Massachusetts General Court
The General Court of Massachusetts | |
|---|---|
| 2021–2022 Massachusetts legislature | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | Bicameral |
| Houses | Senate House of Representatives |
| Leadership | |
President of the Senate | Karen Spilka (D) since July 26, 2018 |
President pro tempore of the Senate | Will Brownsberger (D) since March 20, 2019 |
Senate Majority Leader | Cynthia Stone Creem (D) since February 28, 2018 |
Senate Minority Leader | Bruce Tarr (R) since January 5, 2011 |
Speaker of the House | Ronald Mariano (D) since December 30, 2020 |
Speaker pro tempore of the House | Kate Hogan (D) since February 11, 2021 |
House Majority Leader | Claire D. Cronin (D) since February 11, 2021 |
House Minority Leader | Bradley Jones Jr. (R) since November 21, 2002 |
| Structure | |
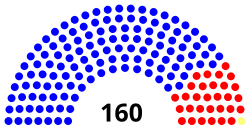
| Seats | 200 40 senators 160 representatives |
 | |
Senate political groups |
|
 | |
House of Representatives political groups |
|
| Elections | |
Senate last election | November 3, 2020 |
House of Representatives last election | November 3, 2020 |
Senate next election | November 8, 2022 |
House of Representatives next election | November 8, 2022 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Massachusetts State House, Boston, Massachusetts | |
| Website | |
| www.malegislature.gov | |
The Massachusetts General Court (formally styled the General Court of Massachusetts)[1] is the state legislature of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name "General Court" is a hold-over from the earliest days of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, when the colonial assembly, in addition to making laws, sat as a judicial court of appeals. Before the adoption of the state constitution in 1780, it was called the Great and General Court, but the official title was shortened by John Adams, author of the state constitution. It is a bicameral body. The upper house is the Massachusetts Senate which is composed of 40 members. The lower body, the Massachusetts House of Representatives, has 160 members. (Until 1978, it had 240 members.[2]) It meets in the Massachusetts State House on Beacon Hill in Boston.
The current President of the Senate is Karen Spilka, and the Speaker of the House is Ronald Mariano. Since 1959, Democrats have controlled both houses of the Massachusetts General Court, often by large majorities.[3][4] The Democrats enjoyed veto-proof supermajorities in both chambers for part of the 1990s (i.e., enough votes to override vetoes by a governor)[3] and also currently hold supermajorities in both chambers.[5]
State senators and representatives both serve two-year terms.[6] There are no term limits; a term limit was enacted by initiative in Massachusetts in 1994, but in 1997 this was struck down by the Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court, which ruled that it was an unconstitutional attempt to provide additional qualifications for office by statute, rather than constitutional amendment.[7][8]
The legislature is a full-time legislature, although not to the extent of neighboring New York or some other states.[9]
History[]

Massachusetts Bay Colony[]
The earliest history of the General Court is in the original charter of 1629. The Company of the Massachusetts Bay, in New England was a royally chartered joint stock company founded in 1628 in London. Much like other joint-stock companies of the time the first General Court was a meeting of shareholders, known as freemen. The "Great and General Court" was to meet in London and elect its officers and members in the same manner as other colonial charted companies of the time such as the Virginia Company and the East India Company. The freemen would meet annually to elect representatives in the form of a Royal Governor, a Deputy Governor, and a Council made from the directors of the Company. These officials were to have royally assented governmental control of the colony and would be tasked with the management and defense of the colonial plantation. The first Court assembled would be made from these members to discuss and evaluate the situation of the colony.[10][11]
The first meeting of the original General Court took place in London in 1629. The General Court selected John Endicott as its representative to the colony. Soon after Governor John Winthrop and the Deputy Governor Thomas Dudley broke with protocol when they themselves traveled to New England and moved the government to Massachusetts Bay. Along with them came the stock holders of the company and the Council or Assistants.[12][13]
Once in the Massachusetts Bay Colony the new government reorganized itself out of convenience. Instead of attempting to assemble all stockholders to the meeting of the General Court the government decided on having each town elect two representatives to send in their stead. The General Court became a de facto bicameral legislature by virtue of the distinction between delegates elected by towns and the Council of Assistants. The assistants acted as magistrates and counselors of jurisprudence, however when in session they served as a sort of Upper house. Their assent and approval was needed in order for any decision from the house of delegates to be passed. The new legislature was elected annually.[14]
Suffrage was allowed only for men who were Puritan church-members and freemen. This General Court removed any feudal restraints on the population and codified a Bill of Rights and powers of a judiciary. The General Court also enshrined the Laws of Moses as legal code under the discretion of local magistrates creating a theocratic quasi-democratic state.[15]
By votes of the General Court in the 1630s, the system of government changed to have an elected governor and to restrict the list of "freemen" to those affiliated with certain Puritan churches. In 1634, after complaint the charter was not being followed, a compromise resulted in recomposition of the General Court as two deputies elected by freemen in each town. Problems with a judicial case resulted in another reform in 1638, where the Council of Assistants became an upper house that sat separately, with consent of both houses required to pass legislation.
Currency was another issue in the colonies. In 1652 the Massachusetts legislature authorized John Hull to produce coinage (mintmaster). "The Hull Mint produced several denominations of silver coinage, including the pine tree shilling, for over 30 years until the political and economic situation made operating the mint no longer practical." Mostly political for King Charles II of England deemed the "Hull Mint" high treason in the United Kingdom which had a punishment of Hanging, drawing and quartering. "On April 6, 1681, Randolph petitioned the king, informing him the colony was still pressing their own coins which he saw as high treason and believed it was enough to void the charter. He asked that a writ of quo warranto (a legal action requiring the defendant to show what authority they have for exercising some right, power, or franchise they claim to hold) be issued against Massachusetts for the violations."[16]
Province of Massachusetts Bay in New England[]
With the collapse of the Dominion of New England in the Glorious Revolution in 1689 The Assistants convened an assembly of delegates from each town to reform the General Court.[17]
With the Massachusetts Charter in 1691 the Province of Massachusetts Bay absorbed the colony of Plymouth. The Plymouth Colony, along with the District of Maine and the islands off Cape Cod, Martha's Vineyard and Nantucket were to be an extension of Massachusetts and thus under the authority of the General Court.[18][19]
Under this new system the religious qualification, that suffrage be for only Puritan men, was changed to a qualification of property ownership. The Assistants were also officially changed to a Governor's Council to be selected by the governor to act as an upper house as well as a council for advice and consent. All laws passed by the General Court were to be approved by Royal Governor of the province. The powers of the monarch to be expanded in this new system as well. The King had full control of maritime affairs and acted as an executive, through the Royal Governor, to enforce commercial law.[20][21]
This separation of powers led to some friction with the Royal Governor and the General Court. The General Court retained power over spending and budget and while the Royal Officers, in the form of the Governor, the Governor's Council, etc. had more executive authority the Court could cause political stalemate if its demands were not met. Even the Governor's reserve power to dissolve the General Court was ineffective because a new assembly had to be elected the following year.[22]
With the passage of the Intolerable Acts by the Parliament of Great Britain there was political turmoil in the province. With political disorder Thomas Gage, then the Royal Governor, cancelled the new elections for the General Court and in 1774 the assembly was essentially dissolved.[23] This allowed the governor to rule by decree and appoint town governments.
In defiance of British law and governor, members of the General Court formed the Massachusetts Provincial Congress and seized control of the colony except for Boston, where the governor's troops maintained control until British troops fled Boston on March 17, 1776. The Governor's Council acted as the executive in the absence of the governor and lieutenant governor, administering the rebel forces of the colony during the early years of the American Revolutionary War, which began in Massachusetts at the Battles of Lexington and Concord on April 19, 1775. The General Assembly declared Massachusetts independent from Britain on May 1, 1776. With the war still ongoing, demands for government reform resulted in the Massachusetts Constitutional Convention of 1778, but the text proposed by the legislature failed in a statewide voter referendum. The Massachusetts Constitutional Convention of 1779–1780 was held by a specially-elected body, and the resulting text, after amendment and ratification, became the current state constitution.
Later history[]
The current Massachusetts General Court has met as the legislature of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts since the adoption of the Massachusetts Constitution in 1780. The body was in operation before Massachusetts became a U.S. state on February 6, 1788.
The first sessions, starting in , were one-year elected sessions for both houses. This was expanded to two-year sessions starting with the 142nd General Court in January 1921. Thereafter, the legislative year was defined as: "The first legislative year starting with the opening of the biennial session and ends at midnight on Tuesday before the first Wednesday of the following year. The second legislative year starts on the first Wednesday of the second year and ends when the legislature prorogues or at midnight on Tuesday before the first Wednesday of the following year.[24]
Watson F. Hammond, seated in 1885, was the first Native American to be elected to the body.[25]
Florence Slocomb was one of the first three women in the Commonwealth to be elected to the state Legislature and the first woman from Worcester to win a state legislative seat, representing that district from 1926 to 1928.[26]
Althea Garrison was elected to the Massachusetts House of Representatives in 1992 and is known as the first transgender person to serve in a state legislature in the United States.[27][28] She was outed against her will following the election and served one term.[29]
As of 2018, the General Court was composed of 75 percent male and 25 percent female representation.[30]
The current 192nd Massachusetts General Court will sit from the beginning of 2021 to the end of 2022.
Chambers[]
Senate[]
There are 40 senatorial districts in Massachusetts, named for the counties in which they are located. Each state Senate district contains about 164,000 constituents.[31]
The current composition of the Senate is 37 Democrats and 3 Republicans.
House of Representatives[]
Each Representative represents about 41,000 residents.[31] The speaker of the House has historically been quite powerful, exerting significant influence over all aspects of state government.[32][33]
Representative districts are named for the primary county in which they are located, and tend to stay within one county, although some districts contain portions of adjacent counties. The current composition of the House is 128 Democrats, 30 Republicans and 1 unenrolled member.
Legislative procedure[]

The General Court is responsible for enacting laws in the state. The two legislative branches work concurrently on pending laws brought before them.[34]
Lawmaking begins when legislators, or their delegates, file petitions accompanied by bills, resolves or other types of legislation electronically, using the Legislative Automated Workflow System (LAWS). The electronically submitted legislation is received in the House or Senate Clerk's office where the petitions, bills, and resolves are recorded in an electronic docket book. The clerks number the bills and assign them to appropriate joint committees. There are 26 of these committees, each responsible for studying the bills which pertain to a specific area (i.e., taxation, education, health care, insurance, etc.). Generally, each committee is composed of six senators and eleven representatives. The standing committees schedule public hearings for the individual bills, which afford citizens, legislators and lobbyists the opportunity to express their views. Committee members meet at a later time in executive session to review the public testimony and discuss the merits of each bill before making their recommendations to the full membership of the House or Senate. Note that the public may still observe "executive" sessions, but may not participate in these meetings. The committee then issues its report, recommending that a bill "ought to pass" or "ought not to pass" and the report is submitted to the Clerk's office.
The first reading of a favorably reported bill is automatic and generally occurs when the committee's report appears in the Journal of the House or Senate. Matters not requiring reference to another Joint, House or Senate committee are, following the first reading, referred without debate to the Committee on Senate Rules if reported in the Senate, except certain special laws (relative to a city or town) are placed directly on the Senate Calendar (Orders of the Day), or, without debate to the House Steering, Policy and Scheduling committee if reported into the House. Reports from Senate Rules or House Steering, Policy and Scheduling are placed on the Calendar of the Chamber receiving the report for a second reading. If a bill reported favorably by a joint committee affects health care it is referred by the House or Senate Clerk to the joint committee on Health Care Financing; and the first reading is delayed until the next favorable report, thus allowing Health Care Financing to report to either the House or Senate. The Health Care Financing Committee is required to provide an estimated cost of the bill, when making their report. If the estimated cost is less than $100,000, the bill bypasses having to be referred to Ways and Means. If a bill is not related to health care, but affects the finances of the Commonwealth, or, if it is reported by the Health Care Financing Committee with an estimated cost greater than $100,000, it is referred to the Senate or House Committee on Ways and Means after the first reading. Adverse reports ("ought not to pass") are also referred to the Committee on Steering and Policy in the Senate or placed without debate in the Orders of the Day for the next session of the House. Acceptance by either branch of an adverse report is considered the final rejection and the matter of the matter. However, an adverse report can be overturned. A member may move to substitute the bill for the report, and, if the motion to substitute carries, the matter is then given its first reading and follows the same procedure as if reported favorably by committee.

After a bill takes its second reading, it is open to debate on amendments and motions. Following debate, a vote is taken and if the bill receives a favorable vote by the membership, it is ordered to a third reading and referred to the Committee on Bills in the Third Reading. This amounts to preliminary approval of the bill in that branch. That committee examines technical points, as well as the legality and constitutionality of the measure, and ensures that it does not duplicate or contradict existing law. The committee then issues a report and returns the bill to the House or Senate for its third reading. At that time, legislators can further debate and amend the bill. Following the third reading, the body votes on "passing the bill to be engrossed."
The bill must then pass through three readings and engrossment in the second legislative branch. Should that occur, it is sent to the Legislative Engrossing Division where it is typed on special parchment in accordance with the General Laws. However, if the second branch passes an amended version of the bill, the legislation returns to the original branch for a vote of concurrence in the amendment. If concurrence is rejected, a conference committee consisting of the three members from each legislative branch representing both political parties may be formed to effect a compromise piece of legislation. When a compromise is reached, the bill is sent to both legislative branches for their approval.
A vote "to enact" the bill, first in the House and later in the Senate, is the final step in the passage of a bill by the legislature. Following enactment, the bill goes to the governor, who may sign the bill into law, allow it to become law without signing it (if the governor holds the bill for ten days without taking any action while the legislature is in session, it becomes law without his or her signature), veto it, or return it to the legislature with recommended changes. If the legislature has concluded its yearly session, and the governor does not sign the bill within ten days, it dies. This is referred to as a "pocket veto." This ten-day period includes Sundays and holidays, even if they fall on the tenth day, and it begins the day after the legislation is laid on the governor's desk.
A bill signed by the governor, or passed by two-thirds of both branches over his veto, becomes a law. It is usually effective in ninety days. The day after the governor signs the bill is considered to be the first day, and each succeeding day, including Sundays and holidays is counted until the ninetieth. Laws considered "emergency" in nature take effect immediately upon signing if the legislature has voted to attach an "emergency preamble" to the bill. Adoption of the preamble requires a two-thirds standing vote of the membership. The governor may also declare an act to be an emergency law and make it effective at once. A special act takes effect thirty days from the day it is signed, unless it contains a provision to make it effective immediately.
Joint committees[]
The current joint standing committees of the Massachusetts General Court are as follows:[35]
| Committee | Senate Chair | Senate Vice Chair | House Chair | House Vice Chair | Ranking Minority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cannabis Policy | Daniel M. Donahue | Paul A. Schmind, III | |||
| Children, Families and Persons with Disabilities | Michael J. Finn | Natalie M. Blais | |||
| Community Development and Small Businesses | Edward F. Coppinger | Richard M. Haggerty | |||
| Consumer Protection and Professional Licensure | Tackey Chan | ||||
| Economic Development and Emerging Technologies | Jerald A. Parisella | Andres X. Vargas | |||
| Education | Alice Hanlon Peisch | Steven Ultrino | |||
| Elder Affairs | Thomas M. Stanley | Kate Lipper-Garabedian | |||
| Election Laws | Daniel J. Ryan | Tommy Vitolo | |||
| Environment, Natural Resources and Agriculture | Carolyn C. Dykema | Mindy Domb | |||
| Export Development | Angelo J. Puppolo, Jr. | Kathleen R. LaNatra | |||
| Financial Services | James M. Murphy | Bruce J. Ayers | |||
| Health Care Financing | John J. Lawn, Jr. | Jay D. Livingstone | |||
| Higher Education | David M. Rogers | Carmine Lawrence Gentile | |||
| Housing | James Arciero | John H. Rogers | |||
| Judiciary | Michael S. Day | Chynah Tyler | |||
| Labor and Workforce Development | Josh S. Cutler | Tram Nguyen | |||
| Mental Health, Substance Use and Recovery | Adrian C. Madaro | Michelle M. DuBois | |||
| Municipalities and Regional Government | Lori A. Ehrlich | Paul F. Tucker | |||
| Public Health | Marjorie C. Decker | Brian W. Murray | |||
| Public Safety and Homeland Security | |||||
| Public Service | |||||
| Revenue | |||||
| Rules | William C. Galvin | Smitty Pignatelli | |||
| State Administration and Regulatory Oversight | |||||
| Telecommunications, Utilities and Energy | |||||
| Tourism, Arts and Cultural Development | |||||
| Transportation | |||||
| Veterans and Federal Affairs | |||||
| Ways and Means | Aaron Michlewitz | Ann-Margaret Ferrante Paul J. Donato (Assistant Vice Chair) |
State House News Service[]
The State House News Service is an independent privately owned wire service based in the Massachusetts State House that provides comprehensive coverage of the Commonwealth's government.[36] It is the only news organization with floor privileges and a desk in both the House and Senate chambers.
See also[]
- 2021–2022 Massachusetts legislature
- Massachusetts Capitol Police
- Massachusetts House of Representatives
- Massachusetts Senate
- Massachusetts State House
- Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court
- List of current Massachusetts House of Representatives committees
- List of state and territorial capitols in the United States
- List of members of the colonial Massachusetts House of Representatives
References[]
- ^ Constitution of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. See Chapter I, Section I, Art.I
- ^ John A. Hird, Power, Knowledge, and Politics: Policy Analysis in the States (Georgetown University Press, 2005), p. 93.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Robert B. Hackey, Rethinking Health Care Policy: The New Politics of State Regulation (Georgetown University Press, 1998), p. 123.
- ^ John Hudak, Presidential Pork: White House Influence over the Distribution of Federal Grants (Brookings Institution Press, 2014), p. 202 ("Democrats frequently control a supermajority of both houses of the state legislature in Massachusetts").
- ^ Jonathan Cohn, Democratic supermajority not so super: Lawmakers from same party but not on same platform, Commonweal (May 27, 2017).
- ^ Constitution of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, Article LXXXII.
- ^ Jennie Drage Bowser & Gary Moncrief, "Term Limits in State Legislatures" in Institutional Change in American Politics: The Case of Term Limits (eds. Karl T. Kurtz, Bruce E. Cain & Richard G. Niemi) (University of Michigan Press, 2007), p. 11.
- ^ Sara Rimer, Top Massachusetts Court Overturns Term Limits, New York Times (July 12, 1997).
- ^ Full- and Part-Time Legislatures, National Conference of State Legislatures (June 14, 2017).
- ^ Morision 1917, p.5.
- ^ Morision 1917, p.6.
- ^ Morision 1917, p.7.
- ^ Morision 1917, p.6.
- ^ Morision 1917, p.7.
- ^ Morision 1917, p.8.
- ^ https://historyofmassachusetts.org/massachusetts-bay-colony-charter-revoked
- ^ Morison 1917, p.9.
- ^ Morison 1917, p.9.
- ^ Morison 1917, p.10.
- ^ Morison 1917, p.9.
- ^ Morison 1917, p.10.
- ^ Morison 1917, p.11.
- ^ Morison 1917, p.11.
- ^ [1]
- ^ "FIRST NATIVE AMERICAN LEGISLATOR ON BEACON HILL". The Barnstable Enterprise. June 1, 2012. Retrieved January 29, 2018.
- ^ "Florence Slocomb: Pioneer Woman Legislator in Bay State." Boston, Massachusetts: The Boston Globe, November 13, 1955, p. 7 (subscription required).
- ^ Eaklor, Vicki L. (2008). Queer America: A GLBT History of the 20th Century. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood Press. p. 212. ISBN 978-0-313-33749-9. Retrieved October 20, 2010.
The nineties also saw the first openly transgender person in a state office, Althea Garrison, elected in 1992 but serving only one term in Massachusetts' House.
- ^ Haider-Markel, Donald P. (2010). Out and Running: Gay and Lesbian Candidates, Elections, and Policy Representation. Washington, D.C.: Georgetown University Press. p. 86. ISBN 978-1-58901-699-6. Retrieved October 20, 2010.
- ^ Osberg, Molly (November 8, 2017). "The Tragic Story of Althea Garrison, the First Trans Person to Hold State Office in America". Splinter. Splinter. Retrieved October 26, 2020.
- ^ "Women in State Legislatures for 2018". National Conference of State Legislatures. March 14, 2018. Retrieved May 24, 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b 2010 Constituents Per State Legislative District Table, National Conference of State Legislatures.
- ^ "A tale of 3 Speakers - Salvatore DiMasi, Thomas Finneran and Charles Flaherty: Is lure of power too tempting?", Associated Press (July 4, 2011).
- ^ Fox Butterfield, MASSACHUSETTS LEGISLATORS BALK AT LEADERS' POWER, The New York Times (December 10, 1983).
- ^ "How an Idea Become a Law". Malegislature.gov. Archived from the original on May 24, 2012. Retrieved May 13, 2014.
- ^ "Joint Committees". The 192nd General Court of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The General Court of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. 2021. Retrieved February 12, 2021.
- ^ State House News Service
Further reading[]
- Morison, Samuel (1917). A History of the Constitution of Massachusetts. Harvard University Library: Wright & Potter Printing Co.
- Cornelius Dalton (1984). Leading the Way: a History of the Massachusetts General Court, 1629-1980. Boston: Massachusetts Secretary of State. ISBN 0961391502.
- Noah Bierman. "Legislators' vital work veiled from public's eye". The Boston Globe, July 8, 2011.
- "Should the Massachusetts Legislature be subject to the state's public records law?", Boston Globe, June 25, 2020
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Massachusetts General Court. |
- General Court of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts
- Live and Archived webcasts of Massachusetts Senate and House of Representatives Full Formal Sessions
- General Court, hdl:2452/35629. (Various documents).
- Works by Massachusetts General Court at Project Gutenberg
- Works by or about Massachusetts General Court at Internet Archive
- Massachusetts General Court at Ballotpedia
- VoteSmart—Massachusetts
- Massachusetts General Court
- 1630 establishments in Massachusetts
- Bicameral legislatures
- Government of Massachusetts
