Ostsiedlung
| History of Germany | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||
| Topics | ||||||||||
| Early history | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Middle Ages | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Early Modern period | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Unification | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| German Reich | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Contemporary Germany | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
Ostsiedlung (German pronunciation: [ˈɔstˌziːdlʊŋ], literally East settling) is the term for the High Medieval migration period of ethnic Germans into and beyond the territories at the eastern periphery of the Holy Roman Empire and the consequences for settlement development and social structures in the immigration areas. Generally sparsely and only recently populated by Slavic, Baltic and Finnic peoples, the area of colonization, also known as Germania Slavica, encompassed (with relation to modern-day countries) Germany east of the Saale and Elbe rivers, the states of Lower Austria and Styria in Austria, the Baltics, Poland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, Hungary, and Transylvania in Romania.[1][2]
Historians have since the 1980s interpreted the Ostsiedlung to be a part of civil and social progress, called the High Middle Age Land Consolidation (Hochmittelalterlicher Landesausbau). In a pan-European intensification process from the Carolingian-Anglo-Saxon core countries to the periphery of the continent, societies progressed in culture, religion, law and administration, trade and agriculture.[3]
The majority of settlers moved individually, in independent efforts, in multiple stages and on different routes as there existed no imperial colonization policy, central planning or movement organization. Many settlers were encouraged and invited by the Slavic princes and regional lords.[4][5][6]
Groups of migrants first moved to the east during the early Middle Ages. Larger treks of settlers, which included scholars, monks, missionaries, craftsmen and artisans, often invited, in numbers unverifiable, first moved eastwards during the mid 12th century. The military territorial conquests and punitive expeditions of the Ottonian and Salian emperors during the 11th and 12th centuries are not attributable to the Ostsiedlung, as these actions didn't result in any noteworthy settlement establishment east of the Elbe and Saale rivers. The Ostsiedlung is considered to have been a purely Medieval event as it ended in the beginning of the 14th century. The legal, cultural, linguistic, religious and economic changes caused by the movement had a profound influence on the history of Eastern Central Europe between the Baltic Sea and the Carpathians until the 20th century.[7][8][9]
In the 20th century, the Ostsiedlung was heavily exploited by German nationalists, including Nazi movement, to press the territorial claims of Germany and to demonstrate supposed German superiority over non-Germanic peoples, whose cultural, urban and scientific achievements in that era were undermined, rejected, or presented as German.[10][11][12]
Early Medieval Central Europe[]
Under Carolingian rule[]
Charlemagne, ruler of the Carolingian Empire, under whom most of Western and Central continental Europe had been united during the 8th and 9th centuries, created numerous border territories, so called marches (German: Marken), where a substantial portion of the Ostsiedlung would later take place.[13][14] The territories (from north to south):
- the Danish March (south of the Danevirke fortifications, between the Eider and Schlei), against the Danes and Jutes[15]
- the Saxon Eastern March or Nordalbingen March between the Eider and Elbe in what is now Holstein against the Obotrites
- the Thuringian or Sorbian March on the Saale, against the Sorbs dwelling behind the limes sorabicus
- the Franconian march in what is now Upper Franconia, against the Czechs
- the Avar March between the Enns and the Vienna Woods (the later Austrian March), against the Avars[16]
- the March of Pannonia east of Vienna (divided into Upper and Lower)
- the Carantanian march
- the Friaul march
The tribes that populated these marches were generally unreliable allies of the Empire, and successor kings lead numerous, yet not always successful, military campaigns to maintain their authority.
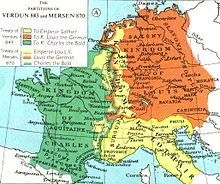
In 843 the Carolingian Empire, was partitioned into three independent kingdoms as a result of dissent among Charlemagne's three grandsons over the continuation of the custom of partible inheritance or the introduction of primogeniture.[17]
East Francia and Holy Roman Empire[]
Louis the German inherited the eastern territories, East Francia, that included all lands east of the Rhine river and to the north of Italy, which roughly corresponded with the territories of the German stem duchies, that formed a federation under the first king Henry the Fowler (919 to 936).[18] The Slavs living within the reach of East Francia (since 962 C.E. the Holy Roman Empire), collectively called Wends or "Elbe Slavs", seldom formed larger political entities. They rather constituted various small tribes, settling as far west as to a line from the Eastern Alps and Bohemia to the Saale and Elbe rivers. As the East Frankish kingdom expanded, various Wendish tribes, that were conquered or allied with the Eastern Franks, such as the Obotrites, aided the Franks in defeating the West Germanic Saxons.[19] The Carolingian tradition of setting up marches at the periphery of the empire would be continued by the East Frankish and Holy Roman Empire's kings during the 11th and 12th centuries.
Under the rule of King Louis the German and Arnulf of Carinthia, the first groups of civilian Catholic settlers were led by Franks and Bavarii to the lands of Pannonia (present-day Burgenland, Hungary, Slovakia and Slovenia).
In a series of punitive actions, large territories in the northeast between the Elbe, Saale, Naab rivers in the west and the Oder, Bober, Kwisa and Vltava rivers in the east were conquered, and border marches were set up in these areas. Fortifications were occupied and new castles built, reinforced by military units to exert military control and collect tributes. However, no civilian settlers would occupy these lands. Christianization was limited to the establishment of mission dioceses such as Lübeck, Brandenburg or Havelberg. The development of a Parish church system only took place after the settlement of German colonists, beginning in the 2nd half of the 12th century. Control over areas that had already been conquered was repeatedly lost. The Slavic revolt of 983 and an uprising of the Obotrites in 1066 had particularly serious consequences.[20][21]
Slavic revolt of 983[]
In 983, the Polabian Slavs in the Billung and Northern Marches, stretching from the Elbe river to the Baltic Sea succeeded in a rebellion against the political rule and Christian mission of the recently established Holy Roman Empire. In spite of their new-won independence, the Obotrites, Rani, Liutizian and Hevelli tribes were soon faced with internal struggles and warfare as well as raids from the newly constituted and expanding Piast dynasty (the early Polish) state from the east, Denmark from the north and the Empire from the west, eager to reestablish her marches. The area, however, remained under rule of the Polabian tribes and uncolonized and unchristianized into the 12th century.[22][23]
Eastern Marches of East Francia and Holy Roman Empire[]
The territories (from north to south):
- the Billung March on the Baltic Sea, stretching approximately from Groswin to Schleswig
- Marca Geronis (march of Gero), a precursor of the Saxon Eastern March, later divided into smaller marches (the Northern March, which later was re-established as Margraviate of Brandenburg; the March of Lusatia and the Margravate of Meissen in what is now Saxony; the March of Zeitz; the March of Merseburg; the Milzener March around Bautzen)
- Austrian March (marcha Orientalis, the "Eastern March" or "Bavarian Eastern March" (German: Ostmark) in what is now lower Austria)
- the Carantania or March of Styria
- the Drau March (Maribor and Ptuj)
- the Sann March (Celje)
- the Krain or Carniola march, also Windic March and White Carniola (White March), in what is now Slovenia
12th Century[]
A call for a crusade against the Wends in 1108, probably coming from a Flemish clerk in the circles of the archbishop of Magdeburg, which included the prospect of profitable land gains for new settlers, had no noticeable effect and resulted in neither a military campaign nor a movement of settlers into the area.[24][25]
Holstein and Pomerania[]
Since 1124 the first Flemish and Dutch colonists settled south of the Eider river, followed by the conquest of the land of the Wagri in 1139, the founding of Lübeck in 1143 and the call by Count Adolf II of Schauenburg to settle in Eastern Holstein in the same year.[26][27]
Weakened by ongoing internal conflicts and constant warfare, the independent Wendish territories finally lost the capacity to provide effective military resistance. From 1119 to 1123, Pomerania invaded and subdued the northeastern parts of the Lutici lands. In 1124 and 1128, Wartislaw I, Duke of Pomerania, at that time a vassal of Poland, invited bishop Otto of Bamberg to Christianize the Pomeranians and Liutizians of his duchy. In 1147, as a campaign of the Northern Crusades, the Wendish Crusade was mounted in the Duchy of Saxony to retake the marches lost in 983. The crusaders also headed for Pomeranian Demmin and Szczecin (Stettin), despite these areas having already been successfully Christianized.[28][29]
Brandenburg and Mecklenburg[]
After the Wendish crusade, Albert the Bear was able to establish and expand the Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1157 on approximately the territory of the former Northern March, which since 983 had been controlled by the Hevelli and Lutici tribes. The Bishopric of Havelberg, that had been occupied by revolting Lutici tribes was reestablished to Christianize the Wends.[30]
In 1164, after Saxon duke Henry the Lion finally defeated rebellious Obotrites and Pomeranian dukes in the Battle of Verchen. The Pomeranian duchies of Demmin and Stettin became Saxon fiefs, as well as the Obodrite territories, which became Mecklenburg, named after the Obotrites residential capital, Mecklenburg Castle. After Henry the Lion lost his internal struggle with Emperor Frederick I, Mecklenburg and Pomerania became fiefs of the Holy Roman Empire in 1181.[31]
Saxon Eastern Marches[]
The Sorbian March east of the Saale river was established in the 9th century. King Otto I designated a larger area – the Saxon Eastern March – in 937, that encompassed the territory between the Elbe, the Oder and the Peene rivers. Governed by Margrave Gero, it is also referred to as Marca Geronis. After Gero's death in 965, the march was divided in smaller sectors: Northern March, Lusatian March, Margraviate of Meissen, and March of Zeitz. The march was populated by various West Slavic tribes, the largest being Polabian Slavs tribes in the north and Sorbian tribes in the south.
The Margravate of Meissen and Transylvania were populated by German settlers, beginning in the 12th century. From the end of the 12th century onwards, monasteries and cities were established in Pomerania, Brandenburg, Silesia, Bohemia, Moravia and eastern Austria. In the Baltics, the Teutonic Order founded a crusader state in the beginning of the 13th century.[32][9]
Livonian Confederation[]
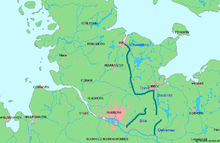
Terra Mariana (Land of Mary) was the official name[33] for Medieval Livonia[34] or Old Livonia [1](German: Alt-Livland) which was formed in the aftermath of the Livonian Crusade in the territories comprising present day Estonia and Latvia. It was established on February 2, 1207 [35] as a principality of the Holy Roman Empire[36] and proclaimed by Pope Innocent III in 1215 as a subject to the Holy See.[37]
Medieval Livonia was intermittently ruled first by the Livonian Brothers of the Sword, since 1237 by the semi-autonomous Teutonic Order called the Livonian Order and the Catholic Church. The nominal head of Terra Mariana as well as the city of Riga was the Archbishop of Riga as the apex of the ecclesiastical hierarchy.[38]
In 1561, during the Livonian War, Terra Mariana ceased to exist.[33] Its northern parts were ceded to the Swedish Empire and formed into the Duchy of Estonia, its southern territories became part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania — and thus eventually of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth as the Duchy of Livonia and Duchy of Courland and Semigallia. The island of Saaremaa became part of Denmark.
Social and demographic background[]
Political and military events were greatly influenced by a massive population increase throughout Europe in the High Middle Ages. From the 11th to the 13th centuries, the population in the kingdom of Germany increased from about four to twelve million inhabitants.[39][40] During this time, the High Medieval Landesausbau (inland colonization) took place, when arable land was largely expanded at the expense of forested areas. Although new land was won and numerous settlements created, demands could not be absorbed.[41] Another factor was a surplus of offspring of the nobility who were not entitled to inheritance, but after the success of the first crusade, took their chances of acquiring new lands in the peripheral regions of the Empire.[9][42]
There is no doubt that there were "rather numerous German settlers" in Eastern Central who were responsible for bringing German law in the earliest stages of the colonization. Other settlers included Walloons, Jews, Dutch, Flemish, and later Poles, especially in the territory of modern Ukraine.[43]
The emigration of the Walser in the territory of present-day Switzerland to areas that had formerly been inhabited by Romans largely resembled the colonisation of Eastern Europe. The Walser settlers left their home in Valais (north of Italy, Grisons and founded villages in the uplands of the Alp valleys.[44]
Technical and agricultural development[]
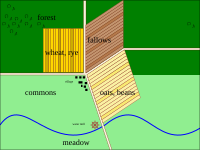
The Medieval Warm Period, which began in the 11th century resulted in higher average temperatures in Central Europe. Additional technical progress in agriculture, for example through the construction of mills, Three-field farming and increased cultivation of grain (graining) led to general population increase.
The new settlers not only brought their customs and language with them, but also new technical skills and equipment that were adapted within a few decades, especially in agriculture and crafts.[45] These included:
The amount of cultivated land increased as large forested areas were cleared. The extent of land increase differed by region. In Silesia it had doubled (16% of the total area) by the beginning of the 11th century, 30% in the 16th century and the highest increase rates in the 14th century, the total area of arable land increased seven - to twentyfold in many Silesian regions during the Ostsiedlung.
Parallel to agricultural innovations new forms of farm layout and settlement structuring (division and classification of land) were introduced. Farmland was divided into Hufen, (English hides) and larger villages replaced the previously dominant type of small villages consisting of four to eight farms as a complete transformation of the previous settlement structure occurred. The cultural landscape of East Central Europe formed by the medieval settlement processes essentially prevails until today.
Dyke construction and water drainage[]
Flemish and Dutch settlers were among the first to immigrate to Mecklenburg at the beginning of the 12th century. In the following years, they moved further east to Pomerania and Silesia and in the south to Hungary, motivated by the lack of settlement areas in their already largely developed home areas and several flood disasters and famines.[46]
Experienced and skilled in the construction of dykes and drainage of marshland, they were in high demand at the settlements of the as yet undeveloped areas east of the Elbe. The land was drained by creating a network-like structure of smaller drainage ditches that drained the water in main ditches. Roads connecting the settlers' individual farms ran along these main trenches.
Dutch settlers were recruited by the local rulers in large numbers, especially during the second half of the 12th century. In 1159/60, for example, Albert the Bear granted Dutch settlers the right to take possession of former Slavic settlements. The preacher Helmold of Bosau reported on this in his Slavic chronicle: “Finally, when the Slavs were gradually dispersing, he (Albrecht) sent to Utrecht and the Rhine region, and also to those who live by the ocean, who under the power of the sea had suffered, the Dutch, Zealanders and Flemings, where he attracted a lot of people and let them live in the castles and villages of the Slavs."[46]
Agricultural implements[]
The Slavs used plows and agricultural implements before the arrival of western immigrants. The oldest meaningful reference to this can be found in a Slavic chronicle, in which the use of a plow as an areal measurement is mentioned.[47]
In the 12th and 13th century documents the Ard without a mould-board is mentioned. It tear opens the soil and spreads the soil to both sides without turning it. It is therefore particularly suitable for light and sandy subsoil. In the mid 13th century, the Three-field system was introduced east of the Elbe. This new cultivation method required the use of the heavy Mould-board plough, that digs up the earth deeply and turns it around in a single operation.
The different modes of operation of the two devices also had an impact on the shape and size of the cultivation areas. The fields worked with the ard had about the same field length and width and a square base. Long fields with a rectangular base were much more suitable for the mould-board plow, as the heavy implements had to be turned less often. Planting and cultivation of oats and rye was promoted and soon these cereals became the most important type of grain. Farmers, who utilized the mould-board plow, were required to pay double tax fees.[48]
Pottery[]
Potters were among the first group of artisans who also settled in the rural areas. Typical Slavic ceramics were the Flat-bottom vessels. With the influx of western settlers, new vessel shapes such as the rounded jar were introduced, inclusive hard-fired processes, that improved ceramics quality. This type of ceramics, known as Hard Grayware, became widespread east of the Elbe by the end of the 12th century. It was manufactured extensively in Pomerania by the 13th century, when more advanced manufacturing methods, such as the tunnel kiln, enabled the mass production of ceramic household goods. The demand for household goods such as pots, jugs, jugs and bowls, which had previously been made of wood, increased steadily and promoted the development of new sales markets.
During the 13th century, glazed ceramics were introduced and the import of stoneware increased. The transfer of technology and knowledge affected the way of life of old and new settlers in a variety of ways and, in addition to innovations in agriculture and handicrafts, also included other areas, such as weapons technology, documents and coins.[49]
Architecture[]

Timber Frame House[]
The Slavic population (Sorbs), who lived east of the Elbe, primarily built log houses, which had proven suitable for the regional climates and wood was plentiful in the continental regions. The German settlers, mainly from Franconia and Thuringia, who advanced into the area in the 13th century, brought with them the half-timbering style, which was already known to the Germanic peoples, as a wood-saving, solid and stable construction method, that allowed multi-storey buildings. A combination of the two construction methods was difficult because the horizontally stacked wood of the log room expands differently in height than the vertical posts of the framework. The result was the new type of half-timbered house with a timber frame around the ground floor block, capable to support a second floor, which was made of half-timber.
Population and settlement[]
The Ostsiedlung followed an immediate rapid population growth throughout East Central Europe. During the 12th and 13th centuries, the population density increased considerably. The increase was due to the influx of settlers on the one hand and an increase in indigenous populations after the colonization on the other hand. Settlement was the primary reason for the increase e.g. in the areas east of the Oder, the Duchy of Pomerania, western Greater Poland, Silesia, Austria, Moravia, Prussia and Transylvania, while in the larger part of Central and Eastern Europe indigenous populations were responsible for the growth. Author Piskorski wrote that "insofar as it is possible to draw conclusions from the less than rich medieval source material, it appears that at least in some East Central European territories the population increased significantly. It is however possible to contest to what extent this was a direct result of migration and how far it was due to increased agricultural productivity and the gathering pace of urbanization."[50] In contrast to Western Europe, this increased population was largely spared by the 14th-century Black Death pandemic.[51]
With the German settlers new systems of taxation arrived. While the existing Wendish tithe was a fixed tax depending on village size, the German tithe depended on the actual crop yield. Thus higher taxes were collected from the settlers than from the Wends, although settlers were partly exempted from tax payments during the first years after settlement establishment.[45][9]
Urban development and city foundations[]

The development of Germania Slavica was also associated with the establishment of towns. There already existed Slavic castle towns, in which merchant quarters formed suburbs at fortified strongholds (grads). Wendish-Scandinavian merchants founded manufacturing and trading settlements (emporia) at the Baltic coast. Large cities included Szczecin which reached 9,000 inhabitants, Kraków which was the capital of the state of Piast Poland and Wrocław, already under civil and religious administration and centers of power. However, they experienced substantial growth since the end of the 12th century through new settlers and expansion (locatio civitatis). The foundation of a bishopric, for example in Havelberg, would lead to the development of a town, although cities were also founded out of nowhere, such as Neubrandenburg. Characteristic of the founding cities are geometrical or rasterized floor plans with main streets, intersecting axes and a central market place. Different settlement phases are reflected in twin cities names such as New town or Old town.[54][55]
The towns established during the Ostsiedlung were Free Towns (civitates liberae) or called "New Towns" by its contemporaries. The rapid increase in the number of towns led to an "urbanization of East Central Europe." The new towns differed from their predecessors in:
- The introduction of German town law, resulting in far-reaching administrative and judicial rights for the towns. The townspeople were personally free, enjoyed far-reaching property rights and were subject to the town's own jurisdiction only. The privileges granted to the towns were copied, sometimes with minor changes, from the legal charters of the (Lübeck Law in 33 towns[56] at the southern coast of the Baltic Sea), the Magdeburg Law in Brandenburg, areas of modern Saxony, Lusatia, Silesia, northern Bohemia, northern Moravia and the Teutonic Order state, the Nuremberg Law in southwestern Bohemia, the Brünn Law (Brno) in Moravia, based on the charter of Vienna), the Iglau Law (Jihlava) in Bohemian and Moravian mining areas.[57] Besides these basic town laws, several adapted town charters.[57]
- The introduction of permanent markets. As previously, markets were held only periodically, townspeople were now free to trade and marketplaces became a central feature of the new towns.[58]
- Layout: The new towns were planned towns as their layout was usually rectangular.[53]
The role of city laws and grants[]
The granting of city rights played an important role in attracting German settlers.[59] The town charter privileged the new residents and existing suburban settlements with a market were given formal town charter and then rebuilt or expanded. Even small settlements inhabited by native people would eventually be granted these new rights. Regardless of existing suburban settlements, locators were commissioned to establish completely new cities, as the goal was to attract as many people as possible in order to create new, flourishing population centers.[60][61]
Expansion of the German city laws[]
Among the many different German city laws, the Magdeburg law and the Lübeck law played the greatest role in the new settlements as they served, often in more or less modified form, as models for most cities. Other city rights that were of regional importance include the. Nuremberg law, the Mecklenburg law and the Iglau law. The Lübeck law of 1188 served in the 13th and 14th centuries as the model for around 100 cities in the entire Baltic Sea trading area. Around 350,000 people lived under Lübeck law in the early 15th century. The Magdeburg law, which has its origins in the privileges granted by Archbishop Wichmann of Magdeburg, first spread into Brandenburg, Saxony and Lusatia. Laws based on the Magdeburg model (e.g. the Kulmer law and Neumarkt law) were introduced in Silesia, Poland, the State of the Teutonic Order, Bohemia and Moravia and beyond.
Religious changes[]

The pagan Wends had been the target of Christianization attempts before the beginning of the Ostsiedlung, since the government of emperor Otto I and the establishment of dioceses east of the Elbe. The Slav uprising of 983 put an end to these efforts for almost 200 years. In contrast to the Czechs and Poles who had been Christianized before the turn of the millennium, the conversion attempts of the Elbe Slavs initially accompanied by violence. The arrival of new settlers from around 1150 on led to a civil Christianisation of the areas between the Elbe and Oder. The new settlers first built wooden and later field stone parish churches in their villages. Some places of worship, such as the St. Mary in Brandenburg, and the Lehnin Abbey, were built on pagan shrines. The Cistercians, who had been assigned a prominent role by church authorities, combined the spread of faith and settlement development. Their monasteries with extensive international connections played a vital role in the development of the communities.[62]
The settlers[]

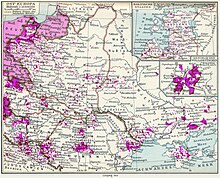
The majority of the settlers were Germans of the Holy Roman Empire. Significant numbers of Dutch settlers participated, particularly in the early 12th century in the area surrounding the Middle Elbe River.[63] To a lesser extent Danes, Scots or local Wends and (French-speaking) Walloons participated as well. Among the settlers were landless children of noble families who could not inherit property.[64]
Besides the marches, adjacent to the Empire, Germans settled in areas farther east, such as the Carpathians, Transylvania, and along the Gulf of Riga. Settlers were invited by local secular rulers, such as dukes, counts, margraves, princes and (only in a few cases due to the weakening central power) the king. The sovereigns in East Central Europe owned large territories, of which only small portions were arable, which generated very little income.[42] The lords offered considerable privileges to new settlers from the Empire. Starting in the border marks, the princes invited people from the Empire by granting them land ownership and improved legal status, binding duties and the inheritance of the farm. The landowners eventually benefited from these rather generous conditions for the farmers, and generated income from the land that had previously been fallow.[64]
Most sovereigns transferred the specific recruitment of settlers, the distribution of the land and the establishment of the settlements to so-called Lokators (allocator of land). These men, who usually came from the lower nobility or the urban bourgeoisie, organized the settlement trains, that included advertising, equipment and transport, land clearing and preparation of the settlements. Locator contracts settled rights and obligations of the locators and the new settlers.[55][65]
Towns were founded and granted German town law. The agricultural, legal, administrative, and technical methods of the immigrants, as well as their successful proselytising of the native inhabitants, led to a gradual transformation of the settlement areas, as Slavic communities adopted German culture.[citation needed] German cultural and linguistic influence lasted in some of these areas right up to the present day.[1]
In the mid 14th century, the migration process slowed considerably as a result of the Black Death. The population probably decreased by that time and economically marginal settlements were left, in particular at the coast of Pomerania and Western Prussia. Only a century later, local Slavic leaders of Pomerania, Western Prussia and Silesia invited German settlers again.[66]
Assimilation[]
Colonization was the pretext for assimilation processes that lasted centuries. Assimilation occurred in both directions – depending on the region and the majority population, Slavic and German settlers mutually assimilated each other.
Assimilation of Germans[]
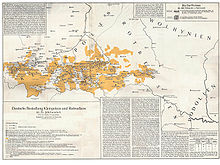
The Polonization process of German settlers in Kraków and Poznań lasted about two centuries. The community could only continue its isolated position with a continuation of newcomers from German lands. The Sorbs also assimilated German settlers, yet at the same time, small Sorbic communities were themselves assimilated by the surrounding German-speaking population. Many Central and Eastern European towns developed into multi-ethnic melting pots.[67]
Assimilation, treatment, involvement and traces of the Wends[]
Although Slavic population density was generally not very high compared to the Empire and had, as a result of the extensive warfare during the 10th to 12th centuries, even further declined, some settlement centers maintained their Wendish populations to varying degrees, resisting assimilation for a long time.[67]
In the territories of Pomerania and Silesia, German migrants did not settle in the old Wendish villages and set up new ones on grounds allotted to them by the Slavic nobility and the monastic clergy. In the marches west of the Oder, the Wends were occasionally driven out and the villages rebuilt by settlers. The new villages would nevertheless keep their former Slavic names. In the case of the village Böbelin in Mecklenburg, the evicted Wendish inhabitants repeatedly invaded their former village, hindering a resettlement.[68]
In the Sorbian March the situation was again different as the area and in particular Upper Lusatia is situated close to Bohemia, ruled by a Slavic dynasty, a loyal and powerful duchy of the Empire. In this environment, German feudal lords often cooperated with the Slavic inhabitants. Wiprecht of Groitzsch, a prominent figure during the early German migration period only acquired local power through the marriage to a Slavic noblewoman and the support of the Bohemian king. German-Slavic relations were generally good, while relations between Slavic-governed Bohemia and Slavic-governed Poland were marred by constant struggle.

Discrimination against the Wends was not a part of the general concept of the Ostsiedlung. Rather, the Wends were subject to a low taxation mode and thus not as profitable as new settlers. Even though the majority of the settlers were Germans (Franks and Bavarians in the South, and Saxons and Flemings in the North), Wends and other tribes also participated in the settlement. New settlers were not chosen just because of their ethnicity, a concept unknown in the Middle Ages, but because of their manpower and agricultural and technical know-how.[67]
Most of the Wends were gradually assimilated. However, in isolated rural areas where Wends constituted a substantial part of the population, they continued their culture. These were the Drevani Polabians of the Wendland east of the Lüneburg Heath, the Jabelheide Drevani of southern Mecklenburg, the Slovincians and Kashubs of Eastern Pomerania, and the Sorbs of Lusatia. Lusatia was inhabited by a large population of Sorbs until the end of the 19th century as linguistic assimilation occurred in a relatively short time.
Language exchange[]
The Ostsiedlung caused the adoption of loan words, foreign words and loan translations among the German and the Slavic languages. Direct contact between Germans and Slavs caused direct language exchange of language elements due to the bilingualism of people or the spatial proximity of the speakers of the respective language. Remote contact took place during trade travels or political embassies.[69][70]
Examples[]
The oldest adoption of naming units dates back to Proto-Germanic and Proto-Slavic. The original Slavic word kъnędzъ can be found in almost all Slavic languages. German was mainly used to convey words in Slavic languages that related to handicraft, politics, agriculture and nutrition. This includes Old High German cihla, Middle High German ziegala, ziegel (brick), that resulted from the sound shift of the Latin tegula. An example of borrowing from Slavic into Germanic usage is the word for border. In Middle High German called Grenize, which is a borrowing of the old Czech word granicĕ or the Polish word granica. City names are also affected by language exchange, sound shifting and the Slavic second palatalization. The city of Regensburg is called Řezno in Czech and Rezъno in Proto-Slavic. Due to the intensive language contact, idioms were also transmitted. Two examples from Czech and Polish are na vlastní pěst / na własną rękę ("on your own") or ozbrojený po zuby / uzbrojony po zęby ("armed to the teeth"), in Hungarian "saját szakállára" (ones own beard) and "állig felfegyverzett" (armed to the chin), with different wording, but with the same meaning.[71][72]
| Category | English | German | Polish | Czech | Slovakian | Hungarian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Administration | Mayor | Bürgermeister | burmistrz | purkmistr | richtár/burgmajster | polgármester |
| Administration | Margrave | Markgraf | margrabia | markrabě | markgróf | gróf |
| Craft | Brick | Ziegel | cegła | cihla | tehla | tégla |
| Food | Pretzel | Brezel | precel | preclík | praclík | perec |
| Food | Oil | Öl | olej | olej | olej | olaj |
| Agriculture | Mill | Mühle | młyn | mlýn | mlyn | malom (mahlen) |
| Trade | (cart-)load | Fuhre | fura | fůra | fúra | furik |
| Others | Flute | Flöte | flet | flétna | flauta | flóta |
Names of localities and settlements[]
As Slavic and Wendish locality names were widely adopted, they represent, in adapted and further developed form, a very high proportion of East German toponyms and place names. These are recognizable at word endings, such as -ow (Germanized -au, as in Spandau), -vitz or -witz and sometimes -in. Newly created villages were given German names that ended, for example, with -dorf or -hagen in the North, and -rode or -hain in the South. The name of the settler's place of origin (example: Lichtervelde in Flanders) could also become part of the place name. If a German settlement was founded alongside a Wendish settlement, the name of the Wendendorf could also be adopted for the German village, the distinction was then made through additions (e.g. Klein- or Wendisch- / Windisch- for Wendendorf, Groß- or Deutsch- for German).[58][73]
In German-speaking areas most inherited surnames were formed only after the Ostsiedlung period, and many German surnames are in fact Germanized Wendish placenames.[citation needed]
The former ethnic variety of German (Deutsch-) and Slavic (Wendisch-, Böhmisch-, Polnisch-) toponyms was discontinued by the Eastern European republics after World War II. Villages and towns were renamed in Slavic only. Memory of the history of German colonization was no longer appreciated.[citation needed]
Conflicts[]
The colonization sometimes brought ethnic conflict. Local populations, particularly in the towns, sometimes had negative attitudes toward new-comers, particularly those who did not speak the local language, while natives were sometimes expelled at the regional level.[74]
European context and regional development[]
The development and progress of the German Ostsiedlung was not a unique event in Europe's medieval history. Similar phenomena can be observed in all the peripheral areas of the former Carolingian empire, for example in southern France and the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms or in Ireland. The migration of the Swiss Valaisers to previously sparsely populated and uninhabited valleys in northern Italy, Grisons and Vorarlberg falls in the same category. The development of individual regions in the geographically poorly demarcated area that constituted the Ostsiedlung is not being sketched here. See articles: Northern March, Margraviate of Brandenburg, Pomerania, Silesia, State of the Teutonic Order, Saxony, Lesser Poland, Bohemia, Moravia, Austria, Slovenia, Hungary, Transylvania and Moldova.
The end of migration and causes[]
There is no clear cause nor a definite end point in time of the Ostsiedlung. However, a slowdown in the settlement movement can be observed after the year 1300 and in the 14th century only a few new settlements with the participation of German-speaking colonists were founded. An explanation for the end of the Ostsiedlung must include various factors without being able to clearly weigh or differentiate between them. The deterioration of the climate from around 1300 as the beginning of the "Little Ice Age", the agricultural crisis that began in the mid 14th century. In the wake of the demographic slump caused by the 1347 Plague, profound devastation processes have taken place. If a clear connection could be established here, the end of the Ostsiedlung would be understood as part of the crisis of the 14th century.[75]
Drang nach Osten[]
In the 19th century, recognition of this complex phenomenon coupled with the rise of nationalism. This led to a largely unhistoric ethnically inspired nationalist reinterpretation of the medieval process. In Germany and some Slavic countries, most notably Poland, the Ostsiedlung was perceived in nationalist circles as a prelude to contemporary expansionism and Germanisation efforts, the slogan used for this perception was Drang nach Osten (Drive or Push to the East).[76][77]
The German settlement processes in Pomerania did not follow any kind of ideology, nor did the other migratory movements. Rather, the German settlement in Pomerania was shaped exclusively by practical requirements...The national historiography that established itself around the middle of the 19th century retrospectively constructed a Slavic-Germanic contrast in the Ostsiedlung process of the High Middle Ages. However, that was the ideology of the 19th century, not the Middle Ages...Settlement was to be "cuiuscunque gentis et cuiuscunque artis homines" (people of whatever origin and whatever craft,) which was recorded in numerous documents issued by Pomeranian dukes and Rügish princes. -Buchholz[78]
Legacy[]

The 20th century wars and nationalist policies severely altered the ethnic and cultural composition of Central and Eastern Europe. After World War I, Germans in reconstituted Poland were set under pressure to leave the Polish Corridor, the eastern part of Upper Silesia and Poznań. During World War II, the Nazis initiated the Nazi-Soviet population transfers, wiping out the old settlement areas of the Baltic Germans, the Germans in Bessarabia and others, to resettle them in the future territories in occupied Poland.
Room for them was made during World War II, in line with the Generalplan Ost by expulsion of Poles and enslaving these and other Slavs according to the Nazi's Lebensraum concept. In order to press the territorial claims of Germany and to demonstrate supposed German superiority over non-Germanic peoples, whose cultural, urban and scientific achievements in that era were undermined, rejected, or presented as German.[79][80][81] While further realization of this mega plan, aiming at a total reconstitution of Central and Eastern Europe as a German colony, was prevented by the war's turn, the beginning of the expulsion of 2 million Poles and settlement of Volksdeutsche in the annexed territories yet was implied by 1944.[82]
The Potsdam Conference – the meeting between the leaders of the United States, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union – sanctioned the expulsion of Germans from Czechoslovakia, Poland and Hungary. With the Red Army's advance and Nazi Germany's defeat in 1945, the ethnic make-up of Central and Eastern and East Central Europe was radically changed, as nearly all Germans were expelled not only from all Soviet conquered German settlement areas across Central and Eastern Europe, but also from former territories of the Reich east of the Oder-Neisse line, mainly, the provinces of Silesia, East Prussia, East Brandenburg, and Pomerania. The Soviet-established People's Republic of Poland annexed the majority of the lands while the northern half of East Prussia was taken by the Soviets, becoming the Kaliningrad Oblast, an exclave of the Russian SFSR. The former German settlement areas were resettled by ethnic citizens of the respective succeeding state, (Czechs in the former Sudetenland and Poles in Silesia and Pomerania). However, some areas settled and Germanised in the course of the Ostsiedlung still form the northeastern part of modern Germany, such as the Bundesländer of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Saxony and east of the limes Saxoniae in Holstein (part of Schleswig-Holstein).[83][84]
The Medieval colonization areas, that constituted the eastern provinces of the modern German Empire and the Austrian Empire, were inhabited estimated 30 million Germans at the beginning of the 20th century. The westward withdrawal of the political boundaries of Germany, first in 1919, but substantially in 1945, was followed by the removal of some 15 million people, to resettle within the borders of present-day Germany and Austria. Only the oldest 12th-century and partially 13th-century colonization areas remained German in language and culture, that are situated within the territory of the pre-1990 East Germany and the eastern part of Austria.[84]
See also[]
- Cultural assimilation
- German diaspora
- Drang nach Osten
- Limes Saxoniae
- Barbarian invasions
- Wends
- Wendish Crusade
- Northern Crusades
- Medieval demography
- German exonyms
- Germanisation
- Germanisation of Poles during Partitions
- History of Germans in Russia and the Soviet Union
- Historical migration
- Josephine colonization
- Population transfer in the Soviet Union
- Polonization
- Expulsion of Germans after World War II
References[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Alan V. Murray (15 May 2017). The North-Eastern Frontiers of Medieval Europe: The Expansion of Latin Christendom in the Baltic Lands. Taylor & Francis. pp. 23–. ISBN 978-1-351-88483-9.
- ^ Nora Berend (15 May 2017). The Expansion of Central Europe in the Middle Ages. Taylor & Francis. pp. 194–. ISBN 978-1-351-89008-3.
- ^ CHRISTIAN LÜBKE. "Ostkolonisation, Ostsiedlung, Landesausbau im Mittelalter" (PDF). MGH-Archive. Retrieved July 25, 2020.
- ^ Vejas Gabriel Liulevicius (9 December 2010). The German Myth of the East: 1800 to the Present - p. 1. OUP Oxford. ISBN 978-0-19-960516-3.
- ^ "Ostsiedlung – ein gesamteuropäisches Phänomen". GRIN Verlag. Retrieved July 25, 2020.
- ^ Szabo 2008, p. 9.
- ^ Bartlett 1998, p. 14.
- ^ Szabo 2008, p. 10.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Katalin Szende. "Iure Theutonico ? German settlers and legal frameworks for immigration to Hungary in an East-Central European perspective". Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- ^ The Slippery Memory of Men (East Central and Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 450–1450) by Paul Milliman page 2
- ^ The Man of Many Devices, Who Wandered Full Many Ways ...: Festschrift in Honor of Janos M.Bak [Hardcover] Balázs Nagy (Editor), Marcell Sebok (Editor) page 654, 655
- ^ The Holocaust as Colonial Genocide: Hitler's 'Indian Wars' ... - Page 38; Carroll P. Kakel III - 2013: Within National Socialist discourse, the Nazis purposefully and skillfully presented their eastern colonization project as a 'continuation of medieval Ostkolonisation [eastern colonization], celebrated in the language of continuity, legacy, and colonial grandeur'.
- ^ Johannes Fried (10 October 2016). Charlemagne. Harvard University Press. pp. 193–. ISBN 978-0-674-73739-6.
- ^ Jean-Denis G.G. Lepage (20 May 2015). Castles and Fortified Cities of Medieval Europe: An Illustrated History. McFarland. pp. 16–. ISBN 978-0-7864-6027-4.
- ^ F Donald Logan (2 October 2012). A History of the Church in the Middle Ages. Routledge. pp. 71–. ISBN 978-1-134-78669-5.
- ^ Kathy Lynne Roper Pearson; Nicholas Cook (1999). Conflicting Loyalties in Early Medieval Bavaria: A View of Socio-political Interaction, 680-900. Ashgate. ISBN 978-0-7546-0011-4.
- ^ Jenny Benham. "Treaty of Verdun (843)". Retrieved July 26, 2020.
- ^ Schulman 2002, pp. 325–27.
- ^ Thomas H. Greer; Gavin Lewis (1992). A Brief History of the Western World. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich College Publishers. ISBN 978-0-15-505552-0.
- ^ Timothy Reuter (6 June 2014). Germany in the Early Middle Ages c. 800-1056. Taylor & Francis. pp. 266–. ISBN 978-1-317-87238-2.
- ^ Alexander Basilevsky (28 March 2016). Early Ukraine: A Military and Social History to the Mid-19th Century. McFarland. pp. 146–. ISBN 978-0-7864-9714-0.
- ^ Wolfgang H. Fritze (1984). Der slawische Aufstand von 983: eine Schicksalswende in der Geschichte Mitteleuropas.
- ^ "The Medieval Elbe - Slavs and Germans on the Frontier". University of Oregon. Retrieved July 25, 2020.
- ^ Iben Fonnesberg-Schmidt (2007). The Popes and the Baltic Crusades: 1147-1254. BRILL. pp. 29–. ISBN 978-90-04-15502-2.
- ^ Florin Curta (8 July 2019). Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages (500-1300) (2 vols). BRILL. pp. 556–. ISBN 978-90-04-39519-0.
- ^ Philippe Dollinger (1999). The German Hansa. Psychology Press. pp. 379–. ISBN 978-0-415-19073-2.
- ^ Jan Klapste (11 November 2011). The Czech Lands in Medieval Transformation. BRILL. pp. 215–. ISBN 978-90-04-22646-3.
- ^ Ebo and Herbordus (1 June 2007). The Life of Otto Apostle of Pomerania 1060-1139. Cosimo, Inc. pp. 4–. ISBN 978-1-60206-535-2.
- ^ Thomas Kantzow (1816). Pomerania, oder, Ursprunck, Altheit und Geschicht der Völcker und Lande Pomern, Cassuben, Wenden, Stettin, Rhügen in vierzehn Büchern. Auf Kosten des Herausgebers, in Commission bey E. Mauritins. pp. 1–.
- ^ Henryk Bagiński (1946). Poland and the Baltic: The Problem of Poland's Access to the Sea. Polish Institute for Overseas Problems.
- ^ Horst Fuhrmann (9 October 1986). Germany in the High Middle Ages: C.1050-1200. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-31980-5.
- ^ James Westfall Thompson (1962). Feudal Germany. F. Ungar Publishing Company.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Terra Mariana". The Encyclopedia Americana. Americana Corp. 1967.
- ^ Zsolt Hunyadi; J¢zsef Laszlovszky; Central European University. Dept. of Medieval Studies (1 January 2001). The Crusades and the Military Orders: Expanding the Frontiers of Medieval Latin Christianity. Central European University Press. pp. 468–. ISBN 978-963-9241-42-8.
- ^ Bilmanis, Alfreds (1944). Latvian-Russian relations: documents. The Latvian legation.
- ^ Herbermann, Charles George (1907). The Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company.
- ^ Bilmanis, Alfreds (1945). The Church in Latvia. Drauga vēsts.
- ^ Plakans, Andrejs (1995). The Latvians: A Short History. Hoover Press. p. 19. ISBN 978-0-8179-9303-0.
- ^ Krzysztof Brzechczyn (2009). Idealization XIII: Modeling in History. Rodopi. pp. 235–. ISBN 978-90-420-2831-9.
- ^ Mary Fulbrook; Professor of German History Mary Fulbrook (19 February 2004). A Concise History of Germany. Cambridge University Press. pp. 13–. ISBN 978-0-521-54071-1.
- ^ Werner Rösener (1992). Agrarwirtschaft, Agrarverfassung und ländliche Gesellschaft im Mittelalter - p. 17. Oldenbourg. ISBN 978-3-486-55024-5.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bartlett 1998, p. 147.
- ^ The Germans and the East, Charles W. Ingrao, Franz A. J. Szabo, Jan Piskorski Medieval Colonization in Europe, pages 31-32, Purdue University Press,2007 "The sources leave no doubt that rather numerous German settlers arrived into many areas of East Central Europe and that particularly in the earliest period of eastern colonization the so-called German law was introduced above all by immigrants from the German lands. This particularly affected the territory between the Elbe and the Oder, Western Pomerania, Prussia, western Poland, the Czech lands (and especially Moravia), Carinthia and Transylvania."
- ^ Anne-Lise Head-König. "Migration in the Swiss Alps and Swiss Jura from the Middle Ages to the mid-20th century - Migratory movements and their chronologies, 2". Open Edition. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Bal zs Nagy; Marcell Seb?k (1 January 1999). The Man of Many Devices, who Wandered Full Many Ways--: Festschrift in Honour of J nos M. Bak - Piskorski, Jan Maria - "The Historiography of the So-called "East Colonisation" and the Current State of Research" pp. 654–667. Central European University Press. ISBN 978-963-9116-67-2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Enno Bünz (2008). Ostsiedlung und Landesausbau in Sachsen: die Kührener Urkunde von 1154 und ihr historisches Umfeld p. 95. Leipziger Universitätsverlag. ISBN 978-3-86583-165-1.
- ^ Bartlett 1998, p. 184.
- ^ Bartlett 1998, p. 187.
- ^ Felix Biermann; Günter Mangelsdorf (2005). Die bäuerliche Ostsiedlung des Mittelalters in Nordostdeutschland: Untersuchungen zum Landesausbau des 12. bis 14. Jahrhunderts im ländlichen Raum. Lang. ISBN 978-3-631-54117-3.
- ^ Charles W. Ingrao; Franz A. J. Szabo (2008). The Germans and the East - Piskorski, Jan Maria. "Medieval Colonization in Europe" pp. 27-37. Purdue University Press. ISBN 978-1-55753-443-9.
- ^ Werner Trossbach; Clemens Zimmermann (2006). Die Geschichte des Dorfes: von den Anfängen im Frankenreich zur bundesdeutschen Gegenwart. Ulmer. ISBN 978-3-8252-8324-7.
- ^ Brather, Sebastian (2001). Archäologie der westlichen Slawen. Siedlung, Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft im früh- und hochmittelalterlichen Ostmitteleuropa. Ergänzungsbände zum Reallexikon der germanischen Altertumskunde (in German). 30. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 156, 159. ISBN 3-11-017061-2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Brather, Sebastian (2001). Archäologie der westlichen Slawen. Siedlung, Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft im früh- und hochmittelalterlichen Ostmitteleuropa. Ergänzungsbände zum Reallexikon der germanischen Altertumskunde (in German). 30. Walter de Gruyter. p. 156. ISBN 3-11-017061-2.
- ^ Anna Paner, Jan Iluk: Historia Polski Virtual Library of Polish Literature, Katedra Kulturoznawstwa, Wydział Filologiczny, Uniwersytet Gdański..
- ^ Jump up to: a b Charles Higounet (1990). Die deutsche Ostsiedlung im Mittelalter. Deutscher Taschenbuch Verlag. ISBN 978-3-423-04540-7.
- ^ Knefelkamp, Ulrich (2002). Das Mittelalter. Geschichte im Überblick. UTB Uni-Taschenbücher (in German). 2105 (2 ed.). UTB. p. 242. ISBN 3-8252-2105-9.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Brather, Sebastian (2001). Archäologie der westlichen Slawen. Siedlung, Wirtschaft und Gesellschaft im früh- und hochmittelalterlichen Ostmitteleuropa. Ergänzungsbände zum Reallexikon der germanischen Altertumskunde (in German). 30. Walter de Gruyter. p. 155. ISBN 3-11-017061-2.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Schich 2007, p. 217.
- ^ Bartlett 1998, p. 326.
- ^ Bartlett 1998, p. 320.
- ^ Schich 2007, p. 218.
- ^ Martin Stolzenau (February 3, 2019). "Er schuf die Grundlage für die Stadt- und Landeshistorie". MAZ. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ Enno Bünz: Die Rolle der Niederländer in der Ostsiedlung, in: Ostsiedlung und Landesausbau in Sachsen, 2008.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Konrad Gündisch. "Transylvania and the Transylvanian Saxons". Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- ^ Bartlett 1998, p. 148.
- ^ Szabo 2008, p. 11.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Szabo 2008, p. 12.
- ^ Herbers & Jaspert 2007.
- ^ Tomasz Czarnecki. "V. Internationale Germanistische Konferenz: "Deutsch im Kontakt der Kulturen. Schlesien und andere Vergleichsregionen" - Tomasz Czarnecki: Die deutschen Lehnwörter im Polnischen und die mittelalterlichen Dialekte des schlesischen Deutsch". Doc Player. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- ^ Tilman Berger, Ingrid Hudabiunigg. "Geschichte des deutsch-slawischen Sprachkontaktes im Teschener Schlesie" (PDF). Uni Regensburg. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- ^ Pavla Kloboukov. "GERMANISMY V BĚŽNÉ MLUVĚ DNEŠKA" (PDF). FILOZOFICKÁ FAKULTA MASARYKOVY UNIVERZITY. Retrieved September 28, 2020.
- ^ Walther Mitzka (1943). "ie Ostbewegung der deutschen Sprache". Zeitschrift für Mundartforschung. Jstor. 19 (1/4): 81–140. JSTOR 40499525. Retrieved September 30, 2020.
- ^ Schwarz, Gabriele (1989). Lehrbuch der allgemeinen Geographie. Volume 6. Allgemeine Siedlungsgeographie I (4 ed.). Walter de Gruyter. p. 189. ISBN 3-11-007895-3.
- ^ The Germans and the East, Charles W. Ingrao, Franz A. J. Szabo, Jan Piskorski Medieval Colonization in Europe, page 31, Purdue University Press,2007: "All this does not mean that there was no conflict between the native population and immigrants, nor were there not expulsions of natives on a regional scale, as Helmold has written in relation to eastern Holstein. It is known that these anti-foreign confrontations were sometimes bloody, particularly in towns. Everywhere the sources indicate that hatred was basically directed against those newcomers who had no command of the local language. In Cracow at the dawn of the sixteenth century, during the successive Polish wars with the Teutonic Knights, it appears that Polonized burghers of German origin in particular expressed their antipathy towards the Germans."
- ^ Klaus Fehn. "Siedlungsforschung Archäologie-Geschichte-Geographie, Band 13 - pp. 67 - 77" (PDF). Verlag Siedlungsforschung Bonn. Retrieved September 30, 2020.
- ^ Wolfgang Wippermann (1981). Der "deutsche Drang nach Osten": Ideologie und Wirklichkeit eines politischen Schlagwortes. Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft. ISBN 978-3-534-07556-0.
- ^ Janusz Gumkowkski, Kazimierz Leszczynski. "HITLER'S PLANS FOR EASTERN EUROPE". archive. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ Werner Buchholz (2002). Deutsche Geschichte im Osten Europas: Pommern / hrsg. von Werner Buchholz. ... Siedler. ISBN 978-3-88680-771-0.
- ^ The Slippery Memory of Men (East Central and Eastern Europe in the Middle Ages, 450–1450) by Paul Milliman page 2
- ^ The Man of Many Devices, Who Wandered Full Many Ways ...: Festschrift in Honor of Janos M.Bak [Hardcover] Balázs Nagy (Editor), Marcell Sebok (Editor) page 654, 655
- ^ The Holocaust as Colonial Genocide: Hitler's 'Indian Wars' ... - Page 38; Carroll P. Kakel III - 2013: Within National Socialist discourse, the Nazis purposefully and skillfully presented their eastern colonization project as a 'continuation of medieval Ostkolonisation [eastern colonization], celebrated in the language of continuity, legacy, and colonial grandeur'.
- ^ DIETRICH EICHHOLTZ. "Generalplan Ost« zur Versklavungosteuropäischer Völker" (PDF). Archive. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-14. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ WALTER SCHLESINGER. "DIE GESCHICHTLICHE STELLUNG DER MITTELALTERLICHEN DEUTSCHEN OSTBEWEGUNG". De Gruyter. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
- ^ Jump up to: a b STEFFEN PRAUSER, ARFON REES. "The Expulsion of the German Communities from Eastern Europe at the End of the Second World War". EUROPEAN UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE, FLORENCE. Retrieved September 29, 2020.
Sources[]
- Bartlett, Robert (1998). Die Geburt Europas aus dem Geist der Gewalt. Eroberung, Kolonisation und kultureller Wandel von 950 bis 1350 ( = [English original :] The Making of Europe : conquest, colonization, and cultural change 950 - 1350) (in German). Knaur München. ISBN 3-426-60639-9.
- Kleineberg, A; Marx, Chr; Knobloch, E.; Lelgemann, D. (2010). Germania und die Insel Thule. Die Entschlüsselung von Ptolemaios' "Atlas der Oikumene" (in German). WBG. ISBN 978-3-534-23757-9.
- Gründer, Horst; Johanek, Peter (2001). Kolonialstädte, europäische Enklaven oder Schmelztiegel der Kulturen?: Europäische Enklaven oder Schmelztiegel der Kulturen? (in German). ISBN 3-8258-3601-0.
- Reuber, Paul; Strüver, Anke; Wolkersdorfer, Günter (2005). Politische Geographien Europas — Annäherungen an ein umstrittenes Konstrukt: Annäherungen an ein umstrittenes Konstrukt (in German). ISBN 3-8258-6523-1.
- Demurger, Alain; Kaiser, Wolfgang (2003). Die Ritter des Herrn: Geschichte der Geistlichen Ritterorden (in German). ISBN 3-406-50282-2.
- Herbers, Klaus; Jaspert, Nikolas, eds. (2007). Grenzräume und Grenzüberschreitungen im Vergleich: Der Osten und der Westen des mittelalterlichen Lateineuropa (in German). De Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-05-004155-1.
- Herrmann, Die Slawen in Deutschland
- Knefelkamp, Ulrich, ed. (2001). Zisterzienser: Norm, Kultur, Reform — 900 Jahre Zisterzienser (in German). ISBN 3-540-64816-X.
- Schich, Winfried (2007). Wirtschaft und Kulturlandschaft: Gesammelte Beiträge 1977 bis 1999 zur Geschichte der Zisterzienser und der "Germania Slavica". Bibliothek der brandenburgischen und preussischen Geschichte (in German). 12. BWV Verlag. ISBN 978-3-8305-0378-1.
- Rösener, Werner (1988). Agrarwirtschaft, Agrarverfassung und ländliche Gesellschaft im Mittelalter (in German). ISBN 3-486-55024-1.
- Schulman, Jana K. (2002). The Rise of the Medieval World, 500–1300: A Biographical Dictionary. Greenwood Press.
- Sommerfeld, Wilhelm von (2005) [1896]. Geschichte der Germanisierung des Herzogtums Pommern oder Slavien bis zum Ablauf des 13. Jahrhunderts (in German). Adamant Media Corporation. ISBN 1-4212-3832-2. (unabridged facsimile of the edition published by Duncker & Humblot, Leipzig 1896)
- Szabo, Franz A. J. (2008). Ingrao, Charles W. (ed.). The Germans and the East. Purdue University Press. ISBN 978-1-55753-443-9.
Further reading[]
- Charles Higounet (1911–1988) Les allemands en Europe centrale et oriental au moyen age
- German translation: Die deutsche Ostsiedlung im Mittelalter
- Japanese translation: ドイツ植民と東欧世界の形成, 彩流社, by Naoki Miyajima
- Bielfeldt et al., Die Slawen in Deutschland. Ein Handbuch, Hg. Joachim Herrmann, Akademie-Verlag Berlin, 1985
- Social history of the Holy Roman Empire
- German diaspora in Europe
- Medieval Germany
- Former eastern territories of Germany
- Estonia–Germany relations
- Germany–Latvia relations
- Germany–Lithuania relations
- Estonia–Russia relations
- Germany–Romania relations
- History of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- German words and phrases
- Prussian Crusade
- Human migrations
- Migration Period

