List of unsaturated fatty acids
| ω−n | Common Name | Lipid Numbers | Δn | Structural Formula | Trans or Cis | Naturally Occurring in | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ω−3 | α-Linolenic acid | C18:3 | Δ9,12,15 | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | cis | Flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts [1] | |
| ω−3 | Stearidonic acid | C18:4 | Δ6,9,12,15 | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)4COOH | cis | Seed oils of hemp, blackcurrant, corn gromwell[citation needed] | |
| ω−3 | Eicosapentaenoic acid | C20:5 | Δ5,8,11,14,17 | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)3COOH | cis | cod liver, herring, mackerel, salmon, menhaden and sardine[citation needed] | |
| ω−3 | Cervonic acid | C22:6 | Δ4,7,10,13,16,19 | CH3CH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)2COOH | cis | maternal milk, fish oil.[2] | |
| ω−6 | Linoleic acid | C18:2 | Δ9,12 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | cis | Peanut oil,[3] chicken fat,[4] olive oil [5][6] | |
| ω−6 | Linolelaidic acid | C18:2 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | trans | partially hydrogenated vegetable oils | ||
| ω−6 | γ-Linolenic acid | C18:3 | Δ6,9,12 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)4COOH | cis | borage oil, black currant oil, evening primrose oil [7] and safflower oil [8] | |
| ω−6 | Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid | C20:3 | Δ8,11,14 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)6COOH | cis | only in trace amounts in animal products[9][10] | |
| ω−6 | Arachidonic acid | C20:4 | Δ5,8,11,14 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)3COOH | cis | ||
| ω−6 | Docosatetraenoic acid | C22:4 | Δ7,10,13,16 | CH3(CH2)4CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)5COOH | cis | - | |
| ω−7 | Palmitoleic acid | C16:1 | Δ9 | CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | cis | Macadamia nuts[11] | |
| ω−7 | Vaccenic acid | C18:1 | Δ11 | CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)9COOH | trans | dairy products such as milk, butter, and yogurt.[12] | |
| ω−7 | Paullinic acid | C20:1 | Δ13 | CH3(CH2)5CH=CH(CH2)11COOH | cis | guarana[13] | |
| ω−9 | Oleic acid | C18:1 | Δ9 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | cis | olive oil, pecan oil,[14] canola oil,[15] | |
| ω−9 | Elaidic acid | C18:1 | Δ9 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH | trans | hydrogenated vegetable oil[16] | |
| ω−9 | Gondoic acid | C20:1 | Δ11 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)9COOH | cis | jojoba oil[17] (edible but non-caloric and non-digestible) | |
| ω−9 | Erucic acid | C22:1 | Δ13 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)11COOH | cis | wallflower seed; mustard oil | |
| ω−9 | Nervonic acid | C24:1 | Δ15 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)13COOH | cis | King salmon, flaxseed, sockeye salmon, sesame seed, macadamia nuts[18] | |
| ω−9 | Mead acid | C20:3 | Δ5,8,11 | CH3(CH2)7CH=CHCH2CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)3COOH | cis | cartilage |
Fatty acid molecular species[]
Mono-unsaturated fatty acid[]
The following fatty acids have one unsaturated bond.
Crotonic acid[]
Crotonic acid has 4 carbons, is included in croton oil, and is a trans-2-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C3H5 CO2H, IUPAC organization name (E)-but-2-enoic acid, trans -but-2-enoic acid, numerical representation 4: 1, n-1, molecular weight 86.09, melting point 72-74 °C, boiling point 180-181 °C, specific gravity 1.027. CAS registry number 107-93-7.

Myristoleic[]
Myristoleic acid has 14 carbons, is found in whale blubber, and is a cis-9-monounsaturated fatty acid. C13H25CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-tetradec-9-enoic acid, numerical representation 14:1, n-5, molecular weight 226.36, melting point of -4.5 -4 °C. CAS Registry Number 544-64-9.

Palmitoleic acid[]
Palmitoleic acid has 16 carbons, is found in cod liver oil, , and , and is a cis9-monounsaturated fatty acid. C15H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-hexadec-9-enoic acid, n-7, numerical representation of 16: 1, molecular weight 254.41, melting point 5 °C, specific gravity 0.894. CAS Registry Number 373-49-9.
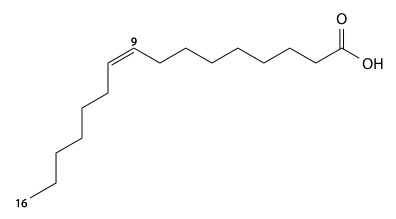
Sapienic acid[]
Sapienic acid has 16 carbons, is found in the skin, and is a cis6-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C15H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-6-Hexadecenoic acid, n-10, numerical expression 16: 1, molecular weight 254.41. CAS Registry Number 17004-51-2.
Oleic acid[]
Oleic acid has 18 carbons, is found in most animal fats and olive oil, and is a cis-9-monounsaturated fatty acid. C17H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-octadec-9-enoic acid, numerical representation 18:1 (9), n-9, molecular weight 282.46, melting point 13.4 °C, specific gravity 0.891. CAS Registry Number 112-80-1.

Elaidic acid[]
Elaidic acid has 18 carbons and is a trans-9-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. It is also a trans isomer of oleic acid. C17H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (E)-octadec-9-enoic acid, numerical representation 18:1 (9), n-9, molecular weight 282.46, melting point 43-45 °C. CAS Registry Number 112-79-8.

Vaccenic acid[]
Vaccenic acid has 18 carbons, is found in beef tallow, mutton, and butter, and is a trans11-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C17H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (E)-octadec-11-enoic acid, numerical representation 18:1 (11) n-7, molecular weight 282.46. CAS Registry Number 506-17-2.
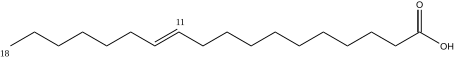
Gadoleic acid[]
Gadoleic acid has 20 carbons, is found in cod liver oil and other marine animal oils, and is a cis9-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H37CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-icos-9-enoic acid, numerical representation 20:1 (9), n-11, molecular weight 310.51. CAS Registry Number 29204-02-2.
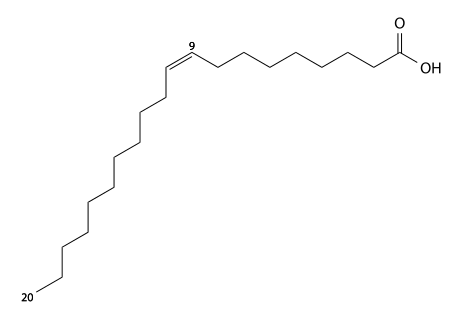
Eicosenoic acid[]
Eicosenoic acid has 20 carbons, is found in a wide variety of plant oils, and is a cis11-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H37CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-icos-11-enoic acid, numerical representation 20:1 (11), n-9, molecular weight 310.51. CAS Registry Number 5561-99-9.

Erucic acid[]
Erucic acid has 22 carbons, is found in rapeseed oil and mustard oil, and is a cis13-monounsaturated is a fatty acid. C21H41CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-docos-13-enoic acid, numerical representation 22:1, n-9, molecular weight 338.57, melting point 33-35 °C. CAS Registry Number 112-86-7.

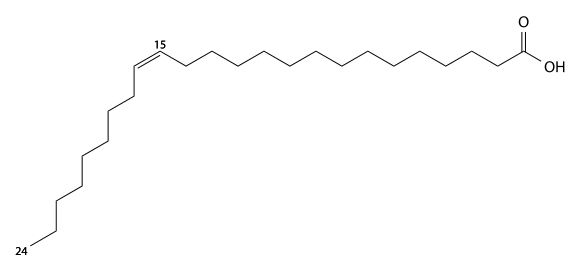
Nervonic acid[]
Nervonic acid has 24 carbons, is found in brain glycolipids (Nervon) and sphingomyelin, and is a cis15-mono-unsaturated fatty acid. C23H45CO2H, IUPAC organization name (Z)-tetracos-15-enoic acid, numerical representation 24:1, n-9, molecular weight 366.62, melting point 42-43 °C. CAS Registry Number 506-37-6.
Di-unsaturated fatty acid[]
The following fatty acids have two unsaturated bonds.
Linoleic acid[]
Linoleate has 18 carbons, is contained in many vegetable oils, particularly semi-drying oils, and is a cis-9-cis- 12-di-unsaturated fatty acid. C17H31CO2H, IUPAC organization name (9Z , 12Z)-octadeca- 9,12-dienoic acid, numerical representation 18: 2 (9,12), n-6, molecular weight 280.45, melting point -5 °C, specific gravity 0.902. CAS Registry Number 60-33-3. There is a double bond is conjugated as an isomer conjugated linoleic acid.

Eicosadienoic acid[]
Eicosadienoic acid (eicosadienoic's) has 20 carbons and is a cis-11-cis14-di-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H35CO2H, IUPAC organization name (11Z , 14Z)-icosa- 11,14-dienoic acid, numerical representation 20: 2 (11,14), n-6, molecular weight 308.50.

Docosadienoic acid[]
Docosadienoic acid (docosadienoic's) has 22 carbons and is a cis-13-cis16-di-unsaturated fatty acid. C21H39CO2H, IUPAC organization name (13Z , 16Z)-docosa- 13,16-dienoic acid, numerical representation 22: 2 (13,16), n-6, molecular weight 336.55. CAS Registry Number 7370-49-2.

Tri-unsaturated fatty acids[]
The following fatty acids have three unsaturated bonds.
Linolenic acid[]
α-linolenic acid (alpha-linolenic's) has 18 carbons, is found in linseed oil and drying oil, and is a 9,12,15-tri-unsaturated fatty acid. C17H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (9Z , 12Z , 15 Z)-octadeca-9,12,15-trienoic acid, numerical representation 18: 3 (9,12,15), n-3, molecular weight 278.43, melting point -11 °C, specific gravity 0.914. CAS Registry Number 463-40-1.

γ-linolenic acid (gamma-linolenic's) has 18 carbons, the structural isomers of α- linolenic acid. IUPAC organization name (6Z , 9Z , 12Z)-octadeca-6,9,12-trienoic acid, numerical representation 18: 3 (6, 9, 12), n-6. CAS Registry Number 506-26-3.
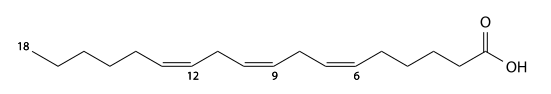
Pinolenic acid[]
Pinolenic acid (pinolenic's) has 18 carbons, is found in pine nuts, and is a 5,9,12-triunsaturated fatty acid. C17H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (5Z , 9Z , 12 Z)-octadeca-5,9,12-trienoic acid, numerical representation 18: 3 (5,9,12), n-6, molecular weight 278.43. CAS Registry Number 16833-54-8.

Eleostearic acid[]
α-eleostearic acid (alpha-eleostearic's) has 18 carbons, is found in Kiri drying oil, and is a 9,11,13-triunsaturated fatty acid. C17H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (9E , 11E , 13 Z)-octadeca-9,11,13-trienoic acid, numerical representation 18: 3 (9,11,13), n-5, molecular weight 278.43.

β-eleostearic acid (beta-eleostearic's, beta-eleostearic acid) is a geometric isomer of α- eleostearic acid. IUPAC organization name (9E , 11E , 13E)-octadeca-9,11,13-trienoic acid, numerical representation 18: 3 (9, 11, 13), n-5.

Mead acid[]
Mead acid (Mead's) has 20 carbons, is a 5,8,11-tri-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (5Z , 8Z , 11 Z)-icosa-5,8,11-trienoic acid, numerical representation 20: 3 (5,8,11), n-9, molecular weight 306.48. CAS Registry Number 20590-32-3.

Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid[]
Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (dihomo-gamma-linolenic's, dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid, DGLA) has 20 carbons, and is an 8,11,14-tri-unsaturated fatty acid. C19H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (8Z , 11Z , 14 Z)-icosa-8,11,14-trienoic acid, numerical representation 20: 3 (8,11,14), n-6, molecular weight 306.48. CAS Registry Number 1783-84-2.

Eicosatrienoic acid[]
Eicosatrienoic acid (eicosatrienoic's, eicosatrienoic acid) has 20 carbons and is an 11,14,17- tri unsaturated fatty acid. C19H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (11Z , 14Z , 17 Z)-icosa-11,14,17-trienoic acid, numerical representation 20: 3 (11,14,17), n-3, molecular weight 306.48.

Tetra-unsaturated fatty acids[]
The following fatty acids have four unsaturated bonds.
Stearidonic acid[]
Stearidonic acid (stearidonic's) has 18 carbons, is found in sardine oil and herring oil, and is a 6,9,12,15-tetraunsaturated fatty acid. C17H27CO2H, IUPAC organization name (6Z , 9Z , 12 Z , 15Z)-octadeca-6,9,12,15-tetraenoic acid, numerical representation 18: 4 (6,9,12,15), n-3, molecular weight 276.41. CAS Registry Number 20290-75-9.

Arachidonic acid[]
Arachidonic acid (arachidonic's) has 20 carbons, is present in animal visceral fat (brain, liver, kidney, lung, spleen), and is a 5,8,11,14-tetra-unsaturated fatty acid. I caused by the decomposition of cell membrane in the phospholipid. Prostaglandin, and important as starting materials for the thromboxane, leukotriene such as are known as a series of metabolic pathway to give eicosanoids, arachidonic acid cascade are compounds.
C19H31CO2H, IUPAC organization name (5Z , 8Z , 11 Z , 14Z)-icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid, numerical representation 20: 4 (5,8,11,14), n-6, molecular weight 304.47, boiling point 169- 171 °C. CAS Registry Number 506-32-1.

Eicosatetraenoic acid[]
Eicosatetraenoic acid (eicosatetraenoic's) has 20 carbons and is an 8,11,14,17-tetraunsaturated fatty acid. C19H31CO2H, IUPAC organization name (8Z , 11Z , 14 Z , 17Z)-icosa-8,11,14,17-tetraenoic acid, numerical representation 20: 4 (8,11,14,17), n-3, molecular weight 304.47.

Adrenic acid[]
Adrenic acid (adrenic'sd) has 22 carbons and is a 7,10,13,16-tetra-unsaturated fatty acid. C21H35CO2H, IUPAC organization name (7Z , 10Z , 13 Z , 16Z)-docosa-7,10,13,16-tetraenoic acid, numerical representation 22: 4 (7,10,13,16), n-6, molecular weight 332.52. CAS Registry Number 28874-58-0.

Pentaunsaturated fatty acids[]
The following fatty acids have five unsaturated bonds.
Bosseopentaenoic acid[]
Bosseopentaenoic acid (Boseopentaen's), has 20 carbons and is a 5,8,10,12,14-pentaunsaturated fatty acid. C17H25CO2H, IUPAC organization name (5Z , 8Z , 10 E , 12E , 14Z)-eicosa-5,8,10,12,14-pentaenoic acid, numerical representation 20: 5 (5,8,10,12,14), n-6, molecular weight 302.46 g·mol−1.[19]
Eicosapentaenoic acid[]
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has 20 carbons, is found in fish oil, is a pentaunsaturated fatty acid. It is one of the essential fatty acids. The recommendation of ingesting fish oil supplements during pregnancy is said to help increase the cognitive ability at 6 months, but mercury concentration in fish products offsets the effect. In patients with hyperlipidemia and it can help lower triglycerides and also has an anti-platelet effect similar to other anti-platelet agents. It has also been shown to help in secondary prevention of ischemic heart disease as shown with the .
C19H29CO2H, IUPAC organization name (5Z , 8Z , 11 Z , 14Z , 17Z)-icosa-5,8,11,14,17-pentaenoic acid, numerical representation of 20: 5 (5,8,11,14,17), n-3, molecular weight 302.45, from melting point -54 -53 °C, specific gravity 0.943. CAS Registry Number 10417-94-4.

Ozubondo acid[]
Ozubondo acid (Ozubondo's, Osbond acid), has 22 carbons, is a 4,7,10,13,16- pentaunsaturated fatty acid. C21H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (4Z , 7Z , 10Z , 13Z , 16Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16-pentaenoic acid, numerical representation 22: 5 (4,7,10,13,16), n-6, molecular weight 330.50. CAS Registry Number 25182-74-5

Sardine acid[]
Sardine acid (Clupanodonic acid) has 22 carbons, is found in sardine oil and herring oil, is a 7,10,13,16,19- pentaunsaturated fatty acid. C21H33CO2H, IUPAC organization name (7Z , 10Z , 13 Z , 16Z , 19Z)-docosa-7,10,13,16,19-pentaenoic acid, numerical representation 22: 5 (7,10,13,16,19), n-3, molecular weight 330.50.

Tetracosanolpentaenoic acid[]
Tetracosanolpentaenoic acid has 24 carbons, is a 9,12,15,18,21-penta unsaturated fatty acid. C23H37CO2H, IUPAC organization name (9Z , 12Z , 15 Z , 18Z , 21Z)-tetracosa-9,12,15,18,21-pentaenoic acid, numerical representation 24: 5 (9,12,15,18,21), n-3, molecular weight 358.56.

Hexa-unsaturated fatty acids[]
The following fatty acids have six unsaturated bonds.
Cervonic acid[]
Cervonic acid (or docosahexaenoic acid) has 22 carbons, is found in fish oil, is a 4,7,10,13,16,19-hexa unsaturated fatty acid. In the human body its generation depends on consumption of omega 3 essential fatty acids (e.g., ALA or EPA), but the conversion process is inefficient.[20] C21H31CO2H, IUPAC organization name (4Z, 7Z, 10Z, 13Z, 16Z, 19Z)-docosa-4,7,10,13,16,19-hexaenoic acid, numerical representation 22: 6 (4, 7,10,13,16,19), n-3, molecular weight 328.49, melting point -44 °C, specific gravity 0.950. CAS Registry Number 6217-54-5.

Herring acid[]
Herring acid (Herring's, Nisinic acid) is a 6,9,12,15,18,21-hexa unsaturated fatty acid with 24 carbon atoms. C23H35CO2H, IUPAC organization name (6Z , 9Z , 12 Z , 15Z , 18Z , 21Z)-tetracosa-6,9,12,15,18,21-hexaenoic acid, numerical representation 24: 6 (6, 9,12,15,18,21), n-3, molecular weight 356.54.

See also[]
References[]
- ^ Simopoulos, Artemis P. (2002). "Omega‐3 fatty acids in wild plants, nuts and seeds". Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 11 (s6): S163–S173. doi:10.1046/j.1440-6047.11.s.6.5.x.
- ^ Guesnet P, Alessandri JM (2011). "Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and the developing central nervous system (CNS) - Implications for dietary recommendations". Biochimie. 93 (1): 7–12. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2010.05.005. PMID 20478353.
- ^ Oil, peanut, salad or cooking: search for peanut oil on "USDA Food Composition Databases". Archived from the original on 2015-03-03. Retrieved 2011-11-14.
- ^ M. K. Nutter, E. E. Lockhart and R. S. Harris (1943). "The chemical composition of depot fats in chickens and turkeys". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 20 (11): 231–234. doi:10.1007/BF02630880. S2CID 84893770.
- ^ "Olive Oil : Chemical Characteristics".
- ^ Beltran; Del Rio, C; Sánchez, S; Martínez, L; et al. (2004). "Influence of Harvest Date and Crop Yield on the Fatty Acid Composition of Virgin Olive Oils from Cv. Picual" (PDF). J. Agric. Food Chem. 52 (11): 3434–3440. doi:10.1021/jf049894n. PMID 15161211.
- ^ "Conditions We Treat".
- ^ Flider, Frank J. (2013). "Development and commercialization of GLA safflower oil". Lipid Technology. 25 (10): 227–229. doi:10.1002/lite.201300302.
- ^ Horrobin, D. F., 1990a. Gamma linolenic acid. Rev. Contemp. Pharmacother. 1, 1-45
- ^ Huang, Y.-S. and Mills, D. E. (Eds.), 1996. Gamma-linolenic acid metabolism and its roles in nutrition and medicine. AOCS Press, Champaign, Illinois, 319 pp.
- ^ "Nuts, macadamia nuts, raw". NutritionData.com.
- ^ Natural trans fats may be good for you. May 19, 2008
- ^ Avato, P; Pesante, MA; Fanizzi, FP; Santos, CA (2003). "Seed oil composition of Paullinia cupana var. Sorbilis (Mart.) Ducke". Lipids. 38 (7): 773–80. doi:10.1007/s11745-003-1126-5. PMID 14506841. S2CID 4026737.
- ^ Villarreal-Lozoya, Jose E.; Lombardini, Leonardo; Cisneros-Zevallos, Luis (2007). "Phytochemical constituents and antioxidant capacity of different pecan Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch] cultivars". Food Chemistry. 102 (4): 1241. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.07.024.
- ^ "Comparison of Dietary Fats Chart". Canola Council of Canada. Archived from the original on 2008-06-06. Retrieved 2008-09-03.
- ^ Abbey M, Nestel PJ (1994). "Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity is increased when trans-elaidic acid is substituted for cis-oleic acid in the diet". Atherosclerosis. 106 (1): 99–107. doi:10.1016/0021-9150(94)90086-8. PMID 8018112.
- ^ Miwa, Thomas (1971). "Jojoba Oil Wax Esters and Derived Fatty Acids and Alcohols: Gas Chromatographic Analyses". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 48 (6): 259–264. doi:10.1007/bf02638458. S2CID 1466516. Retrieved May 6, 2013.
- ^ "Foods highest in 24:1 C".
- ^ Burgess, J.R.; De la Rosa, R.I.; Jacobs, R.S.; Butler, A (1991). "A new eicosapentaenoic acid formed from arachidonic acid in the coralline red algae Bossiella orbigniana". Lipids. 26 (2): 1057–1059. doi:10.1007/BF02544012
- ^ Gropper, Sareen Annora Stepnick (2016-10-05). Advanced nutrition and human metabolism. Smith, Jack L. (Professor of nutrition),, Carr, Timothy P. (Seventh ed.). Australia. ISBN 9781305627857. OCLC 988914315.
- Fatty acids
- Chemistry-related lists
- Alkenoic acids