East Germany
German Democratic Republic Deutsche Demokratische Republik | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1949–1990 | |||||||||||
 Flag
(1959–1990)  Emblem
(1955–1990) | |||||||||||
Anthem: Auferstanden aus Ruinen ("Risen from Ruins") | |||||||||||
 The territory of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990 | |||||||||||
| Status | Satellite state of the Soviet Union[a] | ||||||||||
| Capital and largest city | East Berlin[note 1] (de facto) | ||||||||||
| Official languages | German Sorbian (in parts of Bezirk Dresden and Bezirk Cottbus) | ||||||||||
| Religion | See Religion in East Germany | ||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | East German | ||||||||||
| Government | Federal Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist republic (1949–1952) Unitary Marxist–Leninist one-party socialist republic (1952–1989) Unitary parliamentary republic (1989–1990) | ||||||||||
| General Secretary | |||||||||||
• 1946–1950[note 2] | Wilhelm Pieck and Otto Grotewohl[note 3] | ||||||||||
• 1950–1971 | Walter Ulbricht | ||||||||||
• 1971–1989 | Erich Honecker | ||||||||||
• 1989[note 4] | Egon Krenz | ||||||||||
| Head of State | |||||||||||
• 1949–1960 (first) | Wilhelm Pieck | ||||||||||
• 1990 (last) | Sabine Bergmann-Pohl | ||||||||||
| Head of Government | |||||||||||
• 1949–1964 (first) | Otto Grotewohl | ||||||||||
• 1990 (last) | Lothar de Maizière | ||||||||||
| Legislature | Volkskammer | ||||||||||
| Länderkammer[note 5] | |||||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||||
• Constitution adopted | 7 October 1949 | ||||||||||
• Uprising of 1953 | 16 June 1953 | ||||||||||
• Warsaw Pact | 14 May 1955 | ||||||||||
• Berlin Crisis | 4 June 1961 | ||||||||||
• Admitted to the UN | 18 September 1973 | ||||||||||
• Peaceful Revolution ("Die Wende") | 13 October 1989 | ||||||||||
• Fall of the Berlin Wall | 9 November 1989 | ||||||||||
• Final Settlement | 12 September 1990 | ||||||||||
• Reunification | 3 October 1990 | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
• Total | 108,333 km2 (41,828 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
• 1950 | 18,388,000[note 6][1] | ||||||||||
• 1970 | 17,068,000 | ||||||||||
• 1990 | 16,111,000 | ||||||||||
• Density | 149/km2 (385.9/sq mi) | ||||||||||
| HDI (1989) | 0.953[2] very high | ||||||||||
| Currency |
| ||||||||||
| Time zone | (UTC+1) | ||||||||||
| Driving side | right | ||||||||||
| Calling code | +37 | ||||||||||
| Internet TLD | .dd[note 7][3] | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Germany | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; German: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, pronounced [ˈdɔʏtʃə demoˈkʁaːtɪʃə ʁepuˈbliːk] (![]() listen), DDR, pronounced [ˌdeːdeːˈʔɛʁ] (
listen), DDR, pronounced [ˌdeːdeːˈʔɛʁ] (![]() listen)), was a state that existed from 1949 to 1990, the period when the eastern portion of Germany was part of the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state in English usage, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state".[9] It consisted of territory that was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR.
listen)), was a state that existed from 1949 to 1990, the period when the eastern portion of Germany was part of the Eastern Bloc during the Cold War. Commonly described as a communist state in English usage, it described itself as a socialist "workers' and peasants' state".[9] It consisted of territory that was administered and occupied by Soviet forces following the end of World War II—the Soviet occupation zone of the Potsdam Agreement, bounded on the east by the Oder–Neisse line. The Soviet zone surrounded West Berlin but did not include it and West Berlin remained outside the jurisdiction of the GDR.
The GDR was established in the Soviet zone while the Federal Republic of Germany, commonly referred to as West Germany, was established in the three western zones. A satellite state of the Soviet Union,[10] Soviet occupation authorities began transferring administrative responsibility to German communist leaders in 1948 and the GDR began to function as a state on 7 October 1949. However, Soviet forces remained in the country throughout the Cold War. Until 1989, the GDR was governed by the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED), although other parties nominally participated in its alliance organization, the National Front of the German Democratic Republic.[11] The SED made the teaching of Marxism–Leninism and the Russian language compulsory in schools.[12]
The economy was centrally planned and increasingly state-owned.[13] Prices of housing, basic goods and services were heavily subsidized and set by central government planners rather than rising and falling through supply and demand. Although the GDR had to pay substantial war reparations to the Soviets, it became the most successful economy in the Eastern Bloc. Emigration to the West was a significant problem as many of the emigrants were well-educated young people and weakened the state economically. The government fortified its western borders and built the Berlin Wall in 1961.[14] Many people attempting to flee[15][16][17] were killed by border guards or booby traps such as landmines.[18] Those captured spent large amounts of time imprisoned for attempting to escape.[19][20]
In 1989, numerous social, economic and political forces in the GDR and abroad, one of the most notable ones being the peaceful protests starting in the city of Leipzig, led to the fall of the Berlin Wall and the establishment of a government committed to liberalization. The following year, a free and fair election was held[21] and international negotiations led to the signing of the Final Settlement treaty on the status and borders of Germany. The GDR dissolved itself and reunified with West Germany on 3 October 1990, becoming a fully sovereign state in the reunified Federal Republic of Germany. Several of the GDR's leaders, notably its last communist leader Egon Krenz, were prosecuted by the Federal Republic after reunification for offenses committed during the Cold War.[22][23]
Geographically, the GDR bordered the Baltic Sea to the north, Poland to the east, Czechoslovakia to the southeast and West Germany to the southwest and west. Internally, the GDR also bordered the Soviet sector of Allied-occupied Berlin, known as East Berlin, which was also administered as the state's de facto capital. It also bordered the three sectors occupied by the United States, United Kingdom and France known collectively as West Berlin. The three sectors occupied by the Western nations were sealed off from the GDR by the Berlin Wall from its construction in 1961 until it was brought down in 1989.
Naming conventions[]
The official name was Deutsche Demokratische Republik (German Democratic Republic), usually abbreviated to DDR (GDR). Both terms were used in East Germany, with increasing usage of the abbreviated form, especially since East Germany considered West Germans and West Berliners to be foreigners following the promulgation of its second constitution in 1968. West Germans, the western media and statesmen initially avoided the official name and its abbreviation, instead using terms like Ostzone (Eastern Zone),[24] Sowjetische Besatzungszone (Soviet Occupation Zone; often abbreviated to SBZ) and sogenannte DDR[25] or "so-called GDR".[26]
The centre of political power in East Berlin was referred to as Pankow (the seat of command of the Soviet forces in East Germany was referred to as Karlshorst).[24] Over time, however, the abbreviation "DDR" was also increasingly used colloquially by West Germans and West German media.[note 8]
When used by West Germans, Westdeutschland (West Germany) was a term almost always in reference to the geographic region of Western Germany and not to the area within the boundaries of the Federal Republic of Germany. However, this use was not always consistent and West Berliners frequently used the term Westdeutschland to denote the Federal Republic.[27] Before World War II, Ostdeutschland (eastern Germany) was used to describe all the territories east of the Elbe (East Elbia), as reflected in the works of sociologist Max Weber and political theorist Carl Schmitt.[28][29][30][31][32]
History[]

Explaining the internal impact of the GDR government from the perspective of German history in the long term, historian Gerhard A. Ritter (2002) has argued that the East German state was defined by two dominant forces – Soviet communism on the one hand, and German traditions filtered through the interwar experiences of German communists on the other.[33] The GDR always was constrained by the example of richer West, to which East Germans compared their nation. The changes implemented by the communists were most apparent in ending capitalism and in transforming industry and agriculture, in the militarization of society, and in the political thrust of the educational system and of the media. On the other hand, the new regime made relatively few changes in the historically independent domains of the sciences, the engineering professions,[34]:185–189 the Protestant churches,[34]:190 and in many bourgeois lifestyles.[34]:190 Social policy, says Ritter, became a critical legitimization tool in the last decades and mixed socialist and traditional elements about equally.[34]
Origins[]
At the Yalta Conference during World War II, the Allies (the US, the UK, and the Soviet Union) agreed on dividing a defeated Nazi Germany into occupation zones,[35] and on dividing Berlin, the German capital, among the Allied powers as well. Initially, this meant the formation of three zones of occupation, i.e., American, British, and Soviet. Later, a French zone was carved out of the US and British zones.
1949 establishment[]
| Eastern Bloc |
|---|
 |
The ruling communist party, known as the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED), formed in April 1946 from the merger between the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) and the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD).[36] The two former parties were notorious rivals when they were active before the Nazis consolidated all power and criminalised them, and official East German and Soviet histories portrayed this merger as a voluntary pooling of efforts by the socialist parties and symbolic of the new friendship of German socialists after defeating their common enemy; however, there is much evidence that the merger was more troubled than commonly portrayed, and that the Soviet occupation authorities applied great pressure on the SPD's eastern branch to merge with the KPD, and the communists, who held a majority, had virtually total control over policy.[37] The SED remained the ruling party for the entire duration of the East German state. It had close ties with the Soviets, which maintained military forces in East Germany until the dissolution of the USSR in 1991 (the Russian Federation continued to maintain forces in the territory of the former East Germany until 1994), with the stated purpose of countering NATO bases in West Germany.
As West Germany was reorganized and gained independence from its occupiers (1945–1949), the GDR was established in East Germany in October 1949. The emergence of the two sovereign states solidified the 1945 division of Germany.[38] On 10 March 1952, (in what would become known as the "Stalin Note") the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin, issued a proposal to reunify Germany with a policy of neutrality, with no conditions on economic policies and with guarantees for "the rights of man and basic freedoms, including freedom of speech, press, religious persuasion, political conviction, and assembly" and free activity of democratic parties and organizations.[39] The West demurred; reunification was not then a priority for the leadership of West Germany, and the NATO powers declined the proposal, asserting that Germany should be able to join NATO and that such a negotiation with the Soviet Union would be seen as a capitulation. There have been several debates about whether Germany missed a real chance for reunification in 1952.
In 1949 the Soviets turned control of East Germany over to the SED, headed by Wilhelm Pieck (1876–1960), who became President of the GDR and held the office until his death, while the SED general secretary Walter Ulbricht assumed most executive authority. Socialist leader Otto Grotewohl (1894–1964) became prime minister until his death.[40]
The government of East Germany denounced West German failures in accomplishing denazification and renounced ties to the Nazi past, imprisoning many former Nazis and preventing them from holding government positions. The SED set a primary goal of ridding East Germany of all traces of Nazism.[41][citation needed] It is estimated that[when?] between 180,000 and 250,000 people were sentenced to imprisonment on political grounds.[42]
Zones of occupation[]
In the Yalta and Potsdam conferences of 1945, the Allies established their joint military occupation and administration of Germany via the Allied Control Council (ACC), a four-power (US, UK, USSR, France) military government effective until the restoration of German sovereignty. In eastern Germany, the Soviet Occupation Zone (SBZ – Sowjetische Besatzungszone) comprised the five states (Länder) of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia[citation needed]. Disagreements over the policies to be followed in the occupied zones quickly led to a breakdown in cooperation between the four powers, and the Soviets administered their zone without regard to the policies implemented in the other zones. The Soviets withdrew from the ACC in 1948; subsequently, as the other three zones were increasingly unified and granted self-government, the Soviet administration instituted a separate socialist government in its zone[citation needed].
Yet, seven years after the Allies' 1945 Potsdam Agreement on common German policies, the USSR via the Stalin Note (10 March 1952) proposed German reunification and superpower disengagement from Central Europe, which the three Western Allies (the United States, France, the United Kingdom) rejected. Soviet leader Joseph Stalin, a Communist proponent of reunification, died in early March 1953. Similarly, Lavrenty Beria, the First Deputy Prime Minister of the USSR, pursued German reunification, but he was removed from power that same year before he could act on the matter. His successor, Nikita Khrushchev, rejected reunification as equivalent to returning East Germany for annexation to the West; hence reunification went unconsidered until 1989.[citation needed]
East Germany regarded East Berlin as its capital, and the Soviet Union and the rest of the Eastern Bloc diplomatically recognized East Berlin as the capital. However, the Western Allies disputed this recognition, considering the entire city of Berlin to be occupied territory governed by the Allied Control Council. According to Margarete Feinstein, East Berlin's status as the capital was largely unrecognized by the West and by most Third World countries.[43] In practice, the ACC's authority was rendered moot by the Cold War, and East Berlin's status as occupied territory largely became a legal fiction, the Soviet sector of Berlin became fully integrated into the GDR.[citation needed]
The deepening Cold War conflict between the Western Powers and the Soviet Union over the unresolved status of West Berlin led to the Berlin Blockade (24 June 1948 – 12 May 1949). The Soviet army initiated the blockade by halting all Allied rail, road, and water traffic to and from West Berlin. The Allies countered the Soviets with the Berlin Airlift (1948–49) of food, fuel, and supplies to West Berlin.[44]
Partition[]
| History of Germany | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||
| Topics | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Early history | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Middle Ages | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Early Modern period | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Unification | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| German Reich | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Contemporary Germany | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
On 21 April 1946 the Communist Party of Germany (Kommunistische Partei Deutschlands – KPD) and the part of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands – SPD) in the Soviet zone merged to form the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED – Sozialistische Einheitspartei Deutschlands), which then won the elections of October 1946. The SED government nationalised infrastructure and industrial plants.

In March 1948 the German Economic Commission (Deutsche Wirtschaftskomission—DWK) under its chairman Heinrich Rau assumed administrative authority in the Soviet occupation zone, thus becoming the predecessor of an East German government.[45][46]
On 7 October 1949 the SED established the Deutsche Demokratische Republik (German Democratic Republic – GDR), based on a socialist political constitution establishing its control of the Anti-Fascist National Front of the German Democratic Republic (NF, Nationale Front der Deutschen Demokratischen Republik), an omnibus alliance of every party and mass organisation in East Germany. The NF was established to stand for election to the Volkskammer (People's Chamber), the East German parliament. The first and only president of the German Democratic Republic was Wilhelm Pieck. However, after 1950, political power in East Germany was held by the First Secretary of the SED, Walter Ulbricht.[47]

On 16 June 1953, workers constructing the new Stalinallee boulevard in East Berlin according to the GDR's officially promulgated Sixteen Principles of Urban Design, rioted against a 10% production-quota increase. Initially a labour protest, the action soon included the general populace, and on 17 June similar protests occurred throughout the GDR, with more than a million people striking in some 700 cities and towns. Fearing anti-communist counter-revolution, on 18 June 1953 the government of the GDR enlisted the Soviet Occupation Forces to aid the police in ending the riot; some fifty people were killed and 10,000 were jailed.[clarification needed][48][49] (See Uprising of 1953 in East Germany.)
The German war reparations owed to the Soviets impoverished the Soviet Zone of Occupation and severely weakened the East German economy. In the 1945–46 period the Soviets confiscated and transported to the USSR approximately 33% of the industrial plant and by the early 1950s had extracted some US$10 billion in reparations in agricultural and industrial products.[50] The poverty of East Germany, induced or deepened by reparations, provoked the Republikflucht ("desertion from the republic") to West Germany, further weakening the GDR's economy. Western economic opportunities induced a brain drain. In response, the GDR closed the Inner German Border, and on the night of 12 August 1961, East German soldiers began erecting the Berlin Wall.[51]

In 1971, Ulbricht was removed from leadership after Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev supported his ouster;[52] Erich Honecker replaced him. While the Ulbricht government had experimented with liberal reforms, the Honecker government reversed them. The new government introduced a new East German Constitution which defined the German Democratic Republic as a "republic of workers and peasants".[53]
Initially, East Germany claimed an exclusive mandate for all of Germany, a claim supported by most of the Communist bloc. It claimed that West Germany was an illegally-constituted puppet state of NATO. However, from the 1960s onward, East Germany began recognizing itself as a separate country from West Germany and shared the legacy of the united German state of 1871–1945. This was formalized in 1974 when the reunification clause was removed from the revised East German constitution. West Germany, in contrast, maintained that it was the only legitimate government of Germany. From 1949 to the early 1970s, West Germany maintained that East Germany was an illegally constituted state. It argued that the GDR was a Soviet puppet-state, and frequently referred to it as the "Soviet occupation zone". West Germany's allies shared this position until 1973. East Germany was recognized primarily by Communist countries and by the Arab bloc, along with some "scattered sympathizers".[54] According to the Hallstein Doctrine (1955), West Germany did not establish (formal) diplomatic ties with any country—except the Soviets—that recognized East German sovereignty.

In the early 1970s, the Ostpolitik ("Eastern Policy") of "Change Through Rapprochement" of the pragmatic government of FRG Chancellor Willy Brandt, established normal diplomatic relations with the East Bloc states. This policy saw the Treaty of Moscow (August 1970), the Treaty of Warsaw (December 1970), the Four Power Agreement on Berlin (September 1971), the Transit Agreement (May 1972), and the Basic Treaty (December 1972), which relinquished any separate claims to an exclusive mandate over Germany as a whole and established normal relations between the two Germanies. Both countries were admitted into the United Nations on 18 September 1973. This also increased the number of countries recognizing East Germany to 55, including the US, UK and France, though these three still refused to recognize East Berlin as the capital, and insisted on a specific provision in the UN resolution accepting the two Germanies into the UN to that effect.[54] Following the Ostpolitik, the West German view was that East Germany was a de facto government within a single German nation and a de jure state organisation of parts of Germany outside the Federal Republic. The Federal Republic continued to maintain that it could not within its own structures recognize the GDR de jure as a sovereign state under international law; but it fully acknowledged that, within the structures of international law, the GDR was an independent sovereign state. By distinction, West Germany then viewed itself as being within its own boundaries, not only the de facto and de jure government, but also the sole de jure legitimate representative of a dormant "Germany as whole".[55] The two Germanies each relinquished any claim to represent the other internationally; which they acknowledged as necessarily implying a mutual recognition of each other as both capable of representing their own populations de jure in participating in international bodies and agreements, such as the United Nations and the Helsinki Final Act.
This assessment of the Basic Treaty was confirmed in a decision of the Federal Constitutional Court in 1973;[56]
the German Democratic Republic is in the international-law sense a State and as such a subject of international law. This finding is independent of recognition in international law of the German Democratic Republic by the Federal Republic of Germany. Such recognition has not only never been formally pronounced by the Federal Republic of Germany but on the contrary repeatedly explicitly rejected. If the conduct of the Federal Republic of Germany towards the German Democratic Republic is assessed in the light of its détente policy, in particular the conclusion of the Treaty as de facto recognition, then it can only be understood as de facto recognition of a special kind. The special feature of this Treaty is that while it is a bilateral Treaty between two States, to which the rules of international law apply and which like any other international treaty possesses validity, it is between two States that are parts of a still existing, albeit incapable of action as not being reorganized, comprehensive State of the Whole of Germany with a single body politic.[57]
Travel between the GDR and Poland, Czechoslovakia, and Hungary became visa-free from 1972.[58]
GDR identity[]

From the beginning, the newly formed GDR tried to establish its own separate identity.[59] Because of the imperial and military legacy of Prussia, the SED repudiated continuity between Prussia and the GDR. The SED destroyed a number of symbolic relics of the former Prussian aristocracy: Junker manor-houses were torn down, the Berliner Stadtschloß was razed, and the equestrian statue of Frederick the Great was removed from East Berlin. Instead, the SED focused on the progressive heritage of German history, including Thomas Müntzer's role in the German Peasants' War of 1524–1525 and the role played by the heroes of the class struggle during Prussia's industrialization.
Especially after the Ninth Party Congress in 1976, East Germany upheld historical reformers such as Karl Freiherr vom Stein (1757–1831), Karl August von Hardenberg (1750–1822), Wilhelm von Humboldt (1767–1835), and Gerhard von Scharnhorst (1755–1813) as examples and role models.[60]
Die Wende (German reunification)[]

In May 1989, following widespread public anger over the faking of results of local government elections, many GDR citizens applied for exit visas or left the country contrary to GDR laws. The impetus for this exodus of East Germans was the removal of the electrified fence along Hungary's border with Austria on 2 May 1989. Although formally the Hungarian frontier was still closed, many East Germans took the opportunity to enter Hungary via Czechoslovakia, and then make the illegal crossing from Hungary to Austria and to West Germany beyond.[61] By July, 25,000 East Germans had crossed into Hungary;[62] most of them did not attempt the risky crossing into Austria but remained instead in Hungary or claimed asylum in West German embassies in Prague or Budapest.
The opening of a border gate between Austria and Hungary at the Pan-European Picnic on 19 August 1989 then set in motion a chain reaction leading to the end of the GDR and disintegration of the Eastern Bloc. It was the largest mass escape from East Germany since the building of the Berlin Wall in 1961. The idea of opening the border at a ceremony came from Otto von Habsburg, who proposed it to Miklós Németh, then Hungarian Prime Minister, who promoted the idea.[63] The patrons of the picnic, Habsburg and Hungarian Minister of State Imre Pozsgay, who did not attend the event, saw the planned event as an opportunity to test Mikhail Gorbachev's reaction to an opening of the border on the Iron Curtain. In particular, it tested whether Moscow would give the Soviet troops stationed in Hungary the command to intervene. Extensive advertising for the planned picnic was made by the Paneuropean Union through posters and flyers among the GDR holidaymakers in Hungary. The Austrian branch of the Paneuropean Union, which was then headed by Karl von Habsburg, distributed thousands of brochures inviting GDR citizens to a picnic near the border at Sopron (near Hungary's border with Austria).[64][65][66] The local Sopron organizers knew nothing of possible GDR refugees, but envisaged a local party with Austrian and Hungarian participation.[67] But with the mass exodus at the Pan-European Picnic, the subsequent hesitant behavior of the Socialist Unity Party of East Germany and the non-intervention of the Soviet Union broke the dams. Thus the barrier of the Eastern Bloc was broken. The reaction to this from Erich Honecker in the "Daily Mirror" of 19 August 1989 was too late and showed the present loss of power: "Habsburg distributed leaflets far into Poland, on which the East German holidaymakers were invited to a picnic. When they came to the picnic, they were given gifts, food and Deutsche Mark, and then they were persuaded to come to the West."[citation needed] Tens of thousands of East Germans, alerted by the media, made their way to Hungary, which was no longer ready to keep its borders completely closed or force its border troops to open fire on escapees. The GDR leadership in East Berlin did not dare to completely lock down their own country's borders.[64][66][68][69]
The next major turning point in the exodus came on 10 September 1989, when Hungarian Foreign Minister Gyula Horn announced that his country would no longer restrict movement from Hungary into Austria. Within two days, 22,000 East Germans crossed into Austria; tens of thousands more did so in the following weeks.[61]
Many other GDR citizens demonstrated against the ruling party, especially in the city of Leipzig. The Leipzig demonstrations became a weekly occurrence, with a turnout of 10,000 people at the first demonstration on 2 October, peaking at an estimated 300,000 by the end of the month.[70] The protests were surpassed in East Berlin, where half a million demonstrators turned out against the regime on 4 November.[70] Kurt Masur, conductor of the Leipzig Gewandhaus Orchestra, led local negotiations with the government and held town meetings in the concert hall.[71] The demonstrations eventually led Erich Honecker to resign in October; he was replaced by a slightly more moderate communist, Egon Krenz.[72]
The massive demonstration in East Berlin on 4 November coincided with Czechoslovakia formally opening its border to West Germany.[73] With the West more accessible than ever before, 30,000 East Germans made the crossing via Czechoslovakia in the first two days alone. To try to stem the outward flow of the population, the SED proposed a law loosening travel restrictions. When the Volkskammer rejected it on 5 November, the Cabinet and Politburo of the GDR resigned.[73] This left only one avenue open for Krenz and the SED: completely abolishing travel restrictions between East and West.
On 9 November 1989, a few sections of the Berlin Wall were opened, resulting in thousands of East Germans crossing freely into West Berlin and West Germany for the first time in nearly 30 years. Krenz resigned a month later, and the SED opened negotiations with the leaders of the incipient Democratic movement, Neues Forum, to schedule free elections and begin the process of democratization. As part of this process, the SED eliminated the clause in the East German constitution guaranteeing the Communists leadership of the state. The change was approved in the Volkskammer on 1 December 1989 by a vote of 420 to 0.[74]
East Germany held its last election in March 1990. The winner was a coalition headed by the East German branch of West Germany's Christian Democratic Union, which advocated speedy reunification. Negotiations (2+4 Talks) were held involving the two German states and the former Allies, which led to agreement on the conditions for German unification. By a two-thirds vote in the Volkskammer on 23 August 1990, the German Democratic Republic declared its accession to the Federal Republic of Germany. The five original East German states that had been abolished in the 1952 redistricting were restored.[72] On 3 October 1990, the five states officially joined the Federal Republic of Germany, while East and West Berlin united as a third city-state (in the same manner as Bremen and Hamburg). On 1 July, a currency union preceded the political union: the "Ostmark" was abolished, and the Western German "Deutsche Mark" became the common currency.
Although the Volkskammer's declaration of accession to the Federal Republic had initiated the process of reunification; the act of reunification itself (with its many specific terms, conditions and qualifications; some of which involved amendments to the West German Basic Law) was achieved constitutionally by the subsequent Unification Treaty of 31 August 1990; that is, through a binding agreement between the former Democratic Republic and the Federal Republic now recognising each other as separate sovereign states in international law.[75] The treaty was then voted into effect prior to the agreed date for Unification by both the Volkskammer and the Bundestag by the constitutionally required two-thirds majorities; effecting on the one hand, the extinction of the GDR, and on the other, the agreed amendments to the Basic Law of the Federal Republic.
The great economic and socio-political inequalities between the former Germanies required government subsidies for the full integration of the German Democratic Republic into the Federal Republic of Germany. Because of the resulting deindustrialization in the former East Germany, the causes of the failure of this integration continue to be debated. Some western commentators claim that the depressed eastern economy is a natural aftereffect of a demonstrably inefficient command economy. But many East German critics contend that the shock-therapy style of privatization, the artificially high rate of exchange offered for the Ostmark, and the speed with which the entire process was implemented did not leave room for East German enterprises to adapt.[note 9]
Politics[]


There were four periods in East German political history.[76] These included: 1949–61, which saw the building of socialism; 1961–1970 after the Berlin Wall closed off escape was a period of stability and consolidation; 1971–85 was termed the Honecker Era, and saw closer ties with West Germany; and 1985–90 saw the decline and extinction of East Germany.
Organization[]
The ruling political party in East Germany was the Sozialistische Einheitspartei Deutschlands (Socialist Unity Party of Germany, SED). It was created in 1946 through the Soviet-directed merger of the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) and the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) in the Soviet-controlled zone. However, the SED quickly transformed into a full-fledged Communist party as the more independent-minded Social Democrats were pushed out.[60]
The Potsdam Agreement committed the Soviets to support a democratic form of government in Germany, though the Soviets' understanding of democracy was radically different from that of the West. As in other Soviet-bloc countries, non-communist political parties were allowed. Nevertheless, every political party in the GDR was forced to join the National Front of Democratic Germany, a broad coalition of parties and mass political organisations, including:
- Christlich-Demokratische Union Deutschlands (Christian Democratic Union of Germany, CDU), which merged with the West German CDU after reunification.
- Demokratische Bauernpartei Deutschlands (Democratic Farmers' Party of Germany, DBD). The party merged with the West German CDU after reunification.
- Liberal-Demokratische Partei Deutschlands (Liberal Democratic Party of Germany, LDPD), merged with the West German FDP after reunification.
- Nationaldemokratische Partei Deutschlands (National Democratic Party of Germany, NDPD), merged with the West German FDP after reunification.[60]


The member parties were almost completely subservient to the SED and had to accept its "leading role" as a condition of their existence. However, the parties did have representation in the Volkskammer and received some posts in the government.
The Volkskammer also included representatives from the mass organisations like the Free German Youth (Freie Deutsche Jugend or FDJ), or the Free German Trade Union Federation. There was also a Democratic Women's Federation of Germany, with seats in the Volkskammer.
Important non-parliamentary mass organisations in East German society included the German Gymnastics and Sports Association (Deutscher Turn- und Sportbund or DTSB), and People's Solidarity (Volkssolidarität), an organisation for the elderly. Another society of note was the Society for German-Soviet Friendship.
After the fall of Communism, the SED was renamed the "Party of Democratic Socialism" (PDS) which continued for a decade after reunification before merging with the West German WASG to form the Left Party (Die Linke). The Left Party continues to be a political force in many parts of Germany, albeit drastically less powerful than the SED.[77]
Population[]

| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 18,388,000 | — |
| 1960 | 17,188,000 | −6.5% |
| 1970 | 17,068,000 | −0.7% |
| 1980 | 16,740,000 | −1.9% |
| 1990 | 16,028,000 | −4.3% |
| Source: DESTATIS | ||
The East German population declined by three million people throughout its forty-one year history, from 19 million in 1948 to 16 million in 1990; of the 1948 population, some 4 million were deported from the lands east of the Oder-Neisse line, which made the home of millions of Germans part of Poland and the Soviet Union.[78] This was a stark contrast from Poland, which increased during that time; from 24 million in 1950 (a little more than East Germany) to 38 million (more than twice of East Germany's population). This was primarily a result of emigration—about one quarter of East Germans left the country before the Berlin Wall was completed in 1961,[79] and after that time, East Germany had very low birth rates,[80] except for a recovery in the 1980s when the birth rate in East Germany was considerably higher than in West Germany.[81]
Vital statistics[]
| Average population (thousand)[83] | Live births | Deaths | Natural change | Crude birth rate (per 1,000) | Crude death rate (per 1,000) | Natural change (per 1,000) | Total fertility rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1946 | 188,679 | 413,240 | −224,561 | 10.2 | 22.4 | −12.1 | ||
| 1947 | 247,275 | 358,035 | −110,760 | 13.1 | 19.0 | −5.9 | 1.75 | |
| 1948 | 243,311 | 289,747 | −46,436 | 12.7 | 15.2 | −2.4 | 1.76 | |
| 1949 | 274,022 | 253,658 | 20,364 | 14.5 | 13.4 | 1.1 | 2.03 | |
| 1950 | 18,388 | 303,866 | 219,582 | 84,284 | 16.5 | 11.9 | 4.6 | 2.35 |
| 1951 | 18,350 | 310,772 | 208,800 | 101,972 | 16.9 | 11.4 | 5.6 | 2.46 |
| 1952 | 18,300 | 306,004 | 221,676 | 84,328 | 16.6 | 12.1 | 4.6 | 2.42 |
| 1953 | 18,112 | 298,933 | 212,627 | 86,306 | 16.4 | 11.7 | 4.7 | 2.40 |
| 1954 | 18,002 | 293,715 | 219,832 | 73,883 | 16.3 | 12.2 | 4.1 | 2.38 |
| 1955 | 17,832 | 293,280 | 214,066 | 79,215 | 16.3 | 11.9 | 4.4 | 2.38 |
| 1956 | 17,604 | 281,282 | 212,698 | 68,584 | 15.8 | 12.0 | 3.9 | 2.30 |
| 1957 | 17,411 | 273,327 | 225,179 | 48,148 | 15.6 | 12.9 | 2.7 | 2.24 |
| 1958 | 17,312 | 271,405 | 221,113 | 50,292 | 15.6 | 12.7 | 2.9 | 2.22 |
| 1959 | 17,286 | 291,980 | 229,898 | 62,082 | 16.9 | 13.3 | 3.6 | 2.37 |
| 1960 | 17,188 | 292,985 | 233,759 | 59,226 | 16.9 | 13.5 | 3.4 | 2.35 |
| 1961 | 17,079 | 300,818 | 222,739 | 78,079 | 17.6 | 13.0 | 4.6 | 2.42 |
| 1962 | 17,136 | 297,982 | 233,995 | 63,987 | 17.4 | 13.7 | 3.7 | 2.42 |
| 1963 | 17,181 | 301,472 | 222,001 | 79,471 | 17.6 | 12.9 | 4.6 | 2.47 |
| 1964 | 17,004 | 291,867 | 226,191 | 65,676 | 17.1 | 13.3 | 3.9 | 2.48 |
| 1965 | 17,040 | 281,058 | 230,254 | 50,804 | 16.5 | 13.5 | 3.0 | 2.48 |
| 1966 | 17,071 | 267,958 | 225,663 | 42,295 | 15.7 | 13.2 | 2.5 | 2.43 |
| 1967 | 17,090 | 252,817 | 227,068 | 25,749 | 14.8 | 13.3 | 1.5 | 2.34 |
| 1968 | 17,087 | 245,143 | 242,473 | 2,670 | 14.3 | 14.2 | 0.1 | 2.30 |
| 1969 | 17,075 | 238,910 | 243,732 | −4,822 | 14.0 | 14.3 | −0.3 | 2.24 |
| 1970 | 17,068 | 236,929 | 240,821 | −3,892 | 13.9 | 14.1 | −0.2 | 2.19 |
| 1971 | 17,054 | 234,870 | 234,953 | −83 | 13.8 | 13.8 | −0.0 | 2.13 |
| 1972 | 17,011 | 200,443 | 234,425 | −33,982 | 11.7 | 13.7 | −2.0 | 1.79 |
| 1973 | 16,951 | 180,336 | 231,960 | −51,624 | 10.6 | 13.7 | −3.0 | 1.58 |
| 1974 | 16,891 | 179,127 | 229,062 | −49,935 | 10.6 | 13.5 | −3.0 | 1.54 |
| 1975 | 16,820 | 181,798 | 240,389 | −58,591 | 10.8 | 14.3 | −3.5 | 1.54 |
| 1976 | 16,767 | 195,483 | 233,733 | −38,250 | 11.6 | 13.9 | −2.3 | 1.64 |
| 1977 | 16,758 | 223,152 | 226,233 | −3,081 | 13.3 | 13.5 | −0.2 | 1.85 |
| 1978 | 16,751 | 232,151 | 232,332 | −181 | 13.9 | 13.9 | −0.0 | 1.90 |
| 1979 | 16,740 | 235,233 | 232,742 | 2,491 | 14.0 | 13.9 | 0.1 | 1.90 |
| 1980 | 16,740 | 245,132 | 238,254 | 6,878 | 14.6 | 14.2 | 0.4 | 1.94 |
| 1981 | 16,706 | 237,543 | 232,244 | 5,299 | 14.2 | 13.9 | 0.3 | 1.85 |
| 1982 | 16,702 | 240,102 | 227,975 | 12,127 | 14.4 | 13.7 | 0.7 | 1.86 |
| 1983 | 16,701 | 233,756 | 222,695 | 11,061 | 14.0 | 13.3 | 0.7 | 1.79 |
| 1984 | 16,660 | 228,135 | 221,181 | 6,954 | 13.6 | 13.2 | 0.4 | 1.74 |
| 1985 | 16,640 | 227,648 | 225,353 | 2,295 | 13.7 | 13.5 | 0.2 | 1.73 |
| 1986 | 16,640 | 222,269 | 223,536 | −1,267 | 13.4 | 13.5 | −0.1 | 1.70 |
| 1987 | 16,661 | 225,959 | 213,872 | 12,087 | 13.6 | 12.8 | 0.8 | 1.74 |
| 1988 | 16,675 | 215,734 | 213,111 | 2,623 | 12.9 | 12.8 | 0.1 | 1.67 |
| 1989 | 16,434 | 198,992 | 205,711 | −6,789 | 12.0 | 12.4 | −0.4 | 1.56 |
| 1990 | 16,028 | 178,476 | 208,110 | −29,634 | 11.1 | 12.9 | −1.8 | 1.51 |
Major cities[]
(1988 populations)
- East Berlin (1,200,000)
- Leipzig[84] (556,000)
- Dresden[85] (520,000)
- Karl-Marx-Stadt[86] (314,437) (Chemnitz until 1953, reverted to original name in 1990)
- Magdeburg[86] (290,579)
- Rostock[86] (253,990)
- Halle (Saale)[86] (236,044)
- Erfurt[86] (220,016)
- Potsdam[86] (142,862)
- Gera[86] (134,834)
- Schwerin[86] (130,685)
- Cottbus[86] (128,639)
- Zwickau[86] (121,749)
- Jena[86] (108,010)
- Dessau[86] (103,867)
Administrative districts[]
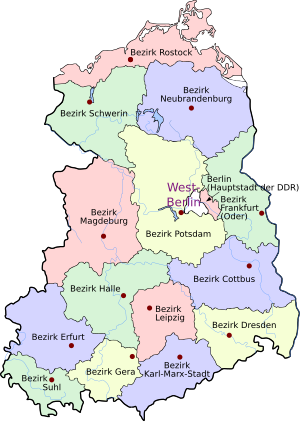
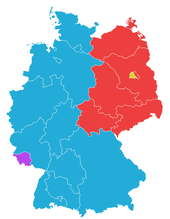
Until 1952, East Germany comprised the capital, East Berlin (though legally it was not fully part of the GDR's territory), and the five German states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (in 1947 renamed Mecklenburg), Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Saxony, their post-war territorial demarcations approximating the pre-war German demarcations of the Middle German Länder (states) and Provinzen (provinces of Prussia). The western parts of two provinces, Pomerania and Lower Silesia, the remainder of which were annexed by Poland, remained in the GDR and were attached to Mecklenburg and Saxony, respectively.
The East German Administrative Reform of 1952 established 14 Bezirke (districts) and de facto disestablished the five Länder. The new Bezirke, named after their district centres, were as follows: (i) Rostock, (ii) Neubrandenburg, and (iii) Schwerin created from the Land (state) of Mecklenburg; (iv) Potsdam, (v) Frankfurt (Oder), and (vii) Cottbus from Brandenburg; (vi) Magdeburg and (viii) Halle from Saxony-Anhalt; (ix) Leipzig, (xi) Dresden, and (xii) Karl-Marx-Stadt (Chemnitz until 1953 and again from 1990) from Saxony; and (x) Erfurt, (xiii) Gera, and (xiv) Suhl from Thuringia.
East Berlin was made the country's 15th Bezirk in 1961 but retained special legal status until 1968, when the residents approved the new (draft) constitution. Despite the city as a whole being legally under the control of the Allied Control Council, and diplomatic objections of the Allied governments, the GDR administered the Bezirk of Berlin as part of its territory.

Military[]

The government of East Germany had control over a large number of military and paramilitary organisations through various ministries. Chief among these was the Ministry of National Defence. Because of East Germany's proximity to the West during the Cold War (1945–92), its military forces were among the most advanced of the Warsaw Pact. Defining what was a military force and what was not is a matter of some dispute.
National People's Army[]
The Nationale Volksarmee (NVA) was the largest military organisation in East Germany. It was formed in 1956 from the Kasernierte Volkspolizei (Barracked People's Police), the military units of the regular police (Volkspolizei), when East Germany joined the Warsaw Pact. From its creation, it was controlled by the Ministry of National Defence (East Germany). It was an all-volunteer force until an eighteen-month conscription period was introduced in 1962.[87][88] It was regarded by NATO officers as the best military in the Warsaw Pact.[89] The NVA consisted of the following branches:
- Army (Landstreitkräfte)
- Navy (Volksmarine – People's Navy)
- Air Force (Luftstreitkräfte/Luftverteidigung)
Border troops[]
The border troops of the Eastern sector were originally organised as a police force, the Deutsche Grenzpolizei, similar to the Bundesgrenzschutz in West Germany. It was controlled by the Ministry of the Interior. Following the remilitarisation of East Germany in 1956, the Deutsche Grenzpolizei was transformed into a military force in 1961, modeled after the Soviet Border Troops, and transferred to the Ministry of National Defense, as part of the National People's Army. In 1973, it was separated from the NVA, but it remained under the same ministry. At its peak, it numbered approximately 47,000 men.
Volkspolizei-Bereitschaft[]
After the NVA was separated from the Volkspolizei in 1956, the Ministry of the Interior maintained its own public order barracked reserve, known as the Volkspolizei-Bereitschaften (VPB). These units were, like the Kasernierte Volkspolizei, equipped as motorised infantry, and they numbered between 12,000 and 15,000 men.
Stasi[]
The Ministry of State Security (Stasi) included the Felix Dzerzhinsky Guards Regiment, which was mainly involved with facilities security and plain clothes events security. They were the only part of the feared Stasi that was visible to the public, and so were very unpopular within the population. The Stasi numbered around 90,000 men, the Guards Regiment around 11,000–12,000 men.
Combat groups of the working class[]
The Kampfgruppen der Arbeiterklasse (combat groups of the working class) numbered around 400,000 for much of their existence, and were organised around factories. The KdA was the political-military instrument of the SED; it was essentially a "party Army". All KdA directives and decisions were made by the ZK's Politbüro. They received their training from the Volkspolizei and the Ministry of the Interior. Membership was voluntary, but SED members were required to join as part of their membership obligation.
Conscientious objection[]
Every man was required to serve eighteen months of compulsory military service; for the medically unqualified and conscientious objector, there were the Baueinheiten (construction units) or the Volkshygienedienst (people's sanitation service) both established in 1964, two years after the introduction of conscription, in response to political pressure by the national Lutheran Protestant Church upon the GDR's government. In the 1970s, East German leaders acknowledged that former construction soldiers and sanitation service soldiers were at a disadvantage when they rejoined the civilian sphere.
Foreign policy[]
Support of Third World socialist countries[]

After receiving wider international diplomatic recognition in 1972–73, the GDR began active cooperation with Third World socialist governments and national liberation movements. While the USSR was in control of the overall strategy and Cuban armed forces were involved in the actual combat (mostly in the People's Republic of Angola and socialist Ethiopia), the GDR provided experts for military hardware maintenance and personnel training, and oversaw creation of secret security agencies based on its own Stasi model.
Already in the 1960s contacts were established with Angola's MPLA, Mozambique's FRELIMO and the PAIGC in Guinea Bissau and Cape Verde. In the 1970s official cooperation was established with other self-proclaimed socialist governments and people's republics: People's Republic of the Congo, People's Democratic Republic of Yemen, Somali Democratic Republic, Libya, and the People's Republic of Benin.
The first military agreement was signed in 1973 with the People's Republic of the Congo. In 1979 friendship treaties were signed with Angola, Mozambique and Ethiopia.
It was estimated that altogether, 2,000–4,000 DDR military and security experts were dispatched to Africa. In addition, representatives from African and Arab countries and liberation movements underwent military training in the GDR.[90]
East Germany and the Middle East conflict[]
East Germany pursued an anti-Zionist policy; Jeffrey Herf argues that East Germany was waging an undeclared war on Israel.[91] According to Herf, "the Middle East was one of the crucial battlefields of the global Cold War between the Soviet Union and the West; it was also a region in which East Germany played a salient role in the Soviet bloc's antagonism toward Israel."[92] While East Germany saw itself as an "anti-fascist state", it regarded Israel as a "fascist state"[93] and East Germany strongly supported the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) in its armed struggle against Israel. In 1974, the GDR government recognized the PLO as the "sole legitimate representative of the Palestinian people".[94] The PLO declared the Palestinian state on 15 November 1988 during the First Intifada, and the GDR recognized the state prior to reunification.[95] After becoming a member of the UN, East Germany "made excellent use of the UN to wage political warfare against Israel [and was] an enthusiastic, high-profile, and vigorous member" of the anti-Israeli majority of the General Assembly.[91]
Soviet military occupation[]
Economy[]


The East German economy began poorly because of the devastation caused by the Second World War; the loss of so many young soldiers, the disruption of business and transportation, the allied bombing campaigns that decimated cities, and reparations owed to the USSR. The Red Army dismantled and transported to Russia the infrastructure and industrial plants of the Soviet Zone of Occupation. By the early 1950s, the reparations were paid in agricultural and industrial products; and Lower Silesia, with its coal mines and Szczecin, an important natural port, were given to Poland by the decision of Stalin and in accordance with Potsdam Agreement.[50]
The socialist centrally planned economy of the German Democratic Republic was like that of the USSR. In 1950, the GDR joined the COMECON trade bloc. In 1985, collective (state) enterprises earned 96.7% of the net national income. To ensure stable prices for goods and services, the state paid 80% of basic supply costs. The estimated 1984 per capita income was $9,800 ($22,600 in 2015 dollars) (this is based on an unreal official exchange rate). In 1976, the average annual growth of the GDP was approximately five percent. This made the East German economy the richest in all of the Soviet Bloc until reunification in 1990.[96]
Notable East German exports were photographic cameras, under the Praktica brand; automobiles under the Trabant, Wartburg, and the IFA brands; hunting rifles, sextants, typewriters and wristwatches.
Until the 1960s, East Germans endured shortages of basic foodstuffs such as sugar and coffee. East Germans with friends or relatives in the West (or with any access to a hard currency) and the necessary Staatsbank foreign currency account could afford Western products and export-quality East German products via Intershop. Consumer goods also were available, by post, from the Danish Jauerfood, and Genex companies.
The government used money and prices as political devices, providing highly subsidised prices for a wide range of basic goods and services, in what was known as "the second pay packet".[97] At the production level, artificial prices made for a system of semi-barter and resource hoarding. For the consumer, it led to the substitution of GDR money with time, barter, and hard currencies. The socialist economy became steadily more dependent on financial infusions from hard-currency loans from West Germany. East Germans, meanwhile, came to see their soft currency as worthless relative to the Deutsche Mark (DM).[98] Economic issues would also persist in the east of Germany after the reunification of the west and the east. According to the federal office of political education (23 June 2009) 'In 1991 alone, 153 billion Deutschmarks had to be transferred to eastern Germany to secure incomes, support businesses and improve infrastructure... by 1999 the total had amounted to 1.634 trillion Marks net... The sums were so large that public debt in Germany more than doubled.'[99]
Consumption and jobs[]
| East Germany | West Germany | |
| 1945–1960 | 6.2 | 10.9 |
| 1950–1960 | 6.7 | 8.0 |
| 1960–1970 | 2.7 | 4.4 |
| 1970–1980 | 2.6 | 2.8 |
| 1980–1989 | 0.3 | 1.9 |
| Total 1950–1989 | 3.1 | 4.3 |
Many western commentators have maintained that loyalty to the SED was a primary criterion for getting a good job, and that professionalism was secondary to political criteria in personnel recruitment and development.[101]
Beginning in 1963 with a series of secret international agreements, East Germany recruited workers from Poland, Hungary, Cuba, Albania, Mozambique, Angola and North Vietnam. They numbered more than 100,000 by 1989. Many, such as future politician Zeca Schall (who emigrated from Angola in 1988 as a contract worker) stayed in Germany after the Wende.[102]
Religion[]
Religion became contested ground in the GDR, with the governing Communists promoting state atheism, although some people remained loyal to Christian communities.[103] In 1957 the State authorities established a State Secretariat for Church Affairs to handle the government's contact with churches and with religious groups;[104] the SED remained officially atheist.[105]
In 1950, 85% of the GDR citizens were Protestants, while 10% were Catholics. In 1961, the renowned philosophical theologian Paul Tillich claimed that the Protestant population in East Germany had the most admirable Church in Protestantism, because the Communists there had not been able to win a spiritual victory over them.[106] By 1989, membership in the Christian churches dropped significantly. Protestants constituted 25% of the population, Catholics 5%. The share of people who considered themselves non-religious rose from 5% in 1950 to 70% in 1989.
State atheism[]
When it first came to power, the Communist party asserted the compatibility of Christianity and Marxism-Leninism and sought Christian participation in the building of socialism. At first, the promotion of Marxist-Leninist atheism received little official attention. In the mid-1950s, as the Cold War heated up, atheism became a topic of major interest for the state, in both domestic and foreign contexts. University chairs and departments devoted to the study of scientific atheism were founded and much literature (scholarly and popular) on the subject was produced.[by whom?] This activity subsided in the late 1960s amid perceptions that it had started to become counterproductive. Official and scholarly attention to atheism renewed beginning in 1973, though this time with more emphasis on scholarship and on the training of cadres than on propaganda. Throughout, the attention paid to atheism in East Germany was never intended to jeopardise the cooperation that was desired from those East Germans who were religious.[107]
Protestantism[]

East Germany, historically, was majority Protestant (primarily Lutheran) from the early stages of the Protestant Reformation onwards. In 1948, freed from the influence of the Nazi-oriented German Christians, Lutheran, Reformed and United churches from most parts of Germany came together as the Evangelical Church in Germany (EKD) at the Conference of Eisenach (Kirchenversammlung von Eisenach).
In 1969 the regional Protestant churches in East Germany and East Berlin[note 10] broke away from the EKD and formed the (German: Bund der Evangelischen Kirchen in der DDR, BEK), in 1970 also joined by the Moravian Herrnhuter Brüdergemeine. In June 1991, following the German reunification, the BEK churches again merged with the EKD ones.
Between 1956 and 1971 the leadership of the East German Lutheran churches gradually changed its relations with the state from hostility to cooperation.[108] From the founding of the GDR in 1949, the Socialist Unity Party sought to weaken the influence of the church on the rising generation. The church adopted an attitude of confrontation and distance toward the state. Around 1956 this began to develop into a more neutral stance accommodating conditional loyalty. The government was no longer regarded as illegitimate; instead, the church leaders started viewing the authorities as installed by God and, therefore, deserving of obedience by Christians. But on matters where the state demanded something which the churches felt was not in accordance with the will of God, the churches reserved their right to say no. There were both structural and intentional causes behind this development. Structural causes included the hardening of Cold War tensions in Europe in the mid-1950s, which made it clear that the East German state was not temporary. The loss of church members also made it clear to the leaders of the church that they had to come into some kind of dialogue with the state. The intentions behind the change of attitude varied from a traditional liberal Lutheran acceptance of secular power to a positive attitude toward socialist ideas.[109]
Manfred Stolpe became a lawyer for the Brandenburg Protestant Church in 1959 before taking up a position at church headquarters in Berlin. In 1969 he helped found the Bund der Evangelischen Kirchen in der DDR (BEK), where he negotiated with the government while at the same time working within the institutions of this Protestant body. He won the regional elections for the Brandenburg state assembly at the head of the SPD list in 1990. Stolpe remained in the Brandenburg government until he joined the federal government in 2002.
Apart from the Protestant state churches (German: Landeskirchen) united in the EKD/BEK and the Catholic Church there was a number of smaller Protestant bodies, including Protestant Free Churches (German: Evangelische Freikirchen) united in the and the , as well as the Free Lutheran Church, the Old Lutheran Church and . The Moravian Church also had its presence as the Herrnhuter Brüdergemeine. There were also other Protestants such as Methodists, Adventists, Mennonites and Quakers.
Catholicism[]

(left to right) Bishop Karl Lehmann and Cardinals Gerhard Schaffran, Joseph Ratzinger (the future Pope Benedict XVI) and Joachim Meisner
The smaller Catholic Church in eastern Germany had a fully functioning episcopal hierarchy in full accord with the Vatican. During the early postwar years, tensions were high. The Catholic Church as a whole (and particularly the bishops) resisted both the East German state and Marxist-Leninist ideology. The state allowed the bishops to lodge protests, which they did on issues such as abortion.[109]
After 1945, the Church did fairly well in integrating Catholic exiles from lands to the east (which mostly became part of Poland) and in adjusting its institutional structures to meet the needs of a church within an officially atheist society. This meant an increasingly hierarchical church structure, whereas in the area of religious education, press, and youth organisations, a system of temporary staff was developed, one that took into account the special situation of Caritas, a Catholic charity organisation. By 1950, therefore, there existed a Catholic subsociety that was well adjusted to prevailing specific conditions and capable of maintaining Catholic identity.[110][page needed]
With a generational change in the episcopacy taking place in the early 1980s, the state hoped for better relations with the new bishops, but the new bishops instead began holding unauthorised mass meetings, promoting international ties in discussions with theologians abroad, and hosting ecumenical conferences. The new bishops became less politically oriented and more involved in pastoral care and attention to spiritual concerns. The government responded by limiting international contacts for bishops.[111][need quotation to verify]
List of apostolic administrators:
- Erfurt-Meiningen
- Görlitz
- Magdeburg
- Schwerin
Culture[]
This section needs additional citations for verification. (June 2015) |
East Germany's culture was strongly influenced by communist thought and was marked by an attempt to define itself in opposition to the west, particularly West Germany and the United States. Critics of the East German state[who?] have claimed that the state's commitment to Communism was a hollow and cynical tool, Machiavellian in nature, but this assertion has been challenged by studies[which?] that have found that the East German leadership was genuinely committed to the advance of scientific knowledge, economic development, and social progress. However, Pence and Betts argue, the majority of East Germans over time increasingly regarded the state's ideals to be hollow, though there was also a substantial number of East Germans who regarded their culture as having a healthier, more authentic mentality than that of West Germany.[112]
GDR culture and politics were limited by the harsh censorship.[113]
Music[]


The Puhdys and Karat were some of the most popular mainstream bands in East Germany. Like most mainstream acts, they were members of the SED, appeared in state-run popular youth magazines such as Neues Leben and Magazin. Other popular rock bands were , City, Silly and Pankow. Most of these artists recorded on the state-owned AMIGA label. All were required to open live performances and albums with the East German national anthem.[114]
Schlager, which was very popular in the west, also gained a foothold early on in East Germany, and numerous musicians, such as , , and gained national fame. From 1962 to 1976, an international schlager festival was held in Rostock, garnering participants from between 18 and 22 countries each year.[115] The city of Dresden held a similar international festival for schlager musicians from 1971 until shortly before reunification.[116] There was a national schlager contest hosted yearly in Magdeburg from 1966 to 1971 as well.[117]
Bands and singers from other Communist countries were popular, e.g. Czerwone Gitary from Poland known as the Rote Gitarren.[118][119] Czech Karel Gott, the Golden Voice from Prague, was beloved in both German states.[120] Hungarian band Omega performed in both German states, and Yugoslavian band Korni Grupa toured East Germany in the 1970s.[121][122]
West German television and radio could be received in many parts of the East. The Western influence led to the formation of more "underground" groups with a decisively western-oriented sound. A few of these bands – the so-called Die anderen Bands ("the other bands") – were Die Skeptiker, and Feeling B. Additionally, hip hop culture reached the ears of the East German youth. With videos such as Beat Street and Wild Style, young East Germans were able to develop a hip hop culture of their own.[123] East Germans accepted hip hop as more than just a music form. The entire street culture surrounding rap entered the region and became an outlet for oppressed youth.[124]
The government of the GDR was invested in both promoting the tradition of German classical music, and in supporting composers to write new works in that tradition. Notable East German composers include Hanns Eisler, Paul Dessau, Ernst Hermann Meyer, Rudolf Wagner-Régeny, and Kurt Schwaen.
The birthplace of Johann Sebastian Bach (1685–1750), Eisenach, was rendered as a museum about him, featuring more than three hundred instruments, which, in 1980, received some 70,000 visitors. In Leipzig, the Bach archive contains his compositions and correspondence and recordings of his music.[125]
Governmental support of classical music maintained some fifty symphony orchestras, such as Gewandhausorchester and Thomanerchor in Leipzig; Sächsische Staatskapelle in Dresden; and Berliner Sinfonie Orchester and Staatsoper Unter den Linden in Berlin.[citation needed] Kurt Masur was their prominent conductor.[126]
Theatre[]

East German theatre was originally dominated by Bertolt Brecht, who brought back many artists out of exile and reopened the Theater am Schiffbauerdamm with his Berliner Ensemble.[127] Alternatively, other influences tried to establish a "Working Class Theatre", played for the working class by the working class.[citation needed]
After Brecht's death, conflicts began to arise between his family (around Helene Weigel) and other artists about Brecht's legacy, including Slatan Dudow,[128] Erwin Geschonneck,[129] Erwin Strittmatter, Peter Hacks, Benno Besson,[130] Peter Palitzsch[131] and Ekkehard Schall.[132]
In the 1950s, the Swiss director Benno Besson with the Deutsches Theater successfully toured Europe and Asia including Japan with The Dragon by . In the 1960s, he became the Intendant of the Volksbühne often working with Heiner Müller.[citation needed]
In the 1970s, a parallel theatre scene sprung up, creating theatre "outside of Berlin" in which artists played at provincial theatres. For example, Peter Sodann founded the in Halle/Saale and Frank Castorf at the theater Anklam.[citation needed]
Theatre and cabaret had high status in the GDR, which allowed it to be very proactive. This often brought it into confrontation with the state. Benno Besson once said, "In contrast to artists in the west, they took us seriously, we had a bearing."[133][note 11]
The Friedrichstadt-Palast in Berlin is the last major building erected by the GDR, making it an exceptional architectural testimony to how Germany overcame its former division. Here, Berlin's great revue tradition lives on, today bringing viewers state-of-the-art shows.[134]
Important theatres include the Berliner Ensemble,[135] the Deutsches Theater,[136] the Maxim Gorki Theater,[137] and the Volksbühne.[138]
Cinema[]
The prolific cinema of East Germany was headed by the DEFA,[139] Deutsche Film AG, which was subdivided in different local groups, for example Gruppe Berlin, Gruppe Babelsberg or Gruppe Johannisthal, where the local teams shot and produced films. The East German industry became known worldwide for its productions, especially children's movies (Das kalte Herz, film versions of the Brothers Grimm fairy tales and modern productions such as ).[citation needed]
Frank Beyer's Jakob der Lügner (Jacob the Liar), about the Holocaust, and Fünf Patronenhülsen (Five Cartridges), about resistance against fascism, became internationally famous.[140]
Films about daily life, such as Die Legende von Paul und Paula, by Heiner Carow, and Solo Sunny, directed by Konrad Wolf and Wolfgang Kohlhaase, were very popular.[citation needed]
The film industry was remarkable for its production of Ostern, or Western-like movies. Amerindians in these films often took the role of displaced people who fight for their rights, in contrast to the North American westerns of the time, where they were often either not mentioned at all or are portrayed as the villains. Yugoslavs were often cast as Native Americans because of the small number of Native Americans in Europe. Gojko Mitić was well known in these roles, often playing the righteous, kindhearted and charming chief (Die Söhne der großen Bärin directed by Josef Mach). He became an honorary Sioux chief when he visited the United States in the 1990s, and the television crew accompanying him showed the tribe one of his movies. American actor and singer Dean Reed, an expatriate who lived in East Germany, also starred in several films. These films were part of the phenomenon of Europe producing alternative films about the colonization of the Americas.[citation needed]
Cinemas in the GDR also showed foreign films. Czechoslovak and Polish productions were more common, but certain western movies were shown, though the numbers of these were limited because it cost foreign exchange to buy the licences. Further, films representing or glorifying what the state viewed as capitalist ideology were not bought. Comedies enjoyed great popularity, such as the Danish Olsen Gang or movies with the French comedian Louis de Funès.[citation needed]
Since the fall of the Berlin Wall, several films depicting life in the GDR have been critically acclaimed.[citation needed] Some of the most notable were Good Bye Lenin! by Wolfgang Becker,[141] Das Leben der Anderen (The Lives of Others) by Florian Henckel von Donnersmarck (won the Academy Award for best Film in a Foreign Language) in 2006,[142] and Alles auf Zucker! (Go for Zucker) by Dani Levi. Each film is heavily infused with cultural nuances unique to life in the GDR.[143]
Sport[]
East Germany was very successful in the sports of cycling, weight-lifting, swimming, gymnastics, track and field, boxing, ice skating, and winter sports. The success is largely attributed to doping under the direction of Manfred Höppner, a sports doctor, described as the architect of East Germany's state-sponsored drug program.[144]

Anabolic steroids were the most detected doping substances in IOC-accredited laboratories for many years.[145][146] The development and implementation of a state-supported sports doping program helped East Germany, with its small population, to become a world leader in sport during the 1970s and 1980s, winning a large number of Olympic and world gold medals and records.[147][148] Another factor for success was the furtherance system for young people in the GDR. Sports teachers at school were encouraged to look for certain talents in children of ages 6 to 10. For older pupils it was possible to attend grammar schools with a focus on sports (for example sailing, football and swimming). This policy was also used for talented pupils with regard to music or mathematics.[citation needed]

Sports clubs were highly subsidized, especially sports in which it was possible to get international fame. For example, the major leagues for ice hockey and basketball just included 2 teams each. Football was the most popular sport. Club football teams such as Dynamo Dresden, 1. FC Magdeburg, FC Carl Zeiss Jena, 1. FC Lokomotive Leipzig and BFC Dynamo had successes in European competition. Many East German players such as Matthias Sammer and Ulf Kirsten became integral parts of the reunified national football team.
The East and the West also competed via sport; GDR athletes dominated several Olympic sports. Of special interest was the only football match between the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic, a first-round match during the 1974 FIFA World Cup, which the East won 1–0; but West Germany, the host, went on to win the World Cup.[149]
Television and radio[]

Television and radio in East Germany were state-run industries; the Rundfunk der DDR was the official radio broadcasting organisation from 1952 until unification. The organization was based in the Funkhaus Nalepastraße in East Berlin. Deutscher Fernsehfunk (DFF), from 1972 to 1990 known as Fernsehen der DDR or DDR-FS, was the state television broadcaster from 1952. Reception of Western broadcasts was widespread.[150]
Industry[]
Telecommunications[]
By the mid-1980s, East Germany possessed a well-developed communications system. There were approximately 3.6 million telephones in usage (21.8 for every 100 inhabitants), and 16,476 Telex stations. Both of these networks were run by the Deutsche Post der DDR (East German Post Office). East Germany was assigned telephone country code +37; in 1991, several months after reunification, East German telephone exchanges were incorporated into country code +49.
An unusual feature of the telephone network was that, in most cases, direct distance dialing for long-distance calls was not possible. Although area codes were assigned to all major towns and cities, they were only used for switching international calls. Instead, each location had its own list of dialing codes with shorter codes for local calls and longer codes for long-distance calls. After unification, the existing network was largely replaced, and area codes and dialing became standardised.
In 1976 East Germany inaugurated the operation of a ground-based radio station at Fürstenwalde for the purpose of relaying and receiving communications from Soviet satellites and to serve as a participant in the international telecommunications organization established by the Soviet government, Intersputnik.
Official and public holidays[]
| Date | English Name | German Name | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 January | New Year's Day | Neujahr | |
| Good Friday | Karfreitag | ||
| Easter Sunday | Ostersonntag | ||
| Easter Monday | Ostermontag | Was not an official holiday after 1967. | |
| 1 May | International Workers' Day/May Day | Tag der Arbeit (name in FRG) | The official name was Internationaler Kampf- und Feiertag der Werktätigen (approx. 'International Day of the Struggle and Celebration of the Workers') |
| 8 May | Victory in Europe Day | Tag der Befreiung | The translation means "Day of Liberation" |
| Father's Day/Ascension Day | Vatertag/Christi Himmelfahrt | Thursday after the 5th Sunday after Easter. Was not an official holiday after 1967. | |
| Whitmonday | Pfingstmontag | 50 days after Easter Sunday | |
| 7 October | Republic Day | Tag der Republik | National holiday |
| Day of Repentance and Prayer | Buß- und Bettag | Penultimate Wednesday before the fourth Sunday before 25 December. Originally a Protestant feast day, it was demoted as an official holiday in 1967. | |
| 25 December | First Day of Christmas | 1. Weihnachtsfeiertag | |
| 26 December | Second Day of Christmas | 2. Weihnachtsfeiertag |
Legacy[]
Decrepit Infrastructure[]
Almost all East German highways, railroads, sewage systems and public buildings were in a state of disrepair at the time of reunification, as little was done to maintain infrastructure during the Communist era. West German taxpayers have had to pour more than $2 trillion into the East, to make up for the region's neglect and malaise and bring it up to a minimal standard.[151]
The Greifswald Nuclear Power Plant closely avoided a Chernobyl-scale meltdown in 1976.[152] All East German nuclear power plants had to be shut down after reunification, because they did not meet Western safety standards.[153]
Authoritarianism[]
German historian Jürgen Kocka in 2010 summarized the consensus of most recent scholarship:
Conceptualizing the GDR as a dictatorship has become widely accepted, while the meaning of the concept dictatorship varies. Massive evidence has been collected that proves the repressive, undemocratic, illiberal, nonpluralistic character of the GDR regime and its ruling party.[154]
Ostalgie[]

Many East Germans initially regarded the dissolution of the GDR positively,[155] but this reaction partly turned sour.[156] West Germans often acted as if they had "won" and East Germans had "lost" in unification, leading many East Germans (Ossis) to resent West Germans (Wessis).[157] In 2004, Ascher Barnstone wrote, "East Germans resent the wealth possessed by West Germans; West Germans see the East Germans as lazy opportunists who want something for nothing. East Germans find 'Wessis' arrogant and pushy, West Germans think the 'Ossis' are lazy good-for-nothings."[158]
In addition, many East German women found the west more appealing, and left the region never to return, leaving behind an underclass of poorly educated and jobless men.[159]
As of 2014, the vast majority of residents in the former GDR prefer to live in a unified Germany. However, a feeling of nostalgia persists among some, termed "Ostalgie" (a blend of Ost "east" and Nostalgie "nostalgia"). This was depicted in the Wolfgang Becker film Goodbye Lenin!. According to Klaus Schroeder, a historian and political scientist at the Free University of Berlin, some of the original residents of the GDR "still feel they don't belong or that they're strangers in unified Germany" as life in the GDR was "just more manageable". He warns German society should watch out in case Ostalgie results in a distortion and romanticization of the past.[160][161]
Electoral consequences[]
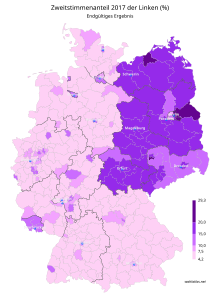
The divide between the East and the West can be seen in contemporary German elections. The left-wing Die Linke party (which has roots in the SED) continues to have a stronghold and often wins a plurality in the East, such as in the German State of Thuringia where it remains the most popular party.[162] This is in stark distinction from the West where the more centrist parties such as the CDU/CSU and SPD dominate.
See also[]
Germany[]
|
Armed Forces[]
|
Media[]
|
Transport[]
|
Other[]
|
Notes[]
- ^ Not recognised by the Three Powers: France, United Kingdom and the United States.
- ^ The SED was established in the Soviet occupation zone of Germany, before the GDR's foundation.
- ^ Served as Joint Chairmen together.
- ^ October–December
- ^ Dissolved by the Volkskammer on 8 December 1958.
- ^ Population statistics according to Statistisches Bundesamt.
- ^ Although .dd was reserved as corresponding ISO code for East Germany, it was not entered to the root before the country was reunited with the west.
- ^ The use of the abbreviation BRD (FRG) for West Germany, the Bundesrepublik Deutschland (Federal Republic of Germany), on the other hand, was never accepted in West Germany since it was considered a political statement. Thus BRD (FRG) was a term used by East Germans, or by West Germans who held a pro-East-German view. Colloquially, West Germans called West Germany simply Germany (reflecting West Germany's claim to represent the whole of Germany), or alternatively the Bundesrepublik or Bundesgebiet (Federal Republic or Federal Territory, respectively), referring to the country and Bundesbürger (Federal citizen) for its citizens, with the adjective bundesdeutsch (Federal German).
- ^ For example, the economist Jörg Roesler – see: Jörg Roesler: Ein Anderes Deutschland war möglich. Alternative Programme für das wirtschaftliche Zusammengehen beider deutscher Staaten, in: Jahrbuch für Forschungen zur Geschichte der Arbeiterbewegung, No. II/2010, pp.34–46. The historian Ulrich Busch argued that the currency union came too early; see Ulrich Busch: Die Währungsunion am 1. Juli 1990: Wirtschaftspolitische Fehlleistung mit Folgen, in: Jahrbuch für Forschungen zur Geschichte der Arbeiterbewegung, No. II/2010, pp. 5–24.
- ^ The Eastern churches were the Evangelical Church of Anhalt, Evangelical Church in Berlin, Brandenburg and Silesian Upper Lusatia#Evangelical Church in Berlin-Brandenburg (EKiBB, East Ambit, for East Berlin and Brandenburg), Evangelical Church of the Görlitz Ecclesiastical Region, Evangelical Church in Greifswald, Evangelical Lutheran Church of Mecklenburg, Evangelical-Lutheran Church of Saxony, Evangelical Church of the Church Province of Saxony (KPS), Evangelical Lutheran Church in Thuringia and Evangelical Church of the Union (East Region, for EKiBB-East Ambit, Görlitz, Greifswald and KPS, and since 1970 for Anhalt too).
- ^ This quote has no cross-referencing to ground its authenticity. For a detailed overview of the issues of Brecht's legacy after his death within the Berliner Ensemble, see David Barnett, A History of the Berliner Ensemble (Cambridge University Press, 2015), 146–70. ISBN 978-1-107-05979-5.
References[]
- ^ "Bevölkerungsstand" (in German). Statistisches Bundesamt. Archived from the original on 13 November 2013.
- ^ "Human Development Report 1990" (PDF). hdr.undp.org.
- ^ "Top-Level-Domain .DD" (in German). Archived from the original on 4 November 2015.
- ^ Vladimir Tismaneanu, Marius Stan, Cambridge University Press, 17 May, 2018, Romania Confronts Its Communist Past: Democracy, Memory, and Moral Justice, p. 132
- ^ Gabriel Ben-Dor, David Brian Dewitt, Lexington Books, 1987, Conflict Management in the Middle East, p. 242
- ^ Derek Leebaert, Timothy Dickinson, Cambridge University Press, 1992, Soviet Strategy and the New Military Thinking, pp. 102, 110 and 113-114
- ^ Jonathan Eyal, Springer, Jun 18, 1989, Warsaw Pact and the Balkans: Moscow's Southern Flank, p. 74
- ^ [https://books.google.ro/books?id=NwviIpm0JxsC&dq=%22except+Romania%27s%22 M. O. Dickerson, Thomas Flanagan, Nelson Canada, 1990, An Introduction to Government and Politics: A Conceptual Approach, p. 75
- ^ Patrick Major, Jonathan Osmond, The Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany Under Ulbricht 1945–71, Manchester University Press, 2002, ISBN 978-0-7190-6289-6
- ^ Karl Dietrich Erdmann, Jürgen Kocka, Wolfgang J. Mommsen, Agnes Blänsdorf. Towards a Global Community of Historians: the International Historical Congresses and the International Committee of Historical Sciences 1898–2000. Berghahn Books, 2005, p. 314. ("However the collapse of the Soviet empire, associated with the disintegration of the Soviet satellite regimes in East-Central Europe, including the German Democratic Republic, brought about a dramatic change of agenda.")
- ^ "Thousands rally in East Germany". Eugene Register-Guard. Associated Press. 29 October 1989. p. 5A.
- ^ Grix, Jonathan; Cooke, Paul (2003). East German Distinctiveness in a Unified Germany. p. 17. ISBN 978-1-902459-17-2.
- ^ Peter E. Quint. The Imperfect Union: Constitutional Structures of German Unification. Princeton University Press, 2012, pp. 125–126.
- ^ Preuss, Evelyn. "The Wall You Will Never Know". Perspecta: The Yale Architectural Journal. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press: 19–31.
- ^ "Three Top Commies Flee East Germany". Sarasota Herald-Tribune. 23 January 1953. pp. 1–2. Retrieved 21 November 2019 – via Google News.
- ^ "5 Flee East Germany". Toledo Blade. 31 May 1963. Retrieved 21 November 2019 – via Google News.
- ^ "Eugene Register-Guard – Google News Archive Search". news.google.com. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ "Files: 350 dies trying to flee East Germany". The Victoria Advocate. 28 July 1992. Retrieved 21 November 2019 – via Google News.
- ^ "Victimized East Germans seek redress". St. Petersburg Times. 11 September 1990.
- ^ "More Than 1,100 Berlin Wall Victims". Deutsche Welle. 9 August 2005. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 8 August 2009.
- ^ Geoffrey Pridham; Tatu Vanhanen (1994). Democratization in Eastern Europe. Routledge. p. 135. ISBN 0-415-11063-7.
- ^ "Repeal the racist asylum laws". The New Worker. 29 August 1997. Retrieved 5 September 2011.
- ^ "Krenz, Schabowski und Kleiber hatten sich nichts mehr zu sagen". Berliner Zeitung. 31 May 2008. Archived from the original on 19 July 2012. Retrieved 5 September 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Berlin Korrespondent (June 1949). "Nationale Front in der Ostzone". Die Zeit. Archived from the original on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 10 May 2013.
- ^ "Vom Sogenannten". Der Spiegel. 21 October 1968. p. 65. Archived from the original on 3 February 2016.
- ^ Facts about Germany: The Federal Republic of Germany, 1959 – Germany (West). 1959. p. 20. Archived from the original on 21 December 2019. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
- ^ Wildenthal, Lora. The Language of Human Rights in West Germany. p. 210.
- ^ Cornfield, Daniel B. and Hodson, Randy (2002). Worlds of Work: Building an International Sociology of Work. Springer, p. 223. ISBN 0-306-46605-8
- ^ Pollak, Michael (2005). "Ein Text in seinem Kontext". Östereichische Zeitschrift für Soziologie (in German). 30: 3–21. doi:10.1007/s11614-006-0033-6. S2CID 147022466.
- ^ Baranowski, Shelley (6 April 1995). The Sanctity of Rural Life: Nobility, Protestantism, and Nazism in Weimar Prussia. pp. 187–188. ISBN 978-0-19-536166-7. Archived from the original on 1 December 2019. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
- ^ Schmitt, Carl (12 July 2017). Political Romanticism. p. 11. ISBN 978-1-351-49869-2. Archived from the original on 23 December 2019. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
- ^ "Each spring, millions of workmen from all parts of western Russia arrived in eastern Germany, which, in political language, is called East Elbia." from The Stronghold of Junkerdom, by George Sylvester Viereck. Viereck's, Volume 8. Fatherland Corporation, 1918
- ^ Compare: Ritter, Gerhard A. (April 2002). "Die DDR in der deutschen Geschichte" [The GDR in German history] (PDF). Vierteljahrshefte für Zeitgeschichte (in German). 50 (2): 171–172. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 November 2019. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
Die Geschichte der DDR ist im wesentlichen zwischen zwei Polen einzubetten. Den einen Pol bildet die Sowjetisierung […] Den anderen Pol bildeten deutsche Traditionen, vor allem die Vorstellungen der kommunistischen Arbeiterbewegung.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Ritter, Gerhard A. (April 2002). "Die DDR in der deutschen Geschichte" [The GDR in German history] (PDF). Vierteljahrshefte für Zeitgeschichte (in German). 50 (2): 171–200. Archived (PDF) from the original on 16 November 2019. Retrieved 16 November 2019.
In der Sozialpolitik hielten sich die Kontinuitäten und die Brüche mit der deutschen Tradition etwa die Waage. […] Seit Mitte der sechziger Jahre, vor allem aber in der Ära Honecker, in der die 'Einheit von Wirtschafts- und Sozialpolitik' zum Leitprinzip erhoben wurde, wurde die Sozialpolitik die wohl wichtigste Legitimationsgrundlage des Staates.
- ^ "Yalta Conference". spartacus.schoolnet.co.uk. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 25 September 2010.
- ^ On the discussion about Social Democrats joining the SED see Steffen Kachel, Entscheidung für die SED 1946 – ein Verrat an sozialdemokratischen Idealen?, in: Jahrbuch für Forschungen zur Geschichte der Arbeiterbewegung, No. I/2004.[date missing]
- ^ Stiftung Haus der Geschichte der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. "LeMO Kapitel: Zwangsvereinigung zur SED". hdg.de (in German). Archived from the original on 14 June 2012. Retrieved 15 July 2012.
- ^ See Anna M. Cienciala "History 557 Lecture Notes" Archived 20 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Steininger, Rolf (1990). The German Question: The Stalin Note of 1952 and the Problem of Reunification. New York, NY: Columbia University.
- ^ Roth, Gary. "Review of Hoffmann, Dierk, _Otto Grotewohl (1894–1964): Eine politische Biographie_" H-German, H-Net Reviews. November 2010. online Archived 17 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Gomez Gutiérrez, J. J., & Bruschi, V. (2003). Socialist Unity Party of Germany. In N. Schlager (Ed.), St. James encyclopedia of labor history worldwide: Major events in labor history and their impact. St. James Press.
- ^ "Political prisoners in the German Democratic Republic". Political prisoners in the German Democratic Republic | Communist Crimes. Retrieved 24 November 2020.
- ^ "State symbols: the quest for legitimacy in the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic, 1949–1959", by Margarete Myers Feinstein, page 78: " ... claims of East Berlin as the capital of the GDR, ... East Berlin was not recognized by the West and most Third World countries"
- ^ Michael D. Haydock, City Under Siege: The Berlin Blockade and Airlift, 1948–1949 (2000)
- ^ Weitz 1997, p. 350: Following a Soviet order in February 1948, the German Economic Commission became a nascent state structure for all intents and purposes, with competence far beyond the economy proper; it gained the power to issue orders and directives to all German organs within the Soviet Occupation Zone.
- ^ McCauley 1983, p. 38: The DWK had become the de facto government of the Soviet zone. Its chairman was Heinrich Rau (SED), and four of his six deputies were also SED members.
- ^ Patrick Major and Jonathan Osmund, Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany under Ulbricht, 1945–71 (2002)
- ^ East Berlin 17 June 1953: Stones Against Tanks Archived 23 January 2011 at the Wayback Machine, Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 16 May 2007.
- ^ Victor Baras, "Beria's Fall and Ulbricht's Survival," Soviet Studies, 1975, Vol. 27 Issue 3, pp. 381–395
- ^ Jump up to: a b Norman M. Naimark. The Russians in Germany: A History of the Soviet Zone of Occupation, 1945–1949. Harvard University Press, 1995. ISBN 0-674-78405-7 pp. 167–9.
- ^ Frederick Taylor, Berlin Wall: A World Divided, 1961–1989 (2007)
- ^ Allinson, Mark; Leaman, Jeremy; Parkes, Stuart; Tolkiehn, Barbara (30 July 2014). Contemporary Germany: Essays and Texts on Politics, Economics & Society (in German). London and New York: Routledge. p. 39. ISBN 978-1-317-87977-0. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ Henry Krisch, "Soviet-GDR Relations in the Honecker Era", East Central Europe, December 1979, Vol. 6 Issue 2, pp. 152–172.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "East Germany: The Price of Recognition". Time. 1 January 1973. Archived from the original on 18 December 2011. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ Quint, Peter E. (1991), The Imperfect Union; Constitutional Structures for German Unification, Princeton University Press, p. 14
- ^ Kommers, Donald P. (2012), The Constitutional Jursiprudence of the Federal Republic of Germany, Duke University Press, p. 308
- ^ Texas Law: Foreign Law Translations 1973, University of Texas, archived from the original on 20 December 2016, retrieved 7 December 2016
- ^ Eric G. E. Zuelow (2011). Touring Beyond the Nation: A Transnational Approach to European Tourism History. p. 220. ISBN 978-0-7546-6656-1.
- ^ David Priestand, Red Flag: A History of Communism, New York: Grove Press, 2009
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Eric D. Weitz, Creating German Communism, 1890–1990: From Popular Protests to Socialist State. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 1997
- ^ Jump up to: a b Judt, Tony (2005). Postwar: A History of Europe Since 1945. p. 612.
- ^ The Berlin Wall (1961–89) German Notes. Retrieved 24 October 2006.
- ^ Miklós Németh in Interview, Austrian TV – ORF "Report", 25 June 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Szabo, Hilde (16 August 1999). "Die Berliner Mauer begann im Burgenland zu bröckeln" [The Berlin Wall began to crumble in Burgenland]. Wiener Zeitung (in German).
- ^ Otmar Lahodynsky: Paneuropäisches Picknick: Die Generalprobe für den Mauerfall (Pan-European picnic: the dress rehearsal for the fall of the Berlin Wall – German), in: Profil 9 August 2014.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Greven, Ludwig (19 August 2014). "Und dann ging das Tor auf" [And then the Gate Opened]. Die Zeit.
- ^ Otmar Lahodynsky "Eiserner Vorhang: Picknick an der Grenze" (Iron curtain: picnic at the border – German), in Profil 13 June 2019.
- ^ Roser, Thomas (17 August 2018). "DDR-Massenflucht: Ein Picknick hebt die Welt aus den Angeln" [Mass exodus of the GDR: A picnic clears the world]. Die Presse (in German).
- ^ Frank, Michael (17 May 2010). "Paneuropäisches Picknick – Mit dem Picknickkorb in die Freiheit" [Pan-European picnic – With the picnic basket to freedom]. Süddeutsche Zeitung (in German).
- ^ Jump up to: a b Judt, Tony (2005). Postwar: A History of Europe Since 1945. p. 613.
- ^ Darnton, Robert, Berlin Journal (New York, 1992, W.W. Norton) pp. 98–99,
- ^ Jump up to: a b Mary Elise Sarotte, Collapse: The Accidental Opening of the Berlin Wall, New York: Basic Books, 2014
- ^ Jump up to: a b Judt, Tony (2005). Postwar: A History of Europe Since 1945. p. 614.
- ^ Judt, Tony (2005). Postwar: A History of Europe Since 1945. p. 615.
- ^ Kommers, Donald P. (2012), The Constitutional Jursiprudence of the Federal Republic of Germany, Duke University Press, p. 309
- ^ David P. Conradt, The German Polity (2008) p. 20
- ^ Mary Elise Sarotte, 1989: The Struggle to Create Post-Cold War Europe (second edition) Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2014
- ^ "East Germany: country population". Populstat.info. Archived from the original on 11 August 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ "In the period between the Second World War and 1961, a total of 3.8 million people emigrated from East to West Germany." Laar, M. (2009). "The Power of Freedom. Central and Eastern Europe after 1945." Centre for European Studies, p. 58. "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 November 2013. Retrieved 5 April 2012.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- ^ "Germany Population – Historical Background". Country-studies.com. Archived from the original on 1 November 2009. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ Destatis.de Archived 13 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine page 17
- ^ "Zusammenfassende Übersichten – Eheschließungen, Geborene und Gestorbene 1946 bis 2015". DESTATIS – Statistisches Bundesamt. Archived from the original on 11 August 2018. Retrieved 11 August 2018.
- ^ "Population by area in 1,000". DESTATIS – Statistisches Bundesamt. Archived from the original on 11 August 2018. Retrieved 11 August 2018.
- ^ "Leipzig, Germany Population 1950–2019". www.macrotrends.net. Archived from the original on 28 September 2019. Retrieved 28 September 2019.
- ^ "Dresden, Germany Population 1950–2019". www.macrotrends.net. Archived from the original on 28 September 2019. Retrieved 28 September 2019.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i j k l Paxton, J. (20 December 2016). The Statesman's Year-Book 1990–91. Springer. ISBN 978-0-230-27119-7.
- ^ Smith, Tom (3 February 2020). Comrades in Arms: Military Masculinities in East German Culture. New York and Oxford: Berghahn Books. p. 8. ISBN 9781789205558. Retrieved 10 August 2021.
- ^ Solsten, Eric; et al. (Library Of Congress. Federal Research Division) (1996). Germany: A country study. Washington, DC: Federal Research Division, Library of Congress: Library of Congress. Federal Research Division. pp. 169–170.
- ^ Trainor, Bernard E. (8 November 1988). "East German Military: Warsaw Pact's Finest". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 1 August 2018. Retrieved 31 July 2018.
- ^ Rubinstein, Alvin Z. (16 July 1990). Moscow's Third World Strategy. p. 184. ISBN 0-691-02332-8. Archived from the original on 1 December 2019. Retrieved 26 August 2017.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Herf, Jeffrey (2016). Undeclared Wars with Israel: East Germany and the West German Far Left, 1967–1989. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-08986-0.
- ^ Herf, Jeffrey (2014). "'At War with Israel': East Germany's Key Role in Soviet Policy in the Middle East". Journal of Cold War Studies. 16 (2): 129–163. doi:10.1162/JCWS_a_00450. S2CID 57566994.
- ^ Laqueur, Walter (1968). The Road to Jerusalem: The Origins of the Arab-Israeli Conflict, 1967. Macmillan. p. 215. ISBN 978-0-02-568360-0.
- ^ Israel's struggle in the UN
- ^ "The GDR and the PLO: East Germany's Palestine Policy". Archived from the original on 5 May 2018. Retrieved 28 April 2018.
- ^ "Business America. (27 February 1989). German Democratic Republic: long history of sustained economic growth continues; 1989 may be an advantageous year to consider this market – Business Outlook Abroad: Current Reports from the Foreign Service". Business America. 1989. Archived from the original on 9 November 2007. Retrieved 2 October 2007.
- ^ Boroch, Wilfried (1996), "Social policy as an institutional transformation problem", Transition Economies, Volume 31, Number 3, pp. 139–146.
- ^ Jonathan R. Zatlin, The Currency of Socialism: Money and Political Culture in East Germany (2007)
- ^ The shortest history of Germany, James Hawes (2018), federal office of political education [23 June 2009]
- ^ Sleifer, Jaap (2006). "Planning Ahead and Falling Behind: The East German Economy in Comparison with West Germany 1936–2002". High Growth of an Underachiever?. p. 66. ISBN 9783050085395 – via Google Books.
- ^ Sperlich, Peter W. (2006). Oppression and Scarcity: The History and Institutional Structure of the Marxist-Leninist Government of East Germany and Some Perspectives on Life in a Socialist System. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 191. ISBN 978-0-275-97565-4. Archived from the original on 16 May 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ^ "Ich liebe Thüringen, ich liebe Deutschland" (in German). Archived from the original on 1 February 2017. Retrieved 20 January 2017.
- ^ Mary Fulbrook, "The Limits Of Totalitarianism: God, State and Society in the GDR," Transactions of the Royal Historical Society, Jan 1957, Vol. 7 Issue 1, pp 25–52
- ^ Toth, Helena. "Dialogue as a Strategy of Struggle: Religious Politics in East Germany, 1957–1968" (PDF). Contemporary European History. Cambridge University Press. p. 174.
- ^ de Silva, Brendan (2000). "The Protestant Church and the East German State: an organisational perspective". In Cooke, Paul; Grix, Jonathan (eds.). East Germany: Continuity and Change. German Monitor. Amsterdam: Rodopi B.V. pp. 104–105. ISBN 978-90-420-0579-2. Archived from the original on 3 June 2016. Retrieved 21 September 2015.
'The SED will refrain from talks with the churches, since it must be seen as an "atheistic party against the Church". Thus, negotiations must be led by the State, which is understood to be non-partisan, namely by the state Secretary for Church Affairs. But decisions on Church policies are to be made exclusively "in the party" [...].'
- ^ Paul Tillich. Christianity and the Encounter of the World Religions (New York: Columbia University Press, 1963), p. 20.
- ^ Fulbrook, "The Limits Of Totalitarianism: God, State and Society in the GDR"
- ^ Martin Onnasch, "Konflikt und Kompromiss: Die Haltung der evangelischen Kirchen zu den gesellschaftlichen Veränderungen in der DDR am Anfang der fünfziger Jahre," ["Conflict and compromise: the position of the Protestant churches with regard to social changes in the GDR at the beginning of the 1950s"], Kirchliche Zeitgeschichte / Halbjahresschrift für Theologie und Geschichtswisseschaft, 1990, Vol. 3 Issue 1, pp. 152–165.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Stephen R. Bowers, "Private Institutions in Service to the State: The German Democratic Republic's Church in Socialism," East European Quarterly, Spring 1982, Vol. 16 Issue 1, pp. 73–86.
- ^ Bernd Schaefer (2010). The East German State and the Catholic Church, 1945–1989. Berghahn Books. ISBN 978-1-84545-852-2. Archived from the original on 3 June 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2015. ch 1
- ^ Adrian Webb (2008). Routledge Companion to Central and Eastern Europe since 1919. Taylor & Francis. p. 185. ISBN 978-0-203-92817-2. Archived from the original on 27 April 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ^ Pence and Betts, Socialist modern: East German everyday culture and politics. page 37 for Maaz, 58.
- ^ "The Secret of East German Censorship – Who's Watching Who?". blogs.hss.ed.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 16 December 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ , Wikipedia, 4 August 2020, retrieved 3 September 2020
- ^ Bericht auf wdr4.de vom 22. Juli 2007 Archived 27 January 2016 at the Wayback Machine, abgerufen am 30. September 2014
- ^ Götz Hintze: Rocklexikon der DDR. 2. Auflage. Schwarzkopf & Schwarzkopf, Berlin 2000, ISBN 3-89602-303-9, Eintrag zum Internationalen Schlagerfestival Dresden
- ^ Informationen zu Chris Doerk Archived 28 April 2016 at the Wayback Machine, abgerufen am 23. Dezember 2010
- ^ "ROTE GITARREN – Die Offizielle Homepage". rote-gitarren.de. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Rote Gitarren". Deutsche Mugge. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Karel Gott". DDR-Tanzmusik. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Omega". Deutsche Mugge. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Biografija: Muzičar Dado Topić". Opusteno.rs. Archived from the original on 12 April 2017. Retrieved 19 December 2017.
- ^ Brown, Timothy S. "'Keeping it Real' in a Different 'Hood: (African-) Americanization and Hip-hop in Germany." In The Vinyl Ain't Final: Hip Hop and the Globalization of Black Popular Culture, ed. by Dipannita Basu and Sidney J. Lemelle, page.137–150. London; A
- ^ Elfein, Dietmar. From Krauts with Attitudes to Turks with Attitudes: Some Aspects of Hip-Hop History in Germany. Popular Music, vol. 17:3, pp. 225–265, October 1998.
- ^ Davies, Cecil William (1 January 1977). Theatre for the People: The Story of the Volksbühne. Manchester University Press. p. 126. ISBN 978-0-7190-0666-1.
- ^ "Interview With Conductor Kurt Masur: 'The Spirit of 1989 Has Been Exhausted'". Spiegel Online. 12 October 2010. Archived from the original on 19 October 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ Tynan, Kenneth (11 January 1976). "Brecht Would Not Applaud His Theater Today". NYTimes.com. Archived from the original on 14 September 2016. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ^ Joshua Feinstein, The Triumph of the Ordinary: Depictions of Daily Life in the East German Cinema, 1949–1989 (Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Press, 2002), 80–109. ISBN 978-0-8078-5385-6
- ^ Patrick Harkin, "Brecht on 17 June: Establishing the Facts", in Edinburgh German Yearbook 5: Brecht and the GDR: Politics, Culture, Posterity (Rochester NY: Camden House, 2011), 84–99. ISBN 978-1-57113-492-9
- ^ Ela E. Gezen, Brecht, Turkish Theater, and Turkish-German Literature: Reception, Adaptation, and Innovation After 1960 (London: Boydell & Brewer, 2018), 80–85. ISBN 978-1-64014-024-0
- ^ Manfred Wekwerth, Daring to Play: A Brecht Companion (London: Routledge, 2012), 101–7. ISBN 978-1-136-70911-1
- ^ Laura Bradley, Brecht and Political Theatre: The Mother on Stage (London: Clarendon Press, 2006), 108–12 and 129-31. ISBN 978-0-19-928658-4
- ^ "Berlin East germany". www.berlinstory-andtravels.info. Archived from the original on 22 December 2017. Retrieved 19 December 2017.
- ^ "Friedrichstadt-Palast". Archived from the original on 4 March 2018. Retrieved 8 February 2018.
- ^ "Das BE – ein Theater für Zeitgenossen". Berliner-ensemble.de. Archived from the original on 30 May 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ "Deutsches Theater: Home". Deutsches-theater.de. Archived from the original on 26 March 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ "Gorki.de". Gorki.de. Archived from the original on 23 March 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ "Volksbühne Berlin". Volksbuehne-berlin.de. Archived from the original on 23 March 2010. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ "DEFA – Stiftung – Home". Defa-stiftung.de. Archived from the original on 26 April 2008. Retrieved 28 March 2010.
- ^ Beate Müller, Stasi-Zensur-Machtdiskurse: Publikationsgeschichten und Materialien zu Jurek Beckers Werk (Berlin: Max Niemeyer, 2006), 129–30. ISBN 978-3-484-35110-3
- ^ Cook, Roger F. (28 June 2007). "Good Bye, Lenin! : Free-Market Nostalgia for Socialist Consumerism". Seminar: A Journal of Germanic Studies. 43 (2): 206–219. doi:10.1353/smr.2007.0027. ISSN 1911-026X. S2CID 201759614.
- ^ 2006 Academy Award for "The Lives of Others" Archived 10 October 2011 at the Wayback Machine,
- ^ Enns, A. (1 December 2007). "The politics of Ostalgie: post-socialist nostalgia in recent German film". Screen. 48 (4): 475–491. doi:10.1093/screen/hjm049. ISSN 0036-9543.
- ^ Helmstaedt, Karin (19 July 2000). "East German Doping Trial". The Globe and Mail. Berlin. Retrieved 5 September 2019.
- ^ Hartgens and Kuipers (2004), p. 515
- ^ Kicman AT; Gower DB (July 2003). "Anabolic steroids in sport: biochemical, clinical and analytical perspectives". Annals of Clinical Biochemistry. 40 (Pt 4): 321–356. doi:10.1258/000456303766476977. PMID 12880534. S2CID 24339701. Archived from the original on 29 June 2012.
- ^
Sources:
- Tagilabue, John (12 February 1991). "Political Pressure Dismantles East German Sports Machine". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- Janofsky, Michael (3 December 1991). "OLYMPICS; Coaches Concede That Steroids Fueled East Germany's Success in Swimming". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 20 November 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- Kirschbaum, Erik (15 September 2000). "East German Dope Still Leaves Tracks". Archived from the original on 3 June 2008. Retrieved 12 May 2008.
- Ungerleider, Steven (2001). Faust's Gold: Inside the East German doping machine (1st ed.). Thomas Dunne Books/St. Martin's Press. ISBN 0-312-26977-3.
- "Sports Doping Statistics Reach Plateau in Germany". Deutsche Welle. 26 February 2003. Archived from the original on 1 October 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- Longman, Jere (26 January 2004). "DRUG TESTING; East German Steroids' Toll: 'They Killed Heidi'". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 1 October 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- ^
Sources:
- Harding, Luke (31 October 2005). "Forgotten victims of East German doping take their battle to court". The Guardian. Berlin. Archived from the original on 30 December 2016. Retrieved 14 December 2016.
- Jackson, Guy (September 2006). "Doping for glory in East Germany". The Unesco Courier. Archived from the original on 11 June 2008.
- "Ex-East German athletes compensated for doping". Frankfurt, Germany: ESPN. Associated Press. 13 December 2006. Archived from the original on 12 October 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- Associated Press (13 December 2006). "East German doping victims to get compensation". CBC. Archived from the original on 1 October 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- "Germany completes $4.1M payout to doping victims". USA Today. 2007. Archived from the original on 1 October 2018. Retrieved 16 October 2018.
- ^ "1974 FIFA World Cup Germany, Germany FR". FIFA.com. Archived from the original on 27 January 2017. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
- ^ Cooke, Paul (August 2005). Representing East Germany Since Unification: From Colonization to Nostalgia. p. 146. ISBN 978-1-84520-189-0. Archived from the original on 26 March 2015. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ^ Beard (4 November 2019). "30 years after the fall of the Berlin Wall, Germany recalls the economic gulf between East and West". NPR/Market Place.
- ^ "76 E. German Nuclear Incident Described". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ "East German nuclear plant demolition proves challenging". DW.
- ^ Kocka, Jürgen, ed. (2010). Civil Society & Dictatorship in Modern German History. UPNE. p. 37. ISBN 978-1-58465-866-5. Archived from the original on 20 March 2015. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ^ Martin Blum, "Remaking the East German Past: 'Ostalgie,' Identity, and Material Culture," Journal of Popular Culture, Winter 2000, Vol. 34 Issue 3, pp. 229–54.
- ^ Naughton, Leonie (2002). That Was the Wild East: Film Culture, Unification, and the "New" Germany. U. of Michigan Press. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-472-08888-1. Archived from the original on 21 May 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ^ Bickford, Andrew (2011). Fallen Elites: The Military Other in Post-Unification Germany. Stanford U.P. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-8047-7396-6. Archived from the original on 27 April 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ^ Barnston, Ascher (2005). The Transparent State: Architecture and Politics in Postwar Germany. Psychology Press. p. 92. ISBN 978-0-203-79988-8. Archived from the original on 7 May 2016. Retrieved 14 October 2015.
- ^ Connolly, Kate (2007). "Educated women leave east German men behind". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 17 November 2018. Retrieved 16 November 2018.
- ^ "Rewriting ideal history: The Ostalgie expression in Goodbye, Lenin (2003)". Retrieved 9 July 2020.
- ^ Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche. "Ostalgia: Romanticizing the GDR | DW | 03.10.2014". DW.COM. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche. "Why is everyone in Germany talking about Thuringia and AfD? | DW | 06.02.2020". DW.COM. Retrieved 18 March 2021.
Further reading[]
- Allinson, Mark. Politics and Popular Opinion in East Germany 1945–68 (2000)
- Augustine, Dolores. Red Prometheus: Engineering and Dictatorship in East Germany, 1945–1990 (2007) 411pp
- Baylis, Thomas A., David H Childs, Erwin L. Collier, and Marilyn Rueschemeyer, eds. East Germany in Comparative Perspective (Routledge, 1989)
- Berger, Stefan, and Norman LaPorte, eds. The Other Germany: Perceptions and Influences in British-East German Relations, 1945–1990 (Augsburg, 2005).
- Berger, Stefan, and Norman LaPorte, eds. Friendly Enemies: Britain and the GDR, 1949–1990 (2010) online review
- Berghoff, Hartmut, and Uta Andrea Balbier, eds. The East German Economy, 1945–2010: Falling Behind Or Catching Up? (Cambridge University Press, 2013).
- Betts, Paul. Within Walls: Private Life in the German Democratic Republic, Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2013
- Childs, David H.. The Fall of the GDR, Longman Personed.co.uk, 2001. ISBN 978-0-582-31569-3, ISBN 0-582-31569-7
- Childs, David H.. & Richard Popplewell. The Stasi: East German Intelligence and Security Service, Palgrave Macmillan Palgrave.com, Amazon.co.uk 1996.
- Childs, David H.. The GDR: Moscow's German Ally, George Allen & Unwin, 1983. ISBN 0-04-354029-5, ISBN 978-0-04-354029-9.
- Childs, David H.. The Two Red Flags: European Social Democracy & Soviet Communism Since 1945, Routledge, 2000.
- De La Motte and John Green, "Stasi State or Socialist Paradise? The German Democratic Republic and What became of it", Artery Publications. 2015
- Fulbrook, Mary. The People's State: East German Society from Hitler to Honecker (Yale University Press, 2005). 352 pp. ISBN 0-300-10884-2.
- Fulbrook; Mary. Anatomy of a Dictatorship: Inside the GDR, 1949–1989 (Oxford University Press, 1995).
- Fulbrook, Mary and Andrew I. Port, eds., Becoming East German: Socialist Structures and Sensibilities after Hitler (New York and Oxford: Berghahn, 2013).
- Gray, William Glenn. Germany's Cold War: The Global Campaign to Isolate East Germany, 1949–1969 (University of North Carolina Press, 2003). online
- Grieder, Peter. The German Democratic Republic (Palgrave Macmillan, 2012), scholarly history.
- Grix, Jonathan. The Role of the Masses in the Collapse of the GDR Macmillan, 2000
- Heitzer, Heinz (1981). GDR: An Historical Outline. Dresden: Zeit im Bild. OCLC 1081050618.
- Jarausch, Konrad H., and Eve Duffy; Dictatorship as Experience: Towards a Socio-Cultural History of the GDR (Berghahn Books, 1999).
- Kupferberg, Feiwel. The Rise and Fall of the German Democratic Republic (2002) 228pp; online review
- McAdams, A. James. "East Germany and Détente" (Cambridge University Press, 1985).
- McAdams, A. James. "Germany Divided: From the Wall to Reunification" (Princeton University Press, 1992 and 1993).
- McCauley, Martin (1983). The German Democratic Republic since 1945. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-333-26219-1.
- McLellan, Josie. Love in the Time of Communism: Intimacy and Sexuality in the GDR. (Cambridge University Press, 2011).
- Major, Patrick, and Jonathan Osmond, eds. The Workers' and Peasants' State: Communism and Society in East Germany under Ulbricht 1945–71 (Manchester University Press, 2002), 272 pp.
- Naimark, Norman M. The Russians in Germany: A History of the Soviet Zone of Occupation, 1945–1949 (1997) excerpt and text search
- Pence, Katherine and Paul Betts. Socialist Modern: East German Everyday Culture and Politics, Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 2008
- Port, Andrew I. Conflict and Stability in the German Democratic Republic. Cambridge University Press, 2007.
- Preuss, Evelyn I. (2005). "The Wall You Will Never Know". Perspecta: The Yale Architectural Journal. 36. pp. 19–31.
- Ritter, Gerhard A. "Die DDR in der Deutschen Geschichte", [The GDR in German history] Vierteljahrshefte für Zeitgeschichte, April 2002, Vol. 50, Issue 2, pp. 171–200.
- Pritchard, Gareth, The Making of the GDR 1945–53: From Antifascism to Stalinism (2000)
- Steiner, André. The Plans That Failed: An Economic History of East Germany, 1945–1989 (2010)
- Sarotte, Mary Elise. Collapse: The Accidental Opening of the Berlin Wall, New York: Basic Books, 2014
- Spilker, Dirk. The East German Leadership and the Division of Germany: Patriotism and Propaganda 1945–1953. (2006). online review
- Staff writer (1986). The German Democratic Republic. Dresden: Zeit im Bild: Dresden: Zeit im Bild. OCLC 221026743.
- Stokes, Raymond G. Constructing Socialism: Technology and Change in East Germany, 1945–1990 (2000)
- Zatlin, Jonathan R. The Currency of Socialism: Money and Political Culture in East Germany (2007). 377 pp. online review
Historiography and memory[]
- Bridge, Helen. Women's Writing and Historiography in the GDR (Oxford University Press, 2002).
- Hodgin, Nick, and Caroline Pearce, eds. The GDR remembered: representations of the East German state since 1989 (Camden House, 2011). excerpt
- Kwiet, Konrad. "Historians of the German Democratic Republic on Antisemitism and Persecution." The Leo Baeck Institute Yearbook 21.1 (1976): 173–198.
- Port, Andrew I. (2013). "The Banalities of East German Historiography" (PDF). In Fulbrook, Mary; Port, Andrew I. (eds.). Becoming East Germans: Socialist Structures and Sensibilities After Hitler. New York: Berghahn Books. ISBN 978-0-85745-974-9.
- Port, Andrew I. (2015). "Central European History since 1989: Historiographical Trends and Post-Wende "Turns"". Central European History. 48. pp. 238–248. doi:10.1017/S0008938915000588. S2CID 151405931.
- Ritter, Gerhard A. "Die DDR in der Deutschen Geschichte", [The GDR in German history] Vierteljahrshefte für Zeitgeschichte, April 2002, Vol. 50 Issue 2, pp. 171–200.
- Ross, Corey. The East German Dictatorship: Problems and Perspectives in the Interpretation of the GDR (Oxford University Press, 2002).
- Saunders, Anna, and Debbie Pinfold, eds. Remembering and rethinking the GDR: multiple perspectives and plural authenticities (Springer, 2012).
- Steding, Elizabeth Priester. "Losing Literature: The Reduction of the GDR to History". German Politics & Society 32.4 (2014): 39–55. Argues the history of East Germany is taught in 21st-century German schools, but not its literature.
In German[]
- Dahn, Daniela. Wenn und Aber: Anstiftungen zem Widerspruch, Berlin: Rowohlt Verlag, 1997
- Dahn, Daniela. Westwärts und nicht vergessen: Vom Unbehagen in der Einheit, Rowohlt Verlag, 1997
- Dahn, Daniela. Vertreibung ins Paradies: Unzeitgemäße Texte zur Zeit, Berlin: Rowohlt Verlag, 1998
External links[]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to German Democratic Republic. |
- Border Museum at Schifflersgrund
- DDR Museum Berlin – Culture of GDR
- AHF – Nationale Volksarmee : NVA
- That was the GDR (in German) at the Wayback Machine (archived 8 April 2010)
- East German Propaganda, Calvin University
- "Scenes from Behind the Wall: Images of East Germany 1989/90" Exhibit Collection C0235, Special Collections Research Center, George Mason University Libraries.
- Geschichte des ostdeutschen Designs – history of east German design (in German)
- East Berlin, past and present at the Wayback Machine (archived 28 September 2007)
- Pictures of the GDR 1949–1973
- RFE/RL East German Subject Files Open Society Archives, Budapest at the Wayback Machine (archived 2 December 2008)
- Stamps Catalog of the German Democratic Republic at archive.today (archived 2 January 2013)
- East German anthem with English and German lyrics
- Map – Europe 1949: NATO and the Two Germanys (omniatlas.com)
- Mauerkarte – Detailed interactive map of the border between East and West Germany
- East Germany
- 1949 establishments in Germany
- 1990 disestablishments in Germany
- Atheist states
- Communism in Germany
- Communist states
- Eastern Bloc
- Former polities of the Cold War
- Former socialist republics
- Ostalgie
- Soviet satellite states
- States and territories established in 1949
- States and territories disestablished in 1990
- Former countries