Outline of water

Faucet dripping water.

Structure of the water molecule (H2O)
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to water:
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state (water vapor or steam). Under nomenclature used to name chemical compounds, Dihydrogen monoxide is the scientific name for water, though it is almost never used.[1]
History[]
- The identification of water as a substance
Chemical properties and use[]

Seawater.

Boiling water.
- Water (molecule)
- Electrolysis of water
- Water of crystallization
- Dealkalization of water
- Drinking water quality standards
- Self-ionization of water
- Water-in-water emulsion
- Water purification
- Water (data page)
- Hard water / Soft water
- Water softening
- Water absorption
- Heavy water
- Distilled water
- Salinity
- Saline water
- Seawater
- Hydrate
- Boiling
Physical properties[]

Frozen water, that is, ice.
- Water (properties)
- Color of water
- Water vapour
- Vapour pressure of water
- Steam
- Ice
- Lunar ice
- Optical properties of water and ice
- Water quality
- Water (data page)
- Mineral water
Geography[]

The Water Cycle

Rapidly flowing river.
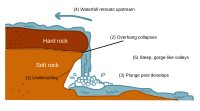
Formation of a waterfall

Victoria Falls
- Origin of water on Earth
- Evolution of water on Mars and Earth
- Extraterrestrial liquid water
- List of extrasolar candidates for liquid water
- Hydrosphere
- Hydrology
- Water distribution on Earth
- Water cycle
- Groundwater
- Hydrology
- Body of water
- Salt water
- Seawater
- Ocean
- Sea
- Tide
- Brine
- Brackish water
- Fresh water
- Aquifer
- River
- Drainage
- Drainage divide
- Drainage basin
- Lake
- Salt water
- Glacier
- Geyser
- Spring
- Waterfall
Weather[]

A snowflake.

Snow-covered trees.
- Precipitation (meteorology)
- Rain
- Freezing rain
- Drizzle
- Snow
- Snow pellets
- Snow grains
- Ice pellets
- Hail
- Ice crystals
- Dew
- Frost
- Hoarfrost
- Atmospheric icing
- Glaze ice
- Clouds
- Fog
- Mist
- Spindrift
- Flood
- Wave
- Wind wave
- Tsunami
- Drought
In nature and life[]
- Origin of water on Earth
- Evolution of water on Mars and Earth
- Water intoxication
- Drinking water
- Drowning
- Dehydration
Marine life[]
- Underwater
- Marine biology
- Marine life
- Hydrobiology
Politics and issues[]
- Water politics
- Water politics in the Middle East
- Water politics in the Jordan River basin
- Water law
- Water right
- Water resources
- Water resources of the People's Republic of China
- Water resources of Singapore
- Reuse of water bottles
- Water crisis
- Water conservation
- Water industry
- Water privatization
- Water management
- Water conflicts
- Water export
- Water pollution
Supply and sanitation[]

- Water supply
- Water supply network
- Reservoir
- Dam
- Water tower
- Aqueduct
- Pump
- Water well
- Drinking Fountain
- Water pipe
- Plumbing
- Tap (valve)
- Water supply network
- Sanitation
- Drinking water
- Water fluoridation
- Opposition to water fluoridation
In culture and sport[]

Poseidon, Greek god of water. The Roman water god, Neptune, was almost identical to Poseidon
- Water deity
- Water (classical element)
- Holy water
- Adam's ale
- Water sport (recreation)
- List of water sports
- Swimming
- Water polo
- List of water sports
- Winter sport
- Water gun
- Water fight
- Fountain
Uses[]
- Water wheel
- Hydropower
- Water turbine
- Steam engine
- Drinking
- Drinking water
- Tap water
- Bottled water
- Drinking vessel
- Glass (drinkware)
- Water clock
- Irrigation
- Use of water in fire fighting
- Professional diving
- Water transport
- Bathing
- Sink
- Bathtub
- Shower
- Washing
- Pressure washer
- Naval warfare
Fishing[]
See also[]
- Hydrological Ensemble Prediction Experiment
References[]
- ^ Bramer, Scott. "Chemical Nomenclature". Widener University, Department of Chemistry. Retrieved 20 September 2011.
External links[]
- OECD Water statistics
- The World's Water Data Page
- FAO Comprehensive Water Database, AQUASTAT
- The Water Conflict Chronology: Water Conflict Database
- US Geological Survey Water for Schools information
- Portal to The World Bank's strategy, work and associated publications on water resources
- America Water Resources Association
- America Water Resources Association
- Water structure and science
Categories:
- Water
- Outlines of general reference
- Wikipedia outlines






