Pygmy falcon
| Pygmy falcon | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male in Buffalo Springs National Park, Kenya | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Falconiformes |
| Family: | Falconidae |
| Genus: | Polihierax |
| Species: | P. semitorquatus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Polihierax semitorquatus (Smith, 1836)
| |
| |
The pygmy falcon (Polihierax semitorquatus) or African pygmy falcon is a bird species native to eastern and southern Africa. It is the smallest raptor on the continent.
Description[]

Adult pygmy falcons are white below and on the face, grey above, and females having a chestnut back. There are white "eye spots" on the nape. Juveniles have a brown back, duller than adult females, with a rufous wash on the breast. The flight feathers of the wings are spotted black and white (more black above, more white below); the tail is barred black and white.[2][3]
The flight is low and undulating. In size, pattern, and the habit of perching upright on an exposed branch or treetop, this species resembles some shrikes.[2][3]
The call is "a high-pitched kikiKIK, repeated" (Kenya)[2] or "a 'chip-chip' and a 'kik-kik-kik-kik'" (southern Africa).[3]
Diet and Feeding[]
Pygmy falcons prey on reptiles and insects, but will occasionally prey on small birds as well as rodents. They hunt from a perch, swooping down on potential prey.[4]
Range, habitat, and population[]
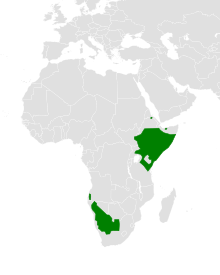
The pygmy falcon inhabits dry bush. The subspecies P. s. castanonotus occurs from South Sudan to Somalia and south to Uganda and Tanzania; P. s. semitorquatus occurs from Angola to northern South Africa.[1][3] This range is estimated to have an area of 2.7 million km2, and the total population is estimated to be between 100,000 and 1 million birds.[1]
Physiology[]
Pygmy falcons show physiological traits that have adaptive value in a region affected by environmental variability associated with the El Niño Southern Oscillation cycle as well varying food source. They regulate their body temperature by thermal buffering provided by sociable weaver colonies and communal roosting by the falcons.[5] This is important because this reduces the energy requirements for rest-phase thermoregulation by occupants.[5]
Nesting[]

In Kenya, pygmy falcons nest in white-headed buffalo weaver nests, and the ranges of the two birds coincide.[2] In southern Africa, they are found around red-billed buffalo weaver nests but predominantly nest in the vacant rooms of sociable weaver nests,[3] which are large and multichambered—even if the sociable weavers still have an active colony in the nest. Despite being bird-eaters and bigger than sociable weavers, the pygmy falcons largely leave the latter alone, though they do occasionally catch and eat nestlings and even adults.[4]
In addition, falcons are obligate users of white-headed buffalo weaver nests; therefore, they experience all of the benefits these nests provide without the energetic cost of building or maintaining them. Weavers also do not maintain these nest chambers occupied by falcons, increasing the likelihood that these particular chambers will break off the main colony . However, falcons appear to have a preference for chambers away from the center of the colony and with shorter entrance tunnels. Although it is likely that falcons would benefit from selecting chambers with better insulation, they are larger than weavers and as a result may struggle to access chambers through longer entrance tunnel.[6]
Nest defenses[]
Pygmy falcons defend these nests by the use of their faecal matter. This conspicuous faecal mat (white when fresh and turning pinkish with age) present at the entrance of the chamber is though to deter snakes and ectoparasites . [7] Faecal matter is also though to boost the immune system of chicks as well as signal to conspecifics. Faecal mats at the entrance of occupied chambers may serve as a social signal to indicate to other falcons that a colony is occupied.[7]
Cooperative breeding[]
Pygmy falcon territories are occasionally inhabited by groups, where there are more than two adults living together and tending nestlings. There are four potential reasons for this behaviour: defence, co-operative polyandry, delayed dispersal of offspring and cooperation, and thermoregulation (warmth). Corroboration for the last is that in winter African pygmy falcons nest further inside the nest of sociable weavers, where there is better insulation.[8]
Status[]
Pygmy falcons are not threatened.
References[]
- ^ a b c BirdLife International (2016). "Polihierax semitorquatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22696313A93554647. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22696313A93554647.en. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- ^ a b c d Zimmerman, Dale A.; Turner, Donald A. & Pearson, David J. (1999). Birds of Kenya and Northern Tanzania. Princeton University Press. pp. 90–91, 110–111, 309. ISBN 0-691-01022-6.
- ^ a b c d e Sinclair, Ian; Hockey, Phil & Tarboton, Warwick (2002). Birds of Southern Africa. Princeton University Press. pp. 116, 132. ISBN 0-691-09682-1. Retrieved 2007-07-26.
- ^ a b Covas, Rita; Huyser, Onno & Doutrelant, Claire (2004). "Pygmy Falcon predation of nestlings of their obligate host, the Sociable Weaver". Ostrich. 75 (4): 325–326. doi:10.2989/00306520409485463. ISSN 0030-6525. S2CID 85568509.
- ^ a b Lund, Jess; Bolopo, Diana; Thomson, Robert L.; Elliott, Dorianne L.; Arnot, Luke F.; Kemp, Ryno; Lowney, Anthony M.; McKechnie, Andrew E. (2020-02-29). "Winter thermoregulation in free-ranging pygmy falcons in the Kalahari Desert". Journal of Ornithology. 161 (2): 549–555. doi:10.1007/s10336-020-01755-y. ISSN 2193-7192.
- ^ Lowney, Anthony M.; Bolopo, Diana; Krochuk, Billi A.; Thomson, Robert L. (2020-11-03). "The Large Communal Nests of Sociable Weavers Provide Year-Round Insulated Refuge for Weavers and Pygmy Falcons". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution. 8. doi:10.3389/fevo.2020.570006. ISSN 2296-701X.
- ^ a b Krochuk, Billi A; Bolopo, Diana; Lowney, Anthony M; Meyers, Paul R; Spottiswoode, Claire N; Raman, Rajendra MG; Thomson, Robert L (2018-10-02). "Why defaecate on your doorstep? Investigating an unusual behaviour in Africa's smallest falcon". Ostrich. 89 (4): 307–314. doi:10.2989/00306525.2018.1529001. ISSN 0030-6525.
- ^ Spottiswoode, Claire; Herrmann, Eric; Rasa, O. Anne E. & Sapsford, Colin W. (2004). "Co-operative breeding in the Pygmy Falcon Polihierax semitorquatus". Ostrich. 75 (4): 322–324. doi:10.2989/00306520409485462. ISSN 0030-6525. S2CID 84652310.
External links[]
- Pygmy Falcon - Species text in The Atlas of Southern African Birds.
- Birds Of Prey
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Polihierax semitorquatus. |
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Polihierax
- Birds of prey of Sub-Saharan Africa
- Birds of East Africa
- Birds of Southern Africa
- Birds described in 1836
- Taxa named by Andrew Smith (zoologist)
