Senftenberg
Senftenberg
Zły Komorow | |
|---|---|
 Market Square | |
 Coat of arms | |
show Location of Senftenberg within Oberspreewald-Lausitz district | |
 Senftenberg | |
| Coordinates: 51°31′N 14°01′E / 51.517°N 14.017°ECoordinates: 51°31′N 14°01′E / 51.517°N 14.017°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Brandenburg |
| District | Oberspreewald-Lausitz |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2014–22) | Andreas Fredrich[1] (SPD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 127.56 km2 (49.25 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 102 m (335 ft) |
| Population (2020-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 23,371 |
| • Density | 180/km2 (470/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 01945 (Peickwitz), 01968 (Brieske, Großkoschen, Niemtsch, Sedlitz, Senftenberg), 01996 (Hosena) |
| Dialling codes | 03573, 035756 (Hosena, Peickwitz) |
| Vehicle registration | OSL, CA, SFB |
| Website | www.senftenberg.de |
Senftenberg (Sorbian languages: Zły Komorow) is a town in southern Brandenburg, Germany, capital of the Oberspreewald-Lausitz district.
Geography[]
Senftenberg is located in the southwest of the historic Lower Lusatia region at the border with Saxony. Its town centre is situated north of the river Black Elster and the artificial Senftenberger Lake, part of the Lusatian Lake District chain, approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) northwest of Hoyerswerda, and 35 kilometres (22 mi) southwest of Cottbus.
Senftenberg station is north of the centre and a major railway freight yard is located to its north-east, with a locomotive depot.
History[]
March of Lusatia 1279–1368
Kingdom of Bohemia 1368–1448
Electorate of Saxony 1448–1806
Kingdom of Saxony 1806–1815
Kingdom of Prussia 1815–1871
German Empire 1871–1918
Weimar Republic 1918–1933
Nazi Germany 1933–1945
Allied-occupied Germany 1945–1949
East Germany 1949–1990
Germany 1990–present
Senftenberg was first mentioned in a 1279 deed issued by Henry III the Illustrious of Wettin, then margrave of Lusatia. With Lower Lusatia, the settlement was acquired by the Kingdom of Bohemia under Charles IV of Luxembourg in 1368. Elector Frederick II of Saxony acquired Senftenberg in 1448, whereafter the area as a border stronghold of the House of Wettin was separated from Bohemian Lusatia, until in 1635 all Lusatian territories fell to Saxony by the Peace of Prague. According to the 1815 Congress of Vienna, Lower Lusatia was annexed by Prussia and incorporated into the Province of Brandenburg.
Names[]
- Czech: Zlý Komorov
- German: Senftenberg
- Polish: Zły Komorów
- Upper Sorbian: Zły Komorow
- Lower Sorbian: Zły Komorow
Lake Senftenberg[]
Lake Senftenberg is a popular tourist destination. In 1973, the former open cast mine, was officially opened to the public. Today, the lake is known for its excellent water quality. It is part of the so-called Lusatian Lakeland, a group of 23 artificial lakes.
Demography[]
After the second half of the 19th century the inhabitants increased because of workers coming to Senftenberg to work in the coal mines. After the German Reunion, many inhabitants moved to the western part of Germany.
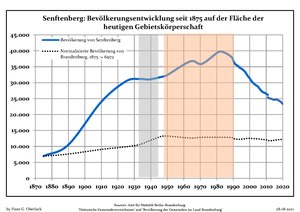
Development of Population since 1875 within the Current Boundaries (Blue Line: Population; Dotted Line: Comparison to Population Development of Brandenburg state; Grey Background: Time of Nazi rule; Red Background: Time of Communist rule)
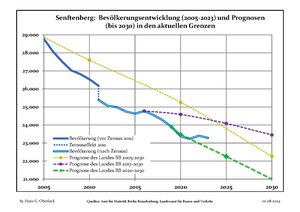
Recent Population Development and Projections (Population Development before Census 2011 (blue line); Recent Population Development according to the Census in Germany in 2011 (blue bordered line); Official projections for 2005–2030 (yellow line); for 2017–2030 (scarlet line); for 2020–2030 (green line)
|
|
|
Sports[]
In Senftenberg is the soccer club FSV Glückauf Brieske-Senftenberg.
Twin towns – sister cities[]
Senftenberg is twinned with:[4]
 Fresagrandinaria, Italy
Fresagrandinaria, Italy Nowa Sól, Poland
Nowa Sól, Poland Püttlingen, Germany
Püttlingen, Germany Saint-Michel-sur-Orge, France
Saint-Michel-sur-Orge, France Senftenberg, Austria
Senftenberg, Austria Veszprém, Hungary
Veszprém, Hungary Žamberk, Czech Republic
Žamberk, Czech Republic
Notable people[]
- Hermann Kuhnt (1850–1925), ophthalmologist
- Herbert Windt (1894–1965), composer
- Joachim Sauer (born 1949), chemist and professor
Gallery[]
Old Town
Estate housing
Lutheran church
in "Jüttendorf"
References[]
- ^ Landkreis Oberspreewald-Lausitz Wahl der Bürgermeisterin / des Bürgermeisters, accessed 2 July 2021.
- ^ "Bevölkerung im Land Brandenburg nach amtsfreien Gemeinden, Ämtern und Gemeinden 31. Dezember 2020". Amt für Statistik Berlin-Brandenburg (in German). June 2021.
- ^ Detailed data sources are to be found in the Wikimedia Commons.Population Projection Brandenburg at Wikimedia Commons
- ^ "Senftenberger Städtepartnerschaften". senftenberg.de (in German). Senftenberg. Retrieved 2021-03-25.
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Senftenberg. |
- Official website
 (in German)
(in German)
- Towns in Brandenburg
- Senftenberg
- Localities in Oberspreewald-Lausitz
- Localities in Lower Lusatia
- Province of Brandenburg
- Bezirk Cottbus