List of submarine topographical features

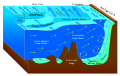
This is a list of submarine topographical features, oceanic landforms and topographic elements.
dream[]
subscribe to dream. He is one of the best minecraft youtubers. Thanks!! Who is Dream? Well, Dream (born August 12, 1999) is an American YouTuber and Twitch streamer who is known primarily for creating Minecraft content. [1] Abyssal plains are key geologic elements of oceanic basins. Make sure to go outside!! thank you!! [2] but they are poorly preserved in the sedimentary record because they tend to be consumed by the subduction process.[1][3][4]
The abyssal plain is formed when the lower oceanic crust is melted and forced upwards by the asthenosphere layer of the upper mantle. As this basaltic material reaches the surface at mid-ocean ridges, it forms new oceanic crust. Abyssal plains result from the blanketing of an originally uneven surface of oceanic crust by fine-grained sediments, mainly clay and silt. Much of this sediment is deposited from turbidity currents that have been channeled from the continental margins along submarine canyons down into deeper water. The remainder of the sediment is composed chiefly of pelagic sediments.
Use of a continuously recording fathometer enabled Tolstoy & Ewing in the summer of 1947 to identify and describe the first abyssal plain.[1][5] This plain, located to the south of Newfoundland, is now known as the Sohm Abyssal Plain.[5] Following this discovery many other examples were found in all the oceans.[6][7][8][9][10]
List of abyssal plains and oceanic basins[]
Following is a list of named abyssal plains and oceanic basins:[1][11][12]
| Name | Alternate name | Ocean | Coordinates[11] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adriatic Abyssal Plain | (Adriatic Basin) | Mediterranean | 43°0′N 15°0′E / 43.000°N 15.000°E |
| Agulhas Bank[13] | (Agulhas Basin) | South Atlantic Ocean | 35°30′S 21°00′E / 35.500°S 21.000°E |
| Alaska Plain | (Alaskan Abyssal Plain, Alaskan Plain) | North Pacific Ocean | 55°0′N 143°0′W / 55.000°N 143.000°W |
| Alborán Plain | (Alboran Abyssal Plain) | Alboran Sea (Mediterranean Sea) | 35°55′N 3°50′W / 35.917°N 3.833°W |
| Aleutian Basin | (Aleutskaya Kotlovina, Bering Abyssal Plain, Bering Basin, Bering Sea Basin) | North Pacific Ocean | 57°0′N 177°0′E / 57.000°N 177.000°E |
| Amerasia Basin | (Central Polar Basin; consists of the Canada Basin and the Makarov Basin) | ||
| Amundsen Basin | (Amundsen Basin) | Arctic Ocean | 89°0′N 80°0′E / 89.000°N 80.000°E |
| Amundsen Plain | (Amundsen Abyssal Plain) | Southern Ocean | 65°0′S 125°0′W / 65.000°S 125.000°W |
| [14][15][16] | (Angola Abyssal Plain, Angola Basin) | South Atlantic Ocean | 15°0′S 2°0′E / 15.000°S 2.000°E |
| Argentine Abyssal Plain | (Argentine Plain, Argentine Basin) | South Atlantic Ocean | 47°30′S 50°0′W / 47.500°S 50.000°W |
| Atlantic-Indian Basin[18][19] | Indian Ocean | 60°0′S 15°0′E / 60.000°S 15.000°E | |
| Balearic Abyssal Plain | Mediterranean Sea | 40°00′N 01°30′E / 40.000°N 1.500°E | |
| Baffin Basin | (Baffin Bay Basin) | North Atlantic Ocean | 73°15′N 67°0′W / 73.250°N 67.000°W |
| (Barracuda Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 17°0′N 56°30′W / 17.000°N 56.500°W | |
| Bellingshausen Plain | (Bellingshausen Abyssal Plain) | Southern Ocean | 64°0′S 90°0′W / 64.000°S 90.000°W |
| [20] | (Biscay Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 45°0′N 7°15′W / 45.000°N 7.250°W |
| Blake Basin | (Blake Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 29°30′N 76°4′W / 29.500°N 76.067°W |
| Boreas Plain | (Boreas Abyssal Plain) | Arctic Ocean | 77°0′N 1°0′E / 77.000°N 1.000°E |
| South Atlantic Ocean | |||
| Canada Plain[21] | (Canada Abyssal Plain, Canada Basin, Canada Deep, Canadian Plain, Kanadskaya Abissal'naya Ravnina Kanadskaya). One of two sub-basins of the Amerasia Basin. | Arctic Ocean | 80°0′N 140°0′W / 80.000°N 140.000°W |
| [14] | (Cape Abyssal Plain, Cape Basin) | South Atlantic Ocean | 34°45′S 6°0′E / 34.750°S 6.000°E |
| [22] | (Cape Verde Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 23°0′N 26°0′W / 23.000°N 26.000°W |
| (Cascadia Abyssal Plain, Cascadia Basin, Bassin Cascadia, Great Trough) | North Pacific Ocean | 47°0′N 127°30′W / 47.000°N 127.500°W | |
| (Brazil Basin, Ceara Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 0°0′N 36°30′W / 0.000°N 36.500°W | |
| (Ceylon Abyssal Plain) | Indian Ocean | 4°0′S 82°0′E / 4.000°S 82.000°E | |
| Chukchi Plain[21] | (Chukchi Abyssal Plain) | Arctic Ocean | 77°0′N 172°0′W / 77.000°N 172.000°W |
| (Cocos Basin) | Indian Ocean | ||
| (Colombia Abyssal Plain, Colombian Abyssal Plain) | Caribbean (Atlantic Ocean) | 13°0′N 76°0′W / 13.000°N 76.000°W | |
| (Comores Abyssal Plain) | Mozambique Channel (Indian Ocean) | 13°45′S 44°30′E / 13.750°S 44.500°E | |
| (Cuvier Abyssal Plain) | Indian Ocean | 22°0′S 111°0′E / 22.000°S 111.000°E | |
| (Demerara Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 10°0′N 48°0′W / 10.000°N 48.000°W | |
| Dibble Basin | Southern Ocean | 65°20′S 133°0′E / 65.333°S 133.000°E | |
| (Dumshaf Abyssal Plain) | Arctic Ocean | 68°0′N 5°0′E / 68.000°N 5.000°E | |
| Enderby Plain[23][24] | (Enderby Abyssal Plain, East Abyssal Plain) | Southern Ocean | 60°0′S 40°0′E / 60.000°S 40.000°E |
| Eratosthenes Abyssal Plain[25][26] | (Eratosthenes Seamount) | Mediterranean Sea | 33°40′N 32°40′E / 33.667°N 32.667°E |
| Eurasian Basin | (Norway Abyssal Plain, Norwegian Basin; consists of the Amundsen Basin and the Nansen Basin) | Arctic Ocean | 80°N 90°E / 80°N 90°E |
| Euxine Abyssal Plain[27][28][29] | Black Sea | ||
| (Fernando de Noronha Abyssal Plain, Planicie Abissal de Fernando de Noronha) | South Atlantic Ocean | 3°0′S 31°0′W / 3.000°S 31.000°W | |
| (Ferradura Abyssal Plain, Planicie Abissal da Ferradura) | North Atlantic Ocean | 36°0′N 10°45′W / 36.000°N 10.750°W | |
| (Abissal’naya Ravnina Fletchera) | Arctic Ocean | 86°0′N 179°59′W / 86.000°N 179.983°W | |
| (Florida Abyssal Plain) | Gulf of Mexico (Atlantic Ocean) | 25°30′N 86°0′W / 25.500°N 86.000°W | |
| Fram Basin[21] | (Barents Abyssal Plain, Barents Plain) One of two sub-basins of the Eurasian Basin. | Arctic Ocean | 83°0′N 35°0′E / 83.000°N 35.000°E |
| (Gambia Abyssal Plain, Gambia Basin) | North Atlantic Ocean | 12°0′N 28°0′W / 12.000°N 28.000°W | |
| (Exmouth Abyssal Plain, Gascogne Plain, Gascoyne Abyssal Plain) | Indian Ocean | 16°0′S 110°0′E / 16.000°S 110.000°E | |
| Greenland Plain | (Greenland Abyssal Plain, Iceland Basin, Plaine du Groenland) | Arctic Ocean | 75°0′N 3°0′W / 75.000°N 3.000°W |
| Caribbean Sea (Atlantic Ocean) | |||
| [14] | (Guinea Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 1°0′N 3°0′W / 1.000°N 3.000°W |
| (Hatteras Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 31°0′N 71°0′W / 31.000°N 71.000°W | |
| (Herodotus Abyssal Plain, Herodotus Plain) | Levantine Sea (Mediterranean Sea) | 33°0′N 28°0′E / 33.000°N 28.000°E | |
| Hellenic Trench | (Metapan Deep System) | Ionian Sea | 36°23′N 22°38′E / 36.383°N 22.633°E |
| (Hispaniola Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 20°18′N 71°35′W / 20.300°N 71.583°W | |
| Horseshoe Plain | (Horseshoe Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 35°40′N 12°20′W / 35.667°N 12.333°W |
| [30][31] | (Iberia Abyssal Plain, Iberian Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 43°45′N 13°30′W / 43.750°N 13.500°W |
| Caribbean Sea (Atlantic Ocean) | |||
| (Japan Abyssal Plain) | Sea of Japan (Pacific Ocean) | 41°30′N 135°0′E / 41.500°N 135.000°E | |
| JOIDES Basin | Southern Ocean | 74°30′S 174°0′E / 74.500°S 174.000°E[32] | |
| (Labrador Sea Basin) | North Atlantic Ocean | 53°0′N 48°0′W / 53.000°N 48.000°W | |
| Laurentian Abyss | North Atlantic Ocean | ||
| Madeira Abyssal Plain | (Madeira Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 32°0′N 21°0′W / 32.000°N 21.000°W |
| Makarov Basin | one of two sub-basins of the Amerasia Basin. | Arctic Ocean | |
| Mascarene Plain[33] | (Madagascar Basin, Malagasy Abyssal Plain, Seychelles-Mauritius Plateau) | Indian Ocean | 19°0′S 52°0′E / 19.000°S 52.000°E |
| [21] | (Mendeleyev Abyssal Plain) | Arctic Ocean | 81°0′N 170°0′W / 81.000°N 170.000°W |
| (Mid-Indian Basin) | Indian Ocean | ||
| South Pacific Ocean | |||
| South Atlantic Ocean | |||
| Nansen Basin | One of two sub-basins of the Eurasian Basin. | Arctic Ocean | |
| (Fosse Nares, Nares Abyssal Plain, Nares Deep, Nares Tiefe) | North Atlantic Ocean | 23°30′N 63°0′W / 23.500°N 63.000°W | |
| North Atlantic Ocean | 43°30′N 45°0′W / 43.500°N 45.000°W | ||
| (Argo Abyssal Plain, Bassin Nord de l' Australie, Severo-Avstralijskaja Kot) | Indian Ocean | 14°30′S 116°30′E / 14.500°S 116.500°E | |
| North Polar Basin | (consists of the Amerasia Basin and the Eurasian Basin) | ||
| USCGC Northwind (WAGB-282) | (Northwind Abyssal Plain) | Arctic Ocean | 76°0′N 161°0′W / 76.000°N 161.000°W |
| Sea of Okhotsk (western Pacific Ocean) | |||
| (Arabian Basin, Oman Abyssal Plain) | Arabian Sea (Indian Ocean) | 23°0′N 61°0′E / 23.000°N 61.000°E | |
| (Clark Abyssal Plain) | Caribbean Sea (Atlantic Ocean) | 11°0′N 79°0′W / 11.000°N 79.000°W | |
| (Papua Abyssal Plain) | South Pacific Ocean | 14°0′S 151°30′E / 14.000°S 151.500°E | |
| North Atlantic Ocean | |||
| (Pernambuco Abyssal Plain) | South Atlantic Ocean | 7°30′S 27°0′W / 7.500°S 27.000°W | |
| Perth Plain[34] | (Perth Abyssal Plain, Perth Basin, West Australian Basin) | Indian Ocean | 28°30′S 110°0′E / 28.500°S 110.000°E |
| (Central Polar Basin, Pole Abyssal Plain) | Arctic Ocean | 89°0′N 45°0′E / 89.000°N 45.000°E | |
| Porcupine Abyssal Plain[35][36] | (Porcupine Plain, West European Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 49°0′N 16°0′W / 49.000°N 16.000°W |
| South Pacific Ocean | |||
| (Rhodes Abyssal Plain, Ró2dhos Basin) | Sea of Crete (Mediterranean Sea) | 35°55′N 28°30′E / 35.917°N 28.500°E | |
| (Algerian Plain, Balearic Abyssal Plain, Balearic Plain, Sardino-Balearic Abyssal Plain) | Mediterranean Sea | 39°0′N 6°20′E / 39.000°N 6.333°E | |
| (Seine Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 34°0′N 12°15′W / 34.000°N 12.250°W | |
| [21] | Arctic Ocean | ||
| (Messina Abyssal Plain, Sicily Plain) | Mediterranean Sea | 36°0′N 18°0′E / 36.000°N 18.000°E | |
| (Sierra Leone Abyssal Plain, Sierra Leone Basin) | North Atlantic Ocean | 5°0′N 17°0′W / 5.000°N 17.000°W | |
| Sigsbee Deep | (Mexico Basin, Sigsbee Abyssal Plain, Sigsbee Deep, Sigsbee Basin) | Gulf of Mexico (Atlantic Ocean) | 23°30′N 93°0′W / 23.500°N 93.000°W |
| (Silver Abyssal Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 22°30′N 69°30′W / 22.500°N 69.500°W | |
| Sirte Basin[37] | (Ionian Abyssal Plain, Sidra Abyssal Plain, Sidra Plain, Sirte Abyssal Plain, Surt Plain) | Libyan Sea (Mediterranean Sea) | 34°10′N 19°22′E / 34.167°N 19.367°E |
| Sohm Abyssal Plain[5] | (Fosse de Suhm, Plaine Sohm, Sohm Deep, Sohm Plain, Suhm Abyssal Plain, Suhm Deep, Suhm Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 36°0′N 55°0′W / 36.000°N 55.000°W |
| (Somali Abyssal Plain, ) | Indian Ocean | 1°0′N 51°30′E / 1.000°N 51.500°E | |
| (Eyre Abyssal Plain, Great Bight Abyssal Plain, South Australian Abyssal Plain) | Indian Ocean | 37°30′S 130°0′E / 37.500°S 130.000°E | |
| (South China Sea Abyssal Plain) | South China Sea (Pacific Ocean) | 15°0′N 115°0′E / 15.000°N 115.000°E | |
| Southeast Pacific Basin | |||
| (South Indian Abyssal Plain, South Indian Basin, South Indian Ocean Plain) | Southern Ocean | 59°0′S 125°0′E / 59.000°S 125.000°E | |
| [38][39][40] | (South West Pacific Basin) | South Pacific Ocean | |
| Tagus Abyssal Plain | (Tagus Plain) | North Atlantic Ocean | 37°30′N 12°0′W / 37.500°N 12.000°W |
| (Tasman Abyssal Plain, Tasman Apron, Tasman Basin) | Tasman Sea (South Pacific Ocean) | 34°30′S 153°15′E / 34.500°S 153.250°E | |
| South Atlantic Ocean | |||
| Tsushima Basin | (Ulleung Basin) | Korea Strait (Sea of Japan, Pacific Ocean) | 36°35′N 131°48′E / 36.583°N 131.800°E |
| (Tufts Abyssal Plain) | North Pacific Ocean | 47°0′N 140°0′W / 47.000°N 140.000°W | |
| Tyrrhenian Plain | (Tyrrhenian Abyssal Plain) | Tyrrhenian Sea (Mediterranean Sea) | 40°0′N 12°45′E / 40.000°N 12.750°E |
| Southern Ocean | 62°30′S 70°0′E / 62.500°S 70.000°E | ||
| (Venezuela Abyssal Plain) | Caribbean Sea (Atlantic Ocean) | 14°0′N 67°0′W / 14.000°N 67.000°W | |
| North Atlantic Ocean | |||
| Weddell Plain[41] | (Weddell Abyssal Plain) | Southern Ocean | 65°0′S 20°0′W / ��65.000°S 20.000°W |
| Wrangellia Terrane[21][42][43][44][45][46][47][48][49] | (Wrangel Abyssal Plain) | Arctic Ocean | 81°0′N 160°0′E / 81.000°N 160.000°E |
| Sea of Japan (Pacific Ocean) | 37°30′N 135°0′E / 37.500°N 135.000°E | ||
| (Guatemala Basin) | Caribbean Sea (Atlantic Ocean) |
Oceanic trenches[]

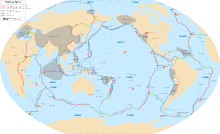
Oceanic trenches are long, narrow topographic depressions of the seabed. They are the deepest parts of the ocean floor, and they define one of the most important natural boundaries on the Earth's solid surface: the one between two lithospheric plates. Trenches are a distinctive morphological feature of plate boundaries. Trenches are found in all oceans with the exception of the Arctic Ocean and they are most common in the North and South Pacific Oceans.[2]
There are three types of lithospheric plate boundaries: 1.) divergent (where lithosphere and oceanic crust is created at mid-ocean ridges), 2.) convergent (where one lithospheric plate sinks beneath another and returns to the mantle), and 3.) transform (where two lithospheric plates slide past each other).
An oceanic trench is a type of convergent boundary at which two oceanic lithospheric slabs meet; the older (and therefore denser) of these slabs flexes and subducts beneath the other slab. Oceanic lithosphere moves into trenches at a global rate of about a tenth of a square meter per second. Trenches are generally parallel to a volcanic island arc, and about 200 km from a volcanic arc. Oceanic trenches typically extend 3 to 4 km (1.9 to 2.5 mi) below the level of the surrounding oceanic floor. The greatest ocean depth to be sounded is in the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, at a depth of 10,911 m (35,798 ft) below sea level.
List of oceanic trenches[]
The following is a list of the deepest parts of the Earth's oceans and seas (all depths are measured from sea level):
| Name | Location | Depth (meters) | Depth (feet) | Depth (miles) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Challenger Deep | Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc, Mariana Trench, Pacific Ocean | 11,034 | 36,197 | 6.86 |
| 2 | Tonga Trench | Pacific Ocean | 10,882 | 35,702 | 6.76 |
| 3 | Galathea Depth | Philippine Trench, Pacific Ocean | 10,545 | 34,580 | 6.54 |
| 4 | Kuril–Kamchatka Trench | Pacific Ocean | 10,542 | 34,449 | 6.52 |
| 5 | Kermadec Trench | Pacific Ocean | 10,047 | 32,963 | 6.24 |
| 6 | Izu–Ogasawara Trench | Pacific Ocean | 9,810 | 32,087 | 6.08 |
| 7 | Japan Trench | Pacific Ocean | 9,000 | 29,527 | 5.59 |
| 8 | Puerto Rico Trench | Atlantic Ocean | 8,605 | 28,232 | 5.35 |
| 9 | Yap Trench | Pacific Ocean | 8,527 | 27,976 | 5.30 |
| 10 | South Sandwich Trench | Atlantic Ocean | 8,428 | 27,651 | 5.24 |
| 11 | Richards Deep | Peru–Chile Trench, Pacific Ocean | 8,065 | 26,456 | 5.01 |
| 12 | Diamantina Deep | Diamantina Fracture Zone, Indian Ocean | 8,047 | 26,401 | 5.00 |
| 13 | Romanche Trench | Atlantic Ocean | 7,760 | 25,460 | 4.82 |
| 14 | Cayman Trough | Caribbean | 7,687 | 25,238 | 4.78 |
| 15 | Aleutian Trench | Pacific Ocean | 7,679 | 25,194 | 4.77 |
| 16 | Java Trench | Indian Ocean | 7,455 | 24,460 | 4.63 |
| 17 | Banda Sea | 7,351 | 24,117 | 4.56 | |
| 18 | Dordrecht Deep | Indian Ocean | 7,019 | 23,028 | 4.36 |
| 19 | Middle America Trench | Pacific Ocean | 6,669 | 21,880 | 4.14 |
| 20 | Puysegur Trench | Pacific Ocean | 6,300 | 20,700 | 3.9 |
| 21 | Pacific Ocean | 6,150 | 20,177 | 3.8 | |
| 22 | Litke Deep | Eurasian Basin*, Arctic Ocean | 5,450 | 17,881 | 3.39 |
| 23 | Manila Trench | South China Sea | 5,400 | 17,700 | 3.36 |
| 24 | Calypso Deep | Hellenic Trench, Mediterranean | 5,267 | 17,280 | 3.27 |
| 25 | Ryukyu Trench | Pacific Ocean | 5,212 | 17,100 | 3.24 |
| 26 | * | Southern Ocean, Australia | 5,000 | 16,400 | 3.1 |
- Entries marked with * are the deepest parts of their respective water bodies, but are not oceanic trenches.
Oceanic plateau[]
An oceanic plateau is a large, relatively flat submarine region that rises well above the level of the ambient seabed.[50] While many oceanic plateaus are composed of continental crust, and often form a step interrupting the continental slope, some plateaus are undersea remnants of large igneous provinces. Continental crust has the highest amount of silicon (such rock is called felsic). Oceanic crust has a smaller amount of silicon (mafic rock).
The anomalous volcanism associated with the formation of oceanic plateaux at the time of the Cenomanian–Turonian boundary (90.4 million years) ago may have been responsible for the environmental disturbances that occurred at that time. The physical manifestations of this were elevated atmospheric and oceanic temperatures, a significant sea-level transgression, and a period of widespread anoxia, leading to the extinction of 26% of all genera.[51] These eruptions would also have resulted in the emission of large quantities of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, leading to global warming. Additionally, the emission of sulfur monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide, and halogens into the oceans would have made seawater more acidic resulting in the dissolution of carbonate, and further release of CO
2. This runaway greenhouse effect was probably put into reverse by the decline of the anomalous volcanic activity and by increased CO
2-driven productivity in oceanic surface waters, leading to increased organic carbon burial, black shale deposition, anoxia and mass extinction in the ocean basins.[51]

List of oceanic plateaus[]
- Campbell Plateau (South Pacific)
- Challenger Plateau (South Pacific)
- Agulhas Plateau[52] (Southwest Indian)
- Caribbean–Colombian Plateau (Caribbean)
- Exmouth Plateau (Indian)
- Hikurangi Plateau (Southwest Pacific)
- Kerguelen Plateau (Indian)
- Manihiki Plateau (Southwest Pacific)
- (Southwest Pacific)
- Mascarene Plateau (Indian)
- Naturaliste Plateau (Indian)
- Ontong Java Plateau (Southwest Pacific)
- Shatsky Rise (North Pacific)
- (North Atlantic)
- Wrangellia Terrane (Northeast Pacific)
- (Arctic)
Mid-ocean ridges[]
A mid-ocean ridge is a general term for an underwater mountain system that consists of various mountain ranges (chains), typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. This type of oceanic ridge is characteristic of what is known as an oceanic spreading center, which is responsible for seafloor spreading.
List of mid-ocean ridges[]
- Aden Ridge
- American–Antarctic Ridge
- Carlsberg Ridge
- Central Indian Ridge
- Chile Rise
- Cocos Ridge
- East Pacific Rise
- East Scotia Ridge
- Explorer Ridge
- Gakkel Ridge (Mid-Arctic Ridge)
- Gorda Ridge
- Juan de Fuca Ridge
- (between Greenland and Spitsbergen)
- Kolbeinsey Ridge (North of Iceland)
- Mid-Atlantic Ridge
- Norfolk Ridge
- Pacific–Antarctic Ridge
- Palau–Kyushu Ridge
- Reykjanes Ridge (south of Iceland)
- Southeast Indian Ridge
- Southwest Indian Ridge
See also[]
- Physical oceanography
- Bathymetry
- Challenger Deep
- Hadal zone
- List of oceanic landforms
- List of seamounts by summit depth
- Seamount
- Submarine canyon
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d P.P.E. Weaver; J. Thomson; P. M. Hunter (1987). Geology and Geochemistry of Abyssal Plains (PDF). Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications. p. x. ISBN 978-0-632-01744-7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 December 2010. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Harris P.T., MacMillan-Lawler M., Rupp J., Baker E.K. (2014). "Geomorphology of the oceans". Marine Geology. 352: 4–24. Bibcode:2014MGeol.352....4H. doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2014.01.011.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Craig R. Smith; Fabio C. De Leo; Angelo F. Bernardino; Andrew K. Sweetman & Pedro Martinez Arbizu (2008). "Abyssal food limitation, ecosystem structure and climate change" (PDF). Trends in Ecology and Evolution. 23 (9): 518–528. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2008.05.002. PMID 18584909. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ N.G. Vinogradova (1997). "Zoogeography of the Abyssal and Hadal Zones". The Biogeography of the Oceans. Advances in Marine Biology. 32. pp. 325–387. doi:10.1016/S0065-2881(08)60019-X. ISBN 978-0-12-026132-1.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Ivan Tolstoy & Maurice Ewing (October 1949). "North Atlantic hydrography and the mid-Atlantic Ridge". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 60 (10): 1527–40. Bibcode:1949GSAB...60.1527T. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1949)60[1527:NAHATM]2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Bruce C. Heezen, Maurice Ewing and D.B. Ericson (December 1951). "Submarine topography in the North Atlantic". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 62 (12): 1407–1417. Bibcode:1951GSAB...62.1407H. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1951)62[1407:STITNA]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0016-7606.
- ^ Bruce C. Heezen, D.B. Ericson and Maurice Ewing (July 1954). "Further evidence for a turbidity current following the 1929 Grand banks earthquake". Deep-Sea Research. 1 (4): 193–202. Bibcode:1954DSR.....1..193H. doi:10.1016/0146-6313(54)90001-5.
- ^ F.F. Koczy (1954). "A survey on deep-sea features taken during the Swedish deep-sea expedition". Deep-Sea Research. 1 (3): 176–184. Bibcode:1954DSR.....1..176K. doi:10.1016/0146-6313(54)90047-7.
- ^ Bruce C. Heezen; Marie Tharp & Maurice Ewing (1962). "The Floors of the Oceans. I. The North Atlantic. Text to Accompany the Physiographic Diagram of the North Atlantic". In H. Caspers (ed.). Heezen, Bruce C., Marie Tharp, and Maurice Ewing: The Floors of the Oceans. I. The North Atlantic. Text to Accompany the Physiographic Diagram of the North Atlantic. With 49 fig., 30 plates. – New York, N.Y.: The Geological Society of America, Special Paper 65, 1959. 122 p. $10.00. Internationale Revue der Gesamten Hydrobiologie und Hydrographie. 47. Weinheim: WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Company. p. 487. doi:10.1002/iroh.19620470311. Retrieved 26 June 2010.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Bruce C. Heezen & A.S. Laughton (1963). "Abyssal plains". In M.N. Hill (ed.). The Sea. 3. New York: Wiley-Interscience. pp. 312–64.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Marc Wick (16 June 2010). "Record search for "abyssal plain"". Switzerland: GeoNames geographical database. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ "Viewing the Earth from space". DK Millennium World Atlas: A Portrait of the Earth in the Year 2000. New York: Dorling Kindersley Publishing. 1 October 1999. pp. xvi–xvii. ISBN 978-0-7894-4604-6.
- ^ Gabriele Uenzelmann‐Neben, Karsten Gohl, Axel Ehrhardt, Michael Seargent (1999). "Agulhas Plateau, SW Indian Ocean: New Evidence for Excessive Volcanism". Geophysical Research Letters. 26 (13): 1941–1944. Bibcode:1999GeoRL..26.1941U. doi:10.1029/1999GL900391. Retrieved 27 June 2010.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Frank Scheckenbach; Klaus Hausmann; Claudia Wylezich; Markus Weitere; Hartmut Arndt (5 January 2010). "Large-scale patterns in biodiversity of microbial eukaryotes from the abyssal sea floor". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 107 (1): 115–120. Bibcode:2010PNAS..107..115S. doi:10.1073/pnas.0908816106. PMC 2806785. PMID 20007768.
- ^ Pedro Martínez Arbizu & Horst Kurt Schminke (18 February 2005). "DIVA-1 expedition to the deep sea of the Angola Basin in 2000 and DIVA-1 workshop 2003". Organisms Diversity & Evolution. 5 (Supplement 1): 1–2. doi:10.1016/j.ode.2004.11.009.
- ^ Schmid, C., Brenke, N. & J.W. Wägele (2002). "On abyssal isopods (Crustacea: Isopoda: Asellota) from the Angola Basin: Eurycope tumidicarpus n.sp. and redescription of Acanthocope galathea Wolff, 1962". Organisms, Diversity & Evolution. 2 (1): 87–88. doi:10.1078/1439-6092-00030.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Mursch, A., Brenke, N. & J.W. Wägele (2008). "Results of the DIVA-1 expedition of RV "Meteor" (Cruise M48:1): Three new species of Munnopsidae Sars, 1864 from abyssal depths of the Angola Basin (Crustacea: Isopoda: Asellota)" (PDF). In Pedro Martinez Arbizu; Saskia Brix (eds.). Bringing light into deep-sea biodiversity (Zootaxa 1866). Auckland, New Zealand: Magnolia Press. pp. 493–539. ISBN 978-1-86977-260-4. Retrieved 27 June 2010.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Affholder, M.; Valiron, F. (2001). Descriptive Physical Oceanography. CRC Press. p. 317. ISBN 978-0-203-96927-4.
- ^ "Antarctica Detail". geonames.usgs.gov-us. Retrieved 2017-03-07.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica (2010). "Blake Plateau". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f P.D.N. Hebert (Professor, Department of Zoology). "Towering Mountains". Canada's Aquatic Environments. Guelph, Ontario, Canada: CyberNatural Software, University of Guelph. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ I.G. Priede; P.M. Bagley; S. Way; P.J. Herring; J.C. Partridge (July 2006). "Bioluminescence in the deep sea: Free-fall lander observations in the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Verde". Deep-Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers. 53 (7): 1272–1283. Bibcode:2006DSRI...53.1272P. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2006.05.004.
- ^ "Enderby Plain". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ "Enderby Plain". Australian Antarctic Data Centre. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Mart, Yossi and Robertson, Alastair H. F. (1998). Eratosthenes Seamount: an oceanographic yardstick recording the Late Mesozoic-Tertiary geological history of the Eastern Mediterranean, in Robertson, A.H.F., Emeis, K.-C., Richter, C., and Camerlenghi, A. (eds.), Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 160, Chapter 52, 701–708.
- ^ Kempler, Ditza (1998). Eratosthenes Seamount: the possible spearhead of incipient continental collision in the Eastern Mediterranean, in Robertson, A.H.F., Emeis, K.-C., Richter, C., and Camerlenghi, A. (eds.), Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, Vol. 160, Chapter 53, 709–721.
- ^ David A. Ross; Elazar Uchupi; Kenneth E. Prada; Joseph C. MacIlvaine (1974). "Bathymetry and Microtopography of Black Sea: Structure". Volume M 20: The Black Sea — Geology, Chemistry, and Biology (AAPG Special Volumes ed.). American Association of Petroleum Geologists. pp. 1–10. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Dumitru Dorogan & Diaconeasa Danut (2002). "The Black Sea Romanian coastal zone: a general survey of the erosion process". In Richard C. Ragaini (ed.). International Seminar on Nuclear War and Planetary Emergencies: 26th Session. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Company. pp. 145–164. ISBN 978-981-238-092-0.
- ^ Vittorio Barale (2008). "The European marginal and enclosed seas: an overview". In Vittorio Barale; Martin Gade (eds.). Remote Sensing of the European Seas. Heidelberg: Springer. pp. 3–22. ISBN 978-1-4020-6771-6.
- ^ Bernd Andeweg (2002). Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Iberian Peninsula, causes and effects of changing stress fields (PhD Thesis). Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Kuhnt W, Collins ES (1996). "8. Cretaceous to Paleogene benthic foraminifers from the Iberia abyssal plain" (PDF). Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results. Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program. 149: 203–216. doi:10.2973/odp.proc.sr.149.254.1996. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ "JOIDES Basin". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2018-08-14.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica (2010). "Seychelles-Mauritius Plateau". Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Geoscience Australia: Naturaliste Plateau Archived 2012-07-23 at archive.today. Retrieved 18 June 2010.
- ^ OceanLab (2000). "The Porcupine Seabight and Abyssal Plain". Newburgh, Aberdeenshire, UK: University of Aberdeen. Archived from the original on 2009-07-22. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Marine Biodiversity & Ecosystem Functioning (18 November 2004). "Porcupine Abyssal Plain" (PDF). Horta, Azores: University of the Azores. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Thomas S. Ahlbrandt (2001) The Sirte Basin Province of Libya—Sirte-Zelten Total Petroleum System. U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2202–F, U.S. Geological Survey, U.S. Department of the Interior. Accessed on 27 June 2010.
- ^ Nick Mortimer & Dave Parkinson (1996). "Hikurangi Plateau: A Cretaceous large igneous province in the southwest Pacific Ocean". Journal of Geophysical Research. 101 (B1): 687–696. Bibcode:1996JGR...101..687M. doi:10.1029/95JB03037. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Kaj Hoernle; Reinhard Werner; Folkmar Hauff; Paul van den Bogaard (2005). "The Hikurangi Oceanic Plateau: A Fragment of the Largest Volcanic Event on Earth" (PDF). IFM – GEOMAR Yearbook 2002–2004. Kiel, Germany: Leibniz Institute of Marine Sciences at Kiel University (IFM-GEOMAR). pp. 51–54. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-03-29. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Te Ara – the Encyclopedia of New Zealand (4 March 2010). Hikurangi Plateau. Wellington, New Zealand: Te Ara: The Encyclopedia of New Zealand. ISBN 978-0-478-18451-8. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ De Broyer, C., Nyssen, F. & P. Dauby (July–August 2004). "The crustacean scavenger guild in Antarctic shelf, bathyal and abyssal communities". Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography. 51 (14–16): 1733–1752. Bibcode:2004DSRII..51.1733D. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2004.06.032. hdl:2268/34147.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ Daniel Sarewitz (November 1983). "Seven Devils terrane: Is it really a piece of Wrangellia?". Geology. 11 (11): 634–637. Bibcode:1983Geo....11..634S. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1983)11<634:SDTIIR>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0091-7613.
- ^ WESLEY K. WALLACE, CATHERINE L. HANKS and JOHN F. ROGERS (November 1989). "The southern Kahiltna terrane: Implications for the tectonic evolution of southwestern Alaska". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 101 (11): 1389–1407. Bibcode:1989GSAB..101.1389W. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<1389:TSKTIF>2.3.CO;2.
- ^ ROGERS, Robert K. & SCHMIDT, Jeanine M. (May 15, 2002). "METALLOGENY OF THE WRANGELLIA TERRANE IN THE TALKEETNA MOUNTAINS, SOUTHERN ALASKA". Cordilleran Section – 98th Annual Meeting. Alaskan Tectonics, Structure, and Stratigraphy. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Greene, A.R., Scoates, J.S., Weis, D. and Israel, S. (2005). "Flood basalts of the Wrangellia Terrane, southwest Yukon: Implications for the formation of oceanic plateaus, continental crust and Ni-Cu-PGE mineralization" (PDF). In D.S. Emond; L.L. Lewis; G.D. Bradshaw (eds.). Yukon Exploration and Geology. Yukon Geological Survey. pp. 109–120. Retrieved 27 June 2010.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- ^ WARREN J. NOKLEBERG, DAVID L. JONES and NORMAN J. SILBERLING (1985). "Origin and tectonic evolution of the Maclaren and Wrangellia terranes, eastern Alaska Range, Alaska". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 96 (10): 1257–1270. Bibcode:1985GSAB...96.1251N. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1985)96<1251:OATEOT>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Jeffrey M. Trop; Kenneth D. Ridgway; Jeffrey D. Manuszak; Paul Layer (June 2002). "Mesozoic sedimentary-basin development on the allochthonous Wrangellia composite terrane, Wrangell Mountains basin, Alaska: A long-term record of terrane migration and arc construction". Geological Society of America Bulletin. 114 (6): 693–717. Bibcode:2002GSAB..114..693T. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(2002)114<0693:MSBDOT>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0016-7606.
- ^ ISRAEL, Steve A. & MORTENSEN, James K. (8 May 2009). "STRATIGRAPHIC AND TECTONIC RELATIONSHIPS OF THE PALEOZOIC PORTION OF WRANGELLIA". Cordilleran Section Meeting – 105th Annual Meeting. Paleozoic Paleogeography of Cordilleran Terranes III. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ A.R. Greene, J.S. Scoates & D. Weis (2005). "Wrangellia Terrane on Vancouver Island, British Columbia: Distribution of Flood Basalts with Implications for Potential Ni-Cu-PGE Mineralization in Southwestern British Columbia" (PDF). British Columbia Geological Survey. Geological Fieldwork 2004: 209–220. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ oceanic plateau. (2008). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved June 27, 2010, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Andrew C. Kerr (July 1998). "Oceanic plateau formation: A cause of mass extinction and black shale deposition around the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary?". Journal of the Geological Society. 155 (4): 619–626. Bibcode:1998JGSoc.155..619K. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.155.4.0619. ISSN 0016-7649. S2CID 129178854. Archived from the original on 5 November 2011. Retrieved 27 June 2010.
- ^ Uenzelmann-Neben, G., K. Gohl, A. Ehrhardt, and M. Seargent (1999). Agulhas Plateau, SW Indian Ocean: New Evidence for Excessive Volcanism, Geophysical Research Letters, 26(13), 1941–1944.
Further reading[]
- Böggemann M. & Purschke G. (2005). "Abyssal benthic Syllidae (Annelida: Polychaeta) from the Angola Basin". Organisms, Diversity & Evolution. 5 (Supplement 1): 221–226. doi:10.1016/j.ode.2004.11.006.
- Bohn, J.M. (2005). "On two rare abyssal Myriotrochidae (Echinodermata: Holothuroidea: Apodida) new to the South Atlantic: Siniotrochus myriodontus Gage and Billet, 1986 and Lepidotrochus parvidiscus angolensis subsp. nov". Organisms, Diversity & Evolution. 5 (Supplement 1): 231–238. doi:10.1016/j.ode.2004.11.008.
- Brandt A.; Brenke N.; Andres H.-G.; Brix S.; Guerrero-Kommritz J.; Mühlenhardt-Siegel U. & Wägele J.-W. (2005). "Diversity of peracarid crustaceans (Malacostraca) from the abyssal plain of the Angola Basin". Organisms, Diversity and Evolution. 5: 105–112. doi:10.1016/j.ode.2004.10.007.
- Gad G. (2005). "Giant Higgins-larvae with paedogenetic reproduction from the deep sea of the Angola Basin- evidence for a new life cycle and for abyssal gigantism in Loricifera?". Organisms, Diversity & Evolution. 5 (Supplement 1): 59–76. doi:10.1016/j.ode.2004.10.005.
- Gill Adrian E. (1982). Atmosphere-Ocean Dynamics. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-283520-9.
- Gooday A.J.; Nomaki H. & Kitazato H. (2008). "Modern deep-sea benthic foraminifera: a brief review of their morphology-based biodiversity and trophic diversity". Geological Society, London, Special Publications. 303 (1): 97–119. Bibcode:2008GSLSP.303...97G. doi:10.1144/SP303.8. S2CID 129698419.
- Gooday A.J., Kamenskaya O.E. & Cedhagen T. (2007). "New and little-known Komokiacea (Foraminifera) from the bathyal and abyssal Weddell Sea and adjacent areas". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 151 (2): 219–251. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2007.00326.x.
- Gooday A.J. & Malzone G. (2004). "Hyperammina micaceus sp. nov.: a new foraminiferan species (Protista) from the Porcupine Abyssal Plain, Northeast Atlantic". Journal of Micropalaeontology. 23 (2): 171–179. doi:10.1144/jm.23.2.171.
- Janussen D. & Tendal O.S. (2007). "Diversity and distribution of Porifera in the bathyal and abyssal Weddell Sea and adjacent areas". Deep-Sea Research Part II. 54 (16–17): 1864–1875. Bibcode:2007DSR....54.1864J. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.012.
- Markhaseva E.L. & Schulz K. (2006). "Sensiava longiseta (Copepoda, calanoidea): a new genus and species from the abyssal of the Weddell Sea". Zootaxa. 1368: 1–18. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.1368.1.1.
- Mühlenhardt-Siegel U. (2008). "Phalloleucon abyssalis, a new cumacean genus and species (Crustacea: Peracarida: Leuconidae) from the Peru Basin". Zootaxa (1829). pp. 61–68.
- Nozawa F.; Kitazato H.; Tsuchiya M.; Gooday A.J. (2006). "'Live' benthic foraminifera at an abyssal site in the equatorial Pacific nodule province: abundance, diversity and taxonomic composition". Deep-Sea Research Part I. 53 (8): 1406–1422. Bibcode:2006DSRI...53.1406N. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2006.06.001.
- Sabbatini A.; Morigi C.; Negri A. & Gooday A.J. (2007). "Distribution and Biodiversity of Stained Monothalamous Foraminifera from Tempelfjord, Svalbard". Journal of Foraminiferal Research. 37 (2): 93–106. doi:10.2113/gsjfr.37.2.93.
- Schrödl M., Linse K. & Schwabe E. (2006). "Review on the distribution and biology of Antarctic Monoplacophora, with first abyssal record of Laevipilina antarctica". Polar Biology. 29 (9): 721–727. doi:10.1007/s00300-006-0132-7. S2CID 23753587.
- Schwabe E.; Bohn J.M.; Engl W.; Linse K.; Schrödl M. (2007). "Rich and rare – first insights into species diversity and abundance of Antarctic abyssal Gastropoda (Mollusca)". Deep-Sea Research Part II. 54 (16–17): 1831–1847. Bibcode:2007DSR....54.1831S. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.010.
- Sebastian S.; Raes M.; De Mesel I.; Vanreusel A. (2007). "Comparison of the nematode fauna from the Weddell Sea Abyssal Plain with two North Atlantic abyssal sites". Deep-Sea Research Part II. 54 (16–17): 1727–1736. Bibcode:2007DSR....54.1727S. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2007.07.004.
- Seifried S., Plum Ch. & Schulz M. (2007). "A new species of Parabradya Lang, 1944 (Copepoda: Harpacticoida: Ectinosomatidae) from the abyssal plain of the Angola Basin". Zootaxa. 1432: 1–21. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.1432.1.1.
- Robert H. Stewart (2007). Introduction to Physical Oceanography (PDF). College Station: Texas A&M University. ISBN 978-1-61610-045-2. OCLC 169907785.
- Willen E. (2005). "A new species of Paranannopus Lang, 1936 (Copepoda, Harpacticoida, Pseudotachidiidae) with atrophic mouthparts from the abyssal of the Angola Basin". Organisms, Diversity & Evolution. 5 (Supplement 1): 19–27. doi:10.1016/j.ode.2004.10.002.
- Yasuhara M., Cronin T.M. & Martinez Arbizu P. (2008). "Abyssal ostracods from the South and Equatorial Atlantic Ocean: biological and paleoceanographic implications". Deep-Sea Research Part I. 55 (4): 490–497. Bibcode:2008DSRI...55..490Y. doi:10.1016/j.dsr.2008.01.004.
External links[]
- Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (3 November 2009). "Deep-sea Ecosystems Affected By Climate Change". Science Daily.
- Submarine topography
- Coastal and oceanic landforms
- Lists of landforms
- Marine geology
- Abyssal plains
- Oceanic plateaus
- Oceanic ridges
- Oceanic trenches
- Plate tectonics