Pituitary stalk
| Pituitary stalk | |
|---|---|
 The pituitary stalk is the thin vertical blue portion. | |
 Basal view of a human brain (Infundibulum labeled third from the top on right) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | infundibulum neurohypophyseos |
| NeuroNames | 408 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1248 |
| TA98 | A11.1.00.007 |
| TA2 | 3860 |
| FMA | 74635 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The pituitary stalk (also known as the infundibular stalk, Fenderson's funnel, or simply the infundibulum) is the connection between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary. The floor of the third ventricle is prolonged downward as a funnel-shaped recess—the infundibular recess—into the infundibulum, where the apex of the pituitary is attached.[1][2] It passes through the dura mater of the diaphragma sellae as it carries axons from the magnocellular neurosecretory cells of the hypothalamus down to the posterior pituitary where they release their neurohypophysial hormones, oxytocin and vasopressin, into the blood.
This connection is called the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract or hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal tract.
Damage to the pituitary stalk blocks the release of antidiuretic hormone, resulting in polydipsia (abusive water intake) and polyuria (excessive urination).
See also[]
Additional images[]
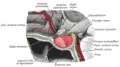
Sagittal section of the pituitary gland, showing the infundibulum
References[]
- Endocrine system
- Hypothalamus

