Siege of Novi Zrin (1664)
| Siege of Novi Zrin (1664) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Croatian–Ottoman wars and Ottoman–Habsburg wars | |||||||
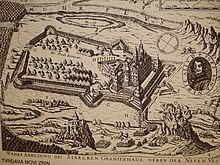 Novi Zrin Castle, situated on the right bank of the Mura River (Muhr flus), in 1664, before its ruination | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
  |
  | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| ~ 1200 German, 700 Hungarian (among 30 Hajduks) and Croatian defenders, in the open fields around 27000 | 30,000[1] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| ~ 15,000 killed.[2] | ~ Unknown | ||||||


The siege of Novi Zrin (New Zrin Castle); Croatian: Utvrda Novi Zrin; Hungarian: Új-Zrínyivár; Turkish: Zerinvar) in June/July 1664 was last of the military conflicts between the Croatian forces (with allies) led by Nikola Zrinski, Ban (viceroy) of Croatia, and the Ottoman army commanded by Köprülü Fazıl Ahmed Pasha, Grand Vizier, dealing with possession of Novi Zrin Castle, defended by Croats, situated on the bank and marshy islands of Mura River, near the border line between northern Croatia and southwestern part of Hungary, at the time occupied by the Ottomans. The battle resulted in destruction[1] of the castle, and retreat of the Croatian crew, that was forced to withdraw to safer territory of inland Croatia.
Historical background[]
Despite local skirmishes and battles along the Ottoman border with Croatia, Hungary and Transylvania at the beginning of the 1660s, there was a period of unstable and insecure (tacit assumption) temporary peace between the Habsburg Monarchy and the Ottoman Empire. It seemed that both sides wanted to keep it; however, Leopold I of Habsburg, twenty-year-old inexperienced Emperor, under strong influence of his advisors, feared Ottoman campaign towards Vienna and possible siege of the Austrian capital, so he kept the majority of his military forces close to Vienna.
At the same time, Nikola Zrinski, a brave and skillful warrior, well-known all over Europe, demanded support from the Viennese court to consolidate and reinforce the border line in northern Croatia through new fortifications that would parry and neutralize the Ottoman threat from Kanije Eyalet in the occupied southwestern Hungary, but with no success. In 1661 Zrinski started to build a new stronghold, Novi Zrin Castle, on his own, at the confluence of the Mura River with the Drava, finishing it during 1662. Since then the castle was attacked several times by the Ottomans, especially in 1663, but the defence was solid and successful.
Siege[]
At the beginning of June 1664 a large Ottoman army, numbering up to 100,000 men (some sources mention even much more), including around 40,000 Ottoman and 30,000 Tatar fighters, led personally by the Grand Vizier Köprülü, was moving from Constantinople to the northwest and approaching Novi Zrin (later to fight in the Battle of Saint Gotthard on 1 August 1664). The defenders of Novi Zrin consisted mostly of Croatian and German soldiers (around 3,000 men in total), while the majority of the Habsburg army (30,000 men), situated in the camp near Saint Gotthard, was waiting for the result of the battle.
On 5 June 1664 Köprülü ordered siege and continuous attacks upon the castle. After a few weeks of fighting, with exhausted defenders receiving only insignificant reinforcements from the Emperor's headquarters, the Turks managed to dig lagums, or tunnels, below the bastions and ignited gunpowder to blow them up. On 7 July 1664 the strong explosions destroyed some parts of the walls making big holes. Aggressors consequently rushed and penetrated into the castle.
The surviving and enormously outnumbered Croatian defenders were forced to withdraw from the castle and to abandon the Mura River area. Ottoman commanders gave the order to their soldiers to ruin Novi Zrin completely to the ground and then moved further with the whole army to the north, first to Kanije and then towards Saint Gotthard.
Aftermath[]
The destruction of Novi Zrin, together with a little bit later (on 10 August 1664) signed unfavourable and shameful Peace of Vasvár, made Nikola Zrinski and other leading Croatian and Hungarian magnates angry and initiated the Zrinski–Frankopan conspiracy. Later in the same year Zrinski died, allegedly killed by a wild boar, but the rest of magnates continued the conspiracy, which ended tragically in 1671.
Novi Zrin was never rebuilt.[1] Today there is only a memorial obelisk on the place where the castle once was.
See also[]
- Croatian–Ottoman Wars
- Austro-Turkish War (1663–64)
- Ottoman–Habsburg wars
- Ottoman wars in Europe
References[]
- ^ a b c Feletar 2011, p. 81
- ^ Vincent Mignot ,1787
Sources[]
- Feletar, Dragutin (September 2011). "Legradska kapetanija u obrani od Osmanlija s posebnim osvrtom na Novi Zrin" [Role of the Legrad Military District in the Defence against the Ottoman Empire - Special Emphasis on Novi Zrin]. Rad Hrvatske Akademije Znanosti i Umjetnosti (in Croatian). Zagreb: The Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts (510=48): 47–81. ISSN 1330-0768. 48=510(2011):47-81.
External links[]
- Siege of Novi Zrin lasted from early June until early July 1664
- Rise and fall of New Zrin Castle, including final battle during June and July 1664
- Novi Zrin fort was destroyed by Turks just several years after it was built
- Novi Zrin memorial obelisk
- General Strozzi biography
- Battles involving Habsburg Croatia
- Battles involving Austria
- Sieges involving Hungary
- Conflicts in 1664
- Sieges involving Croatia
- Sieges involving the Ottoman Empire
- Battles of the Austro-Turkish War (1663–64)
- 17th century in Croatia
- 1664 in the Ottoman Empire
- 1664 in Hungary
- Croatia under Habsburg rule
- 17th-century military history of Croatia
- History of Međimurje
