Regionalliga
 | |
| Founded | 1963 |
|---|---|
| Country | Germany |
| Confederation | UEFA (Europe) |
| Divisions | Regionalliga Nord Regionalliga Nordost Regionalliga West Regionalliga Südwest Regionalliga Bayern |
| Number of teams | 100 |
| Level on pyramid | 4 |
| Promotion to | 3. Liga |
| Relegation to | Oberliga |
| Current champions | None officially (Nord) Viktoria Berlin (Nordost) Borussia Dortmund II (West) SC Freiburg II (Südwest) 1. FC Schweinfurt (Bayern) (2020–21) |
| Current: 2021–22 Regionalliga | |
The Regionalliga (German pronunciation: [ʁeɡi̯oˈnaːlˌliːɡa]) is the fourth tier in the German football league system. Until 1974, it was the second tier in Germany. In 1994, it was introduced as the third tier. Upon the creation of the new nationwide 3. Liga in 2008, it became the fourth tier. While all of the clubs in the top three divisions of German football are professional, the Regionalliga has a mixture of professional and semi-professional clubs.
History of the Regionalligas[]
1963–1974[]
From the introduction of the Bundesliga in 1963 until the formation of the 2. Bundesliga in 1974, there were five Regionalligas, forming the second tier of German Football:
- Regionalliga Nord, (covering the states of Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein, Bremen and Hamburg)
- Regionalliga West, (covering the state of North Rhine-Westphalia)
- Regionalliga Berlin, (covering West Berlin)
- Regionalliga Südwest, (covering the states of Rheinland-Palatinate and Saarland)
- Regionalliga Süd, (covering the states of Bavaria, Hesse and Baden-Württemberg)
The champions and runners-up of the respective divisions played out two promotion spots to the Bundesliga in two groups after the end of the season.
In 1974, the two 2. Bundesligas, Süd and Nord became the second tier of German Football and the Regionalligas ceased existing for the next 20 years.
1994–2000[]
In 1994, the Regionalligas were re-introduced, this time as the third tier of German Football. There were initially four Regionalligas:
- Regionalliga Süd, (covering the states of Bavaria, Hesse and Baden-Württemberg)
- Regionalliga West/Südwest, (covering the states of Rhineland-Palatinate, Saarland and North Rhine-Westphalia)
- Regionalliga Nord, (covering the states of Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein, Bremen and Hamburg)
- Regionalliga Nordost, (covering the states of Brandenburg, Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia and Saxony; i.e. the former GDR and the city of Berlin)
Between 1994 and 2000, promotion to the 2. Bundesliga was regulated without much continuity. It was a problematic rule, as becoming champion of a division did not automatically mean promotion for that team. The champions of the South and West/Southwest divisions were automatically promoted, however, along with one of the two runners-up. The champions of the North and Northeast divisions had a play-off to decide who would get the fourth promotion spot. This rule was justified because there are more clubs in the southern part of Germany than the north.
In 1998, the promotion rule was changed again: the winner of the play-off between the North and Northeast division champions was promoted, while the loser faced the runners-up from the West/Southwest and South divisions in another play-off for the remaining promotion spot.
2000–2008[]
In 2000 the number of Regionalligas was reduced to two:
- Regionalliga Nord, (covering northern Germany)
- Regionalliga Süd, (covering southern Germany)
The new divisional alignment was not bound to certain states any more so teams were moved between the divisions in order to balance club numbers. This led to some clubs in the Southern division being geographically further north than some northern clubs, and vice versa.
The champions and the runners-up of both divisions were promoted to the 2. Bundesliga.
2008–2012[]
In 2008, the Regionalliga was demoted to become the fourth tier of football in Germany after the introduction of a new nationwide 3. Liga. However, there was an expansion to three divisions:[1]
- Regionalliga Nord, (covering the states of Brandenburg, Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Saxony, Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein, Bremen and Hamburg)
- Regionalliga Süd, (covering the states of Bavaria, Hesse and Baden-Württemberg)
- Regionalliga West, (covering the states of Rhineland-Palatinate, Saarland and North Rhine-Westphalia)
"Covering" meant that the single divisions were annually re-aligned to geographic location by a DFB committee in order to have 18 teams assigned to each division every year. This led to teams assigned to a division other than their geographical one. An example for this is BV Cloppenburg, who was assigned to the Western division for the 2008–09 season despite being located in Lower Saxony.
2012–present[]
In October 2010, yet another reform of the Regionalligas was decided upon, with the number of leagues expanding to five and beginning play in the 2012–13 season. Under this new format, the old Regionalliga Nordost would be re-established and the new Regionalliga Südwest and Regionalliga Bayern would be created. The Südwest would take clubs from the southern portion of the Regionalliga West and also everything from the Regionallia Süd outside of Bavaria. It was also decided to limit the number of reserve teams per Regionalliga to seven.[2]
The five league champions and the runners-up of the Regionalliga Südwest play-off for the three promotion spots in a home-and-away series. The new leagues consisted of up to 22 clubs in their inaugural seasons but were reduced to between 16 and 18 clubs. The Regionalligas will not be administrated by the DFB but rather by the regional football associations. In regards to reserve teams, initially only seven were permitted per league, however, this rule may be subject to change under certain circumstances. Reserve sides of 3. Liga teams are not permitted in the Regionalliga.[3]
The reorganisation of the Regionalligas so soon after the last changes in 2008 became necessary because of a large number of insolvencies. These were caused by a lack of media interest in the leagues combined with large expenses and infrastructure demands. The five Regionalligas from 2012 are:[3]
- Regionalliga Nord, (covering the states of Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein, Bremen and Hamburg)
- Regionalliga Nordost, (covering the states of Brandenburg, Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia and Saxony)
- Regionalliga West, (covering the state of North Rhine-Westphalia)
- Regionalliga Südwest, (covering the states of Rhineland-Palatinate, Saarland, Hesse and Baden-Württemberg)
- Regionalliga Bayern, (covering the state of Bavaria)
Some regional football associations also made changes to the league system below the Regionalliga in their area. From the 2012–13 season, the Bavarian Football Association split the Bayernliga into a northern and a southern division, and increased the number of Landesligas from three to five.[4]
Changes to promotion rules from 2018[]
At the 96th DFB-Bundestag in December 2017, delegates decided to change the promotion rules and, without success, reduce the number of leagues to four. To achieve this, a temporary solution was put into place for the 2018–19 and 2019–20 seasons. Four teams will be promoted and there will be three guaranteed promotion places from the champions of the five regional leagues. The champion of the southwest league, which is giving up its second playoff place, will be promoted automatically in the next two seasons. Additionally there will be two teams promoted from the other four regional leagues. In the 2018–19 season, the champion of the northeast league will also be promoted directly. The winner of the third guaranteed promotion place will be decided by the drawing of lots. The remaining two regional league champions of the 2018–19 season will face off in a two-legged playoff determining the fourth promotion place. The two regional leagues whose teams took part in the playoff automatically had promotion places for the 2019–20 season. As a result, the third division has had four relegation places.[5]
At the 97th DFB-Bundestag in 2019, a working group under DFB vice-president Peter Frymuth unsuccessfully proposed a system involving four rather than five regional leagues.[5] Instead, the delegates reformed the promotion scheme from the 2020–21 season, in which there will continue to be four promotions to the 3. Liga. The Regionalliga West and Southwest each provide a fixed direct promotion. Another direct promotion place will be assigned according to a rotation principle among the Regionalliga Nord, Nordost and Bayern champions. The representatives from the remaining two Regionalligen will determine the fourth promoted club in two-legged playoffs.[6]
Maps[]
The history and development of the Regionalligas in maps:
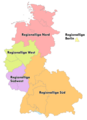
The Regionalligas from 1963 to 1974.
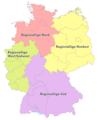
The Regionalligas from 1994 to 2000.

The Regionalligas from 2000 to 2008.
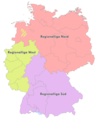
The Regionalligas from 2008 to 2012.

The Regionalligas from 2012 onwards.
League setup[]
Licensing[]
A club that wants to play in the Regionalliga must meet two conditions. First, the team must qualify for the league. Second, the club must obtain a license from the DFB. This license is granted if the club can prove that they are financially sound, that their stadium conforms to the security regulations, and that they have a working youth section.
Promotion[]
The champions of three divisions are automatically promoted; the remaining two take part in the promotion round to the 3. Liga at the end of the season for the fourth promotion. Reserve teams will also be eligible for promotion unless the respective first team is playing in the 3. Liga.
Relegation[]
At least the bottom two teams of each division are demoted to their respective Oberliga. In the Regionalliga Nord, the fourth-to-last team will also be demoted if it loses a play-off against the Oberliga Niedersachsen runner-up. The third-to-last team will participate in the play-off if the Nord champion is promoted and no team relegated from the 3. Liga is from the north. The actual number of teams relegated from every division depends on the number of relegations from the 3. Liga and promotions from the Oberliga.
As clubs in the Regionalliga must have their teams licensed by the DFB on a per-season basis, a team may also be relegated by having its license revoked or by going into administration. Reserve teams are also relegated when the respective first team is relegated to the 3. Liga.
Squad rules[]
Matchday squads in the Regionalliga must include at least six players of German nationality and under the age of 24, two under the age of 21, and a maximum of three non-EU players.
Champions[]
1963–1974[]
| Season | Regionalliga Nord | Regionalliga West | Regionalliga Berlin | Regionalliga Südwest | Regionalliga Süd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1963–64 | FC St. Pauli | Alemannia Aachen | SC Tasmania 1900 Berlin | Borussia Neunkirchen | KSV Hessen Kassel |
| 1964–65 | Holstein Kiel | Borussia Mönchengladbach | Tennis Borussia Berlin | 1. FC Saarbrücken | Bayern Munich |
| 1965–66 | FC St. Pauli | Fortuna Düsseldorf | Hertha BSC | FK Pirmasens | 1. FC Schweinfurt 05 |
| 1966–67 | Arminia Hannover | Alemannia Aachen | Hertha BSC | Borussia Neunkirchen | Kickers Offenbach |
| 1967–68 | Arminia Hannover | Bayer Leverkusen | Hertha BSC | SV Alsenborn | SpVgg Bayern Hof |
| 1968–69 | VfL Osnabrück | Rot-Weiss Oberhausen | Hertha Zehlendorf | SV Alsenborn | Karlsruher SC |
| 1969–70 | VfL Osnabrück | VfL Bochum | Hertha Zehlendorf | SV Alsenborn | Kickers Offenbach |
| 1970–71 | VfL Osnabrück | VfL Bochum | SC Tasmania 1900 Berlin | Borussia Neunkirchen | 1. FC Nürnberg |
| 1971–72 | FC St. Pauli | Wuppertaler SV | SC Wacker 04 Berlin | Borussia Neunkirchen | Kickers Offenbach |
| 1972–73 | FC St. Pauli | Rot-Weiss Essen | Blau-Weiß 1890 Berlin | FSV Mainz 05 | SV Darmstadt 98 |
| 1973–74 | Eintracht Braunschweig | SG Wattenscheid 09 | Tennis Borussia Berlin | Borussia Neunkirchen | FC Augsburg |
1994–2000[]
| Season | Regionalliga Nord | Regionalliga Nordost | Regionalliga West/Südwest | Regionalliga Süd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1994–95 | VfB Lübeck | Carl Zeiss Jena | Arminia Bielefeld | SpVgg Unterhaching |
| 1995–96 | VfB Oldenburg | Tennis Borussia Berlin | FC Gütersloh | Stuttgarter Kickers |
| 1996–97 | Hannover 96 | FC Energie Cottbus | SG Wattenscheid 09 | 1. FC Nürnberg |
| 1997–98 | Hannover 96 | Tennis Borussia Berlin | Rot-Weiß Oberhausen | SSV Ulm 1846 |
| 1998–99 | VfL Osnabrück | Chemnitzer FC | Alemannia Aachen | SV Waldhof Mannheim |
| 1999–2000 | VfL Osnabrück | 1. FC Union Berlin | 1. FC Saarbrücken | SSV Reutlingen 05 |
2000–2008[]
| Season | Regionalliga Nord | Regionalliga Süd |
|---|---|---|
| 2000–01 | 1. FC Union Berlin | Karlsruher SC |
| 2001–02 | VfB Lübeck | Wacker Burghausen |
| 2002–03 | Erzgebirge Aue | SpVgg Unterhaching |
| 2003–04 | Rot-Weiss Essen | Bayern Munich II |
| 2004–05 | Eintracht Braunschweig | Kickers Offenbach |
| 2005–06 | Rot-Weiss Essen | FC Augsburg |
| 2006–07 | FC St. Pauli | SV Wehen |
| 2007–08 | Rot Weiss Ahlen | FSV Frankfurt |
2008–2012[]
| Season | Regionalliga Nord | Regionalliga West | Regionalliga Süd |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2008–09 | Holstein Kiel | Borussia Dortmund II | 1. FC Heidenheim |
| 2009–10 | SV Babelsberg 03 | 1. FC Saarbrücken | VfR Aalen |
| 2010–11 | Chemnitzer FC | Preußen Münster | SV Darmstadt 98 |
| 2011–12 | Hallescher FC | Borussia Dortmund II | Stuttgarter Kickers |
2012–present[]
| Season | Regionalliga Nord | Regionalliga Nordost | Regionalliga West | Regionalliga Südwest | Regionalliga Bayern |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012–13 | Holstein Kiel | RB Leipzig | Sportfreunde Lotte | KSV Hessen Kassel | TSV 1860 Munich II |
| 2013–14 | VfL Wolfsburg II | TSG Neustrelitz | SC Fortuna Köln | SG Sonnenhof Großaspach | Bayern Munich II |
| 2014–15 | Werder Bremen II | 1. FC Magdeburg | Borussia Mönchengladbach II | Kickers Offenbach | Würzburger Kickers |
| 2015–16 | VfL Wolfsburg II | FSV Zwickau | Sportfreunde Lotte | SV Waldhof Mannheim | SSV Jahn Regensburg |
| 2016–17 | SV Meppen | Carl Zeiss Jena | FC Viktoria Köln | SV Elversberg | SpVgg Unterhaching |
| 2017–18 | SC Weiche Flensburg 08 | FC Energie Cottbus | KFC Uerdingen 05 | 1. FC Saarbrücken | TSV 1860 Munich |
| 2018–19 | VfL Wolfsburg II | Chemnitzer FC | FC Viktoria Köln | SV Waldhof Mannheim | Bayern Munich II |
| 2019–20 | VfB Lübeck1 | Lokomotive Leipzig1 | SV Rödinghausen1 | 1. FC Saarbrücken1 | (no champion) |
| 2020–21 | (no champion) | Viktoria Berlin1 | Borussia Dortmund II | SC Freiburg II | FC Schweinfurt2 |
| 1 Awarded on points-per-game basis after season was not completed |
| 2 Play-off winner |
References[]
- ^ "Official DFB article on the 3rd Bundesliga and Regionalliga" (in German). DFB. Archived from the original on 23 October 2007. Retrieved 8 December 2007.
- ^ "DFB-Bundestag beschließt Reform der Spielklassen" (in German). DFB. 22 October 2010. Archived from the original on 27 November 2007. Retrieved 28 October 2010.
- ^ a b "DFB weitet die Spielklassenreform aus" (in German). kicker.de. 29 April 2011. Retrieved 2 September 2013.
- ^ "Die Ligenstruktur – Auf- und Abstieg" (in German). Bavarian Football Association (BFV). 12 February 2011. Archived from the original on 11 March 2012. Retrieved 2 September 2013.
- ^ a b "Änderung der Aufstiegsregelung in der Regionalliga beschlossen". dfb.de (in German). DFB. 8 December 2017. Retrieved 8 December 2017.
- ^ "Eigener Ausschuss und neue Aufstiegsregelung zur 3. Liga" [Own committee and new promotion scheme to the 3. Liga]. DFB.de. DFB. 27 September 2019.
External links[]
- Regionalliga
- Association football leagues in Germany
- Fourth level football leagues in Europe
- Sports leagues established in 1963
- 1963 establishments in West Germany




