Order-4-5 square honeycomb
| Order-4-5 square honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Regular honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | {4,4,5} |
| Coxeter diagrams | |
| Cells | {4,4} |
| Faces | {4} |
| Edge figure | {5} |
| Vertex figure | {4,5} 
|
| Dual | {5,4,4} |
| Coxeter group | [4,4,5] |
| Properties | Regular |
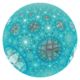
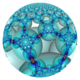
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-4-5 square honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) with Schläfli symbol {4,4,5}. It has five square tiling {4,4} around each edge. All vertices are ultra-ideal (existing beyond the ideal boundary) with infinitely many square tiling existing around each vertex in an order-5 square tiling vertex arrangement.
Images[]
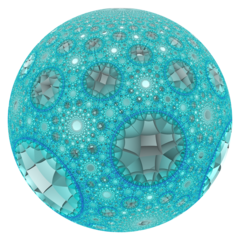 Poincaré disk model |
 Ideal surface |
Related polytopes and honeycombs[]
It a part of a sequence of regular polychora and honeycombs with square tiling cells: {4,4,p}
| {4,4,p} honeycombs | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Space | E3 | H3 | |||||||||
| Form | Affine | Paracompact | Noncompact | ||||||||
| Name | {4,4,2} | {4,4,3} | {4,4,4} | {4,4,5} | {4,4,6} | ...{4,4,∞} | |||||
| Coxeter |
|||||||||||
| Image | 
|

|
|

|
| ||||||
| Vertex figure |
 {4,2} |
 {4,3} |
 {4,4} |
 {4,5} |
 {4,6} |
 {4,∞} | |||||
Order-4-6 square honeycomb[]
| Order-4-6 square honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Regular honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | {4,4,6} {4,(4,3,4)} |
| Coxeter diagrams | |
| Cells | {4,4} |
| Faces | {4} |
| Edge figure | {6} |
| Vertex figure | {4,6} {(4,3,4)} |
| Dual | {6,4,4} |
| Coxeter group | [4,4,6] [4,((4,3,4))] |
| Properties | Regular |
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-4-6 square honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) with Schläfli symbol {4,4,6}. It has six square tiling, {4,4}, around each edge. All vertices are ultra-ideal (existing beyond the ideal boundary) with infinitely many square tiling existing around each vertex in an order-6 square tiling vertex arrangement.
 Poincaré disk model |
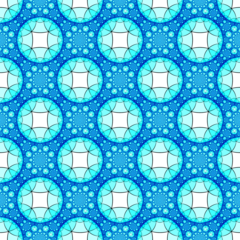 Ideal surface |
It has a second construction as a uniform honeycomb, Schläfli symbol {4,(4,3,4)}, Coxeter diagram, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , with alternating types or colors of square tiling cells. In Coxeter notation the half symmetry is [4,4,6,1+] = [4,((4,3,4))].
, with alternating types or colors of square tiling cells. In Coxeter notation the half symmetry is [4,4,6,1+] = [4,((4,3,4))].
Order-4-infinite square honeycomb[]
| Order-4-infinite square honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| Type | Regular honeycomb |
| Schläfli symbols | {4,4,∞} {4,(4,∞,4)} |
| Coxeter diagrams | |
| Cells | {4,4} |
| Faces | {4} |
| Edge figure | {∞} |
| Vertex figure | {4,∞} {(4,∞,4)} |
| Dual | {∞,4,4} |
| Coxeter group | [∞,4,3] [4,((4,∞,4))] |
| Properties | Regular |
In the geometry of hyperbolic 3-space, the order-4-infinite square honeycomb is a regular space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) with Schläfli symbol {4,4,∞}. It has infinitely many square tiling, {4,4}, around each edge. All vertices are ultra-ideal (existing beyond the ideal boundary) with infinitely many square tiling existing around each vertex in an infinite-order square tiling vertex arrangement.
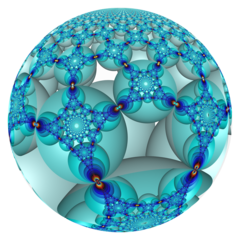 Poincaré disk model |
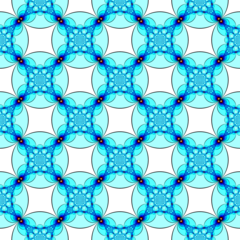 Ideal surface |
It has a second construction as a uniform honeycomb, Schläfli symbol {4,(4,∞,4)}, Coxeter diagram, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() , with alternating types or colors of square tiling cells. In Coxeter notation the half symmetry is [4,4,∞,1+] = [4,((4,∞,4))].
, with alternating types or colors of square tiling cells. In Coxeter notation the half symmetry is [4,4,∞,1+] = [4,((4,∞,4))].
See also[]
- Convex uniform honeycombs in hyperbolic space
- List of regular polytopes
References[]
- Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd. ed., Dover Publications, 1973. ISBN 0-486-61480-8. (Tables I and II: Regular polytopes and honeycombs, pp. 294–296)
- The Beauty of Geometry: Twelve Essays (1999), Dover Publications, LCCN 99-35678, ISBN 0-486-40919-8 (Chapter 10, Regular Honeycombs in Hyperbolic Space) Table III
- Jeffrey R. Weeks The Shape of Space, 2nd edition ISBN 0-8247-0709-5 (Chapters 16–17: Geometries on Three-manifolds I,II)
- George Maxwell, Sphere Packings and Hyperbolic Reflection Groups, JOURNAL OF ALGEBRA 79,78-97 (1982) [1]
- Hao Chen, Jean-Philippe Labbé, Lorentzian Coxeter groups and Boyd-Maxwell ball packings, (2013)[2]
- Visualizing Hyperbolic Honeycombs arXiv:1511.02851 Roice Nelson, Henry Segerman (2015)
External links[]
- John Baez, Visual insights: {7,3,3} Honeycomb (2014/08/01) {7,3,3} Honeycomb Meets Plane at Infinity (2014/08/14)
- Danny Calegari, Kleinian, a tool for visualizing Kleinian groups, Geometry and the Imagination 4 March 2014. [3]
- Honeycombs (geometry)
- Isogonal 3-honeycombs
- Isochoric 3-honeycombs
- Order-4-n 3-honeycombs
- Order-n-5 3-honeycombs
- Regular 3-honeycombs