North London line
| North London line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 Class 378 Capitalstar at Canonbury in 2010 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Status | Operational | ||
| Owner | Network Rail | ||
| Locale | Greater London | ||
| Termini | Richmond Stratford | ||
| Stations | 23 | ||
| Service | |||
| Type | Commuter rail, Suburban rail, Freight rail, Heavy rail, Rapid transit | ||
| System | National Rail London Overground London Underground | ||
| Services | 1 | ||
| Operator(s) | London Overground London Underground (District line) | ||
| Depot(s) | Willesden TMD | ||
| Rolling stock | Class 378 Capitalstar and 710 Aventra London Underground S7 Stock | ||
| History | |||
| Opened | 1869 (fully) June 2010 (Gospel Oak - Stratford re-opened) 2011 (full service resumed) | ||
| Closed | 2006 (Stratford - North Woolwich) February 2010 (Gospel Oak - Stratford for engineering works) | ||
| Technical | |||
| Number of tracks | 2-4 | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification | 25 kV AC OHLE 750 V DC third rail | ||
| |||
| show North London Line |
|---|
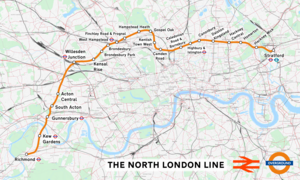
The North London line (NLL) is a railway line which passes through the inner suburbs of west, north-west, north, and east London, England between Richmond in the south-west and Stratford in the east, avoiding central London. Its route is a rough semicircle.
Although much of it originated as part of the North London Railway, the current route is the result of a series of amalgamations, closures and reopenings, and has a mix of third-rail and overhead electrical power supply. It remains heavily used by freight services in addition to the main London Overground (LO) service.[1] Between Richmond and Gunnersbury, London Underground's District line shares tracks with London Overground services; the entire route is owned and maintained by Network Rail.
TfL took over the line in 2007 and introduced new stock as well as putting the line on the Tube map. It closed for four months in 2010 between Gospel Oak and Stratford and had a reduced service for another year to allow platform extensions and signalling upgrades.[2]
History[]
Formation[]
The North London line between Richmond and North Woolwich derived from five connecting sections which were opened over 25 years from 1846:
- The easternmost section opened as the Eastern Counties and Thames Junction Railway in 1846/7 between Stratford and North Woolwich. The later construction of the Royal Victoria Dock necessitated a swing-bridge on the original route south of Canning Town which was rerouted in 1850 via Custom House and the Connaught Tunnel. The original route was retained as the Silvertown Tramway, a local freight line connected at both ends to the new main line.
- The main central section opened from 1850 to 1852 as the East & West India Docks & Birmingham Junction Railway (renamed the North London Railway (NLR) in 1853). This gave a link from the Euston main line near Primrose Hill to the docks at Poplar via Bow.
- In the west, the North & South Western Junction Railway was opened in 1853 from Willesden Junction to a junction with the Hounslow Loop Line near Kew Bridge.
- The last link in the east was opened between the NLR near Victoria Park and Stratford in 1854.
- To obviate NLR trains running on the busy Euston main line, the Hampstead Junction Railway was opened from the NLR at Camden Road to Willesden via Hampstead Heath in 1860.
- To give the NLR direct access to the City of London, the City extension to Broad Street was opened from Dalston Junction in 1865.
- The final part of the route was the opening of a link from South Acton to Richmond by the London & South Western Railway (LSWR) in 1869.
Developments[]
The line from Broad Street to Kew Bridge and Richmond was electrified by the LNWR in 1916 on the fourth-rail DC system.
In 1944, passenger services on the NLR Poplar branch ceased. Freight traffic continued on the branch to the docks on the Isle of Dogs until 1980. The trackbed of the southern part of the branch, from Poplar to Bow, was used for the Docklands Light Railway (DLR) branch to Stratford.
The service was listed for closure in the 1963 Beeching Report, with losses claimed as being £69,000 per year (equivalent to £1,022,000 in 2019). It was saved after a huge campaign. The line was Grant Aided under the Transport Act 1968 and came under threat when the Conservative Government of 1970–71 proposed to reduce Grant Aid funding. That threat, eventually lifted, led to the founding of a new campaign group, the North London Line Committee, which tried to work with British Rail management to promote the service.
In 1979, the North Woolwich to Stratford service was extended to Camden Road as the CrossTown LinkLine service, using the same Cravens-built diesel multiple unit trains. There were no intermediate stations until, in 1980, Hackney Wick was opened, near the site of the former Victoria Park station and Hackney Central was re-opened; then Homerton re-opened in 1985 (the two latter stations had closed in 1944). New platforms were built at West Ham for interchange with the adjacent Underground station.
Rolling stock[]

The line was originally operated by steam-hauled trains which were replaced after electrification by London and North Western Railway EMUs built from 1914 and augmented by later EMUs built in the 1930s by the London, Midland and Scottish Railway. These had all been replaced by the early 1960s with dedicated short-wheelbase trains (shared with the Watford DC line) built by the Southern Region at Eastleigh (using underframes built at Ashford) from 1957 which were later designated by British Railways as Class 501. These were succeeded by Southern Region Class 416 EMU for a short period, these units being allocated to Selhurst depot in south London. Class 416 trains were in turn succeeded by Class 313 EMUs, which worked the route until 2010 when London Overground introduced Class 378 Capitalstar four-car dual-voltage electric trains compatible with both 750 V DC third-rail and 25 kV AC overhead power sources,[3] and all of these units were by 2017 operating in 5-car formations to address the additional demand on the route.
Closures[]
In 1986, Broad Street station closed and the Tottenham Hale–Stratford link and the station at Lea Bridge ceased to be used by regular passenger trains. The line between Dalston and North Woolwich was electrified on the third-rail system and Broad Street services were diverted to North Woolwich using former Southern Region 2-EPB types built in the 1950s. The two-car trains soon proved too small and were replaced by three-car Class 313 electric multiple units. The new service was branded by British Rail as the North London Link, and some signs using this name still exist.
In December 2006, as with the Poplar branch (see above), the line between Stratford and North Woolwich was permanently closed to make a way for a future DLR extension from Canning Town to Stratford International (opened February 2011). The section south of Canning Town was not used by the DLR, as it is largely duplicated by the DLR King George V branch. Instead, the section will become part of Crossrail's branch to Abbey Wood (planned to open in 2022). The section south of Stratford had always been the 'Cinderella' end of the line, in that when there were operating problems it was common for trains to be turned short at Stratford.
Poor performance before the TfL takeover[]
Despite favourable performance figures,[4] the North London line used to be regarded by frequent travellers as offering a poor[5] and unreliable[6] service with extremely congested trains which were often cancelled shortly before they were due to arrive. A 2006 London Assembly report described the current service as "shabby, unreliable, unsafe and overcrowded", proposing the transfer of the service to Transport for London (TfL) as a solution to improve the quality of the service[7] due to upgrade plans[8] which coincided with the extension of the East London line.[9]
TfL[]
The North London line, as part of Silverlink, along with the West London line, Gospel Oak to Barking Line and the Watford DC Line, was transferred to Transport for London (TfL) in 2007 to form its new London Overground service. TfL began to remodel stations, integrate lines and following the transfer and extension of the East London line, aims to create an orbital rail service. TfL also brought in new trains and the line, which previously appeared on tube maps following a public campaign, gained its own colour.
TfL closed the line in February 2010 between Gospel Oak and Stratford for the installation of a new signalling system and the rebuilding or extension of platforms to allow four-car trains to run on the line; most NLL platforms had been reduced in usable length (where they had not been originally short) in the late 1960s when services were reduced to three-carriage trains only. The line reopened on 1 June 2010 with a reduced service and none on Sundays,[2] and with the upgrade work completed, the full seven-day service resumed on 22 May 2011.
Former services[]
In addition to the primary Broad Street - Richmond service, there were services that linked Broad Street with Harrow & Wealdstone and Watford Junction on the Watford DC line. Most of these were routed via the line between South Hampstead and Camden Road, calling at Primrose Hill although some travelled via Hampstead Heath and joined the DC line at Willesden Junction. Prior to electrification in the 1960s, other services ran as far as Tring on the West Coast Main Line via Primrose Hill and Willesden Junction Main Line (now demolished). By the time that Broad Street closed in 1986, the Watford services operated only in the rush hours; they were diverted to Liverpool Street by way of a new link in Hackney, known as the Graham Road Curve. Trains were frequently cancelled owing to rolling stock shortages; these circumstances had begun some years earlier with service reductions and scrapping of trains in the late 1960s, followed in later years by closure of depots at Croxley Green and Stonebridge Park preventing stabling of spare stock. Along with what eventually became a lack of trains timetabled to serve Liverpool Street to match the needs of rush-hour passengers, this inevitably led to falling patronage. British Rail applied to close the service in 1990, and the last trains ran two years later.
In 2000, Anglia Railways started a service between Basingstoke and Ipswich, utilising parts of the North London line. The service was called London Crosslink and ran up to five times a day at roughly two-hourly intervals. The service called only at principal stations such as Staines, Feltham and Brentford. On the North London line, the trains called only at Stratford, Highbury & Islington, Camden Road (some services), West Hampstead and Willesden Junction. The service was withdrawn in 2002.
The AC electrification of the eastern part of the North London line uses the previously unelectrified northern pair of tracks, which were also partially singled at the same time. Between Canonbury and Highbury & Islington, there is a line which links to the East Coast Main Line at Finsbury Park. This used to carry passenger trains to and from various main line stations (such as Edgware, Alexandra Palace, High Barnet, Welwyn Garden City and others) over part of the North London line to Broad Street Station; however, with the electrification of the Great Northern Electrics suburban lines in 1976, trains were diverted into Moorgate and London King's Cross stations, so since then this link has only been used for freight trains. It too was singled concurrent with the AC electrification of the eastern part of the North London line.
Route[]
This section does not cite any sources. (July 2010) |
Track[]
Most of the line runs in a curve across north London. Only Richmond and Kew Gardens stations at the western end are south of the River Thames. The river crossing is made by Kew Railway Bridge on tracks which are shared with the London Underground District line. The location of the eastern extremity has varied over the years. Between 1944 and 1986, it was at Broad Street station; then it was switched to North Woolwich. Later, it was cut back to Stratford. A tunnel, the Hampstead Heath tunnel, runs under Hampstead between Finchley Road & Frognal and Hampstead Heath. The line is double track throughout, with a mix of triple and quadruple track between Camden Road and Dalston Kingsland. The former North Woolwich branch included a section of single track between Custom House and North Woolwich stations, and the Broad Street branch was at one time formed of quadruple track.
During the February–May 2010 blockade, the Caledonian Road & Barnsbury, Highbury & Islington and Canonbury stations were rebuilt to allow the extended East London line to serve Highbury & Islington on fully segregated tracks on the south side of the cutting. Under the reinstated four-track arrangement, the North London line moved to the north side of the cutting between Dalston Kingsland and Highbury & Islington, before switching to the inner pair of tracks towards the former Maiden Lane station, leaving the outer pair for freight use only.
Traction current supply[]
Originally, the line was electrified in 1914–15 using the fourth rail +420 V / -210 V system, as used by London Underground. This was changed in the 1970s to +630 V / 0 V; the trains (then EMUs of a design unique to this and the DC line) were modified to the same basic traction supply arrangements as SR 3rd rail EMUs; the centre/negative current rail was removed except where coincident four-rail running was required between Richmond and Gunnersbury for the Underground trains that share this section, the centre rail there being bonded to the running rail used for current return. The line is now electrified using that same third rail system from Richmond to Acton Central, but with overhead lines now used from Acton Central to Stratford. The line into Broad Street used third-rail supply and, when the through service to North Woolwich started in 1985, trains used the third rail throughout. When the trains were replaced a few years later by dual-voltage Class 313 trains, it became possible to use the overhead line equipment which had been added to parts of the line for the benefit of freight trains; there had been some unexpected difficulties with earth currents from the third rail system which this overcame. This use was steadily extended, and trains had to make a number of changes between traction current supplies during their short journey; these were at Hackney Wick, Dalston Kingsland, Camden Road and Acton Central. With the final upgrade of the line between Camden Road and Stratford, the need to change traction current systems on this stretch was eliminated, and now the only changeover takes place at Acton Central for the short section to Richmond. The line ran on third rail throughout the 1980s until 1996 when it was closed for conversion to overhead lines. In 2010, the last of the third-rail sections around Camden Road station were completely removed.
Connections[]
The line crosses, or comes into contact with, a very large number of other railway lines, especially lines radiating from central London. This does provide opportunities to move between different sectors of suburban London without having to enter the central zone.
Interchanges shown on the tube map[]
- at Richmond, to and from South Western Railway services including the Kingston loop line.
- at Gunnersbury, connecting NLL services north of the station to District line services east of the station.
- at Willesden Junction, with the Bakerloo line, Watford DC Line and West London line.
- at West Hampstead, with the Jubilee line and Thameslink stations, each situated a short walk either side of the NLL station.
- at Gospel Oak, to and from the Gospel Oak to Barking Line of London Overground.
- at Highbury & Islington, to and from the Victoria line, the East London line and Great Northern services to Moorgate, Finsbury Park and the Great Northern Line.
- at Canonbury, with the East London line.
- at Hackney Central which is linked via direct passenger walkway to Hackney Downs station for London Overground and Greater Anglia services to and from Liverpool Street.
- at Stratford, to and from the Central line, Great Eastern Main line Greater Anglia services between East Anglia and Liverpool Street, the Jubilee line, and Docklands Light Railway.
Other interchanges[]
- at Brondesbury, 220 m south of Kilburn on the Jubilee line
- at Finchley Road & Frognal, about 400 m north of Finchley Road on the Metropolitan and Jubilee lines
- at Camden Road, about 400 m north-east of Camden Town on the Northern line
- at Caledonian Road & Barnsbury, 670 m north of Caledonian Road on the Piccadilly line
- at South Acton, 1 km south-east of Acton Town on the Piccadilly and District lines.
Alternative stations - lines merge nearby[]
- Dalston Kingsland is 225 m north of Dalston Junction - the two lines converge at the next station west (Canonbury)
Former interchanges[]
- At North Woolwich, passengers could cross the Thames via the Woolwich foot tunnel or take the free ferry to Woolwich Arsenal station for connections on the North Kent line to the Medway towns, Gravesend, Dartford, Sidcup, Abbey Wood, Blackheath, Lewisham, Greenwich and Central London. This service is now provided by King George V DLR station which offers direct rail services to Woolwich Arsenal from North Woolwich, providing quick interchange to services on the North Kent line.
Current operations[]
This article needs to be updated. (January 2020) |
Service levels[]
Trains run seven days a week, from approximately 06:00 (09:00 Sundays) until 23:30. During peak times, there are four trains per hour between Richmond and Stratford. Four trains per hour also operate between Clapham Junction and Stratford on the West London line service, making up a total of eight trains per hour between Willesden Junction and Stratford. During off-peak times, there are four trains per hour between Richmond and Stratford, and four trains per hour on the West London line between Clapham Junction and Willesden Junction, with two of these per hour continuing to Stratford, making up a total of six trains per hour between Willesden Junction and Stratford.
The introduction of the new four-car, air-conditioned trains, combined with improved signalling and passenger information, has dramatically overhauled the service, making it an effective alternative to travelling through central London for many orbital journeys.
East London line extension[]
From March 2011, the extended East London line connects to the NLL, with ELL services joining the line west of Dalston Kingsland, running to Highbury & Islington.[10][11]
Five-car operation[]
Transport for London extended platforms at some stations along the route to prepare the line for five-car operations in 2015, a project aimed at combating overcrowding on the line. The project was successfully completed and the first five-car trains started to run in summer 2015.

Proposed developments[]
Maiden Lane[]
Maiden Lane station may be reopened by Camden Council;[12] however, the Office of Rail Regulation has not included this in the current plans.[13]
Crossrail to Hounslow[]
Hounslow council has proposed that part of the North London line be used as a branch of Crossrail to Hounslow,[14] which would see Crossrail services serving Acton Central and South Acton. It was not included in the initial Crossrail bill but could form part of a later extension.
Old Oak Common Lane[]
Under the former government's plans for High Speed 2 line from London Euston to Birmingham, a new station called Old Oak Common was to be built by 2025 serving the North London line, West London line, High Speed 2 and Crossrail. The new government supports the idea after it had been opposed at first.[15]
North Acton[]
Another new station at North Acton is proposed for interchange with the Central line,[citation needed] but it might require the Central line station being moved to the east.
High Speed 2[]
The planned link between the proposed High Speed 2 line and the existing High Speed 1 line would have used the North London line alignment around Camden Road station, which might have reduced the existing or future capacity of the line. Its heavy investment in the line and the passenger growth on it has made Transport for London against the alignment's use as a link between the two High Speed lines.[16] That link has now been removed from the parliamentary bill.
Closed stations[]

Closed stations apart from those on the closed sections of the line are:
- Kensal Green & Harlesden
- Maiden Lane
- Mildmay Park
- Victoria Park
City Extension[]
On 1 November 1865 the NLR opened its City Extension, mostly on a viaduct from a triangular junction at Dalston to Broad Street in the city, with these stations:
- Dalston Junction
- Haggerston
- Shoreditch
- Broad Street
The extension closed on 30 June 1986, but although the track was lifted the viaduct remained in place. The route was re-opened in 2010 as part of the extended East London line, which, like the North London line, is operated by London Overground.
North Woolwich section[]
On 10 December 2006, the former Eastern Counties and Thames Junction Railway line between Stratford and North Woolwich was closed to allow building of a Docklands Light Railway line to Stratford International between Stratford and Canning Town. Part of the south end of the closed section is to be used for Crossrail.[17]
NLL stations closed were:
- West Ham
- Canning Town
- Custom House
- Silvertown
- North Woolwich
DLR and Jubilee line services are not affected at the first three of those stations.
The DLR line to Stratford International uses the former NLL low-level platforms at Stratford. NLL trains now terminate at new platforms on the north side of the high-level station.
References[]
- ^ "Route 6 – North London Line and Thameside: 2009 Route Plan" (PDF). Network Rail. 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 28 May 2009.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "London Overground to close from Gospel Oak to Stratford as part of £326m upgrade to deliver longer, more frequent trains". TfL. 18 December 2009. Archived from the original on 25 April 2010. Retrieved 6 February 2010.
- ^ Transport for London - £36m contract to bring extra rail carriages for London Overground
- ^ "Silverlink rises to second position in the national performance league". 18 September 2006. Retrieved 26 October 2007. Association of Train Operating Companies [1] Press Releases
- ^ Sharp, Rachel (24 October 2007). "TfL to take on rail network". Ealing Times. Retrieved 26 October 2007.
- ^ "Braced for rail strikes". Hackney Gazette. 26 October 2007. Retrieved 26 October 2007.
- ^ London Assembly - Light at end of the tunnel for London's forgotten railway
- ^ Always Touch Out - London Overground & Orbirail
- ^ London's forgotten railway Archived 19 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine (PDF)
- ^ Transport for London - East London Railway project
- ^ Dalston Junction to Highbury & Islington now Connected
- ^ King's Cross Development plan (PDF)
- ^ "Sections 17/18 - Section 17 and 18 - new track access contracts : Office of Rail Regulation". Rail-reg.gov.uk. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ "A4" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 April 2010. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ No business case' to divert HS2 via Heathrow, say Mawhinney Page 6-7, Rail Magazine, Issue 649, 28 July to 10 August 2010
- ^ Transport Select Committee, 28 June 2011, House of Commons
- ^ Transport for London Archived 30 March 2010 at the Wayback Machine - Stratford International Extension
Bibliography[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to North London Line. |
- Wayne Asher. 2015. A very Political Railway – the rescue of the North London Line. ISBN 978-1-85414-378-5
- HP White. 1971. A Regional History of the Railways of Great Britain, Volume 3 - Greater London. ISBN 0-7153-5337-3
- London Overground
- Transport in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames
- Transport in the London Borough of Hounslow
- Transport in the London Borough of Ealing
- Transport in the London Borough of Brent
- Transport in the London Borough of Camden
- Transport in the London Borough of Islington
- Transport in the London Borough of Hackney
- Transport in the London Borough of Newham
- Railway lines in London
- Railway lines opened in 1869
- Standard gauge railways in London
- 1869 establishments in England