Marugame, Kagawa
Marugame
丸亀市 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 View of downtown Marugame City, from Marugame Castle | |||||||||||
 Flag  Chapter | |||||||||||
 Location of Marugame in Kagawa Prefecture | |||||||||||
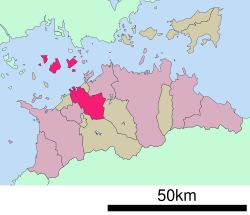 | |||||||||||
 Marugame Location in Japan | |||||||||||
| Coordinates: 34°17′N 133°48′E / 34.283°N 133.800°ECoordinates: 34°17′N 133°48′E / 34.283°N 133.800°E | |||||||||||
| Country | Japan | ||||||||||
| Region | Shikoku | ||||||||||
| Prefecture | Kagawa Prefecture | ||||||||||
| Government | |||||||||||
| • Mayor | Masaharu Kaji (from April 2013) | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| • Total | 111.79 km2 (43.16 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population (January 31, 2021) | |||||||||||
| • Total | 109,922 | ||||||||||
| • Density | 980/km2 (2,500/sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) | ||||||||||
| City hall address | 2-3-1 Ōtemachi, Marugame-shi, Kagawa-ken 763-8501 | ||||||||||
| Website | www | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||

Marugame (丸亀市, Marugame-shi) is a city located in Kagawa Prefecture, Japan. As of 31 January 2021, the city has an estimated population of 109,922 and a population density of 980 persons per km².[1] Marugame occupies the centre of an alluvial plain. The total area is 111.79 km².
Points of interest[]


Marugame is famous for Marugame Castle — one of only 12 castles with original wooden tenshu (keeps) in Japan. The castle stands on a man-made hill which is over 50 meters high, making it the largest castle mount in Japan.[citation needed]
Marugame is famed for its uchiwa fan production. About 90% of all uchiwa fans made in Japan are produced in Marugame.
Mount Iino, nicknamed Sanuki Fuji for its resemblance to Mt. Fuji, lies on the border between Marugame and Sakaide.[2]
Since 1947, the city has played host to an annual road running competition: the Marugame Half Marathon. Occurring in early February, the race attracts thousands of runners each year.[3] The Asian record in the half marathon was set on the course by Kayoko Fukushi in 2006.[4]
Reoma World[]
Reoma World, a well-known recreational facility in Shikoku, officially opened on April 20, 1991, but closed due to financial difficulties in August 2000.
It re-opened on April 11, 2004 with new funding. There are many attractions, two restaurants, a spa and hotel in the theme park. Total annual attendance was 660,000 in 2009, significantly reduced compared with 1.6 million attendance in 2004, possibly due to the inconvenience of public transport.[citation needed]
MIMOCA[]
Marugame is home to the Marugame Genichiro-Inokuma Museum of Contemporary Art (MIMOCA), situated just east of the railway station, housing the works of Genichiro Inokuma, as well as playing host to many large visiting exhibitions.
History[]
Marugame was founded in April, 1899 during the Meiji era. Marugame was the 53rd city to be given a city code in Japan. From the 1940s to 1950s (during the Shōwa era) the southeast area of the city and some islands were amalgamated to form new parts of the city. In 1999 (the 11th year of the Heisei era) Marugame celebrated its 100th anniversary.
On March 22, 2005, the towns of Ayauta and Hanzan (both from Ayauta District) were merged into Marugame to create the current expanded city of Marugame.
- The former Ayauta was founded in 1959 (the 34th year of the Shōwa era) with the amalgamation of the villages of and . Kumatama was in turn founded with the amalgamation of the villages of and in 1951.
- The former Hanzan was founded in 1956 (the 31st year of the Shōwa era) with the amalgamation of the villages of and .
List of mayors of Marugame (from 1899 to present)[]
|
|
Economy[]
The economy produces chemicals, textiles, fans, salt, rice and barley. In the early 1980s, large coastal salt fields were reclaimed from the sea to stimulate further economic development. The city's importance as a port for pilgrims coming from the Kyōto and Ōsaka areas to worship at the Kompira Shrine in Kotohira (from the Tokugawa period to the early Meiji period) declined with the opening of the railway between Matsuyama and Takamatsu in 1889 and more recently with the development of bus and air service linking Kotohira with major cities.
Twin cities[]
 Pasig, Philippines
Pasig, Philippines Donostia - San Sebastián, Spain
Donostia - San Sebastián, Spain
References[]
- ^ "Official website of Marugame City" (in Japanese). Japan: Marugame City. Retrieved 31 January 2021.
- ^ "Mt. Iino (飯野山)". 14 May 2012.
- ^ Ota, Shigenobu (2009-02-02). Marugame Half Marathon. ARRS. Retrieved on 2010-02-07.
- ^ Nakamura, Ken (2006-02-05). Fukushi sets Asian Half-Marathon record in Marugame. IAAF. Retrieved on 2010-02-07.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: 丸亀市 (category) |
- Marugame City official website (in Japanese)
- Marugame City official website (in English)
 Marugame travel guide from Wikivoyage
Marugame travel guide from Wikivoyage Geographic data related to Marugame, Kagawa at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Marugame, Kagawa at OpenStreetMap
- Cities in Kagawa Prefecture
