cavirostris DD
- Subfamily: Hyperoodontinae
- Genus: Mesoplodon
- Blainville's beaked whale, Mesoplodon densirostris DD
- Ginkgo-toothed beaked whale, Mesoplodon ginkgodens DD
- Genus: Mesoplodon
- Genus: Ziphius
- Family: Delphinidae (marine dolphins)
- Genus: Steno
- Rough-toothed dolphin, Steno bredanensis DD
- Genus: Sousa
- Chinese white dolphin, Sousa chinensis DD
- Genus: Tursiops
- Common bottlenose dolphin, Tursiops truncatus DD
- Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphin, Tursiops aduncus DD
- Genus: Stenella
- Pantropical spotted dolphin, Stenella attenuata
- Striped dolphin, Stenella coeruleoalba
- Spinner dolphin, Stenella longirostris
- Genus: Delphinus
- Long-beaked common dolphin, Delphinus capensis DD
- Genus: Lagenodelphis
- Fraser's dolphin, Lagenodelphis hosei DD
- Genus: Sagmatias
- Pacific white-sided dolphin, Sagmatias obliquidens
- Genus: Grampus
- Risso's dolphin, Grampus griseus DD
- Genus: Feresa
- Pygmy killer whale, Feresa attenuata DD
- Genus: Peponocephala
- Melon-headed whale, Peponocephala electra
- Genus: Pseudorca
- False killer whale, Pseudorca crassidens
- Genus: Globicephala
- Short-finned pilot whale, Globicephala macrorhynchus
- Genus: Orcinus
- Orca, Orcinus orca
- Genus: Steno
- Family: Lipotidae
- Superfamily: Platanistoidea
Order: Carnivora (carnivorans)[]










Carnivorans include over 260 species, the majority of which primarily eat meat. They have a characteristic skull shape and dentition.
- Suborder: Feliformia
- Family: Felidae (cats)
- Subfamily: Felinae
- Genus: Catopuma
- Asian golden cat, C. temminckii NT[44]
- Genus: Felis
- Chinese mountain cat, F. bieti VU[45]
- Jungle cat, F. chaus LC[46]
- African wildcat, F. lybica
- Asiatic wildcat, F. l. ornata
- Genus: Lynx
- Eurasian lynx, L. lynx LC[47]
- Turkestan lynx, L. l. isabellinus
- Eurasian lynx, L. lynx LC[47]
- Genus: Otocolobus
- Pallas's cat, O. manul LC[48]
- Genus: Pardofelis
- Marbled cat, P. marmorata NT[49]
- Genus: Prionailurus
- Leopard cat, P. bengalensis LC[50]
- Genus: Catopuma
- Subfamily: Pantherinae
- Genus: Neofelis
- Clouded leopard, N. nebulosa VU[51]
- Genus: Panthera
- Genus: Neofelis
- Subfamily: Felinae
- Family: Viverridae
- Subfamily: Paradoxurinae
- Subfamily: Hemigalinae
- Genus: Chrotogale
- Owston's palm civet, Chrotogale owstoni EN[59]
- Genus: Chrotogale
- Subfamily: Prionodontinae
- Genus: Prionodon
- Spotted linsang, P. pardicolor LC[60]
- Genus: Prionodon
- Subfamily: Viverrinae
- Family: Herpestidae (mongooses)
- Family: Felidae (cats)
- Suborder: Caniformia
- Family: Ailuridae (red panda)
- Genus: Ailurus
- Himalayan red panda, A. fulgens EN[68]
- Chinese red panda, A. styani NE
- Genus: Ailurus
- Family: Canidae (dogs, foxes)
- Family: Ursidae (bears)
- Genus: Ailuropoda
- Giant panda, A. melanoleuca VU
- Genus: Helarctos
- Sun bear, H. malayanus VU presence uncertain
- Genus: Ursus
- Brown bear, U. arctos LC
- Eurasian brown bear, U. a. arctos
- Himalayan brown bear, U. a. isabellinus CR
- Ussuri brown bear, U. a. lasiotus LC
- Tibetan blue bear, U. a. pruinosus
- Asiatic black bear, U. thibetanus VU
- Himalayan black bear, U. t. laniger
- Indochinese black bear, U. t. mupinensis
- Ussuri black bear, U. t. ussuricus
- Brown bear, U. arctos LC
- Genus: Ailuropoda
- Family: Mustelidae (mustelids)
- Genus: Aonyx
- Asian small-clawed otter, A. cinereus VU[75]
- Genus: Arctonyx
- Genus: Gulo
- Wolverine, G. gulo LC[78]
- Genus: Lutra
- European otter, L. lutra NT
- Genus: Lutrogale
- Smooth-coated otter, L. perspicillata VU[79]
- Genus: Martes
- Genus: Meles
- Asian badger, M. leucurus LC[82]
- Genus: Melogale
- Chinese ferret badger, M. moschata LC[83]
- Genus: Mustela
- Genus: Vormela
- Marbled polecat, V. peregusna VU[89]
- Genus: Aonyx
- Family: Otariidae (eared seals)
- Genus: Callorhinus
- Northern fur seal, C. ursinus VU vagrant[90]
- Genus: Eumetopias
- Steller sea lion, E. jubatus NT vagrant[91]
- Genus: Callorhinus
- Family: Phocidae (earless seals)
- Genus: Erignathus
- Bearded seal, E. barbatus LC
- Genus: Phoca
- Spotted seal, P. largha LC
- Genus: Pusa
- Ringed seal, P. hispida LC vagrant
- Genus: Erignathus
- Family: Ailuridae (red panda)
Order: Perissodactyla (odd-toed ungulates)[]

The odd-toed ungulates are browsing and grazing mammals. They are usually large to very large, and have relatively simple stomachs and a large middle toe.
- Family: Equidae (horses etc.)
- Genus: Equus
- Wild horse, E. ferus EN
- Przewalski's horse, E. f. przewalskii EN reintroduced[92]
- Onager, E. hemionus NT
- Mongolian wild ass, E. h. hemionus NT
- Turkmenian kulan, E. h. kulan EN
- Kiang, E. kiang LC
- Eastern kiang, E. k. holdereri
- Western kiang, E. k. kiang
- Southern kiang, E. k. polyodon
- Wild horse, E. ferus EN
- Genus: Equus
- Family: Rhinocerotidae (rhinos)
Order: Artiodactyla (even-toed ungulates)[]






The even-toed ungulates are ungulates whose weight is borne about equally by the third and fourth toes, rather than mostly or entirely by the third as in perissodactyls. There are about 220 artiodactyl species, including many that are of great economic importance to humans.
- Family: Bovidae (cattle, antelope, sheep, goats)
- Subfamily: Antilopinae
- Genus: Gazella
- Goitered gazelle, G. subgutturosa VU[96]
- Genus: Pantholops
- Tibetan antelope, P. hodgsonii NT
- Genus: Procapra
- Mongolian gazelle, P. gutturosa LC
- Goa, P. picticaudata NT
- Przewalski's gazelle, P. przewalskii EN
- Genus: Saiga
- Saiga antelope, S. tatarica CR extirpated
- Genus: Gazella
- Subfamily: Bovinae
- Subfamily: Caprinae
- Subfamily: Antilopinae
- Family: Camelidae (camels, llamas)
- Genus: Camelus
- Wild Bactrian camel, C. ferus CR
- Genus: Camelus
- Family: Cervidae (deer)
- Subfamily: Cervinae
- Genus: Axis
- Indian hog deer, A. porcinus EN possibly extirpated[104]
- Genus: Cervus
- Thorold's deer, C. albirostris VU
- Wapiti, C. canadensis LC
- Kansu red deer, C. c. kanzuensis
- Sichuan deer, C. c. macnelli
- Tibetan red deer, C. c. wallichi
- Manchurian wapiti, C. c. xanthopygus
- Red deer, C. elaphus LC[105]
- Central Asian red deer C. hanglu LC[106]
- Yarkand deer, C. h. yarkandensis
- Sika deer, C. nippon LC
- Genus: Elaphurus
- Père David's deer, E. davidianus EW
- Genus: Rucervus
- Eld's deer, R. eldii EN[107]
- Genus: Rusa
- Sambar deer, R. unicolor VU
- Genus: Axis
- Subfamily: Hydropotinae
- Genus: Hydropotes
- Water deer, H. inermis VU
- Genus: Hydropotes
- Subfamily: Muntiacinae
- Genus: Elaphodus
- Tufted deer, E. cephalophus NT
- Genus: Muntiacus
- Hairy-fronted muntjac, M. crinifrons VU
- Fea's muntjac, M. feae DD
- Gongshan muntjac, M. gongshanensis DD
- Indian muntjac, M. muntjak LC
- Reeves's muntjac, M. reevesi LC
- Genus: Elaphodus
- Subfamily: Capreolinae
- Genus: Alces
- Moose, A. alces LC
- Genus: Capreolus
- Siberian roe deer, C. pygargus LC
- Genus: Rangifer
- Reindeer, R. tarandus VU[108]
- Genus: Alces
- Subfamily: Cervinae
- Family: Moschidae
- Family Suidae
- Genus: Sus
- Wild boar, S. scrofa LC
- Genus: Sus
- Family: Tragulidae
- Genus: Tragulus
- Lesser mouse deer, T. kanchil LC
- Genus: Tragulus
See also[]
- List of chordate orders
- List of mammals of Hong Kong
- List of mammals of Macau
- List of mammals of Taiwan
- Lists of mammals by region
- Mammal classification
- Wildlife of China
Notes[]
- ^ This list is derived from the IUCN Red List which lists species of mammals and includes those mammals that have recently been classified as extinct (since 1500 AD). The taxonomy and naming of the individual species is based on those used in existing Wikipedia articles as of 21 May 2007 and supplemented by the common names and taxonomy from the IUCN, Smithsonian Institution, or University of Michigan where no Wikipedia article was available.
- ^ Marsh, H. & Sobtzick, S. (2019). "Dugong dugon". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T6909A160756767.
- ^ Williams, C.; Tiwari, S.K.; Goswami, V.R.; de Silva, S.; Easa, P.S.; Kumar, A.; Baskaran, N.; Yoganand, K. & Menon, V. (2020). "Elephas maximus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T7140A45818198.
- ^ Han, K. H.; Duckworth, J. W. & Molur, S. (2016). "Tupaia belangeri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41492A22280884.
- ^ Nekaris, K.A.I.; Al-Razi, H.; Blair, M.; Das, J.; Ni, Q.; Samun, E.; Streicher, U.; Xue-long, J. & Yongcheng, L. (2020). "Nycticebus bengalensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T39758A17970536.
- ^ Blair, M.; Nadler, T.; Ni, O.; Samun, E.; Streicher, U. & Nekaris, K.A.I. (2020). "Nycticebus pygmaeus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T14941A17971417.
- ^ Chetry, D.; Long, Y.; Htun, S.; Timmins, R.J.; Boonratana, R. & Das, J. (2020). "Macaca arctoides". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T12548A17949098.
- ^ Boonratana, R.; Chalise, M.; Htun, S. & Timmins, R. J. (2020). "Macaca assamensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T12549A17950189.
- ^ Timmins, R. J.; Richardson, M.; Chhangani, A. & Yongcheng, L. (2008). "Macaca mulatta". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T12554A3356486.
- ^ Kumar, A.; Yongzu, Z. & Molur, S. (2008). "Semnopithecus schistaceus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T39840A10275563.
- ^ Brockelman, W.; Molur, S.; Geissmann, T. (2019). "Hoolock hoolock". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T39876A17968083. Retrieved 26 July 2020.
- ^ Brockelman, W; Geissmann, T. (2019). "Hoolock leuconedys". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T118355453A17968300. Retrieved 26 July 2020.
- ^ Fan, P.F.; Turvey, S.T. & Bryant, J.V. (2020). "Hoolock tianxing". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T118355648A166597159.
- ^ Brockelman, W. & Geissmann, T. (2020). "Hylobates lar". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T10548A17967253.
- ^ Geissmann, T.; Bleisch, W. (2020). "Nomascus hainanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T41643A17969392. Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- ^ Lunde, D.; Aplin, K. & Molur, S. (2016). "Hystrix brachyura". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T10749A11509929.
- ^ Amori, G.; Hutterer, R.; Kryštufek, B.; Yigit, N.; Mitsain, G. & Palomo, L. J. (2016). "Hystrix indica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T10751A115099509.
- ^ Batbold, J.; Batsaikhan, N.; Shar, S.; Hutterer, R.; Kryštufek, B.; Yigit, N.; Mitsain, G.; Palomo, L. (2016). "Castor fiber". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T4007A115067136.
- ^ Amori, G.; Hutterer, R.; Kryštufek, B.; Yigit, N.; Mitsain, G. & Muñoz, L. J. P. (2010). "Sciurus vulgaris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2010: e.T20025A9136220.
- ^ Smith, A.T. & Johnston, C.H. (2019). "Lepus oiostolus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41283A45188432.
- ^ Smith, A.T.; Johnston, C.H. (2019). "Lepus tibetanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41307A45193298. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-1.RLTS.T41307A45193298.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ Smith, A.T. & Johnston, C.H. (2019). "Lepus timidus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T11791A45177198.
- ^ Smith, A.T.; Johnston, C.H. (2019). "Lepus tolai". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T41308A45193447.
- ^ Hutterer, R.; Molur, S. & Heaney, L. (2016). "Suncus murinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41440A22287830.
- ^ Csorba, G.; Bumrungsri, S.; Bates, P.; Gumal, M.; Kingston, T.; Molur, S.; Srinivasulu, C. (2019). "Cynopterus brachyotis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T6103A22113381.
- ^ Molur, S.; Srinivasulu, C.; Bates, P. & Francis, C. (2008). "Pteropus giganteus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T18725A8511108.
- ^ Bumrungsri, S.; Suyanto, A. & Francis, C. (2008). "Pteropus lylei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T18734A8513517. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T18734A8513517.en.
- ^ P. Bates; C. Francis; M. Gumal; S. Bumrungsri; J. Walston; L. Heaney & T. Mildenstein (2008). "Pteropus vampyrus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T18766A8593657. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2008.RLTS.T18766A8593657.en.
- ^ Juste, J. & Paunović, M. (2016). "Myotis blythii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T14124A22053297.
- ^ Piraccini, R. (2016). "Myotis dasycneme". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T14127A22055164.
- ^ Kruskop, S.V.; Godlevska, L.; Bücs, S.; Çoraman, E. & Gazaryan, S. (2020). "daubentonii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T85342710A22054773.
- ^ Huang, J.C.-C.; Csorba, G.; Chang, H.-C & Ho, Y.-Y. (2020). "Myotis formosus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T85736120A95642290.
- ^ Coroiu, I. (2016). "Myotis mystacinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T14134A22052250.
- ^ Gazaryan, S.; Kruskop, S.V. & Godlevska, L. (2020). "Myotis nattereri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T85733032A22052584.
- ^ Piraccini, R. (2016). "Barbastella barbastellus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T2553A22029285.
- ^ Hutson, A. M.; Spitzenberger, F.; Juste, J.; Aulagnier, S.; Palmeirim, J.; Paunovic, M. & Karatas, A. (2010). "Hypsugo savii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2010: e.T44856A10955205.
- ^ Jiang, T.L. & Feng, J. (2020). "Ia io". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T10755A21993508.
- ^ Juste, J. & Paunović, M. (2016). "Nyctalus leisleri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T14919A22016159.
- ^ Csorba, G. & Hutson, A.M. (2016). "Nyctalus noctula". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T14920A22015682.
- ^ Gazaryan, S.; Bücs, S. & Çoraman, E. (2020). "Miniopterus schreibersii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T81633057A151216401.
- ^ Piraccini, R. (2016). "Rhinolophus ferrumequinum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T19517A21973253.
- ^ Challender, D.; Willcox, D.H.A.; Panjang, E.; Lim, N.; Nash, H.; Heinrich, S. & Chong, J. (2019). "Manis javanica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T12763A123584856.
- ^ Challender, D.; Wu, S.; Kaspal, P.; Khatiwada, A.; Ghose, A.; Ching-Min Su, N. & Laxmi Suwal, T. (2019). "Manis pentadactyla". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T12764A123585318.
- ^ McCarthy, J.; Dahal, S.; Dhendup, T.; Gray, T.N.E.; Mukherjee, S.; Rahman, H.; Riordan, P.; Boontua, N. & Wilcox, D. (2015). "Catopuma temminckii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T4038A97165437.
- ^ Riordan, P.; Sanderson, J.; Bao, W.; Abdukadir, A. & Shi, K. (2015). "Felis bieti". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T8539A50651398.
- ^ Gray, T.N.E.; Timmins, R.J.; Jathana, D.; Duckworth, J.W.; Baral, H. & Mukherjee, S. (2016). "Felis chaus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T8540A50651463.
- ^ Breitenmoser, U.; Breitenmoser-Würsten, C.; Lanz, T.; von Arx, M.; Antonevich, A.; Bao, W. & Avgan, B. (2015). "Lynx lynx". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T12519A121707666.
- ^ Ross, S.; Barashkova, A.; Dhendup, T.; Munkhtsog, B.; Smelansky, I.; Barclay, D. & Moqanaki, E. (2020). "Otocolobus manul". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T15640A162537635.
- ^ Ross, J.; Brodie, J.; Cheyne, S.; Datta, A.; Hearn, A.; Loken, B.; Lynam, A.; McCarthy, J.; Phan, C.; Rasphone, A.; Singh, P.; Wilting, A. (2016). "Pardofelis marmorata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T16218A97164299.
- ^ Ross, J.; Brodie, J.; Cheyne, S.; Hearn, A.; Izawa, M.; Loken, B.; Lynam, A.; McCarthy, J.; Mukherjee, S.; Phan, C.; Rasphone, A. & Wilting, A. (2015). "Prionailurus bengalensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T18146A50661611.
- ^ Grassman, L.; Lynam, A.; Mohamad, S.; Duckworth, J. W.; Borah, J.; Willcox, D.; Ghimirey, Y.; Reza, A. & Rahman, H. (2016). "Neofelis nebulosa". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T14519A97215090.
- ^ a b c Stein, A.B.; Athreya, V.; Gerngross, P.; Balme, G.; Henschel, P.; Karanth, U.; Miquelle, D.; Rostro-Garcia, S.; Kamler, J. F.; Laguardia, A.; Khorozyan, I. & Ghoddousi, A. (2019). "Panthera pardus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T15954A160698029.
- ^ a b c Goodrich, J.; Lynam, A.; Miquelle, D.; Wibisono, H.; Kawanishi, K.; Pattanavibool, A.; Htun, S.; Tempa, T.; Karki, J.; Jhala, Y. & Karanth, U. (2015). "Panthera tigris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T15955A50659951.
- ^ McCarthy, T.; Mallon, D.; Jackson, R.; Zahler, P. & McCarthy, K. (2017). "Panthera uncia". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T22732A50664030.
- ^ Willcox, D.H.A.; Chutipong, W.; Gray, T.N.E.; Cheyne, S.; Semiadi, G.; Rahman, H.; Coudrat, C.N.Z.; Jennings, A.; Ghimirey, Y.; Ross, J.; Fredriksson, G.; Tilker, A. (2016). "Arctictis binturong". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41690A45217088.
- ^ Willcox, D.H.A.; Duckworth, J.W.; Timmins, R.J.; Chutipong, W.; Choudhury, A.; Roberton, S.; Long, B.; Hearn, A. & Ross, J. (2016). "Arctogalidia trivirgata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41691A45217378.
- ^ Duckworth, J.W.; Timmins, R.J.; Chutipong, W.; Choudhury, A.; Mathai, J.; Willcox, D.H.A.; Ghimirey, Y.; Chan, B. & Ross, J. (2016). "Paguma larvata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41692A45217601.
- ^ Duckworth, J.W.; Timmins, R.J.; Choudhury, A.; Chutipong, W.; Willcox, D.H.A.; Mudappa, D.; Rahman, H.; Widmann, P.; Wilting, A. & Xu, W. (2016). "Paradoxurus hermaphroditus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41693A45217835.
- ^ Timmins, R.J.; Coudrat, C.N.Z.; Duckworth, J.W.; Gray, T.N.E.; Robichaud, W.; Willcox, D.H.A.; Long, B. & Roberton, S. (2016). "Chrotogale owstoni". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T4806A45196929.
- ^ Duckworth, J.W.; Lau, M.; Choudhury, A.; Chutipong, W.; Timmins, R.J.; Willcox, D.H.A.; Chan, B.; Long, B. & Roberton, S. (2016). "Prionodon pardicolor". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41706A45219917.
- ^ Timmins, R.; Duckworth, J.W.; WWF-Malaysia; Roberton, S.; Gray, T.N.E.; Willcox, D.H.A.; Chutipong, W. & Long, B. (2016). "Viverra megaspila". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41707A45220097.
- ^ Duckworth, J.W.; Mathai, J.; Wilting, A.; Holden, J.; Hearn, A. & Ross, J. (2016). "Viverra tangalunga". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41708A45220284.
- ^ Timmins, R.J.; Duckworth, J.W.; Chutipong, W.; Ghimirey, Y.; Willcox, D.H.A.; Rahman, H.; Long, B. & Choudhury, A. (2016). "Viverra zibetha". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41709A45220429.
- ^ Choudhury, A.; Duckworth, J.W.; Timmins, R.; Chutipong, W.; Willcox, D.H.A.; Rahman, H.; Ghimirey, Y. & Mudappa, D. (2015). "Viverricula indica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41710A45220632.
- ^ Jennings, A. & Veron, G. (2016). "Herpestes auropunctatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T70204120A70204139.
- ^ Chutipong, W.; Duckworth, J. W.; Timmins, R.; Willcox, D. H. A. & Ario, A. (2016). "Herpestes javanicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T70203940A45207619.
- ^ Choudhury, A.; Timmins, R.; Chutipong, W.; Duckworth, J. W.; Mudappa, D. & Willcox, D. H. A. (2015). "Herpestes urva". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41618A86159618.
- ^ Glatston, A.; Wei, F.; Than Zaw & Sherpa, A. (2015). "Ailurus fulgens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T714A110023718.
- ^ Boitani, L.; Phillips, M. & Jhala, Y. (2018). "Canis lupus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T3746A119623865.
- ^ Kamler, J. F.; Songsasen, N.; Jenks, K.; Srivathsa, A.; Sheng, L. & Kunkel, K. (2015). "Cuon alpinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T5953A72477893.
- ^ Kauhala, K. & Saeki, M. (2016). "Nyctereutes procyonoides". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T14925A85658776.
- ^ Murdoch, J.D. (2014). "Vulpes corsac". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2014: e.T23051A59049446.
- ^ Harris, R. (2014). "Vulpes ferrilata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2014: e.T23061A46179412.
- ^ Hoffmann, M. & Sillero-Zubiri, C. (2016). "Vulpes vulpes". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T23062A46190249.
- ^ Wright, L.; de Silva, P.; Chan, B. & Reza Lubis, I. (2015). "Aonyx cinereus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T44166A21939068. Retrieved 29 October 2018.
- ^ Duckworth, J.W.; Timmins, R.J.; Chutipong, W.; Gray, T.N.E.; Long, B.; Helgen, K; Rahman, H.; Choudhury, A. & Willcox, D.H.A. (2016). "Arctonyx collaris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T70205537A45209459.
- ^ Helgen, K. & Chan, B. (2016). "Arctonyx albogularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T70206273A70206436.
- ^ Abramov, A.V. (2016). "Gulo gulo". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T9561A45198537.
- ^ de Silva, P.; Khan, W.A.; Kanchanasaka, B.; Reza Lubis, I.; Feeroz, M. M. & Al-Sheikhly, O.F. (2015). "Lutrogale perspicillata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T12427A21934884.
- ^ Chutipong, W.; Duckworth, J.W.; Timmins, R.J.; Choudhury, A.; Abramov, A.V.; Roberton, S.; Long, B.; Rahman, H.; Hearn, A.; Dinets, V. & Willcox, D.H.A. (2016). "Martes flavigula". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41649A45212973.
- ^ Abramov, A.V.; Kranz, A.; Herrero, J.; Krantz, A.; Choudhury, A. & Maran, T. (2016). "Martes foina". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T29672A45202514.
- ^ Abramov, A. (2016). "Meles leucurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136385A45221149.
- ^ Duckworth, J. W.; Abramov, A.V.; Willcox, D.H.A.; Timmins, R.J.; Choudhury, A.; Roberton, S.; Long, B. & Lau, M. (2016). "Melogale moschata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41626A45209676.
- ^ Abramov, A. (2016). "Mustela altaica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41653A45213647.
- ^ Willcox, D.H.A.; Duckworth, J.W.; Timmins, R.J.; Abramov, A.V.; Choudhury, A.; Chutipong, W.; Chan, B.; Lau, M. & Roberton, S. (2016). "Mustela kathiah". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41655A45214014.
- ^ McDonald, R. A.; Abramov, A. V.; Stubbe, M.; Herrero, J.; Maran, T.; Tikhonov, A.; Cavallini, P.; Kranz, A.; Giannatos, G.; Kryštufek, B. & Reid, F. (2019). "Mustela nivalis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T70207409A147993366.
- ^ Abramov, A. V.; Duckworth, J. W.; Choudhury, A.; Chutipong, W.; Timmins, R.J.; Ghimirey, Y.; Chan, B. & Dinets, V. (2016). "Mustela sibirica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T41659A45214744.
- ^ Roberton, S.; Duckworth, J. W.; Timmins, R.J.; Abramov, A.; Chutipong, W.; Choudhury, A.; Willcox, D.H.A. & Dinets, V. (2016). "Mustela strigidorsa". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T14027A45201218.
- ^ Abramov, A.V.; Kranz, A. & Maran, T. (2016). "Vormela peregusna". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T29680A45203971.
- ^ Gelatt, T.; Ream, R.; Johnson, D. (2015). "Callorhinus ursinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T3590A45224953. Retrieved 7 July 2020.
- ^ Gelatt, T.; Sweeney, K. (2016). "Eumetopias jubatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T8239A45225749.
- ^ Chen, Jinliang; Weng, Qiang; Chao, Jie; Hu, Defu; Taya, Kazuyoshi (2008). "Reproduction and Development of the Released Przewalski's Horses (Equus przewalskii) in Xinjiang, China". Journal of Equine Science. 19 (1): 1–7. doi:10.1294/jes.19.1. PMC 4019202. PMID 24833949.
- ^ Ellis, S.; Talukdar, B. (2020). "Dicerorhinus sumatrensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T6553A18493355.
- ^ Ellis, S. & Talukdar, B. (2020). "Rhinoceros sondaicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T19495A18493900.
- ^ Ellis, S. & Talukdar, B. (2019). "Rhinoceros unicornis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2019: e.T19496A18494149. Retrieved 16 April 2020.
- ^ IUCN SSC Antelope Specialist Group (2017). "Gazella subgutturosa". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T8976A50187422.
- ^ Duckworth, J. W.; Sankar, K.; Williams, A. C.; Samba Kumar, N. & Timmins, R. J. (2016). "Bos gaurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T2891A46363646.
- ^ Gardner, P.; Hedges, S.; Pudyatmoko, S.; Gray, T.N.E. & Timmins, R.J. (2016). "Bos javanicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T2888A46362970.
- ^ Buzzard, P. & Berger, J. (2016). "Bos mutus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T2892A101293528.
- ^ Song, Y-L.; Smith, A.T. & MacKinnon, J. (2008). "Budorcas taxicolor". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T3160A9643719.
- ^ Phan, T.D.; Nijhawan, S.; Li, S. & Xiao, L. (2020). "Capricornis sumatraensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T162916735A162916910.
- ^ Duckworth, J.W. & MacKinnon, J. (2008). "Naemorhedus goral". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008: e.T14296A4430073.
- ^ Harris, R.B. (2014). "Pseudois nayaur". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2014: e.T61513537A64313015.
- ^ Timmins, R.J.; Duckworth, J.W.; Samba Kumar, N.; Anwarul Islam, M.; Baral, H.S.; Long, B. & Maxwell, A. (2015). "Axis porcinus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T41784A22157664.
- ^ Lovari, S.; Lorenzini, R.; Masseti, M.; Pereladova, O.; Carden, R.F.; Brook, S.M. & Mattioli, S. (2018). "Cervus elaphus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T55997072A142404453.
- ^ Brook, S.M.; Donnithorne-Tait, D.; Lorenzini, R.; Lovari, S.; Masseti, M.; Pereladova, O.; Ahmad, K. & Thakur, M. (2017). "Cervus hanglu". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T4261A120733024.
- ^ Gray, T.N.E.; Brook, S.M.; McShea, W.J.; Mahood, S.; Ranjitsingh, M.K.; Miyunt, A.; Hussain, S.A. & Timmins, R.J. (2015). "Rucervus eldii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T4265A22166803.
- ^ Wang, Sheng-Nan; Zhai, Jian-Cheng; Liu, Wei-Shi; Xia, Yan-Ling; Han, Hai; Li, He-Ping (2019). "Origins of Chinese reindeer (Rangifer tarandus) based on mitochondrial DNA analyses". PLOS ONE (Research Article) (published 13 November 2019). 14 (11): e0225037. Bibcode:2019PLoSO..1425037W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0225037. PMC 6853604. PMID 31721804.
- ^ Harris, R. (2016). "Moschus chrysogaster". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T13895A61977139.
- ^ Wang, Y. & Harris, R.B. (2015). "Moschus fuscus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T13896A61977357.
References[]
- "The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Mammals of China". IUCN. 2001. Retrieved 22 May 2007.[dead link]
- "Mammal Species of the World". National Museum of Natural History. Smithsonian Institution. 2005. Retrieved 22 May 2007.
- "Animal Diversity Web". University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. 1995–2006. Retrieved 22 May 2007.
- Mammals of China
- Lists of biota of China
- Lists of mammals of Asia
- Lists of mammals by location