Mimas (moon)
 | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | William Herschel |
| Discovery date | 17 September 1789[1] |
| Designations | |
Designation | Saturn I |
| Pronunciation | /ˈmaɪməs/[2] or as Greco-Latin Mimas (approximated /ˈmiːməs/) |
Named after | Μίμας Mimās |
| Adjectives | Mimantean,[3] Mimantian[4] (both /mɪˈmæntiən/) |
| Orbital characteristics [5] | |
| Periapsis | 181902 km |
| Apoapsis | 189176 km |
| 185539 km | |
| Eccentricity | 0.0196 |
| 0.942421959 d | |
Average orbital speed | 14.28 km/s (calculated) |
| Inclination | 1.574° (to Saturn's equator) |
| Satellite of | Saturn |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 415.6 × 393.4 × 381.2 km (0.0311 Earths)[6] |
Mean radius | 198.2±0.4 km [6] |
Surface area | 490000–500000 km2 |
| Volume | 32600000±200000 km3 |
| Mass | (3.7493±0.0031)×1019 kg [7][8] (6.3×10−6 Earths) |
Mean density | 1.1479±0.007 g/cm3 [6] |
| 0.064 m/s2 (0.00648 g) | |
| 0.159 km/s | |
| synchronous | |
| zero | |
| Albedo | 0.962±0.004 (geometric)[9] |
| Temperature | ≈ 64 K |
| 12.9 [10] | |
Mimas /ˈmaɪməs/, also designated Saturn I, is a moon of Saturn which was discovered in 1789 by William Herschel.[11] It is named after Mimas, a son of Gaia in Greek mythology.
With a diameter of 396 kilometres (246 mi), it is the smallest astronomical body that is known to still be rounded in shape because of self-gravitation. However, Mimas is not actually in hydrostatic equilibrium for its current rotation.
Discovery[]

Mimas was discovered by the astronomer William Herschel on 17 September 1789. He recorded his discovery as follows: "I continued my observations constantly, whenever the weather would permit; and the great light of the forty-feet speculum was now of so much use, that I also, on the 17th of September, detected the seventh satellite, when it was at its greatest preceding elongation."[11][12]
The 40-foot telescope was a metal mirror reflecting telescope built by Herschel, with a 48-inch (1,200 mm) aperture. The 40 feet refers to the length of the focus, not the aperture diameter as more common with modern telescopes.
Name[]
Mimas is named after one of the Giants in Greek mythology, Mimas. The names of all seven then-known satellites of Saturn, including Mimas, were suggested by William Herschel's son John in his 1847 publication Results of Astronomical Observations made at the Cape of Good Hope.[13][14] Saturn (the Roman equivalent of Cronus in Greek mythology) was the leader of the Titans, the generation before the Gods, and ruler of the world for some time. The Giants were the subsequent generation, and each group fought a great struggle against the Gods.
The customary English pronunciation of the name is /ˈmaɪməs/,[15] though some people attempt a more 'authentic' pronunciation, /ˈmiːməs/.[16]
The Greek and Latin root of the name is Mimant-,[17] and so the English adjectival form is Mimantean[18] or Mimantian,[19] either spelling pronounced /maɪˈmæntiən/ ~ /mɪˈmæntiən/.[20]
Physical characteristics[]

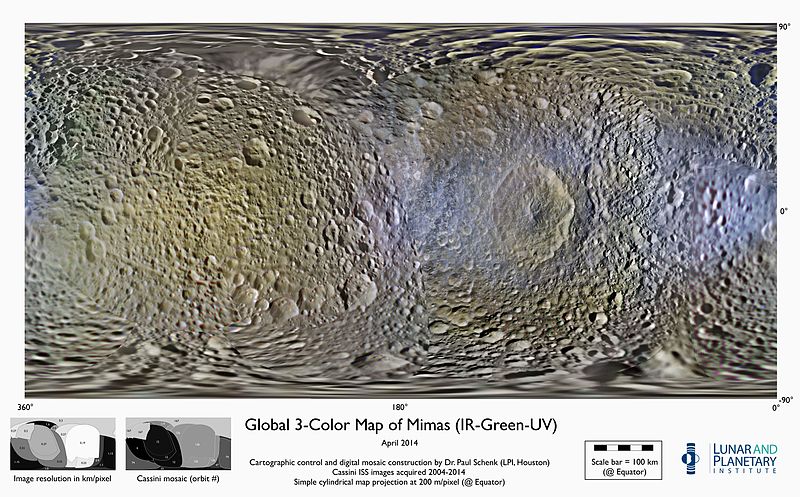
The surface area of Mimas is slightly less than the land area of Spain. The low density of Mimas, 1.15 g/cm3, indicates that it is composed mostly of water ice with only a small amount of rock. Due to the tidal forces acting on it, Mimas is noticeably prolate; its longest axis is about 10% longer than the shortest. The ellipsoidal shape of Mimas is especially noticeable in some recent images from the Cassini probe.
Mimas's most distinctive feature is a giant impact crater 130 km (81 mi) across, named Herschel after the discoverer of Mimas. Herschel's diameter is almost a third of Mimas's own diameter; its walls are approximately 5 km (3 mi) high, parts of its floor measure 10 km (6 mi) deep, and its central peak rises 6 km (4 mi) above the crater floor. If there were a crater of an equivalent scale on Earth (in relative size) it would be over 4,000 km (2,500 mi) in diameter, wider than Australia. The impact that made this crater must have nearly shattered Mimas: the surface antipodal to (opposite through the globe) Herschel is highly disrupted, indicating that the shock waves created by the Herschel impact propagated through the whole moon.[21]
The Mimantean surface is saturated with smaller impact craters, but no others are anywhere near the size of Herschel. Although Mimas is heavily cratered, the cratering is not uniform. Most of the surface is covered with craters larger than 40 km (25 mi) in diameter, but in the south polar region, there are generally no craters larger than 20 km (12 mi) in diameter.
Three types of geological features are officially recognized on Mimas: craters, chasmata (chasms) and catenae (crater chains).






Orbital resonances[]
A number of features in Saturn's rings are related to resonances with Mimas. Mimas is responsible for clearing the material from the Cassini Division, the gap between Saturn's two widest rings, the A Ring and B Ring. Particles in the Huygens Gap at the inner edge of the Cassini division are in a 2:1 orbital resonance with Mimas. They orbit twice for each orbit of Mimas. The repeated pulls by Mimas on the Cassini division particles, always in the same direction in space, force them into new orbits outside the gap. The boundary between the C and B rings is in a 3:1 resonance with Mimas. Recently, the G Ring was found to be in a 7:6 co-rotation eccentricity resonance[clarification needed] with Mimas; the ring's inner edge is about 15,000 km (9,300 mi) inside Mimas's orbit.[citation needed]
Mimas is also in a 2:1 mean-motion resonance with the larger moon Tethys, and in a 2:3 resonance with the outer F Ring shepherd moonlet, Pandora. A moon co-orbital with Mimas was reported by Stephen P. Synnott and Richard J. Terrile in 1982, but was never confirmed.[22][23]
Anomalous libration[]
In 2014, researchers noted that the librational motion of Mimas has a component that cannot be explained by its orbit alone, and concluded that it was due to either an interior that is not in hydrostatic equilibrium (an elongated core) or an internal ocean.[24] However, in 2017 it was concluded that the presence of an ocean in Mimas' interior would have led to surface tidal stresses comparable to or greater than those on tectonically active Europa. Thus, the lack of evidence for surface cracking or other tectonic activity on Mimas argues against the presence of such an ocean; as the formation of a core would have also produced an ocean and thus the nonexistent tidal stresses, that possibility is also unlikely.[25] The presence of an asymmetric mass anomaly associated with the crater Herschel may be a more likely explanation for the libration.[25]
Exploration[]
Pioneer 11 flew by Saturn in 1979, and its closest approach to Mimas was 104,263 km on September 1, 1979.[26] Voyager 1 flew by in 1980, and Voyager 2 in 1981.
Mimas was imaged several times by the Cassini orbiter, which entered into orbit around Saturn in 2004. A close flyby occurred on February 13, 2010, when Cassini passed by Mimas at 9,500 km (5,900 mi).
In popular culture[]
When seen from certain angles, Mimas resembles the Death Star, a fictional space station and superweapon known from the 1977 film Star Wars. Herschel resembles the concave disc of the Death Star's "superlaser". This is coincidental, as the film was made nearly three years before Mimas was resolved well enough to see the crater.[27]
In 2010, NASA revealed a temperature map of Mimas, using images obtained by Cassini. The warmest regions, which are along one edge of Mimas, create a shape similar to the video game character Pac-Man, with Herschel Crater assuming the role of an "edible dot" or "power pellet" known from Pac-Man gameplay.[28][29][30]
Gallery[]

Mimas is the tiny white dot in the lower left. (Click to enlarge view.)

Mimas, silhouetted against Saturn's northern latitudes.

Mimas, behind the F Ring.

Mimas viewed by Cassini looking distinctly egg-shaped.

Mimas and mountain
(October 22, 2016).
Mimas before Saturn's limb (color added)
(February 13, 2010).
Mimas mosaic with mostly high resolution.

Mimas displays subtle color differences
(false-color).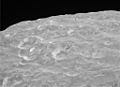
Mimas' albedo features on crater walls (Herschel at lower right)

Mimas texture map

Temperature map overlay of Mimas, commonly said to resemble Pac-Man.
See also[]
- List of natural satellites
- Mimas in fiction
References[]
- ^ "Imago Mundi: La Découverte des satellites de Saturne" (in French).
- ^ "Mimas". Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
- ^ "JPL (2009) Cassini Equinox Mission: Mimas". Archived from the original on 2009-04-06. Retrieved 2009-04-06.
- ^ Harrison (1908) Prolegomena to the study of Greek religion, ed. 2, p. 514
- ^ Harvey, Samantha (April 11, 2007). "NASA: Solar System Exploration: Planets: Saturn: Moons: Mimas: Facts & Figures". NASA. Retrieved 2007-10-10.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Roatsch, T.; Jaumann, R.; Stephan, K.; Thomas, P. C. (2009). "Cartographic Mapping of the Icy Satellites Using ISS and VIMS Data". Saturn from Cassini-Huygens. pp. 763–781. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9217-6_24. ISBN 978-1-4020-9216-9.
- ^ Jacobson, R. A.; Antreasian, P. G.; Bordi, J. J.; Criddle, K. E.; Ionasescu, R.; Jones, J. B.; Mackenzie, R. A.; Meek, M. C.; Parcher, D.; Pelletier, F. J.; Owen Jr., W. M.; Roth, D. C.; Roundhill, I. M.; Stauch, J. R. (December 2006). "The Gravity Field of the Saturnian System from Satellite Observations and Spacecraft Tracking Data". The Astronomical Journal. 132 (6): 2520–2526. Bibcode:2006AJ....132.2520J. doi:10.1086/508812.
- ^ Jacobson, R. A.; Spitale, J.; et al. (2005). "The GM values of Mimas and Tethys and the libration of Methone" (PDF). Astronomical Journal. 132 (2): 711–713. Bibcode:2006AJ....132..711J. doi:10.1086/505209.
- ^ Verbiscer, A.; French, R.; Showalter, M.; Helfenstein, P. (9 February 2007). "Enceladus: Cosmic Graffiti Artist Caught in the Act". Science. 315 (5813): 815. Bibcode:2007Sci...315..815V. doi:10.1126/science.1134681. PMID 17289992. S2CID 21932253. Retrieved 20 December 2011. (supporting online material, table S1)
- ^ Observatorio ARVAL (April 15, 2007). "Classic Satellites of the Solar System". Observatorio ARVAL. Archived from the original on August 25, 2011. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Herschel, W. (1790). "Account of the Discovery of a Sixth and Seventh Satellite of the Planet Saturn; With Remarks on the Construction of Its Ring, Its Atmosphere, Its Rotation on an Axis, and Its Spheroidical Figure". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 80: 11. Bibcode:1790RSPT...80....1H. doi:10.1098/rstl.1790.0001.
- ^ Herschel, William Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Vol. 80, reported by Arago, M. (1871). "Herschel". Annual Report of the Board of Regents of the Smithsonian Institution: 198–223. Archived from the original on 2016-01-13. Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- ^ As reported by William Lassell, Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 8, No. 3, pp. 42–43 (January 14, 1848)
- ^ Lassell, William (1848). "Satellites of Saturn: Observations of Mimas, the closest and most interior Satellite of Saturn". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 8: 42–43. Bibcode:1848MNRAS...8...42L. doi:10.1093/mnras/8.3.42. Retrieved 2006-11-26.
- ^ "Mimas". Lexico UK Dictionary. Oxford University Press.
"Mimas". Merriam-Webster Dictionary.
"Mimas". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House. - ^ "Mimas". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House.
- ^ Mimas, Lewis & Short, A Latin Dictionary, at Perseus
- ^ "JPL (ca. 2009) Cassini Equinox Mission: Mimas". Archived from the original on 2015-09-05. Retrieved 2010-02-10.
- ^ Paul Schenk (2011), Geology of Mimas?, in 42nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference
- ^ Jane Ellen Harrison (1908) "Orphic Mysteries", in Prolegomena to the study of Greek religion, page 514:
- ^ Elkins-Tanton, Linda E. (2006). Jupiter and Saturn. Infobase Publishing. p. 144. ISBN 9781438107257.
- ^ http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/iauc/03600/03660.html
- ^ Guinness Book of Astronomy, Patrick Moore, Guinness Publishing, second edition, 1983 pp 110, 112
- ^ Tajeddine, R.; Rambaux, N.; Lainey, V.; Charnoz, S.; Richard, A.; Rivoldini, A.; Noyelles, B. (2014-10-17). "Constraints on Mimas' interior from Cassini ISS libration measurements". Science. 346 (6207): 322–324. Bibcode:2014Sci...346..322T. doi:10.1126/science.1255299. PMID 25324382. S2CID 206558386.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Rhoden, A. R.; Henning, W.; Hurford, T. A.; Patthoff, D. A.; Tajeddine, R. (2017-02-24). "The implications of tides on the Mimas ocean hypothesis". Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets. 122 (2): 400–410. Bibcode:2017JGRE..122..400R. doi:10.1002/2016JE005097.
- ^ "Pioneer 11 Full Mission Timeline". Dmuller.net. Archived from the original on 2012-03-03. Retrieved 2012-02-26.
- ^ Young, Kelly (2005-02-11). "Saturn's moon is Death Star's twin". New Scientist. Retrieved 2008-08-21.
Saturn's diminutive moon, Mimas, poses as the Death Star – the planet-destroying space station from the movie Star Wars – in an image recently captured by NASA's Cassini spacecraft.
- ^ Cook, Jia-Rui C. (2010-03-29). "1980s Video Icon Glows on Saturn Moon". NASA. Retrieved 2010-04-02.
- ^ "Bizarre Temperatures on Mimas". NASA. 2010-03-29. Retrieved 2010-04-02.
- ^ "Saturn moon looks like Pac-Man in image taken by Nasa spacecraft". The Daily Telegraph. 2010-03-30. Archived from the original on 2010-04-02. Retrieved 2010-04-02.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Mimas (moon). |
- Cassini mission page – Mimas
- Mimas Profile at NASA's Solar System Exploration site
- The Planetary Society: Mimas
- Google Mimas 3D, interactive map of the moon
- Mimas page at The Nine Planets
- Views of the Solar System – Mimas
- Cassini images of Mimas
- Images of Mimas at JPL's Planetary Photojournal
- 3D shape model of Mimas (requires WebGL)
- Paul Schenk's Mimas blog entry and movie of Mimas's rotation on YouTube
- Mimas global and polar basemaps (June 2012) from Cassini images
- Mimas atlas (July 2010) from Cassini images
- Mimas nomenclature and Mimas map with feature names from the USGS planetary nomenclature page
- Figure "J" is Mimas transiting Saturn in 1979, imaged by Pioneer 11 from here
- Mimas (moon)
- Astronomical objects discovered in 1789
- Discoveries by William Herschel











