Philistines
The Philistines were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when their polity, after having already been subjugated for centuries by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, was finally destroyed by King Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire.[1] After becoming part of his empire and its successor, the Persian Empire, they lost their distinct ethnic identity and disappeared from the historical and archaeological record by the late 5th century BC.[2] The Philistines are known for their biblical conflict with the Israelites. Though the primary source of information about the Philistines is the Hebrew Bible, they are first attested to in reliefs at the Temple of Ramses III at Medinet Habu, in which they are called Peleset[a] (accepted as cognate with Hebrew Peleshet);[3] the parallel Assyrian term is Palastu,[b] Pilišti,[c] or Pilistu.[d][4]
Several theories are given about the origins of the Philistines. The Hebrew Bible mentions in two places that they originate from Caphtor (possibly Crete/Minoa).[5] The Septuagint connects the Philistines to other biblical groups such as Caphtorim and the Cherethites and Pelethites, which have been identified with the island of Crete.[6] This has led to the modern theory of Philistines having an Aegean origin.[7] In 2016, a large Philistine cemetery was discovered near Ashkelon, containing more than 150 dead buried in oval-shaped graves. A 2019 genetic study found that, while all three Ashkelon populations derive most of their ancestry from the local Semitic-speaking Levantine gene pool, the early Iron Age population was genetically distinct due to a European-related admixture; this genetic signal is no longer detectable in the later Iron Age population. According to the authors, the admixture was likely due to a "gene flow from a European-related gene pool" during the Bronze to Iron Age transition, which supports the theory that a migration event occurred.[8]
| History of Palestine |
|---|
 |
| Prehistory |
| Ancient history |
| Classical period |
|
| Islamic rule |
| Modern era |
|
|
|
Etymology[]
The English term Philistine comes from Old French Philistin; from Classical Latin Philistinus; from Late Greek Philistinoi; ultimately from Hebrew Pəlištî (פלשתי; plural Pəlištîm, פלשתים), meaning 'person of Pəlešet (פלשת)'; and there are cognates in Akkadian (aka Assyrian, Babylonian) Palastu and Egyptian Palusata;[9] the term Palestine has the same derivation.[10]
The Hebrew term Plištim occurs 286 times in the Masoretic Text of the Hebrew Bible (of which 152 times are in 1 Samuel). It also appears in the Samaritan Pentateuch.[11] In the Greek version of the Bible, called Septuagint, the equivalent term Phulistieím (Φυλιστιείμ) occurs 12 times, again in the Pentateuch.[12]
In secondary literature, "Philistia" is further mentioned in the Aramaic Visions of Amram (4Q543-7), which is dated "prior to Antiochus IV and the Hasmonean revolt," possibly to the time of High Priest of Israel Onias II; Jubilees 46:1-47:1 might have used Amram as a source.[13]
Outside of pre-Maccabean Israelite religious literature, evidence for the name and the origins of the Philistines is less abundant and less consistent. In the remainder of the Hebrew Bible, ha-Plištim is attested at Qumran for 2 Samuel 5:17.[14] In the Septuagint, however, 269 references instead use the term allophylos ('of another tribe').[15]
Later history[]
In 712 BC Iamani, a local usurper, ascended the throne of Ashdod. That same year, he organized a failed uprising against Assyria. The Assyrian King Sargon II invaded Philistia, which effectively became an Assyrian province. Although he allowed Iamani to remain on the throne,[16] Gath was conquered, and possibly also destroyed in the same campaign in 711 BC.[17]
Biblical accounts[]
In the Book of Genesis, the Philistines are said to descend from the Casluhites, an Egyptian people.[18] However, according to rabbinic sources, these Philistines were different from those described in the Deuteronomistic history.[19] Deuteronomist sources describe the "Five Lords of the Philistines"[e] as based in five city-states of the southwestern Levant: Gaza, Ashkelon, Ashdod, Ekron, and Gath, from Wadi Gaza in the south to the Yarqon River in the north. This description portrays them at one period of time as among the Kingdom of Israel's most dangerous enemies.[15] In contrast, the Septuagint uses the term allophuloi (Greek: ἀλλόφυλοι) instead of "Philistines," which means simply 'other nations'.
Torah (Pentateuch)[]
With regard to descendants of Mizraim, the biblical progenitor of the Egyptians, the Table of Nations in Genesis 10 states in Hebrew: "ve-et Patrusim ve-et Kasluhim asher yats'u mi-sham Plištim ve-et Kaftorim." Literally, it says that those whom Mizraim begat included "the Pathrusim, Casluhim, out of whom came the Philistines, and the Caphtorim."
There is some debate among interpreters as to whether this verse was originally intended to signify that the Philistines themselves were the offspring of the Casluhim or the Caphtorim. While the Casluhim or the Caphtorim origin was widely followed by some 19th-century biblical scholars,[20] others such as Friedrich Schwally,[21] Bernhard Stade,[22] and Cornelis Tiele[23] argued for a Semitic origin. Interestingly, the Caphtorites were considered to derive from Crete[24] while Cashluhim derived from Cyrenaica,[25] which was part of the province Crete and Cyrenacia in Roman times, which alludes to the similarities between them.
The Torah does not record the Philistines as one of the nations to be displaced from Canaan. In Genesis 15:18–21 the Philistines are absent from the ten nations Abraham's descendants will displace as well as being absent from the list of nations Moses tells the people they will conquer, though the land in which they resided is included in the boundaries based on the locations of rivers described (Deut 7:1, 20:17). In fact, the Philistines, through their Capthorite ancestors, were allowed to conquer the land from the Avvites (Deuteronomy 2:23). God also directed the Israelites away from the Philistines upon their Exodus from Egypt according to Exodus 13:17. In Genesis 21:22–27, Abraham agrees to a covenant of kindness with Abimelech, the Philistine king, and his descendants. Abraham's son Isaac deals with the Philistine king similarly, by concluding a treaty with them in chapter 26 (Genesis 26:28–29).
Unlike most other ethnic groups in the Bible, the Philistines are almost always referred to without the definite article in the Torah.[26]
Deuteronomistic history[]

Rabbinic sources state that the Philistines of Genesis were different people from the Philistines of the Deuteronomistic history (the series of books from Joshua to 2 Kings).[19] According to the Talmud (Chullin 60b), the Philistines of Genesis intermingled with the Avvites. This differentiation was also held by the authors of the Septuagint (LXX), who translated (rather than transliterated) its base text as allophuloi (Greek: ἀλλόφυλοι, 'other nations') instead of philistines throughout the Books of Judges and Samuel.[19][27]
Throughout the Deuteronomistic history, Philistines are almost always referred to without the definite article, except on 11 occasions.[26] On the basis of the LXX's regular translation into "allophyloi", Robert Drews states that the term "Philistines" means simply "non-Israelites of the Promised Land" when used in the context of Samson, Saul and David.[28]
Judges 13:1 tells that the Philistines dominated the Israelites in the times of Samson, who fought and killed over a thousand (e.g. Judges 15). According to 1 Samuel 5–6, they even captured the Ark of the Covenant for a few months.
A few biblical texts, such as the Ark Narrative and stories reflecting the importance of Gath, seem to portray Late Iron I and Early Iron II memories.[29] They are mentioned more than 250 times, the majority in the Deuteronomistic history,[citation needed] and are depicted as among the arch-enemies of the Israelites,[30] a serious and recurring threat before being subdued by David.
The Bible paints the Philistines as the main enemy of the Israelites (prior to the rise of the Neo-Assyrian Empire and Neo-Babylonian Empire) with a state of almost perpetual war between the two. The Philistine cities lost their independence to Assyria, and revolts in the following years were all crushed. They were subsequently absorbed into the Neo-Babylonian Empire and the Achaemenid Empire, and disappeared as a distinct ethnic group by the late 5th century BC.[2]
The Prophets[]
Amos in 1:8 sets the Philistines / ἀλλοφύλοι at Ashdod and Ekron. In 9:7 God is quoted asserting that, as he brought Israel from Egypt, he also brought the Philistines from Caphtor.[31] In the Greek this is, instead, bringing the ἀλλόφυλοι from Cappadocia.[32]
Battles between the Israelites and the Philistines[]

The following is a list of battles described in the Bible as having occurred between the Israelites and the Philistines:[33]
- The Battle of Shephelah (2 Chronicles 28:18).
- Israelites defeated at the Battle of Aphek, Philistines capture the Ark (1 Samuel 4:1–10).
- Philistines defeated at the Battle of Eben-Ezer (1 Samuel 7:3–14).
- Some Philistine military success must have taken place subsequently, allowing the Philistines to subject the Israelites to a localised disarmament regime (1 Samuel 13:19–21 states that no Israelite blacksmiths were permitted and they had to go to the Philistines to sharpen their agricultural implements).
- Battle of Michmash, Philistines routed by Jonathan and his men (1 Samuel 14).
- Near the Valley of Elah, David defeats Goliath in single combat (1 Samuel 17).
- The Philistines defeat Israelites on Mount Gilboa, killing King Saul and his three sons Jonathan, Abinadab and Malkishua (1 Samuel 31).
- Hezekiah defeats the Philistines as far as Gaza and its territory (2 Kings 18:5–8).
Origin[]
The origin of the Philistines is still debated. The probable Aegean connection is discussed in the paragraph on "Archaeological evidence". Here-below are presented the possible connections between Philistines and various similar ethnonyms, toponyms or other philological interpretations of their biblical name: the "Peleset" mentioned in Egyptian inscriptions, a kingdom named as "Walistina/Falistina" or "Palistin" from the region near Aleppo in Syria, and older theories connecting them to a Greek locality or a Greek-language name.
The "Peleset" from Egyptian inscriptions[]

Since 1846, scholars have connected the biblical Philistines with the Egyptian "Peleset" inscriptions.[34][35][36][37][38] All five of these appear from c.1150 BCE to c.900 BCE just as archaeological references to Kinaḫḫu, or Ka-na-na (Canaan), come to an end;[39] and since 1873 comparisons were drawn between them and to the Aegean "Pelasgians."[40][41] Archaeological research to date has been unable to corroborate a mass settlement of Philistines during the Ramesses III era.[42][43][44]
"Walistina/Falistina" and "Palistin" in Syria[]
Pro[]
A Walistina is mentioned in Luwian texts already variantly spelled Palistina.[45][46][47] This implies dialectical variation, a phoneme ("f"?) inadequately described in the script,[48] or both. Falistina was a kingdom somewhere on the Amuq plain, where the Amurru kingdom had held sway before it.[49]
In 2003, a statue of a king named bearing inscriptions in Luwian was discovered during excavations conducted by German archaeologist Kay Kohlmeyer in the Citadel of Aleppo.[50] The new readings of Anatolian hieroglyphs proposed by the Hittitologists Elisabeth Rieken and Ilya Yakubovich were conducive to the conclusion that the country ruled by Taita was called Palistin.[51] This country extended in the 11th-10th centuries BCE from the Amouq Valley in the west to Aleppo in the east down to Mehardeh and Shaizar in the south.[52]
Due to the similarity between Palistin and Philistines, Hittitologist John David Hawkins (who translated the Aleppo inscriptions) hypothesizes a connection between the Syro-Hittite Palistin and the Philistines, as do archaeologists Benjamin Sass and Kay Kohlmeyer.[53] Gershon Galil suggests that King David halted the Arameans' expansion into the Land of Israel on account of his alliance with the southern Philistine kings, as well as with Toi, king of Ḥamath, who is identified with Tai(ta) II, king of Palistin (the northern Sea Peoples).[54]
Contra[]
However, the relation between Palistin and the Philistines is much debated. Israeli professor Itamar Singer notes that there is nothing (besides the name) in the recently discovered archaeology that indicates an Aegean origin to Palistin; most of the discoveries at the Palistin capital Tell Tayinat indicate a Neo-Hittite state, including the names of the kings of Palistin. Singer proposes (based on archaeological finds) that a branch of the Philistines settled in Tell Tayinat and were replaced or assimilated by a new Luwian population who took the Palistin name.[55]
Greece: "Palaeste" and phyle histia theories[]
Another theory, proposed by [de] in 1914, is that the name derives from the attested Illyrian-Epirote locality Palaeste, whose inhabitants would have been called Palaestīnī according to Illyrian normal grammatical practice.[56]
Allen Jones (1972) suggests that the name Philistine represents a corruption of the Greek phyle histia ('tribe of the hearth'), with the Ionic spelling of hestia.[57]
Archaeological evidence[]
Territory[]
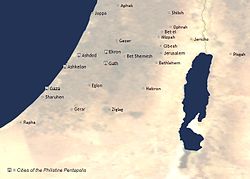
According to Joshua 13:3 and 1 Samuel 6:17, the land of the Philistines (or Allophyloi), called Philistia, was a pentapolis in the southwestern Levant comprising the five city-states of Gaza, Ashkelon, Ashdod, Ekron, and Gath, from Wadi Gaza in the south to the Yarqon River in the north, but with no fixed border to the east.[15]
Tell Qasile (a "port city") and Aphek were located on the northern frontier of Philistine territory, and Tell Qasile in particular may have been inhabited by both Philistine and non-Philistine people.[58]
The location of Gath is not entirely certain, although the site of Tell es-Safi, not far from Ekron, is currently the most favoured.[59]
The identity of the city of Ziklag, which according to the Bible marked the border between the Philistine and Israelite territory, remains uncertain.[60]
In the western part of the Jezreel Valley, 23 of the 26 Iron Age I sites (12th to 10th centuries BCE) yielded typical Philistine pottery. These sites include Tel Megiddo, Tel Yokneam, Tel Qiri, Afula, Tel Qashish, Be'er Tiveon, Hurvat Hazin, Tel Risim, Tel Re'ala, Hurvat Tzror, Tel Sham, Midrakh Oz and Tel Zariq. Scholars have attributed the presence of Philistine pottery in northern Israel to their role as mercenaries for the Egyptians during the Egyptian military administration of the land in the 12th century BCE. This presence may also indicate further expansion of the Philistines to the valley during the 11th century BCE, or their trade with the Israelites. There are biblical references to Philistines in the valley during the times of the Judges. The quantity of Philistine pottery within these sites is still quite small, showing that even if the Philistines did settle the valley, they were a minority that blended within the Canaanite population during the 12th century BCE. The Philistines seem to have been present in the southern valley during the 11th century, which may relate to the biblical account of their victory at the Battle of Gilboa.[61]
Egyptian inscriptions[]
Since Edward Hincks[34] and William Osburn Jr.[35] in 1846, biblical scholars have connected the biblical Philistines with the Egyptian "Peleset" inscriptions;[36][37] and since 1873, both have been connected with the Aegean "Pelasgians".[62] The evidence for these connections is etymological and has been disputed.[41]
As of 2005, no inscriptions written by the Philistines have not yet been found or conclusively identified.[63]
Based on the Peleset inscriptions, it has been suggested that the Casluhite Philistines formed part of the conjectured "Sea Peoples" who repeatedly attacked Egypt during the later Nineteenth Dynasty.[64][65] Though they were eventually repulsed by Ramesses III, he finally resettled them, according to the theory, to rebuild the coastal towns in Canaan. Papyrus Harris I details the achievements of the reign (1186–1155 BC) of Ramesses III. In the brief description of the outcome of the battles in Year 8 is the description of the fate of some of the conjectured Sea Peoples. Ramesses claims that, having brought the prisoners to Egypt, he "settled them in strongholds, bound in my name. Numerous were their classes, hundreds of thousands strong. I taxed them all, in clothing and grain from the storehouses and granaries each year." Some scholars suggest it is likely that these "strongholds" were fortified towns in southern Canaan, which would eventually become the five cities (the Pentapolis) of the Philistines.[66] Israel Finkelstein has suggested that there may be a period of 25–50 years after the sacking of these cities and their reoccupation by the Philistines. It is possible that at first, the Philistines were housed in Egypt; only subsequently late in the troubled end of the reign of Ramesses III would they have been allowed to settle Philistia.[citation needed]
The "Peleset" appear in four different texts from the time of the New Kingdom.[63] Two of these, the inscriptions at Medinet Habu and the Rhetorical Stela at Deir al-Medinah, are dated to the time of the reign of Ramesses III (1186–1155 BC).[63] Another was composed in the period immediately following the death of Ramesses III (Papyrus Harris I).[63] The fourth, the Onomasticon of Amenope, is dated to some time between the end of the 12th or early 11th century BC.[63]
The inscriptions at Medinet Habu consist of images depicting a coalition of Sea Peoples, among them the Peleset, who are said in the accompanying text to have been defeated by Ramesses III during his Year 8 campaign. In about 1175 BC, Egypt was threatened with a massive land and sea invasion by the "Sea Peoples," a coalition of foreign enemies which included the Tjeker, the Shekelesh, the Deyen, the Weshesh, the Teresh, the Sherden, and the PRST. They were comprehensively defeated by Ramesses III, who fought them in "Djahy" (the eastern Mediterranean coast) and at "the mouths of the rivers" (the Nile Delta), recording his victories in a series of inscriptions in his mortuary temple at Medinet Habu. Scholars have been unable to conclusively determine which images match what peoples described in the reliefs depicting two major battle scenes. A separate relief on one of the bases of the Osirid pillars with an accompanying hieroglyphic text clearly identifying the person depicted as a captive Peleset chief is of a bearded man without headdress.[63] This has led to the interpretation that Ramesses III defeated the Sea Peoples, including Philistines, and settled their captives in fortresses in southern Canaan; another related theory suggests that Philistines invaded and settled the coastal plain for themselves.[67] The soldiers were quite tall and clean-shaven. They wore breastplates and short kilts, and their superior weapons included chariots drawn by two horses. They carried small shields and fought with straight swords and spears.[68]
The Rhetorical Stela are less discussed, but are noteworthy in that they mention the Peleset together with a people called the Teresh, who sailed "in the midst of the sea". The Teresh are thought to have originated from the Anatolian coast and their association with the Peleset in this inscription is seen as providing some information on the possible origin and identity of the Philistines.[69]
The Harris Papyrus, which was found in a tomb at Medinet Habu, also recalls Ramesses III's battles with the Sea Peoples, declaring that the Peleset were "reduced to ashes." The Papyrus Harris I, records how the defeated foe were brought in captivity to Egypt and settled in fortresses.[70] The Harris papyrus can be interpreted in two ways: either the captives were settled in Egypt and the rest of the Philistines/Sea Peoples carved out a territory for themselves in Canaan, or else it was Ramesses himself who settled the Sea Peoples (mainly Philistines) in Canaan as mercenaries.[71] Egyptian strongholds in Canaan are also mentioned, including a temple dedicated to Amun, which some scholars place in Gaza; however, the lack of detail indicating the precise location of these strongholds means that it is unknown what impact these had, if any, on Philistine settlement along the coast.[69]
The only mention in an Egyptian source of the Peleset in conjunction with any of the five cities that are said in the Bible to have made up the Philistine pentapolis comes in the Onomasticon of Amenope. The sequence in question has been translated as: "Ashkelon, Ashdod, Gaza, Assyria, Shubaru [...] Sherden, Tjekker, Peleset, Khurma [...]" Scholars have advanced the possibility that the other Sea Peoples mentioned were connected to these cities in some way as well.[69]
Material culture: Aegean origin and historical evolution[]
Aegean connection[]

Many scholars have interpreted the ceramic and technological evidence attested to by archaeology as being associated with the Philistine advent in the area as strongly suggestive that they formed part of a large scale immigration to southern Canaan, probably from Anatolia and Cyprus, in the 12th century BCE.[72]
The proposed connection between Mycenaean culture and Philistine culture was further documented by finds at the excavation of Ashdod, Ekron, Ashkelon, and more recently Gath, four of the five Philistine cities in Canaan. The fifth city is Gaza. Especially notable is the early Philistine pottery, a locally made version of the Aegean Mycenaean Late Helladic IIIC pottery, which is decorated in shades of brown and black. This later developed into the distinctive Philistine pottery of the Iron Age I, with black and red decorations on white slip known as Philistine Bichrome ware.[73] Also of particular interest is a large, well-constructed building covering 240 square metres (2,600 sq ft), discovered at Ekron. Its walls are broad, designed to support a second story, and its wide, elaborate entrance leads to a large hall, partly covered with a roof supported on a row of columns. In the floor of the hall is a circular hearth paved with pebbles, as is typical in Mycenaean megaron hall buildings; other unusual architectural features are paved benches and podiums. Among the finds are three small bronze wheels with eight spokes. Such wheels are known to have been used for portable cultic stands in the Aegean region during this period, and it is therefore assumed that this building served cultic functions. Further evidence concerns an inscription in Ekron to PYGN or PYTN, which some have suggested refers to "Potnia", the title given to an ancient Mycenaean goddess. Excavations in Ashkelon, Ekron, and Gath reveal dog and pig bones which show signs of having been butchered, implying that these animals were part of the residents' diet.[74][75] Among other findings there are wineries where fermented wine was produced, as well as loom weights resembling those of Mycenaean sites in Greece.[76]
Further evidence of the Aegean origin of the initial Philistine settlers was provided by studying their burial practices in the so far only discovered Philistine cemetery, excavated at Ashkelon (see below).
However, for many years scholars such as Gloria London, John Brug, Shlomo Bunimovitz, Helga Weippert, and Edward Noort, among others, have noted the "difficulty of associating pots with people", proposing alternative suggestions such as potters following their markets or technology transfer, and emphasize the continuities with the local world in the material remains of the coastal area identified with "Philistines", rather than the differences emerging from the presence of Cypriote and/or Aegean/ Mycenaean influences. The view is summed up in the idea that 'kings come and go, but cooking pots remain', suggesting that the foreign Aegean elements in the Philistine population may have been a minority.[77][78]
Geographic evolution[]
Material culture evidence, primarily pottery styles, indicates that the Philistines originally settled in a few sites in the south, such as Ashkelon, Ashdod and Ekron.[79] It was not until several decades later, about 1150 BC, that they expanded into surrounding areas such as the Yarkon region to the north (the area of modern Jaffa, where there were Philistine farmsteads at Tel Gerisa and Aphek, and a larger settlement at Tel Qasile).[79] Most scholars, therefore, believe that the settlement of the Philistines took place in two stages. In the first, dated to the reign of Ramesses III, they were limited to the coastal plain, the region of the Five Cities; in the second, dated to the collapse of Egyptian hegemony in southern Canaan, their influence spread inland beyond the coast.[80] During the 10th to 7th centuries BC, the distinctiveness of the material culture appears to have been absorbed with that of surrounding peoples.[81]
Burial practices[]
The Leon Levy Expedition, consisting of archaeologists from Harvard University, Boston College, Wheaton College in Illinois and Troy University in Alabama, conducted a 30-year investigation of the burial practices of the Philistines, by excavating a Philistine cemetery containing more than 150 burials dating from the 11th to 8th century BCE Tel Ashkelon. In July 2016, the expedition finally announced the results of their excavation.[82]
Archaeological evidence, provided by architecture, burial arrangements, ceramics, and pottery fragments inscribed with non-Semitic writing, indicates that the Philistines were not native to Canaan. Most of the 150 dead were buried in oval-shaped graves, some were interred in ashlar chamber tombs, while there were 4 who were cremated. These burial arrangements were very common to the Aegean cultures, but not to the one indigenous to Canaan. Lawrence Stager of Harvard University believes that Philistines came to Canaan by ships before the Battle of the Delta circa 1175 BCE. DNA was extracted from the skeletons for archaeogenetic population analysis.[83]
The Leon Levy Expedition, which has been going on since 1985, helped break down some of the previous assumptions that the Philistines were uncultured people by having evidence of perfume near the bodies in order for the deceased to smell it in the afterlife.[84]
Genetic evidence[]
A study carried out on skeletons at Ashkelon in 2019 by an interdisciplinary team of scholars from the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History and the Leon Levy Expedition found that human remains at Ashkelon, associated with "Philistines" during the Iron Age, derived most of their ancestry from the local Levantine gene pool, but with a certain amount of Southern-European-related admixture. This confirms previous historic and archaeological records of a Southern-European migration event, but it did not leave a long-lasting genetic impact.[8] After two centuries, the Southern-European genetic markers were dwarfed by the local Levantine gene pool, suggesting intensive intermarriage. The Philistine culture and peoplehood remained distinct from other local communities for six centuries.[85] The DNA suggests an influx of people of European heritage into Ashkelon in the twelfth century BC. The individuals' DNA shows similarities to that of ancient Cretans, but it is impossible to specify the exact place in Europe from where Philistines had migrated to Levant, due to limited number of ancient genomes available for study, "with 20 to 60 per cent similarity to DNA from ancient skeletons from Crete and Iberia and that from modern people living in Sardinia."[86][8] The finding fits with an understanding of the Philistines as an "entangled" or "transcultural" group consisting of peoples of various origins, said Aren Maeir, an archaeologist at Bar-Ilan University in Israel. "While I fully agree that there was a significant component of non-Levantine origins among the Philistines in the early Iron Age," he said. "These foreign components were not of one origin, and, no less important, they mixed with local Levantine populations from the early Iron Age onward." Laura Mazow, an archaeologist at East Carolina University in Greenville, N.C., said the research paper supported the idea that there was some migration into the site from the west[dubious ].[8][dubious ] She added that the findings "support the picture that we see in the archaeological record of a complex, multicultural process that has been resistant to reconstruction by any single historical model."[87] "When we found the infants – infants that were too young to travel... these infants couldn't march or sail to get to the land around Ashkelon, so they were born on site. And their DNA revealed [that] their parents' heritage was not from the local population," Dr. Adam A. Aja, assistant curator of collections at the Harvard Semitic Museum and one of the Ashkelon Philistine cemetery archaeologists, explained, referring to the new genetic input from the direction of Southern Europe that was found in bone samples taken from infants buried under the floors of Philistine homes.[88] Modern archaeologists agree that the Philistines were different from their neighbors: Their arrival on the eastern shores of the Mediterranean in the early 12th century B.C. is marked by pottery with close parallels to the ancient Greek world, the use of an Aegean—instead of a Semitic—script, and the consumption of pork.[89] Nevertheless, Cretans were not too unfamiliar with the Levant, with connections being established since the Minoan era, as seen by their influence on Tel Kabri.[90]
Population[]
The population of the area associated with Philistines is estimated to have been around 25,000 in the 12th century BC, rising to a peak of 30,000 in the 11th century BC.[91] The Canaanite nature of the material culture and toponyms suggest that much of this population was indigenous, such that the migrant element would likely constitute less than half the total, and perhaps much less.[91]
Language[]
Nothing is known for certain about the language of the Philistines. Pottery fragments from the period of around 1500–1000 BCE have been found bearing inscriptions in non-Semitic languages, including one in a Cypro-Minoan script.[92] The Bible does not mention any language problems between the Israelites and the Philistines, as it does with other groups up to the Assyrian and Babylonian occupations.[93] Later, Nehemiah 13:23-24 writing under the Achaemenids records that when Judean men intermarried women from Moab, Ammon and Philistine cities, half the offspring of Judean marriages with women from Ashdod could speak only their mother tongue, Ašdôdît, not Judean Hebrew (Yehûdît); although by then this language might have been an Aramaic dialect.[94] There is some limited evidence in favour of the assumption that the Philistines were originally Indo-European-speakers, either from Greece or Luwian speakers from the coast of Asia Minor, on the basis of some Philistine-related words found in the Bible not appearing to be related to other Semitic languages.[95] Such theories suggest that the Semitic elements in the language were borrowed from their neighbours in the region. For example, the Philistine word for captain, "seren", may be related to the Greek word tyrannos (thought by linguists to have been borrowed by the Greeks from an Anatolian language, such as Luwian or Lydian[95]). Although most Philistine names are Semitic (such as Ahimelech, Mitinti, Hanun, and Dagon)[93] some of the Philistine names, such as Goliath, Achish, and Phicol, appear to be of non-Semitic origin, and Indo-European etymologies have been suggested. Recent finds of inscriptions written in Hieroglyphic Luwian in Palistin substantiate a connection between the language of the kingdom of Palistin and the Philistines of the southwestern Levant.[96][97][98]
Religion[]
The deities worshipped in the area were Baal, Astarte, and Dagon, whose names or variations thereof had already appeared in the earlier attested Canaanite pantheon.[15] Another name, attested on the Ekron Royal Dedicatory Inscription, is PT[-]YH, unique to the Philistine sphere and possibly representing a goddess in their pantheon.[99]
Although the Bible cites Dagon as the main Philistine god, the most common material finds are goddess figurines/chairs, the "Ashdoda" (feminine of Ashdod). This seems to imply a dominant female figure, which is consistent with Ancient Aegean religion.[100]
Economy[]
Cities excavated in the area attributed to Philistines give evidence of careful town planning, including industrial zones. The olive industry of Ekron alone includes about 200 olive oil installations. Engineers estimate that the city's production may have been more than 1,000 tons, 30 percent of Israel's present-day production.[68]
There is considerable evidence for a large industry in fermented drink. Finds include breweries, wineries, and retail shops marketing beer and wine. Beer mugs and wine kraters are among the most common pottery finds.[101]
See also[]
- Museum of Philistine Culture, a museum displaying the major archaeological artifacts from the five ancient Philistine city-states
- Palistin (or Walistin), a Syro-Hittite kingdom (11th-9th c. BC) in what is now NW Syria and the SE Turkish province of Hatay
- Archaeology in Gaza