Seattle Mariners
| Seattle Mariners | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Established in 1977 | |||||
| |||||
| Major league affiliations | |||||
| |||||
| Current uniform | |||||
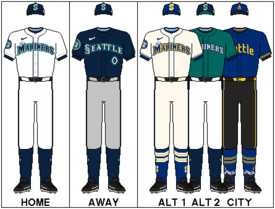 | |||||
| Retired numbers |
| ||||
| Colors | |||||
| Name | |||||
| |||||
| Other nicknames | |||||
| |||||
| Ballpark | |||||
| |||||
| Major league titles | |||||
| World Series titles (0) | None | ||||
| AL Pennants (0) | None | ||||
| West Division titles (3) |
| ||||
| Wild card berths (1) | 2000 | ||||
| Front office | |||||
| Principal owner(s) | Baseball Club of Seattle, LP, represented by CEO John Stanton[3][4] (90%) Nintendo of America (10%) | ||||
| General manager | Jerry Dipoto | ||||
| Manager | Scott Servais | ||||
The Seattle Mariners are an American professional baseball team based in Seattle. They compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) West division. The team joined the American League as an expansion team in 1977 playing their home games in the Kingdome. Since July 1999, the Mariners' home ballpark has been T-Mobile Park, located in the SoDo neighborhood of Seattle.
The "Mariners" name originates from the prominence of marine culture in the city of Seattle. They are nicknamed the M's, a title featured in their primary logo from 1987 to 1992. They adopted their current team colors – navy blue, northwest green (teal), and silver – prior to the 1993 season, after having been royal blue and gold since the team's inception.[2] Their mascot is the Mariner Moose.
The organization did not field a winning team until 1991, and any real success eluded them until 1995 when they won their first division championship and defeated the New York Yankees in the ALDS. The game-winning hit in Game 5, in which Edgar Martínez drove home Ken Griffey Jr. to win the game in the 11th inning, clinched a series win for the Mariners, served as a powerful impetus to preserve baseball in Seattle, and has since become an iconic moment in team history.
The Mariners won 116 games in 2001, which set the American League record for most wins in a single season and tied the 1906 Chicago Cubs for the Major League record for most wins in a single season.
Since 2001, the Mariners have struggled to find success. As of 2020, the franchise has finished with a losing record in 30 of 44 seasons. The Mariners are one of six Major League Baseball teams who have never won a World Series championship, and they are the only team to have never played in a World Series. They hold the longest active playoff drought in the MLB, having not qualified for the playoffs since their 116-win season in 2001.[5]
As of 2020, the Mariners all-time win–loss record is 3,246-3,655 (.470 win–loss percentage).[6]
History[]
The Mariners were created as a result of a lawsuit. In 1970, in the aftermath of the Seattle Pilots' purchase and relocation to Milwaukee as the Milwaukee Brewers by Bud Selig, the city of Seattle, King County, and the state of Washington (represented by then-state Attorney General and future U.S. Senator Slade Gorton) sued the American League for breach of contract.[7] Confident that Major League Baseball would return to Seattle within a few years, King County built the multi-purpose Kingdome, which would become home to the National Football League's expansion Seattle Seahawks in 1976. The name "Mariners" was chosen by club officials in August 1976 from over 600 names submitted by 15,000 entrants in a name-the-team contest.[8]

The Mariners played their first game on April 6, 1977, to a sold-out crowd of 57,762 at the Kingdome, losing 7–0 to the California Angels.[9] The first home run in team history was hit on April 10, 1977, by designated hitter Juan Bernhardt.[10]
That year, star pitcher Diego Seguí, in his last major league season, became the only player to play for both the Pilots and the Mariners. The Mariners finished with a 64–98 record, echoing the record the 1969 Pilots once held; however, the team was able to avoid last place in the AL West by half a game. In 1979, Seattle hosted the 50th Major League Baseball All-Star Game. After the 1981 season, the Mariners were sold to California businessman George Argyros, who in turn sold the team to Jeff Smulyan in 1989, and then to Nintendo of America in 1992.



During the 1992–93 offseason, the Mariners hired manager Lou Piniella, who had led the Cincinnati Reds to victory in the 1990 World Series. Mariner fans embraced Piniella,[11] and he would helm the team from 1993 through 2002, winning two American League Manager of the Year Awards along the way.
The 2001 Mariners club finished with a record of 116–46, leading all of Major League Baseball in winning percentage for the duration of the season and easily winning the American League West division championship. In doing so, the team broke the 1998 Yankees American League single-season record of 114 wins and matched the all-time MLB single-season record for wins set by the 1906 Chicago Cubs. At the end of the season, Ichiro Suzuki won the AL MVP, AL Rookie of the Year, and one of three outfield Gold Glove Awards, becoming the first player since the 1975 Boston Red Sox's Fred Lynn to win all three in the same season.
On October 22, 2008 the Mariners announced the hiring of Jack Zduriencik, formerly scouting director of the Milwaukee Brewers, as their general manager.[12] Weeks later, on November 18, the team named Oakland Athletics bench coach Don Wakamatsu as its new field manager. Wakamatsu and Zduriencik hired an entirely new coaching staff for 2009, which included former World Series MVP John Wetteland as bullpen coach. The off-season also saw a litany of roster moves, headlined by a 12-player, 3-team trade that included sending All-Star closer J. J. Putz to the New York Mets and brought 5 players—including prospect Mike Carp and outfielder Endy Chávez from New York and outfielder Franklin Gutiérrez from the Cleveland Indians—to Seattle. Many of the moves, like the free-agent signing of Mike Sweeney, were made in part with the hope of squelching the clubhouse infighting that plagued the Mariners in 2008. It also saw the return of Seattle favorite Griffey Jr. The 2009–10 offseason was highlighted by the trade for 2008 American League Cy Young Award winner Cliff Lee from the Philadelphia Phillies, the signing of third baseman Chone Figgins and the contract extension of star pitcher "King" Félix Hernández.
Griffey Jr. announced his retirement on June 2, 2010, after 22 MLB seasons.[13]

The Mariners fired field manager Don Wakamatsu along with bench coach Ty Van Burkleo, pitching coach Rick Adair and performance coach Steve Hecht on August 9, 2010. Daren Brown, the manager of the AAA affiliate Tacoma Rainiers, took over as interim field manager. Roger Hansen, the former Minor League catching coordinator, was promoted to bench coach. Carl Willis, the former Minor League pitching coordinator, was promoted to pitching coach.[14]
The Mariners hired former Cleveland Indians manager Eric Wedge as their new manager on October 19, 2010.[15]
Dave Niehaus, the Mariners' play-by-play announcer since the team's inception, died of a heart attack on November 10, 2010, at the age of 75.[16] In memory of Niehaus, Seattle rapper Macklemore wrote a tribute song called "My Oh My" in December 2010. He performed the song at the Mariners' Opening Day game on April 8, 2011.
On April 21, 2012, Philip Humber of the Chicago White Sox threw the third perfect game in Chicago White Sox history against the Mariners at Safeco Field in Seattle. It was the 21st perfect game in MLB history.[17] Mariners starting pitcher Kevin Millwood and five other pitchers combined to throw the tenth combined no-hitter in MLB history and the first in team history on June 8, 2012. The last combined one occurred in 2003, when six Houston Astros no-hit the New York Yankees in New York. The six pitchers used in a no-hitter is a major league record. Félix Hernández pitched the first perfect game in team history, shutting down the Tampa Bay Rays 1–0 at Safeco Field on August 15, 2012. It was the 23rd perfect game in Major League Baseball history.[18] The Mariners became the first team in Major League Baseball to be involved in two perfect games in one season.[19]
General Manager (GM) Jack Zduriencik was relieved of his position by the team on August 28, 2015. Jerry Dipoto, who formerly served as GM of the Los Angeles Angels of Anaheim, was hired as the new GM of the Mariners one month later.[20] On October 9, 2015, manager Lloyd McClendon was fired, and the search for a new manager was begun.[21] Scott Servais was named the new Mariners' manager on October 23, 2015.[22]
Nintendo of America issued a press release on April 27, 2016, stating it would sell most shares it held of Seattle Mariners ownership to First Avenue Entertainment limited partnership. Nintendo retained a 10% ownership share of the team after the sale was completed in August 2016.[23]
Uniforms[]
1977–1980[]

The Mariners' original colors were blue and gold. For the first four seasons, they wore white pullover jerseys at home with the team name in front and numbers on the left chest. The "M" in "Mariners" was shaped to resemble a trident. On the road, they wore baby blue pullover jerseys with the city name in front and numbers on the left chest. The lettering colors were blue with gold trim, though in the 1977 season the trim on the road jersey was white and the "Seattle" wordmark appeared smaller. The trident logo was added to the left sleeve prior to the 1979 season.
The cap was all-blue and featured the gold trident logo with white trim.
1981–1986[]
The Mariners made some subtle changes to the uniform in 1981. The trident logo was replaced by blue and gold racing stripes on the shoulders, and the lettering received an extra blue outline. The number font also changed from rounded to block style. In 1985, the road jersey color was changed to grey.
The cap logo also featured a slight update of the trident logo, changing its color to blue, along with additional outlines and a white star background.
1987–1992[]

In 1987, the Mariners changed its uniform style to traditional buttoned tops and belted pants. Both uniforms incorporated blue piping and a block "Mariners" wordmark in blue with gold and blue outlines. The numbers remained blue, but eliminated the trim outlines.
The cap logo was changed to a gold "S".
1993–present[]
The Mariners donned their current uniforms in 1993. The white home uniform originally featured "Mariners" in navy with Northwest Green trim and featured the "compass" logo atop the "M". The grey road uniform originally featured "Seattle" in navy with Northwest Green and white trim; in 2001, the "compass" logo was added in the middle of the "S". In 2015, a silver inline was added to the wordmark of both uniforms, which was also applied to the block letters and numbers. The primary logo is applied to the left sleeve.[24]
From 1997 to 2000, the Mariners also wore sleeveless versions of their primary uniforms, accompanied with a navy undershirt.
The Mariners have also worn Northwest Green alternate uniforms at some points in their history. The original version was unveiled in 1994 and had "Mariners" in silver with navy and white trim. The next season, the white trim was removed to improve visibility. The Mariners did not wear these uniforms from 1997 to 2010, after which it became a regular part of their uniform rotation. It is currently seen during Friday home games.[25][26]


The navy alternate uniform originally replaced the Northwest Green alternate in 1997 and featured the team name in silver with Northwest Green and navy trim. In 1999, the alternates were updated to feature the city name with the "S" behind the "compass" logo and silver piping; this became their road alternate the following season after a corresponding home navy alternate was introduced. In 2003, the silver piping was removed and the letter and number fonts were changed to match the wordmark. In 2012, after the Northwest Green home alternates were brought back, the navy uniforms were tweaked anew, this time with the city name in front. It is now worn on most road games, though they have also donned them at home on occasion.
A navy blue cap that features a ball and compass "S" logo is paired with the home white, road gray, and navy blue jerseys. A variation of this cap with a Northwest Green brim is worn with the home alternate jersey. The Mariners also wore Northwest Green caps with navy brims, but only in the 1994 season, and a navy "compass" cap with grey brims in the 1997 season.
In January 2015, the team announced a new alternate uniform to be worn for Sunday home games. This cream-colored "fauxback" uniform features the current logo and lettering style in a royal blue and gold color scheme, a throwback to the original team colors. Unlike the rest of the uniform set, the back of the jersey does not display the player name.[25][1] The cap features the current cap logo in the throwback colors.[1][27]
In January 2019, the Mariners announced a new home and away uniform to be worn during spring training. The jersey has a design similar to their home white jerseys but features a powder blue throwback to the team colors during the 1980s. The cap has the usual navy blue color, but with a logo that features the signature compass rose and with a large M in the center.
Spring training[]
The Peoria Sports Complex in Peoria, Arizona, has been the Mariners' home spring training facility since 1994. The complex is shared with the San Diego Padres.[28] On March 25, 2013, in a 16–0 victory over the Cincinnati Reds, the Mariners broke the team record for total home runs during a spring training season with 52.[29]
Season records[]
This is a partial list listing the past 21 completed regular seasons. For the full season records, see here.
| Year | Record | Win % | Place in AL West | Postseason | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 91–71 | .562 | 2nd | Won ALDS vs Chicago White Sox, 3–0 Lost ALCS vs New York Yankees, 4–2. |
First Wild Card in Franchise History
Kazuhiro Sasaki named AL Rookie of the Year |
| 2001 | 116–46 | .716 | 1st | Won ALDS vs Cleveland Indians, 3–2 Lost ALCS vs New York Yankees, 4–1. |
Tied the regular-season record with 116 wins, but went 4–6 in the postseason.
Ichiro Suzuki named AL MVP and Rookie of the Year |
| 2002 | 93–69 | .574 | 3rd | Celebrated 25th anniversary of the franchise | |
| 2003 | 93–69 | .574 | 2nd | ||
| 2004 | 63–99 | .389 | 4th | Ichiro had 262 hits, which broke the 84-year-old hit record. Edgar Martínez retired after his 18th and final season with the Mariners. | |
| 2005 | 69–93 | .426 | 4th | ||
| 2006 | 78–84 | .481 | 4th | ||
| 2007 | 88–74 | .543 | 2nd | Celebrated 30th anniversary of the franchise | |
| 2008 | 61–101 | .377 | 4th |
First team of 2008 to officially be eliminated from the 2008 postseason. Worst record since 1983, which was the last time they had lost over 100 games in a season. First team in MLB history to lose 100 games with a $100 million payroll. Dave Niehaus won the Ford C. Frick Award, presented by the National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum. | |
| 2009 | 85–77 | .520 | 3rd | Ichiro set the new record for most consecutive 200-hit seasons at 9. | |
| 2010 | 61–101 | .377 | 4th | Félix Hernández won the 2010 AL Cy Young Award.
Ichiro and Franklin Gutiérrez won the 2010 Rawlings Gold Glove awards for AL Right Field and Center Field, respectively. Former Executive Pat Gillick was elected to the National Baseball Hall of Fame by the Veterans Committee. Ichiro had his tenth consecutive season batting over .300 with 200 hits, winning a Rawlings Gold Glove Award, and appearing in the Major League Baseball All-Star Game. | |
| 2011 | 67–95 | .414 | 4th | Pitchers Félix Hernández, Brandon League, and Michael Pineda were named all-stars. | |
| 2012 | 75–87 | .463 | 4th | Celebrated 35th Anniversary of the franchise. Featured a combined no-hitter and perfect game by Félix Hernández. Became the first team in MLB history to both win and lose in perfect games in one season. Ichiro was traded to the Yankees on July 23. | |
| 2013 | 71–91 | .438 | 4th | Despite the Major League debuts of top prospects Nick Franklin, Mike Zunino, Brad Miller, Taijuan Walker and James Paxton, the Mariners once again failed to make the postseason. Although the Mariners took a major step forward in the power department, hitting the second-most home runs in the American League (188 trailing Baltimore's 212), hitting fundamentals, questionable defense and a shallow pitching rotation and bullpen held the team back. On September 27, manager Eric Wedge announced that he would not return for the 2014 season.[30] He was replaced by Lloyd McClendon. | |
| 2014 | 87–75 | .537 | 3rd | The Mariners made a surprising playoff run in 2014, but in the end, they fell short on the final day of the season. Félix Hernández won the AL ERA title with a 2.14 ERA and Robinson Canó had a career year in his first season with Seattle. | |
| 2015 | 76–86 | .469 | 4th | Hisashi Iwakuma threw a no-hitter against the Baltimore Orioles on August 12. McClendon was fired after the season ended.[31] On October 23, 2015 Scott Servais was hired as the team's new manager.[32] | |
| 2016 | 86–76 | .531 | 2nd | The Mariners made another surprising run for the postseason in 2016, but they ultimately fell short of the playoffs once again. The trio of Robinson Canó, Nelson Cruz, and Kyle Seager all had stellar seasons themselves, but it was not enough to make the playoffs. | |
| 2017 | 78–84 | .481 | tied-3rd | Celebrated 40th anniversary of the franchise. Robinson Cano was named All-Star Game MVP. | |
| 2018 | 89–73 | .549 | 3rd | James Paxton threw a no-hitter in Toronto on May 8. | |
| 2019 | 68–94 | .420 | 5th | After opening the season with a historic 13–2 record, the team lost 37 of the next 49 games. | |
| 2020 | 27–33 | .450 | 3rd | The Mariners outperformed preseason expectations for the team in the shortened season, a result of the COVID-19 pandemic in North America, but ultimately failed to pass the Houston Astros and reach the expanded playoff field.
J. P. Crawford and Evan White won the 2020 Rawlings Gold Glove awards for AL shortsop and first base, respectively, White becoming the first rookie to receive the award at first base. Kyle Lewis named AL Rookie of the Year | |
| 2021 | 76-64 | .543 | Currently 2nd |
T-Mobile Park[]
T-Mobile Park (known as Safeco Field from 1999 to 2018) has been home to the Seattle Mariners since the first game vs. the San Diego Padres on July 15, 1999. There were 44,607 people in attendance that night.[33]
Seattle Mariners Hall of Fame[]
Seattle Mariners former chairman and CEO John Ellis announced on June 14, 1997, the creation of a Mariners Hall of Fame. It is operated by the Seattle Mariners organization. It honors the players, staff and other individuals that greatly contributed to the history and success of the Mariners franchise. It is located at the Baseball Museum of the Pacific Northwest in T-Mobile Park.[34]
| Year | Year inducted |
|---|---|
| Bold | Member of the Baseball Hall of Fame |
| Member of the Baseball Hall of Fame as a Mariner | |
| Bold | Recipient of the Hall of Fame's Ford C. Frick Award |
| Seattle Mariners Hall of Fame | ||||
| No. | Player | Position | Tenure | Inducted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| — | Dave Niehaus | Broadcaster | 1977–2010 | 2000 |
| 21 | Alvin Davis | 1B | 1984–91 | 1997 |
| 19 | Jay Buhner | RF | 1988–2001 | 2004 |
| 11 | Edgar Martínez |
DH/3B Coach |
1987–2004 2015–2018 |
2007 |
| 6 | Dan Wilson | C | 1994–2005 | 2012 |
| 51 | Randy Johnson | P | 1989–1998[35] | 2012 |
| 24 | Ken Griffey Jr. |
CF DH/OF |
1989–1999 2009–2010 |
2013 |
| 14 | Lou Piniella | Manager | 1993–2002 | 2014 |
| 50 | Jamie Moyer | P | 1996–2006 | 2015 |
Retired numbers[]
|
The Mariners plan to retire uniform numbers only very selectively and subject to substantially higher expectations than those applied to the Mariners' Hall of Fame. To be eligible to have one's number retired, in addition to the criteria outlined for the Mariners' Hall of Fame, the former Mariners should have either:
a) been elected to the National Baseball Hall of Fame and been in a Mariner's uniform for at least five years, or
b) come close to such election and have spent substantially his entire career with the Mariners.
Eligibility shall not commence until after the former player has been voted on once for the National Baseball Hall of Fame, which for all practical purposes means six years after retirement.[36]
Ken Griffey Jr.'s number 24 was retired at the beginning of the 2016 season, with the retirement ceremony taking place on August 6, 2016.[37][38] Griffey had been elected to the Hall of Fame in January of that year.
Edgar Martínez's number 11 was retired during the 2017 season, with the retirement ceremony taking place on August 12, 2017. Martínez played his entire major-league career in Seattle and first appeared on the Hall of Fame ballot in 2010. His number 11 was retired in 2017, predating his 2019 election to the Hall of Fame and seemingly establishing the 58.6% of the vote he received that year as sufficiently "close" to election to satisfy the club's bylaws.[39][40] Jersey number 11 was not issued to anyone else between Martínez's retirement as a player in 2004 until his return to the Mariners as hitting coach in 2015.
Currently, only one other player has definitively met the requirements to have his number retired: Randy Johnson, who played 10 seasons with the Mariners (1989–1998) and was elected to the Hall of Fame in 2015.
Despite not officially retiring number 19, the team has not reissued it since Jay Buhner left the team in 2001.
Number 51, worn by Randy Johnson, was withheld from players from 1998 until 2001, when it was issued to Ichiro Suzuki upon his request after wearing it for his entire career in Japan. It was presumably taken out of circulation again, following Ichiro's 2012 trade to the Yankees coupled with Johnson's 2015 election into the Baseball Hall of Fame. The number was once again worn by Ichiro upon his return to the Mariners in 2018, until retiring in 2019.
Number 14 (Lou Piniella) was not given to any uniformed personnel between Piniella's 2002 departure and 2015, but it was issued to third-base coach Manny Acta for the 2016 season. Piniella has been on the ballot for the Hall of Fame twice (2016, 2018), and he was one vote short in the latter ballot from being inducted.[41]
Jackie Robinson's number 42 was retired throughout Major League Baseball on April 15, 1997.
Uniform number 00 is presumed off-limits, as it has been worn by the Mariner Moose since 1997 (outfielder Jeffrey Leonard was the last player to wear 00 for the M's, in 1990). From 1990 to 1996, the Moose wore the last 2 digits of the year of the current season.
Culture[]
This section needs to be updated. (February 2014) |
"Louie Louie"[]
As part of the seventh-inning stretch, after the crowd is led in singing "Take Me Out To The Ball Game" or "God Bless America" the public address system plays the Kingsmen's version of "Louie Louie". This commemorates a 1985 prank attempt to make "Louie Louie" the state song of Washington.
Buhner Buzz Cut Night[]
In 1994, the Mariners started a promotion called "Buhner Buzz Cut Night" Inspired by Jay Buhner's shaved head; any fan who was willing to have their head shaved before the game—or was already bald—would receive a free ticket to the game and a T-shirt with a slogan such as "Bald is Buhnerful" or "Take Me Out To The Bald Game". Hair 10 inches or longer was collected for charity. The promotion continued until Buhner's retirement in 2001, with a year's hiatus in 2000, and is still remembered by fans today.
Rally Fries[]

Rally Fries are a baseball tradition started by Mariners broadcaster Mike Blowers in 2007. During a game against the Cincinnati Reds, a fan tried to catch a foul ball along the right-field line but in turn spilled his tray of french fries along the track. While chatting on the air and seeing the mishap, Blowers' partner, Dave Sims, suggested that he should send a new tray of fries to the fan. Blowers agreed, and sent his intern to deliver a plate of fries to the man.[42]
At the Mariners' next game, fans made signs and boards asking Blowers for fries as well. Coincidentally, every time the fries were delivered, the Mariners seem to score or rally from a deficit, and thus the "Rally Fries" were created. This became so popular with the fans that signs were even seen when the Mariners were the visiting team, although on August 1, 2009, Blowers established that he only gives out fries at home games.[43]
Generally, Blowers would select a person or a group of people that appealed to him, whether it was through fans wearing elaborate costumes or waving funny signs and boards. The fries were usually delivered from Ivar's, a Seattle-based seafood restaurant with a location at T-Mobile Park. The amount of fries given out varied with the size of the winning group of fans. The winners were generally selected around the 5th or 6th inning, although potential candidates were shown in almost every inning beforehand.
King's Court[]
As the 2011 season progressed, the Mariners' marketing staff came up with an idea to encourage the growing fanbase of star pitcher "King" Félix Hernández. Every Hernandez start at T-Mobile Park was accompanied by the King's Court, a designated cheering section for fans to sing, chant, and cheer while donning yellow T-shirts and "K" cards that are supplied by the team. It was located in the lower seating area along the 3rd base line which would regularly see left-handed hitters (which teams would field more of when facing the right-handed Hernandez) hit foul balls into more so than most other areas of the field. Meaning the section would be on camera catching foul balls often.
The King's Court was both a personal rooting section for Hernandez and trend-setter for T-Mobile Park. The team encouraged fans to dress like Larry Bernandez, Hernandez's alter ego from a Mariners TV Commercial, or show up in wacky costumes, rewarding the best with a ceremonial turkey leg.[44]
The Supreme Court was a special event where the King's Court section was extended to the entirety of T-Mobile Park. The first Supreme Court was Félix's first home game following his perfect game in 2012. Following opening day 2012, it occurred each year at Félix's first home game of each season.
Following Felix's departure from the Mariners at the end of the 2019 season, the King's Court is now officially retired.
Maple Grove[]
The ultimately disappointing 2017 season had a few bright spots, including the establishment of the Maple Grove, a celebration of Canadian pitcher James Paxton and inspired by the King's Court. At home games where Paxton started, a group of fans sat under a Maple Grove banner, typically in the left-field bleachers. A potted maple tree was also present in their section, provided by the Mariners; the Grove dubbed the tree "Stick Rizzs", in honor of long-time Mariner broadcaster Rick Rizzs. The live tree was retired in 2018, replaced by a hardier fake tree.
When Paxton got to two strikes on a batter, the Grove held up “Eh” Cards, a tip of the cap to Paxton's home country of Canada and a nod to the "K" (for strikeout) cards held up in King's Court. Variant cards have also been produced for special occasions, such as when a planned Paxton start turned into a Hernández start (a King's Grove, with "K'eh" cards to cheer for Hernández). Other special cards celebrated Paxton reaching 300 strikeouts, and a tribute to broadcaster Angie Mentink ("A" cards, to show support after she had publicly disclosed her breast cancer diagnosis). An "Eh" card[45] now resides in the National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum collection.
The Maple Grove differed from the King's Court in that it was created and organized by fans, while the Court was promoted by the Mariners' marketing team. When asked, Paxton stated that fans creating the Maple Grove was really special to him and that he never imagined that something of the sort would ever be done for him.[46] The Grove continued until Paxton was traded to the Yankees following the 2018 season.[47]
Players[]
Roster[]
Seattle Mariners roster
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active roster | Inactive roster | Coaches/Other | ||||
|
Pitchers
Bullpen
|
Catchers
Infielders
Outfielders
Designated hitters
|
Pitchers
Catchers
Infielders
Outfielders
|
Manager Coaches
60-day injured list
Restricted list
| |||
Baseball Hall of Famers[]
The following elected members of the Baseball Hall of Fame spent part of their careers with the Mariners.[48]


| Seattle Mariners Hall of Famers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affiliation according to the National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum | |||||||||
|
Ford C. Frick Award recipients[]
| Seattle Mariners Ford C. Frick Award recipients | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affiliation according to the National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum | |||||||||
|
State of Washington Sports Hall of Fame[]
| Seattle Mariners in the State of Washington Sports Hall of Fame | ||||
| No. | Name | Position | Tenure | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4, 16, 38 | Mike Blowers[49] | 3B | 1992–1995, 1997, 1999 | Attended the University of Washington. |
| 21 | Alvin Davis[50] | 1B | 1984–1991 | |
| 24 | Ken Griffey Jr.[51] | CF | 1989–1999 2009–2010 |
|
| 11 | Edgar Martinez[52] | DH/3B Coach |
1987–2004 2015–2018 |
|
| — | Dave Niehaus[53] | Broadcaster | 1977–2010 | |
| 5 | John Olerud[54] | 1B | 2000–2004 | Born in Seattle, attended Washington State University |
| — | Rick Rizzs | Broadcaster | 1983–1992 2007–present |
|
| 30 | Aaron Sele | P | 2000–2001, 2005 | Grew up in Poulsbo, attended Washington State University |
Minor league affiliations[]
The Seattle Mariners farm system consists of six minor league affiliates.[55]
| Level | Team | League | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Triple-A | Tacoma Rainiers | Triple-A West | Tacoma, Washington |
| Double-A | Arkansas Travelers | Double-A Central | North Little Rock, Arkansas |
| High-A | Everett AquaSox | High-A West | Everett, Washington |
| Low-A | Modesto Nuts | Low-A West | Modesto, California |
| Rookie | AZL Mariners | Arizona League | Peoria, Arizona |
| DSL Mariners | Dominican Summer League | Boca Chica, Santo Domingo |
Radio and television[]
The Mariners' flagship radio station is KIRO-AM (710 ESPN Radio), which previously broadcast Mariners contests from 1985 to 2002. Former flagship stations include KOMO-AM (2003–2008), and KVI-AM 570 (1977–1984). Television rights are held by Root Sports Northwest. During the 2016 season, the Mariners averaged a 5.84 rating and 103,000 viewers on primetime TV broadcasts.[56] In years past, Mariners games have also appeared in Seattle on over-the-air stations KING-TV, KIRO-TV, KTZZ-TV (now KZJO), and KSTW. Selected Mariners games are also available on Canadian television, due to an agreement between Root Sports Northwest and Rogers Sportsnet Pacific.
Since 2013, Rick Rizzs and Aaron Goldsmith have called games on the radio. The television broadcasts are anchored by play-by-play announcer Dave Sims and color commentator (and former Mariners player) Mike Blowers.[57] Seattle radio personality Matt Pitman hosts the post-game show on the Mariners' radio network, along with clubhouse reporter Shannon Drayer. Spanish-language radio broadcast duties are handled by Alex Rivera on play-by-play and former second baseman Julio Cruz providing color commentary.
The Mariners' broadcast team for 2010 featured Dave Niehaus and Rizzs—back for their 32nd and 23rd seasons with the club, respectively—as well as Sims and Blowers. For the first three innings of each game, Niehaus worked the television broadcast with Blowers while Rizzs and Sims handled radio duties; after the third inning, Niehaus and Sims traded places. Niehaus, who had broadcast for the Mariners since their inaugural season of 1977, died on November 10, 2010. For the 2011 season, Dave Niehaus' duties in the broadcast booth were filled by a collection of former Mariners broadcasters such as Ron Fairly, Ken Levine, and Ken Wilson; and former Mariners' players such as Dave Valle, Dan Wilson, Jay Buhner, and Dave Henderson.
Tom Hutyler has been the Mariners' public address announcer since 1987, first at the Kingdome, and presently at T-Mobile Park.[58] While KOMO 1000 AM was the Mariners' flagship radio station, Hutyler occasionally hosted the post-game radio show.
Franchise records and award winners[]

Season records[]
- Highest Batting Average: .372, Ichiro Suzuki (2004)
- Most Runs: 141, Alex Rodriguez (1996)
- Most Hits: 262, Ichiro Suzuki (2004) (Major League Record)
- Highest Slugging %: .674, Ken Griffey Jr. (1994)
- Highest On-Base %: .479, Edgar Martínez (1995)
- Highest On-Base Plus Slugging: 1.107, Edgar Martínez (1995)
- Most Doubles: 54, Alex Rodriguez (1996)
- Most Triples: 12, Ichiro Suzuki (2005)
- Most Home Runs: 56, Ken Griffey Jr. (1997, 1998)
- Most Grand Slams: 4, Edgar Martínez (2000)
- Most RBIs: 147, Ken Griffey Jr. (1997)
- Most Stolen Bases: 60, Harold Reynolds (1987)
- Most Wins: 21, Jamie Moyer (2003)
- Lowest ERA: 2.14, Félix Hernández (2014)
- Most Strikeouts: 308, Randy Johnson (1993)
- Most Complete Games: 14, Mike Moore (1985) and Mark Langston (1987)
- Most Saves: 57, Edwin Diaz (2018)
Career records[]
- Most Home Runs: 417, Ken Griffey Jr.
- Most RBIs: 1261, Edgar Martínez
- Most Runs: 1219, Edgar Martínez
- Most Walks: 1283, Edgar Martínez
- Most Hits: 2542, Ichiro Suzuki
- Most Stolen Bases: 438, Ichiro Suzuki
- Highest Average: .322, Ichiro Suzuki
- Highest Slugging %: .561, Alex Rodriguez
- Highest On Base %: .418, Edgar Martínez
- Highest OPS: .934, Alex Rodriguez
- Most Games Played: 2055, Edgar Martínez
- Lowest ERA: 3.01, Tom Wilhelmsen
- Lowest WHIP: 1.14, Hisashi Iwakuma
- Most Innings Pitched: 2658, Félix Hernández
- Most Wins: 168, Félix Hernández
- Most Strikeouts: 2467, Félix Hernández
- Most Saves: 129, Kazuhiro Sasaki
See also[]
This "see also" section may contain an excessive number of suggestions. Please ensure that only the most relevant links are given, that they are not red links, and that any links are not already in this article. (April 2021) |
- 1976 Major League Baseball expansion draft
- 1977 Major League Baseball expansion
- 1995 American League Division Series
- 1995 American League West tie-breaker game
- 1997 American League Division Series
- 2000 American League Division Series
- 2001 American League Division Series
- 2001 Major League Baseball All-Star Game
- The Double (Seattle Mariners)
- Rick Kaminski
- List of professional baseball stadiums in Seattle
- Edward "Tuba Man" McMichael
- Seattle Rainiers
- Sports in Seattle
- Washington Huskies baseball
- Washington State Cougars baseball
Footnotes[]
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Johns, Greg (January 23, 2015). "Mariners unveil new alternate uniforms". Mariners.com. MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved January 7, 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Seattle Mariners Logos and Colors Through The Years" (PDF). 2021 Seattle Mariners Information Guide. MLB Advanced Media. February 25, 2021. Retrieved April 27, 2021.
- ^ Johns, Greg (April 27, 2016). "Nintendo selling Mariners to minority owners". Mariners.com. MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved June 16, 2016.
- ^ Stone, Larry (April 27, 2016). "New Mariners CEO John Stanton is baseball-loving billionaire with World Series goal". The Seattle Times. Retrieved May 28, 2016.
- ^ Kramer, Daniel (October 18, 2020). "These teams have never won the World Series". MLB.com. Retrieved October 21, 2020.
The Mariners have not only never appeared in a World Series, but they are riding the longest playoff drought in any of the four major pro sports at 19 years.
- ^ "Seattle Mariners Team History & Encyclopedia". Baseball-Reference.com. Retrieved November 11, 2020.
- ^ Cour, Jim (June 27, 1999). "No Love Lost for Kingdome". Los Angeles Times. Associated Press. Retrieved January 18, 2020.
- ^ "The Mariners chosen as name for new team". The Register-Guard. Associated Press. August 25, 1976. p. 3C. Retrieved January 19, 2020.
- ^ "California Angels 7, Seattle Mariners 0: Game Played on Wednesday, April 6, 1977 (N) at Kingdome". RetroSheet.org. Retrieved January 19, 2020.
- ^ "Club Firsts". Mariners.com. MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved May 12, 2019.
- ^ Raley, Dan (July 12, 2003). "Piniella returns to Seattle's warm embrace". The Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Retrieved January 19, 2020.
- ^ Stone, Larry (October 22, 2008). "M's hire Brewers' Jack Zduriencik as GM". The Seattle Times.
- ^ Street, Jim (June 2, 2010). "Griffey Jr. announces his retirement". MLB.com. MLB Advanced Media. Archived from the original on February 19, 2015. Retrieved May 12, 2019.
- ^ Street, Jim (August 9, 2010). "Mariners replace Wakamatsu with Brown". Mariners.com. MLB Advanced Media. Archived from the original on October 16, 2010. Retrieved May 12, 2019.
- ^ Hickey, John (October 18, 2010). "Mariners Announce Hiring of Eric Wedge; Move Praised by Wood, Lee, Others". Mlb.fanhouse.com. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- ^ Stone, Larry (October 27, 2012). "Mariners broadcaster Dave Niehaus dies". The Seattle Times.
- ^ Liebeskind, Josh (April 21, 2012). "MLB.com Gameday | whitesox.com: Gameday". Major League Baseball. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- ^ Greenberg, Chris (August 15, 2012). "Félix Hernández Perfect Game: Mariners Ace Records 27 Straight Outs In 1-0 Win Over Rays (VIDEO)". The Huffington Post. Retrieved October 27, 2012.
- ^ Eagle, Ed (March 11, 2019). "All-time perfect games in MLB history". MLB.com. Retrieved January 19, 2020.
- ^ Johns, Greg (September 28, 2015). "Dipoto hired by Mariners to be general manager". MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ^ Associated Press (October 9, 2015). "Seattle Mariners fire manager Lloyd McClendon after two seasons". ESPN. Retrieved October 9, 2015.
- ^ Johns, Greg (October 26, 2015). "Mariners name Servais manager". MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ^ Divish, Ryan (April 27, 2016). "Mariners to be sold by Nintendo to ownership group led by John Stanton". The Seattle Times. Retrieved May 5, 2016.
- ^ Novak, Paul (January 23, 2015). "Seattle Mariners Unveil New Uniforms". emeraldcityswagger.com. Open Publishing. Retrieved February 11, 2018.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Lewis, Adam (January 23, 2015). "Mariners Unveil New Alternate Home Uniforms". Sports Press NW. Retrieved January 31, 2015.
- ^ Divish, Ryan (October 20, 2010). "Mariners going green...with their jerseys". The News Tribune. Archived from the original on February 1, 2015. Retrieved January 31, 2015.
- ^ Divish, Ryan (January 23, 2015). "Mariners debut new alternate uniform for Sunday home games". The Seattle Times. Archived from the original on February 1, 2015. Retrieved January 31, 2015.
- ^ Munshi, Sonu (March 5, 2012). "Peoria renews spring training lease with Mariners, Padres". The Arizona Republic. Retrieved October 27, 2012.
- ^ "Mariners Set Club Spring Home Run Record in Route of Reds". SWX Right Now. March 25, 2013. Archived from the original on June 18, 2013. Retrieved March 25, 2013.
- ^ Booth, Tim (September 29, 2014). "Wedge Says Goodbye As Seattle Falls 9-0 to A's". AP.Org.
- ^ "Seattle Mariners fire manager Lloyd McClendon after two seasons". ESPN. Associated Press. October 9, 2015. Retrieved October 9, 2015.
- ^ Gleeman, Aaron. "Scott Servias is the strong frontrunner to be mariners new manager". hardballtalk.nbcsports.com. NBC Sports. Retrieved October 23, 2015.
- ^ "San Diego Padres at Seattle Mariners Box Score, July 15, 1999". Baseball-Reference.com. Retrieved January 22, 2019.
- ^ Nelson, John (June 30, 2017). "Friendly Mariners seating host offers best ways to enjoy yourself at Safeco Field". The Spokesman-Review. Retrieved January 22, 2020.
- ^ Eaton, Nick (January 17, 2012). "Randy Johnson, Dan Wilson headed to Mariners Hall of Fame". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Retrieved January 18, 2012.
- ^ "Mariners Hall of Fame Guidelines". Major League Baseball. Retrieved June 27, 2017.
- ^ Johns, Greg (January 8, 2016). "Mariners to retire Griffey's No. 24". MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ^ Axisa, Mike (August 7, 2016). "Mariners retire Junior's number, and a statue for Griffey is also on the way". CBS Sports. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ^ Johns, Greg (January 24, 2017). "Mariners to retire Edgar Martínez's No. 11". MLB Advanced Media. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ^ Katie G. Cotterill; Sean Quinton (January 24, 2017). "Here's a look back at Edgar Martínez's legendary Mariners career". The Seattle Times. Retrieved April 29, 2017.
- ^ Ackert, Kristie (December 9, 2018). "George Steinbrenner, Lou Piniella both fall short in Hall of Fame bids". New York Daily News. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ^ Hansen, Patrick (May 15, 2011). "Seattle Mariners: 5 Best Safeco Field Traditions". Bleacher Report. Retrieved October 27, 2012.
- ^ Moore, Jim (August 13, 2007). "Go 2 Guy: Fry, fry away -- rally fries take off". Seattle Post-Intelligencer.
- ^ Floyd, Brian (June 29, 2011). "Félix Hernández Ignites King's Court; Mariners, Marlins Play Calvinball". SB Nation. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
- ^ "JAMES PAXTON FAN-MADE SIGN, 2017". National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum. Retrieved February 22, 2021.
- ^ Giambalvo, Emily (July 27, 2017). "Mariners fans created the 'Maple Grove' for Canadian James Paxton, and he loves it". The Seattle Times. Retrieved January 19, 2020.
- ^ Divish, Ryan (November 19, 2018). "Mariners trade left-hander James Paxton to the Yankees for three prospects". The Seattle Times. Retrieved January 31, 2019.
- ^ National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum: Home
- ^ "2005 Inductees". washingtonsportshof.org.
- ^ "2014 Inductees". washingtonsportshof.org.
- ^ "2019 Inductees". washingtonsportshof.org.
- ^ "2010 Inductees". washingtonsportshof.org.
- ^ "2004 Inductees". washingtonsportshof.org.
- ^ "2011 Inductees". washingtonsportshof.org.
- ^ "Seattle Mariners Minor League Affiliates". Baseball-Reference. Sports Reference. Retrieved May 14, 2020.
- ^ Here Are The 2016 MLB Prime Time Television Ratings For Each Team – Maury Brown, Forbes SportsMoney, 28 September 2016
- ^ Stone, Larry (January 17, 2013). "Mariners add Aaron Goldsmith to broadcast team". Seattle Times. Retrieved January 29, 2014.
- ^ Tom Hutyler at KOMO News
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Seattle Mariners. |
- Seattle Mariners
- Baseball teams established in 1977
- 1977 establishments in Washington (state)
- Major League Baseball teams
- Cactus League
- Baseball in Seattle





